Postoperative rehabilitation
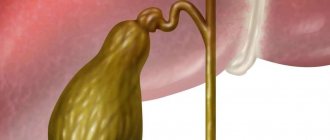
Gallbladder
After the operation, you will have to spend about a year “teaching” the bile ducts to “do the work” of the removed organ. The bottom line is that cholecystectomy has little effect on the patient’s quality of life from a physiological point of view: since stones form in an organ that is already poorly functioning or not functioning at all. For this reason, the human body, after cutting out the bladder, experiences some kind of relief, because it almost painlessly “says goodbye” to one of its many problems. However, the period after surgery is different for each person.
Rehabilitation after cholecystectomy is carried out in the following areas:
- drug therapy;
- strict adherence to the diet;
- adherence to diet;
- physiotherapy.
The stomach, pancreas, liver and intestines at first begin to adapt to the new operating mode. At this time, the patient needs maintenance drug therapy. Taking special medications facilitates and speeds up the digestive process. Postoperative drug therapy is prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis, taking into account the nature of the operation, the general health of the patient, his age and other factors.
Most often, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- antispasmodics - substances that reduce spasm of smooth muscles;
- enzyme preparations – medicines that improve the digestion process and include digestive enzymes;
- drugs that improve intestinal microflora;
- hepatoprotectors – a group of drugs used to treat and restore the liver.
Why is the gallbladder removed?
The body is designed in such a way that there is nothing superfluous in it: each organ performs its specific function and all organs are interconnected.
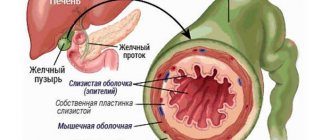
On the other hand, it has the unique ability to adapt to the absence of an organ that is not vital. The gallbladder is one of these organs, although it performs an important function in digestion. It is a collector and regulator of bile, which is produced by liver cells and flows through ducts into the bladder. It is needed for the processing and absorption of fats. When food mass enters the duodenum, the bladder reflexively contracts and releases a portion of bile through the common bile duct.
Often the gallbladder is removed, and here's why. Errors in nutrition (excess, fatty and spicy foods), physical inactivity lead to an increased content of cholesterol in bile, and it is the basis for the formation of stones. First, dense small particles of bile - “sand” - are formed; calcium salts and bilirubin are gradually adsorbed on them, and stones are formed.
The gallbladder is removed in cases where it ceases to perform its function and becomes dangerous to health. This is a necessity when choosing the lesser of two evils.
Indications for gallbladder removal are:
- cholelithiasis;
- obstructive jaundice caused by blockage of the bile ducts;
- acute cholecystitis, when the inflammatory process cannot be stopped;
- chronic cholecystitis with frequent exacerbations and digestive disorders;
- severe persistent dyskinesia of the gallbladder;
- “porcelain” bubble due to the deposition of calcium salts in it;
- polyps, bladder and bile duct tumors.
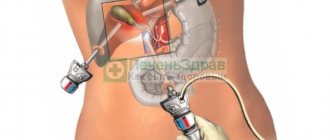
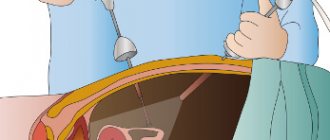
Cholecystectomy can be performed urgently for health reasons in acute cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice; in other cases, the operation is performed routinely after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Cholecystectomy of the gallbladder
Drug therapy after cholecystectomy
Patients who have undergone surgery and are in good health and mood and do not complain of pain in the liver or other discomfort, as a rule, do not need special treatment. All that is required of them is to know what they can eat after removal of the gallbladder and adhere to a special, not very strict diet.
Medicines for “bacterial overgrowth syndrome”
Approximately 40% of patients experience aching pain after cholecystectomy. In addition, there are other consequences of removing the gallbladder using the laparoscopic method, for example:
- belching;
- flatulence;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- problems with stool;
- nausea.
After removal of the gallbladder, the level of bacteria in the duodenum increases
These sensations are often due to the fact that bile ceases to perform its bactericidal function, microbes multiply in the duodenum, as a result of which their number begins to exceed the norm. Scientists call this condition small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome. It is treated with antimicrobial agents (furazolidone and biseptol). Courses of antibiotics and medications designed to restore intestinal microflora significantly improve the well-being of these patients. In this case, antibiotics are prescribed strictly according to indications. As a rule, they are recommended to be taken for 5-7 days, then a course of medications is required to restore normal microflora in the intestines:
- Linux;
- bifidum;
- bifidobacterin, etc.
