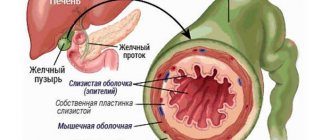
The gallbladder in a healthy person is pear-shaped - the organ is divided into three parts. Constriction is considered a developmental pathology, and it can be congenital or acquired. The change in shape occurs more often at the junction of the body and the lower component. If the constriction is diagnosed in several places at once, necrosis of the gallbladder tissue forms, but, fortunately, this is a rare phenomenon.
Etiology
The reasons for the formation of a congenital form of constriction of the gallbladder in a child remain not fully understood. Some experts tend to consider the cause to be intrauterine developmental anomalies or complicated heredity. However, such theories have not yet received scientific confirmation.
The acquired variety of such a disease is determined by the influence of several prerequisites, which can be physiological or pathological, i.e. associated with the course of a particular disease. Among the diseases it is worth highlighting:
- formation of calculi in case of gallstones;
- the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the mucous layer of the gallbladder;
- liver damage due to the influence of a wide range of pathological processes to which this organ is susceptible;
- various liver injuries;
- an increase in liver volume, which can occur against the background of hepatitis or cirrhosis.
The group of physiological prerequisites includes:
- lack of physical activity, which may be caused by a person being overweight or having a professional background that requires prolonged sitting or prolonged standing;
- performing strenuous physical activity or lifting weights;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications;
- lack of diet;
- weight loss, which can be caused by following strict diets, voluntary refusal of food, or severe cancer;
- pregnancy - the appearance of constrictions during this period of life is explained by the enlargement of the uterus and the active growth of the fetus. Such processes cause compression and displacement of internal organs, in particular the gallbladder and liver.
Diet for gallbladder constriction
Having a special diet is important to carry out along with treatment of the disease. In addition to avoiding unhealthy foods, you should consume all kinds of cereals, vegetable broths, fermented milk drinks, and cottage cheese. Constriction of the gallbladder requires a balanced diet and plenty of fluids. It is important not to overeat during meals.
The diet for constriction of the gallbladder in children and adults should include taking decoctions and special infusions. They help prevent the onset of cholecystitis. The use of such folk remedies becomes possible after consultation with a doctor.
Gallbladder constriction is one of the ailments that can be caused by a number of factors. Usually this disease does not cause any concern to a person. If you experience severe discomfort, you should go to the hospital to prevent other dangerous pathologies.
Classification
Depending on the causes of occurrence, such a disease may be:
- congenital or primary;
- acquired.
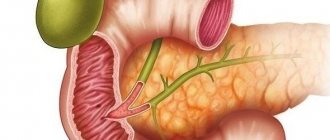
Also, the constriction of the gallbladder can be divided according to its location. So it may occur:
- in the area of the body of this organ;
- in the cervix;
- between the body and the neck;
- in the bile duct;
- in the area of the bottom of the gallbladder.
In addition, the number of bends may differ.
Bend and constriction of the gallbladder
How to determine the disease
It should be understood that it is almost impossible to determine the disease without examining a specialist. The conclusion should be made by professionals who conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body. It is these studies that provide a clear picture of the shape and size of the gallbladder.
It is impossible to determine the presence of a problem based only on the clinical picture. In order to identify pathology, an ultrasound is usually prescribed. Tomography is often performed in the area of the gallbladder.
Constrictions of this organ can be observed in a variety of areas. Most often they occur in the area of the bottom and neck of the gallbladder. With an ultrasound examination, a specialist can determine the area of increased echogenicity. It looks like the lumen of the gallbladder.
If the gallbladder is located in the patient’s body more or less accessible, the doctor has the opportunity to study the problem in detail and accurately determine whether the patient is suffering from a constriction or an inflection. These phenomena are similar to each other, but their treatment must differ.
Symptoms
Congenital inflection of this organ is often characterized by an asymptomatic course. In such cases, the disease can only be detected by chance, for example, during a preventative ultrasound or when a similar examination is prescribed to diagnose a completely different ailment.
In some cases, symptoms of the disease may appear, but they will be of an erased nature, which is why a person may simply not pay attention to them. Such clinical manifestations include:
- the appearance of nausea immediately after a person wakes up;
- abdominal discomfort that may occur after eating junk food;
- bloating;
- frequent urge to vomit.
Often such symptoms are attributed to other disorders.
