Using ultrasound diagnostics, the presence of a hypoechoic or hyperechoic neoplasm can be determined. In the first case listed, the patient has nodes that have a reduced level of density. Such a diagnosis can be either normal or a disease. Only a doctor can determine why a hypoechoic formation occurred. It is impossible to do this on your own. The presence of a disorder can only be determined using an ultrasound machine. All tissues and organs have a certain level of echogenicity. Hypoechogenicity is characterized by a reduced level of density. This can be clearly seen on the monitor during an ultrasound.
Hypoechoic and hyperechoic formations can be clearly seen on ultrasound
What is a hypoechoic formation?
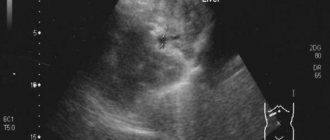
Hypoechoic formation is a formation localized in any organ and having echogenicity below the normal level. This area weakly reflects ultrasonic rays. The monitor is darker than other areas.
A hypoechogenic formation contains water or a cavity. On the monitor, the area is visualized as gray or black spots. With hyperechogenicity, the zones are light or even completely white.
To decipher the picture, a special scale with 6 categories of gray shade is used. The diagnosis is made by specialist doctors. Often hypoechoic formations are cysts. In this case, the patient is additionally referred for a biopsy.
You can decipher the image using a special scale
What is echogenicity called and how is it detected on ultrasound?
The concept of echogenicity refers to the ability of tissues and internal organs to reflect ultrasonic impulses and waves. A reduced level of ultrasound reflection ability is called hypoechogenicity, and an increased level is called hyperechogenicity.
On the monitor screen of an ultrasound machine, this indicator is visualized in the form of a gray scale, which, depending on the state of performance of the organ under study, changes its shade level.
For example, a hypoechoic formation in the pancreas is visualized as one dark gray spot or a black spot. But the average level of this indicator is visualized as a light gray shade of the pancreas with distinct, even contours. An increase in echogenicity, or hyperechogenicity, appears as a lighter area, up to white shades.
It is important to remember that the norm of the pancreas echogenicity indicator corresponds to the level of this indicator of a healthy liver. Any decrease or increase in echogenicity is also always compared with liver parameters.
The root causes of hypoechogenicity
The formation can have any localization. Formations also have different underlying causes of development and symptoms.
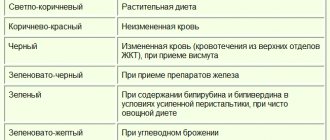
The root causes of hypoechogenicity, depending on the location of the formation, are listed in the table below.
| Liver and gallbladder | The causes of hypoechogenicity include: • polyps; • lymphoma; • angiosarcomas. |
| Bladder | The following factors provoking the lesion are identified: • fibroids; • transitional cell malignant process. |
| Abdomen and pelvis | Among the root causes that contribute to the finding of hypoechogenicity on ultrasound are: • hernia; • abdominal hematomas; • phlegmon; • inflammatory process in the lymph nodes; • spread of metastases; • carcinoma of the cecum: • testicular cancer in men. |
| Subclavian zone | The violation is a consequence of: • benign neoplasms; • cysts; • thymomas of the thymus. |
Locations of formation localization
The clinical picture and the main diagnosis depend on the localization of the formation with a low density index. Pathological changes may affect:
- thyroid gland;
- uterus;
- mammary gland;
- spleen;
- ovaries;
- kidneys;
- pancreas;
- liver.
Hypoechogenicity is not a diagnosis, but only the result of an examination. That is why in an area with low density you should not worry ahead of time.
If the pathological process has affected the thyroid gland, then the presence of cysts and nodules can be suspected. Cancer is diagnosed in only 5 patients out of 100. An altered structure of the uterus indicates an inflammatory process, fibroids or miscarriage. Often the symptom indicates neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
Hypoechogenicity in the mammary glands may indicate various pathologies
Most often, hypoechogenicity is observed in the mammary glands. The symptom indicates:
- cancer;
- adenosis;
- the presence of cystic formations.