During treatment with antibiotics, you must take multivitamins.
Treatment of other digestive system problems
Sometimes people who have undergone surgery may experience pain of a different nature due to other problems of the digestive system. The causes of discomfort may be concomitant pancreatitis, liver damage, stomach disease or biliary tract dysfunction.
Previously, these diseases were combined into a single group “postcholecystectomy syndrome”. Today, operated patients are prescribed individual treatment, which depends on the nature of the problem. So, for disorders caused by biliary tract dysfunction, it is necessary to take antispasmodics:
- no-shpu;
- duspatalin;
- buscopan, etc.
The new generation antispasmodic mebeverine, which promotes easy flow of bile into the duodenum, has proven itself well. This product is available with a doctor's prescription. Medicines that eliminate spasms can be taken in a course lasting 2-4 weeks, and they can also be recommended for use only when pain occurs.
With concomitant pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas, provoked by damage to its own enzymes), enzyme agents and medications that reduce gastric secretion are needed. Enzyme medications include:
- Creon;
- pancreatin;
- micrazim, etc.
Enzymes also have an analgesic effect. The course duration and dosage are selected individually.
If the pain is caused by increased gas formation in the intestines, then to eliminate these symptoms you need to drink:
- meteospasmil;
- espumizan;
- sub-simplex, etc.
Plus, you should exclude from your diet foods that contribute to the accumulation of gases:
- bananas;
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- grapes and raisins;
- fresh bread;
- fried and fatty foods;
- whole milk.
To ensure the normal functioning of the duodenum and sphincter of Oddi, you need to drink prokinetics (drugs that stimulate gastrointestinal motility) 15 minutes before meals:
- motilium;
- debridate;
- cerucal.
As well as multienzyme and restorative medications: Essentiale Forte, Creon, Festal, vitamins.
Advice: independent choice of medications may not only not improve, but also worsen the condition. You must inform your doctor about the side effects of prescribed medications. Only he can replace one remedy with another, taking into account the overall picture of the rehabilitation period.
How to avoid relapse?
Duodenal examination of the duodenum
First of all, you need to understand that bladder problems arise due to an unhealthy liver. If the liver is not healthy, it reduces the quality of bile. The operation does not affect the composition of bile. This means that the production of stone-forming bile by hepatocytes (liver cells) can persist. This phenomenon is called “biliary insufficiency”. Therefore, the main task in the postoperative period is a biochemical analysis of the composition of bile, carried out at regular intervals. Ultrasound examination cannot show the corresponding result. Therefore, doctors choose duodenal examination of the duodenum. In order to find out whether there is a risk of relapse or secondary formation of stones, 5 ml of liquid is placed in the refrigerator for 12 hours. If a precipitate forms during this time, it means that the bile produced by the liver is capable of forming new stones.
In this case, the doctor prescribes medications containing bile and bile acids:
- cholenzyme;
- lyobil;
- allohol.
These drugs are used for replacement therapy for biliary insufficiency caused by the absence of the gallbladder. There are other tablets that stimulate the formation and secretion of bile: osalmide and cyclovalone.
Advice: all appointments for patients in the postoperative period are made strictly on an individual basis! You should not take choleretic drugs on the advice of friends, acquaintances and pharmacy workers!
To protect the mucous membranes from the toxic effects of bile acids, you need to drink ursodeoxycholic acid 300-500 mg before bed. This acid is included in the following medications:
- enterosan;
- hepatosan;
- ursofalk;
- ursosan.
The last two drugs have exactly the same effect, the only difference is that the first is more common in the East, and the second in Europe.
Hepatoprotectors
Hepatoprotectors are not painkillers, but they protect liver cells, have a beneficial effect on the composition of bile and have an anti-inflammatory effect. These drugs are usually included in complex treatment and are prescribed in courses lasting 1-6 months. These include:
- hepabene;
- ursosan;
- eslidine;
- Essentiale Forte;
- milk thistle extract.
Timely and correct assessment of the patient’s clinical symptoms after removal of the gallbladder makes it possible to select the optimal therapy and, as a result, improve the quality of life of the operated patient.
After cholecystectomy, it is recommended to be observed by a gastroenterologist or therapist for six months. If during this time no digestive disorders are detected, the patient is removed from the dispensary register.