The acquired type of constriction in the gallbladder can also be asymptomatic, but in the vast majority of cases, it still has a rather intense manifestation of the clinical picture. The main symptoms are:
- the appearance of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. The pain is often aching in nature;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- sensation of bitter taste in the mouth;
- profuse sweating;
- causeless weight loss;
- loss of appetite or complete aversion to food;
- stool disorder - in this case, the stool has a liquid consistency, only sometimes patients complain of constipation;
- irradiation of pain to the back and collarbone;
- loss of consciousness is the least common symptom;
- heartburn and belching;
- change in the shade of urine - it becomes darker, and stool - they become discolored;
- heaviness and discomfort in the stomach.
Why an organ becomes deformed
During examination, a congenital inflection of the gallbladder or acquired is observed. In the first case, the cause is an unbalanced diet of the expectant mother and a difficult pregnancy; in the second, a violation of the child’s diet and eating habits.
Bend of the gallbladder in a child
When the body is hungry, bile is produced to digest food. At this moment you need to feed the baby. If food arrives at an unfavorable time for intake, there is not enough bile to fully digest it. Overeating occurs, which is harmful for the baby - he feels heaviness in the stomach and nausea. In this regard, the gallbladder is deformed. The famous doctor Komarovsky believes that a child should be fed only when he is hungry. “Aggressive” foods are contraindicated for a child - fried, smoked, spicy foods.
We recommend reading:
Types of gallbladder deformation
Congenital s-shaped gallbladder is rare in newborns. Because of this, the baby behaves restlessly, especially at night, vomits after eating, and the child has a pale skin color. Over time, the organs unfold and change their position somewhat. In this regard, the gallbladder takes on the correct expanded shape, and the cause of concern disappears. Lifting significant weights is dangerous both for the unformed skeleton and for the correct position of the gallbladder. An important factor in good health is a positive mood, lack of stress and mental stress. In an effort to make a child prodigy out of a son or daughter, this can result in serious consequences for the health and psyche of the little person. You should not expose your child to various debilitating diets for weight loss.
Diagnostics
To identify the presence of a bend in the gallbladder, it is necessary to conduct several instrumental examinations of the patient, but before prescribing them, the gastroenterologist should independently perform several manipulations, including:
- conducting a detailed survey of the patient - this will enable the doctor to find out the first time of appearance and severity of the symptoms of the disease;
- familiarization with medical history and family history - to identify etiological factors, which will be individual in each case;
- carrying out a physical examination - it must necessarily include a study of the condition of the skin and visible mucous membranes, as well as palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity over the entire surface, with attention focusing on the area of the right hypochondrium. When pressing on the projection of the affected organ, the patient will feel severe pain.
Instrumental diagnosis of gallbladder constriction includes:
- Ultrasound is the main diagnostic technique that will indicate the deformation of this organ;
- CT is a modern alternative to the previous procedure;
- Cholangiography is a method of contrast examination of the bile ducts.
Cholecystograms for congenital constrictions of the gallbladder
Only after studying the results of all the above examinations and differentiating the constriction of the gallbladder with other ailments that have similar symptoms, the gastroenterologist draws up the most effective tactics for treating the disease.
Treatment of a deformed organ
It takes a long time to treat gallbladder deformation with the help of medications and physiotherapy. The child should be consulted by a good doctor - a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe painkillers and choleretic drugs. Infusions of herbs help in the treatment, which gently help remove bile so that there is no stagnation. Physiotherapy increases blood circulation in the diseased organ, which means it increases the intensity of bile outflow. Sick children are recommended for sanatorium-resort treatment. Therapy for adults differs from treatment for children. Excesses of the gallbladder in adults occur against the background of long-term changes in other organs of the digestive system. If the process progresses to stone formation, surgical removal of the organ is required. Otherwise, clots may block the bile ducts.
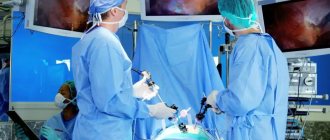
Treatment is complemented by a diet that excludes fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, alcohol, coffee and drinks containing preservatives and dyes. In some cases, physiotherapeutic procedures help correct the position of the organ. Nowadays, abdominal surgery has been replaced by a more gentle method of removing the gallbladder - laparoscopy.
Treatment
If the disease does not cause discomfort and does not cause any clinical signs, then a person can live with it all his life without even knowing about its presence. In adult patients, treatment, in most cases, will be conservative. Thus, therapy will be aimed at:
- taking medications - to normalize the production and outflow of bile, prevent the formation of stones and change its chemical composition;
- maintaining a gentle diet, which involves avoiding fatty and spicy foods, smoked foods and preservatives, carbonated drinks and dried fruits. In this case, you need to eat often, up to five times a day, but in small portions. The ingredients of the dishes must be chewed thoroughly. All food must be boiled or steamed. The diet is prepared by a gastroenterologist or nutritionist;
- undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures;
- using traditional medicine recipes - this can only be done after consulting with your doctor;
- performing physical therapy exercises.