In the kidneys, an area of low density indicates either cancer or cystic formations. With a malignant tumor, the boundaries of hypoechogenicity are erased and the structure is uneven. Additionally, the patient may be recommended a biopsy.
Changes in the pancreas may be explained by:
- metastases;
- cysts;
- pancreatitis.
Hypoechogenicity can manifest itself in absolutely any human internal organ. Some of the underlying causes require drug therapy or urgent surgery. Ignoring any doctor’s orders is strictly prohibited. First of all, it is important to exclude the possible presence of a cancer process.
Such formations may indicate cancer and are observed in different organs
In some cases, hypoechogenicity does not cause any discomfort and does not provoke the appearance of negative symptoms. The reduced density will be discovered completely by accident.
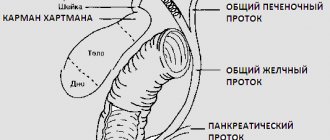
Pancreatic cysts on ultrasound
Single small simple cysts occur as incidental findings in the healthy pancreas. In chronic pancreatitis, small simple cysts are quite common. If a cyst is suspected, note the enhancement of the contour of the far wall and the effect of signal enhancement in the tissue behind. Simple cysts are isolated from the parenchyma by a smooth thin wall. There should be no partitions or wall irregularities inside; the contents of the cyst are anechoic. Simple cysts are always benign. But, if the cyst is not obviously “simple”, further investigation is required.
| Photo. Simple pancreatic cysts on ultrasound. A, B — Single simple cysts in the area of the body (A) and neck (B) of the pancreas with a thin smooth wall and anechoic contents. B - Classic signs of chronic pancreatitis: the main pancreatic duct is dilated against the background of parenchymal atrophy, the contour of the gland is uneven with notches, there is calcification and small cysts in the parenchyma. | ||
Important. Simple pancreatic cysts are common, but don't forget about cystic tumors. Cancer is the most dangerous disease of the pancreas.
There are two types of pancreatic cystic tumors: benign microcystic adenoma and malignant macrocystic adenoma. Microcystic adenoma consists of many small cysts and appears as a dense formation on ultrasound. Macrocystic adenoma usually includes fewer than five cysts larger than 20 mm. Sometimes polypoid formations can be seen in such cysts.
| Photo. A, B - Benign microcystic adenoma of the pancreas: a large cystic formation in the head of the pancreas. B - Pancreatic adenoma with macro- and microcystic components. | ||
With pancreatitis, pancreatic secretions digest surrounding tissue and pseudocysts form. Pseudocysts from the abdominal cavity can extend into the chest and mediastinum. Pseudocysts are often found in patients who have suffered acute pancreatitis (see below).
As a result of pronounced dilation of the pancreatic duct, retention pseudocysts may form distal to the site of obstruction.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture varies depending on the underlying cause and location of the deviation. The main danger signs include:
- difficulty swallowing and eating;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- pain and discomfort at or near the site of hypoechogenicity;
- hoarseness and hoarseness in the voice;
- unreasonable decrease or increase in body weight;
- improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- constant drowsiness and feeling of fatigue;
- sudden mood swings;
- change in body temperature;
- dullness of hair;
- brittleness of the nail plate.
Patients often complain of drowsiness and fatigue
All symptoms are common. The patient may have several symptoms or all at once. It all depends on the factor that provoked the decrease in density.
In the presence of serious illnesses, the patient’s well-being rapidly decreases. Every day a person has less and less strength. Usual things become a real test. The skin becomes drier.
Signs of general intoxication of the body appear. Aggression may occur without obvious reasons. High risk of underweight.
Dilated pancreatic duct on ultrasound
The internal diameter of the normal pancreatic duct is less than 3 mm. The duct is better visualized with transverse scanning in the middle third of the body of the pancreas. In order to make sure that you have found the duct, you need to see the pancreatic tissue on both sides of it. The splenic vein posteriorly or the gastric wall anteriorly may be falsely interpreted as the pancreatic duct.
The walls of the pancreatic duct should be smooth and the lumen should be clean. When the duct is dilated, the walls become uneven; scan not only the head of the pancreas, but also the entire biliary tract.