We recommend reading: what you can eat before gallbladder removal
Attention! The information on the site is presented by specialists, but is for informational purposes only and cannot be used for independent treatment. Be sure to consult your doctor!
| All reviews | 28.09.2007 How to make it easier for the body to adapt to life without a gallbladder? Any operation is stressful. But you can be glad that yours is one of the most common. In addition, recently it is increasingly being done using an endoscopic method, which is less traumatic than abdominal surgery. Your task for the next 1.5-2 years is to help the bile ducts take over the functions of the removed gallbladder. This entire period will take place under the sign of four “pillars” - diet, nutrition, drug therapy and gymnastics. |
Choleretic medications
Choleretic drugs are prescribed to patients after cholecystectomy to protect the liver from stagnation of secretions and prevent inflammatory processes. Spicy and fatty foods are contraindicated for cholelithiasis. Natural remedies Allohol and Cholenzym promote the absorption of beneficial microelements from food and prevent upset and bloating.
Allochol increases the volume of bile produced by the liver and reduces the risk of re-formation of stones. Consists of pig bile, activated carbon, garlic and nettle extracts. Thanks to the presence of activated carbon, it neutralizes toxins in the intestines and interferes with metabolism.
Cholenzym is a complex that includes: an enzyme from dried animal pancreatic glands, it is natural and promotes the breakdown of food during heaviness and constipation.
For cholecystectomy, an effective herbal remedy is holosas based on rose hips. A sugary-sweet medicine, containing large quantities of flavonoids, pectin, acids, vitamins and essential oils, has an anti-inflammatory effect, improves the production of bile and stabilizes its transport through the liver ducts.
Today, tomorrow and throughout life
“Today” begins on the 1st postoperative day and ends with discharge from the hospital, regardless of the type of operation: endoscopic or abdominal. At this time, when the sutures are healing, and the intestines are weakened and are not at all ready to work at full capacity, the diet should be strict. You can only drink: weak tea, juice from non-acidic fruits, half diluted with water, mineral water like Borjomi without carbonation - 1/2 glass 4-6 times a day. On the 2nd day you are allowed to eat slimy soup, pureed rice or oatmeal, and jelly. From the 3rd day, you can add low-fat cottage cheese, boiled meat, fish, chicken in the form of steam cutlets, white bread crackers - a little of everything. And so on until discharge. “Tomorrow” comes when you cross the threshold of the house, and lasts 1.5-2 months. The diet is gentle: it minimally loads not only the biliary system, but also the pancreas, stomach, and duodenum, which, as a rule, also suffer from gallbladder disease. It is forbidden to eat anything that contains refractory fats - lard, fatty pork and lamb, goose, duck. Exclude from the menu rich broths, fried meat, fish and vegetable dishes, smoked meats, canned food, salted and smoked fish, chum salmon and grain caviar, marinades, including pickled and salted mushrooms, sorrel, spinach, onions, garlic, hot seasonings, fresh vegetables and fruits, since they have a strong juice effect. You will have to give up rye bread (you can only eat white bread baked yesterday or dried), as well as fried dough products: pancakes, pies, pasties, whites. Forget about cakes, cream puffs, whipped cream. Meat, fish and vegetable dishes - not only boiled or steamed, but also chopped, preferably pureed. Food should not be too hot and not too cold. Warm - just what you need. One can only remember about ice cream and drinks with ice, since the cold reflexively causes a spasm of the bile ducts and an attack of pain. For the same reason, you should avoid okroshka from the refrigerator in hot weather. Since rare and plentiful meals can also provoke spasms of the bile ducts, you should eat at least 6-7 times a day (the last time no later than 2 hours before bedtime). I recommend drinking no more than 1.5 liters of liquid so as not to increase the amount of bile secreted. Of course, gastronomic restrictions do not add joy, but one should not make a tragedy out of this. Today's abundance of products plus a little imagination - and a lot of tasty and healthy dishes will appear on the table, like on a self-assembled tablecloth. These are a variety of vegetarian soups - vegetable, cereal, dairy, meat, fish, poultry dishes in the form of steamed cutlets, rolls, souffles, cottage cheese and dishes made from it, mild cheeses and fermented milk products, boiled or pureed vegetables - carrots, cabbage, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, corn, fruits and berries in the form of compotes, jelly, mousses, all kinds of cereals, casseroles, pasta dishes. You will stick to this diet No. 5 for the next 2 years, although not so strictly. Meals remain fractional, but no longer 6-7, but 5-6 times a day. As for the liquid, if desired, the amount can be increased to 2 liters. All other gastronomic indulgences are best done with the permission of a doctor. For those who are overweight, I advise you to reduce your calorie intake by eating flour, pasta, sweets, and sugar. It is useful to have a fasting day once a week: apple, meat, kefir. Those who have undergone surgery are recommended to have a rice-compote day: drink 1.5 liters of dried fruit compote in 5 doses, and for breakfast, lunch and dinner eat 3-4 tablespoons of rice porridge with dried fruit compote. Both compote and porridge are cooked without sugar. Do not forget about vitamins and, first of all, ascorbic acid: you need to take it one tablet 3 times a day. A pharmaceutical vitamin will successfully replace rosehip infusion, which is rich in vitamin C and also has a choleretic effect. Pour boiling water over the crushed berries (at the rate of a tablespoon of berries per glass of boiling water) and leave in a thermos for 8-10 hours. Drink 1/2 glass 2 times a day. For those who have had their gallbladder removed due to gallstone disease, foods rich in cholesterol will always have to be limited: removing the gallbladder does not yet cure gallstone disease. If you violate your diet, cholesterol stones can form in the bile ducts again and again, “pushing” you to repeat surgery. As for those who have undergone cholecystectomy for non-calculous cholecystitis, if you feel well 2 years after the operation, you can gradually move away from diet No. 5.