Surgical treatment is sought when:
- ineffectiveness of conservative methods of therapy;
- severe course of the disease, the symptoms of which are so pronounced that they reduce the patient’s quality of life;
- formation of stones in the gallbladder or ducts.
Therapy for such a disorder in children consists only of following a dietary diet. This is due to the fact that the disease does not entail the development of complications and does not cause any clinical manifestations. Moreover, a congenital constriction of the gallbladder can straighten out on its own as the child’s body grows.
Hardening of the gallbladder walls: treatment of pathology
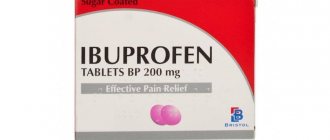
Treatment of cholecystitis is based on diet therapy and the use of medications. In case of calculous inflammation, an operation is performed - gallbladderectomy. Drugs that improve the flow of bile include the medications “Allohol”, “Holosas”, “Ursosan”. In case of exacerbation, antibiotics are prescribed. To reduce spasm of the organ muscles and relieve pain, the drug “No-shpa” is used.
Prevention
As preventive measures, you must follow several simple rules:
- lead a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- avoid emotional and physical stress;
- take medications only as prescribed by a clinician;
- eat properly and balanced;
- promptly treat pathologies that can lead to the development of the underlying disease. To do this, you need to undergo a full medical examination several times a year.
The prognosis of gallbladder constriction will depend on the factors causing the disease.
Diagnostic tests
With the help of the patient's complaints, examination and anamnesis, the doctor can only make a presumptive diagnosis. When palpating, he notes pain under the right hypochondrium and in the epigastric region (the area where the stomach is located).
To confirm the diagnosis, general laboratory tests of stool, blood and urine are prescribed. Based on their results, the presence of inflammatory processes and complications is determined.
In the blood, the level of cholesterol, bilirubin, protein, and changes in liver enzymes are important for biochemistry.
The most reliable methods for detecting deformities of the gallbladder are instrumental, primarily ultrasound.
Additionally, other diagnostics are prescribed:
- Layer-by-layer scanning using CT to clarify deformations and changes identified in the organ using ultrasound.
- Cholangiography is an X-ray examination of the bile ducts after injection of a contrast agent into them. Establishes their passability, condition and functionality.
An ultrasound scan examines the size and shape of the organ, the presence of constrictions, the number and location. The inflammatory process in it, thickening of the walls, and adhesions are determined. Assess level of functioning.
In a healthy organ, the bile secretion is homogeneous - echo-negative. During deformation and stagnation, its structure is disrupted. An echogenic suspension appears in the gallbladder. It reflects ultrasonic waves during ultrasound.
The study determines the presence of precipitate and its quantity. This compacted secretion is the first sign of the development of cholelithiasis.
During an ultrasound scan of the organ, flakes are visualized - this is a suspension. Even the smallest particles are detected. Its composition may vary. To determine it, duodenal intubation is prescribed, bile is collected and the echo suspension in it is examined.
Timely detection and treatment of pathology at this stage prevents serious consequences and complications. The reasons for the formation of suspensions during organ deformation have not been fully studied; the provoking factor is considered to be stagnation and disruption of the outflow of bile from it.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor determines what to do next, that is, what treatment methods to use. Patients with congenital anomalies of organ development without functional impairment are observed. Treatment is carried out only during the period of exacerbation of the disease.
The acquired pathology is examined, and conservative therapy is most often prescribed. It can last up to 3 months and is aimed at eliminating inflammation, relieving pain, and normalizing the functioning of the gallbladder.
Surgery is performed only in case of severe development of the disease.
Bend of the gallbladder in a child, treatment
Once your child is diagnosed with a kinked gallbladder, the doctor will prescribe treatment. As a rule, it is conservative and its purpose is to improve the flow of bile. Treatment includes the following methods:
- a diet that excludes the consumption of fried, fatty, spicy, sour foods;
- for the period of exacerbation - a special diet, taking choleretic drugs, antispasmodics and painkillers;
- in case of inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed;
- phytotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
The information in the articles is for general informational purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. See your doctor first. All copyrights to materials belong to their respective owners