The main causes of dilatation of the pancreatic duct: tumor of the head of the pancreas or ampulla of Vater's papilla (combined with jaundice and dilatation of the biliary tract); stones of the common bile or pancreatic duct; chronic pancreatitis; postoperative adhesions.
| Photo. A man with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus complains of weight loss and abdominal pain for several months. Ultrasound shows an enlarged common pancreatic duct with an uneven wall. Upon further examination, calcifications with a shadow behind them are clearly visible in the duct (B). | ||
| Photo. A patient with acute pancreatitis: a large pseudocyst has formed at the level of the tail (see above), the dilated pancreatic duct opens into a pseudocyst. | ||
Diagnostic methods
The only way to detect a hypoechoic area is to resort to ultrasound diagnostics. In this case, the examination is carried out with a special device that emits ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is a painless and completely safe procedure
In contact with internal organs, ultrasonic waves are reflected and returned. Thanks to this, everything that happens is displayed on the monitor. Subsequently, the doctor deciphers the results obtained.
Ultrasound is harmless regardless of the patient's age. The method can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The method does not require special preparation. An exception is abdominal ultrasound examination. In this case, sometimes you need to fill your bladder or follow a diet.
Before performing an ultrasound, an acoustic gel is applied to the area being examined. The product promotes better glide. Does not interfere with visualization and does not cause an allergic reaction.
After diagnosis, you need to remove the remaining gel. This can be done using dry wipes. The doctor will decipher the indicators and confirm or deny the likelihood of the presence of hypoechoic tissue.
From this video you can learn more about benign formations in the mammary gland:
Types of hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas and their significance
29.06.2017
Often, in the final description of an ultrasound examination of the pancreas, many patients can read that there are hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas. The presence of such a symptom may indicate the development of a serious pathological disorder in the organ under study. In this review, we will take a closer look at what hyperechoic inclusions are and what types of them exist.
The concept of hyperechogenicity
Have you been treating PANCREATITIS for many years without success?
Chief gastroenterologist of the Russian Federation: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of pancreatitis with...
Read more "
Terminology such as the level of echogenicity of internal organs is used only for ultrasound examinations and denotes the degree to which the organs under study can reflect an ultrasonic wave directed at it through a special sensor of an ultrasound machine.
Each organ has its own norm for this indicator, which depends on its level of density. Organs with greater density will have a higher level of echogenicity than organs with a looser structure.
An increase in the level of echogenicity of the pancreas indicates the proliferation of fibrous tissue and the development of hyperechogenicity.
During the development of hyperechogenicity in the pancreas, the following types of hyperechoic inclusions can be visualized:
- Small pinpoint hyperechoic inclusions representing calcifications. As is known, the functional ability of the pancreas is to produce special enzymes, a small part of which can be retained in the lumens of small glands. Over time, calcium salts begin to deposit in these gaps, which leads to the formation of stones, or calcifications. People usually call them small pebbles, which in themselves do not pose a huge danger. If the conclusion of an ultrasound examination indicates that the parenchyma has a moderately increased level of echogenicity, then we are talking about the development of a chronic inflammatory process, namely chronic pancreatitis.
- Hyperechoic linear inclusions, which are not a specific sign for a particular pathological process, representing the presence of dense tissue, in most cases, the formation of foci of replacement of healthy tissue with connective tissue.
The presence of hyperechoic inclusions can be determined with the development of the following pathological disorders:
- lipomatous lesion of the pancreas, which is a process of replacement of glandular tissues with fat, in which this organ does not increase in size;
- development of acute pancreatitis accompanied by swelling of the gland, manifested by sharp pain in the abdominal area, discharge of vomit and the development of diarrhea;
- the occurrence of tumor-like neoplasms, accompanied by pallor of the skin, a sharp decrease in body weight, stool disorders and loss of appetite;
- the development of pancreatic necrosis, characterized by the death of tissue of a parenchymal organ at the cellular level, manifested by the occurrence of unbearable pain in the abdominal area, which can provoke a painful shock, as well as the uninterrupted process of vomiting and diarrhea;
- fibrous lesion of the pancreas, characterized by the proliferation of connective tissues.