Folk remedies
After removal of the gallbladder, in agreement with the doctor and in the absence of contraindications, it is possible to use decoctions and infusions based on medicinal plants as part of therapy. Among the most popular recipes for traditional medicine, experts call:
- An infusion of corn silk, intended for cleaning the ducts for removing bile, for the preparation of which 1 tbsp of the product is poured into 200 ml of boiling water, infused for several hours and consumed after filtering, 1 tbsp (5 times during the day).
- An infusion based on bird knotweed, used to prevent the formation of stones and relieve pain. To prepare the composition, you need to pour 2 tablespoons of the crushed plant into 0.5 liters of boiling water, then boil for 2-3 minutes, leave for 3-4 hours and drink 0.5 cups 20 minutes before meals three times a day.
- An infusion based on a collection of herbs used to normalize the general condition of the gastrointestinal tract after extirpation of the gastrointestinal tract, which has sedative, analgesic and antispasmodic effects. To prepare it, you need to mix 2 parts of calendula flowers and St. John's wort, 1 part of valerian and chamomile root with 3 parts of immortelle. The prepared mixture is poured into 200 ml of boiling water, infused for 60 minutes, and consumed after straining, 1 glass before meals.
Read: Where is the gallbladder located and what is it?
A gastroenterologist may recommend the inclusion of these drugs in the treatment in order to prevent the re-formation of stones and prevent the formation of stagnant zones in the area of the ducts for excreting bile.
When is a “second front” needed?
The postoperative period proceeds calmly, without complications, if the gallbladder is removed either during the period of remission of cholecystitis, or in the early stages of cholelithiasis, until other nearby organs are involved in the pathological process: pancreas, liver, stomach, duodenum. Statistics show: if, contrary to the advice of doctors, the operation is delayed, 20% of patients develop concomitant diseases - pancreatitis, hepatitis, peptic ulcer. After cholecystectomy, their course worsens. Unpleasant sensations appear in the right hypochondrium, in the pit of the stomach, nausea, belching, bitterness in the mouth, there may be unstable stools, and bloating. In other words, a very unpleasant so-called postcholecystectomy syndrome develops. In this case, diet alone is not enough; you need to open a “second front” and call for drug therapy to help. The doctor decides which medicine to prescribe in each specific case. Some will need drugs that normalize the function of the sphincters of the bile ducts and duodenum: cerucal, motilium (one tablet 2-3 times a day). Others are enzyme preparations that promote better digestion and absorption of food, reducing bloating: festal, digestal, creon (1-2 tablets or tablets 3-4 times a day with meals). The doctor may prescribe a remedy to reduce the stagnation of bile in the bile ducts: flamin, holagogum, 1-2 tablets or capsules of Zraza per day, 30 minutes before meals. To improve liver function, Essentiale Forte is usually prescribed (2 capsules 3 times a day). If the doctor deems it necessary, he will recommend blind tubes with mineral water and explain how to carry them out.
The functioning of the digestive system, symptoms and consequences of bladder removal
Normally, bile is secreted and flows through the ducts into the duodenum after the action of an irritant, which can be food intake. The rate of secretion depends on the type and quantity of food consumed. When the gallbladder is removed, the ducts ensure continuous delivery of secretions to the intestines, independent of the action of the irritant. A constant supply of the enzyme can cause a number of consequences, among which are symptoms and conditions such as:
- The accumulation of large volumes of digestive juices and their stagnation, causing irritation of the intestinal mucosa.
- Violation of the process of absorption of nutrients.
- Nausea, belching and vomiting in case of reflux of secreted secretions.
- Possibility of damage to the intestinal walls with the release of bile into the abdominal cavity.
- Disturbance of the intestinal microflora, leading to flatulence.
- The appearance of liver or intestinal colic.
- There is a danger of penetration of pigments that make up bile into the bloodstream, which can result in general intoxication of the body.
- Disruption of metabolism and metabolic processes that regulate the supply of necessary substances and fats, associated with damage to muscle tissue in the area surrounding the channels for the passage of bile into the duodenum.
- The development of inflammatory processes and dysbacteriosis associated with disruption of metabolic processes.
- Stagnation of bile, formation of stones and an increase in the likelihood of secondary development of cholelithiasis, the elimination of which in most cases is possible only with the help of surgery.
Read: What is the role of bile in the human body
Depending on the individual characteristics of the disease, the onset of one or more of the listed conditions, called post-chocystectomy syndrome by specialists, is possible.
Surgery and the stress that follows is a normal reaction of the body to a surgical procedure. During the time required to restore the body's functioning, the patient may feel weakness, increased formation of gases, a bitter taste in the mouth and other symptoms.
Gymnastics for the abdomen
Of course, there is no question of any gymnastics in the first month after abdominal surgery - any tension in the abdominal muscles causes pain. Only after this time do they begin to do special exercises to form a good mobile postoperative scar and strengthen the abdominal muscles. And obese patients with a fat, saggy belly also need to wear a bandage. Your doctor will tell you where to buy it. Those who have undergone surgery using endoscopy also need to do exercises - they help the outflow of bile. In the first six months to a year, do not engage in work associated with significant tension in the abdominal muscles (washing floors, lifting weights, digging beds...). And one last thing. Don't rush to the resort. For the first six months, it is better to stay in a familiar environment and, if necessary, consult with your doctor.
What happens in the body after gallbladder removal?
People who have had their gallbladder removed have a different digestive system. In order to avoid complications and reappearance of diseases of the hepatobiliary tract, you need to understand what happens in the body after surgery.
The gallbladder stores bile and supplies it to the intestinal lumen as needed. Thanks to the presence of this organ, toxic substances in bile do not irritate the intestinal mucosa and are found there only when there is food to digest. When the gallbladder is removed, a number of changes occur that the body needs to adapt to:
- bile cannot accumulate for a long time, so it constantly enters the intestines, and over time begins to be produced in smaller quantities;
- Digestive processes may become difficult, especially when trying to digest heavy foods;
- after some time, the body adapts to the changes, and bile is found in small quantities in the biliary tract.
Many patients worry about whether it is possible to live a full life without a gallbladder and how this will affect daily habits. Yes, within a month or two after the operation you can return to your usual diet and activity, but you should not abuse the foods that caused the need to remove the organ. However, you should not act as if there was no surgical intervention and ignore the signals from your own body.
You should monitor your diet even long after cholecystectomy.
Set of exercises
Perform each exercise 10-15 times, but if you feel tired, reduce the load and reduce their repetition. 1. Starting position (i.p.) - lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, feet spaced slightly wider than shoulders. After a deep breath, bend your knees in one direction or the other. 2. I. p. - lying on your back, legs bent at the knees. Place a bag of sand (weighing 250-300 g) on the upper abdomen. As you exhale, try to raise it as high as possible, and as you inhale, lower it. The same thing with a bag placed on the lower abdomen. 3. I. p. - lying on the left side, legs bent at the knee and hip joints. As you exhale, move your right leg back, gradually increasing the amplitude and decreasing the angle of flexion. The same thing on the right side. 4. I. p. - lying on your back, legs extended and spread as far as possible to the sides, arms along the body. Cross movement of straight legs - right over left, left over right. Breathing is voluntary. 5. I. p. - sitting on a chair, leaning back, grasp the seat with your hands. Take a deep breath. As you exhale, leaning on your arms and legs, lift your pelvis and return to the starting position. 6. I. p. - sitting on the mat, arms along the body, legs together. After a deep breath, alternately tilt the body to the right and left. Then bend the torso to the left with the right arm raised up and to the right with the left arm raised. 7. I. p. - standing behind a chair, holding the back. After taking a deep breath, as you exhale, move your right leg to the side and back. The same with the left foot. 8. I. p. - standing, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the belt. Turn the body to the right and left alternately. Breathing is voluntary.