The occurrence of hyperechogenicity in the organ under study can also be temporary, manifested in the following cases:
- against the background of the development of infectious pathology of the upper respiratory tract, such as influenza, pneumonia, or one of many infectious pathologies;
- after a radical change in diet;
- with a sharp change in lifestyle;
- when performing an ultrasound after a hearty breakfast or lunch.
In such cases, the level of echogenicity increases to a moderate level, while hyperechogenicity in pathological disorders has higher outcome rates.
Chief gastroenterologist of the Russian Federation: “PANCREATITIS does not go away?! A simple treatment method has already healed hundreds of patients at home! To cure the pancreas forever you need...”Read more »
Types of hyperechoic inclusions
Hyperechoic inclusions in the parenchymal organ under study can be:
- pseudocyst, which is a liquid formation that occurs after elimination of an acute form of pancreatic lesion of the gland, is characterized by the formation of an uneven and jagged contour;
- as mentioned above, these can be calcifications or small pebbles;
- metastatic tumors;
- certain segments of adipose or connective tissue;
- cystic fibrous areas of gland tissue.
Treatment methods
For the prevention and treatment of pancreatic diseases, our readers recommend Monastic tea. This is a unique product that includes 9 biologically active medicinal herbs useful for the pancreas, which not only complement, but also enhance each other’s actions. Monastic tea will not only eliminate all symptoms of inflammation of the gland, but will also permanently eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
Read more "
The treatment regimen for increased echogenicity of the pancreas should be prescribed only by a highly qualified gastroenterological specialist.
To begin developing the most effective treatment regimen, a specialist must initially establish the true cause that provoked the formation of hyperechogenicity.
If the formation of this symptomatology was provoked by the development of an acute form of pancreatitis, then therapeutic treatment should consist of taking special medications, the pharmacological action of which is aimed at reducing the production of hydrochloric acid in the gastric cavity and inhibiting enzymatic activity in the pancreatic cavity.
When this ultrasound indicator increases, caused by the development of lipomatous lesions, experts recommend following a special dietary diet that excludes all foods containing animal fats.
If the etiological factor is the formation of calcifications or the development of fibrous lesions of the organ being studied, then experts initially prescribe adherence to a strict dietary diet, and in the absence of positive dynamics, doctors question the treatment of the pathology through surgical intervention.
The formation of reactive pancreatic lesions requires therapeutic elimination of the underlying pathology in compliance with a special dietary diet.
It is important to remember that an increased level of echogenicity is just a symptom of ultrasound examination of a parenchymal organ. To prescribe therapeutic treatment, specialists do not need only these ultrasound results. In order to develop the most effective tactics for eliminating pathology, it is necessary to undergo a number of additional examinations, based on the results of which the tactics of therapeutic procedures will be built.
What to do if you have pancreatitis?
Ignoring or improperly treating pancreatitis can lead to dire consequences:
- diabetes;
- liver and kidney failure;
- oncology, which threatens partial or complete removal of the pancreas.
Not to mention strict diets, constant intake of enzymes and periods of exacerbation, when there is no longer any strength to live... “But it is possible to forget about pancreatitis forever,” says the chief gastroenterologist of the Russian Federation...
Read more "
pankreatit03.ru
Treatment measures
Treatment is selected by the doctor. Sometimes therapy is not necessary at all. Depending on the diagnosis, the patient may be recommended:
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- traditional therapy;
- homeopathic treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- taking medications.
There is no single treatment therapy. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, since hypoechogenicity can be provoked by various provoking factors.
Possible risks
The most serious cause of hypoechogenicity is malignancy. Some tumors cannot be excised. The patient's condition is constantly deteriorating. Body weight rapidly decreases and appetite disappears.
Cancer is a serious disease that, without treatment, always leads to death.
With cancer, the functioning of the body as a whole is disrupted. If left untreated, the patient may experience spontaneous death. Every day will begin with unbearable torment.
In order to avoid serious complications, preventive diagnosis is preferred. An ultrasound should be performed annually.