S. G. Burkov
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
Comments
Composition and release form
The drug is available in capsules and tablets. The main active ingredient is mebeverine hydrochloride.
- One capsule of Duspatalin contains 200 mg of the active component and excipients, which include magnesium stearate, copolymers of methacrylic (Eudragit E30D) and ethacrylic acids, talc, hypromellose, glycerol triacetate. The shell also includes gelatin and titanium dioxide (E171). The ink contains shellac, black iron dioxide (E172), propylene glycol, ammonia solution, potassium hydroxide.
- Tablets are sold in quantities from 10 to 120 pieces, capsules (pills with an opaque gelatin shell with granules) are sold in quantities of 10-90 pieces.
General tips for relieving discomfort after surgery
Not all patients who have undergone laparoscopy feel great on the first day after losing their gallbladder.
For some people, this operation is difficult to tolerate. We are talking about elderly patients who are overweight.
If after surgery you feel severe discomfort in the right hypochondrium, there is a risk of damage to the sphincter.
Important! Be sure to notify the surgeon on duty if you are feeling unwell. Probably after this he will increase the dose of pain medication, which is injected into a vein for patients for 7 days after laparoscopy.
After damage to the sphincter, you can take any medications after medical consultation. Doctors insist that with such a complication you need to take antibiotics.
- Adjust your diet. In the first month of the recovery period, it is very important to follow the rules of the therapeutic diet. This is especially true for elderly and overweight patients. On the first day after surgery, a person is denied not only food, but also water. To prevent dehydration, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal infusions and moisten your lips with water.
- To normalize intestinal microflora, you need to drink low-calorie dairy products, such as yoghurt. They are recommended to be prepared at home.
- To prevent postoperative dysbiosis, you should take medications that restore intestinal motility.
- If you experience diarrhea on the first day after surgery, you should take lactulose disaccharide. The chemicals included in its composition promote the export of toxins and other pathogenic microorganisms from the body.
- Medicines that neutralize acid are prescribed for pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, as well as heartburn.
Medicines to be taken after surgery
So, your gallbladder was removed during laparoscopy. The question arises: what to take now?
Since the yellow liquid without a reservoir organ passes through the duct directly into the duodenum, the concentration of juice in the stomach increases.
Without drug therapy to “smooth out” this process, there is a risk of developing pathologies.
Doctors prescribe the following groups of medications to their patients:
- Choleretic.
- Sedatives.
- Ferents.
- Antispasmodics.
- Hepatoprotectors.
Most patients after surgery need to take all of these medications. Let's take a closer look at the specifics of their reception.
Choleretic
These medications should be taken by every person who has undergone laparoscopy.
Choleretic drugs after removal of the gallbladder help cleanse the body of the yellow substance and normalize the process of its entry into the stomach.
What is bile for? Without it, the gastrointestinal tract will not be able to absorb food, and will also not be able to digest it.
And, since the mechanism of yellow liquid entering the stomach after surgery has changed, the body needs time to restore normal functioning.
Without taking choleretic medications in the first month after removal of the reservoir organ, there is a high risk of stone formation in the duct.
Their presence in almost 70% of cases brings a person to the surgeon’s operating table. However, non-compliance with medical recommendations during the recovery period, namely refusal to use medications, is fraught with the recurrence of pathology.
Only in this case, concretions, that is, stones, will form in the duct through which the yellow liquid enters the duodenum, and then into the stomach.
Types of drugs
Many medications have been developed to support the digestive system after gallbladder removal. Their composition is varied, but they must be selected taking into account the intensity of the postcholecystectomy syndrome, the patient’s condition and the duration of the surgical intervention.
In total, there are 4 groups of drugs:
- enzymes;
- hepatoprotectors;
- antispasmodics;
- choleretic agents.
The patient is recommended to follow a special diet (table No. 5). Meals should be small and not include heavy foods that contribute to excess bile production.
Special gymnastic exercises help eliminate pain and discomfort. Great care is taken during physical exercise. If you are overweight, it is better to exercise in special groups under the supervision of staff.
Enzymes
Enzyme preparations are intended for better digestibility of food (unloading of the stomach and pancreas, inhibition of gas formation). All medicines presented have an approximate price, depending on the number of pieces in the package, the manufacturer and the weight of the components.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P8ZDMezif4U
Monotherapy with pancreatin:
- Gastenorm: from 200 rub.
- Creon: from 400 rub.
- Mezim: from 300 rub.
- Micrasim: from 600 rub.
- Pangrol: from 400 rub.
- Panzinorm: from 130 rub.
Enzyme medications with one active substance are used over a long course. Medicines help relieve stress on the pancreas and provide constant support to liver cells.
Combined drugs:
- Festal: from 200 rub.
- Digestal: from 150 rub.
- Enzistal: from 130 rub.
- Biofestal: from 130 rub.
- Normoenzyme: from 160 rub.
This type of enzyme ensures the breakdown of complex carbohydrates and fats. Compensates for insufficient gall bladder secretion and activates the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Hepatoprotectors
Thanks to the action of this group of drugs, liver cells are stimulated and restored. With the help of hepatoprotectors, the liver can withstand severe stress from the influence of medications, unhealthy foods and other influences.
- Essentiale, Essentiale forte N: from 450 rub.
- Gepagard: from 300 rub.
- Phosphogliv: from 500 rub.
- Hepatosan: from 300 rub.
Combicin: from 300 rub.
Painkillers
To relieve pain after postcholecystectomy syndrome, two main types of drugs are used - analgesics and antispasmodics.
It has antispasmodic activity against the smooth muscles of the digestive tract. The drug is available in the form of tablets or injection solution.
- Hyoscine butyl bromide: from 250 rub.
After taking the drug, there is a blockade of cholinergic receptors, a decrease in the tone and contractile activity of the muscles of the digestive tract. The medicine is indispensable for relieving biliary colic.
- Papaverine (ampoules, tablets, suppositories): from 40 rub.
Helps with spastic pain and colic caused by sudden compression of smooth muscles. The drug has an optimal cost and quickly helps in critical attacks.
- Bencyclane (Halidor): from 400 rub.
A myotropic antispasmodic that has a weak anesthetic and sedative effect. Has no effect on blood pressure. Used for severe spastic pain.
Eating without gall - diet, menu and individual recipes
After surgery to remove the gallbladder, you must strictly follow a diet with table No. 5.
Conditions for following the diet:
- exclusion of spicy, fatty, sour, fried, salty foods;
- avoidance of animal fats;
- increasing the amount of plant foods in order to activate metabolic processes in the liver tissues and reduce the risk of stone formation;
- drinking a sufficient amount of non-carbonated mineral waters, such as “Luzhanskaya”, “Morshinskaya”, “Naftusya”, “Polyana Kvasova”, “Berezovskaya”;
- split meals at the same time (up to 5 times a day) in small portions, which will help the body adjust to the regular production of bile;
- overeating is unacceptable.
It is recommended to enrich the daily diet with the necessary complex of minerals and trace elements. For these purposes, special herbal-based pharmaceutical products and herbal remedies are prescribed. We are talking about pumpkin seeds, pectins with plant fiber, etc.
Cooking requirements:
- Soups are cooked vegetarian.
- Meat, fish, poultry and products made from them are steamed.
- Choleretic products should be limited and consumed only on the recommendation of a doctor. We are talking about black bread, vegetable oils, white cabbage, eggs.
Dangerous manifestations
After removal of the gallbladder, patients experience disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs, often manifesting in the form of pain in the upper abdomen and right hypochondrium. The main symptoms that characterize this condition are:
- Sharp pain in the abdominal area.
- Nausea.
- Flatulence.
- Stomach upset.
- Hepatic colic and jaundice are possible.
This occurs due to a violation of the sphincter - a special muscle formation surrounding the bile and pancreatic ducts at the place where they pass through the wall of the duodenum.
It regulates the frequency of bile and gastric juice entering the duodenum, prevents food from entering the small intestine into the ducts and ensures the accumulation of bile in the gallbladder.
If the sphincter malfunctions, bile enters the intestine intermittently, the digestion and absorption of fats is disrupted, and signs of dysbiosis and chronic inflammatory bowel disease appear. Stagnation of bile increases the risk of stones forming in the liver ducts, which often leads to surgery.
Complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
This is a minimally invasive method and is preferred due to its high accuracy, small area of damage and quick recovery. However, the risk of complications after laparoscopic removal cannot be excluded. Possible:
- mechanical damage to tissues, organs and blood vessels;
- thermal injuries that occur due to excessive electrocoagulation lead to impaired circulation of the biliary system;
- leakage of bile as a result of damage to the ducts or gallbladder - provokes peritonitis;
- loss of stones from the gallbladder - occurs during resection of the bed or removal of the organ from the abdominal cavity.
The consequences of removal by laparoscopy are associated with insufficient visibility. The doctor sees only a certain area and cannot assess the condition as a whole.
Complications after removal of the gallbladder using the classical abdominal method are the same as with the laparoscopic method. Additionally, hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, suppuration of sutures, thromboembolism, and infection occur.
The consequences include the formation of adhesions. After laparoscopy, wounds heal quickly, scars heal or are barely noticeable. And with open surgery, scars remain.
Indications for use
Duspatalin not only helps with pain, but is also effective in treating concomitant reflex disorders such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and constipation, and bloating. By tidying up the functioning of the intestinal muscles, it simultaneously relieves these unpleasant symptoms.
The annotation to the drug contains a list of pathologies for which Duspatalin helps:
- abdominal cramps accompanied by combat syndrome;
- intestinal and biliary colic;
- dyskinesia of the gallbladder and ducts;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- acute cholecystitis;
- condition after removal of the gallbladder with stones;
- secondary spastic conditions due to impaired outflow of hepatic secretions.
The medicine should be taken half an hour before meals, swallowed whole and washed down with a glass of water. The standard dosage is one capsule three times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the onset of clinical effect - the course is not limited by other factors. Long-term use is possible until the pain goes away.
- 1 week - in the evening the dose is reduced by half a tablet;
- Week 2 - limited to 2 tablets per day;
- Week 3 - drink only half the tablet in the evening;
- Week 4 - leave a single dose of 1 tablet.
Duspatalin is contraindicated in pregnant women and patients allergic to mebeverine.
Important! According to the instructions for Duspatalin, tablets can be taken by patients over 12 years of age. For adolescents under 18 years of age, the drug is prescribed with caution and the capsule form is chosen.
When using the medication, undesirable reactions are possible:
- allergic manifestations, mainly on the skin - urticaria, exanthema, Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock (with hypersensitivity).
Such adverse reactions have been identified in post-marketing practice, so the frequency of their occurrence has not been precisely established.
There are drug substitutes that are used for irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. These include Trimedat, No-shpa, Drotaverine, Mebeverine, Dicetel, Sparex, Odeston. Many of them have a different active ingredient that has a similar therapeutic effect, that is, they relieve spasms and pain. It is worth noting that Duspatalin analogues are cheaper than the original.
Many problems associated with the biliary system require a special approach. Stone deposition or complicated types of cholelithiasis are indications for removal of the gallbladder. The operation to amputate an organ is called cholecystectomy.
Within 6-12 months after surgery, the patient can return to a full life.
Until that time, you should listen carefully to your doctor: find out what medications to take after removal of the gallbladder, and what foods you can eat.
- Consequences of gallbladder removal
- Treatment
- Enzymes
- Antispasmodics
- Choleretic drugs
- Hepatoprotectors
How to avoid complications
Any operation is a colossal burden for the body, especially when removing the gallbladder. Failure to follow nutritional rules and a therapeutic diet after removal of the gallbladder has a negative impact on well-being. A person is worried about discomfort, aching pain in the right side, nausea, belching, and bitterness in the mouth.
In order for your health to remain good after removal of the gallbladder, it is important to establish fractional meals. It should be served six times, the portion should not exceed 1 glass. The breaks between meals should be the same. On average - 3-4 hours with an eight-hour break for a night's rest. It is advisable to start the morning with a glass of warm water. A liquid at a comfortable temperature will dilate the ducts and prepare them for the release of bile.
People who have cholelithiasis as an indication for cholecystectomy need to be especially attentive to their diet. Despite the removal of the affected organ with stones, when favorable conditions are created, they appear again. Failure to comply with medical recommendations can lead to the development of complications - inflammatory process in the liver, hepatosis, cirrhosis.
Antispasmodics
These medications facilitate the flow of secretions into the intestines and relieve spasms of the biliary tract. They are taken regularly or symptomatically when pain occurs. During an attack, the effect of the drug occurs after about 20 minutes.
Postoperative drug therapy includes taking one of the following:
- Drotaverine;
- No-shpa;
- Buscopan;
- Riabal;
- Spasmalgon;
- Duspatalin;
- Mebeverine.
No-shpa
Drotaverine