Indications for MRI
This method of instrumental diagnostics is a method of visualizing internal organs, which is based on recording the response of the atoms of the body’s cells in response to the influence of an electromagnetic wave of a certain frequency. This technique allows for layer-by-layer scanning of a specific anatomical area of the body. Its implementation is indicated for a number of pathological processes of the colon, they include:
- Detection of malignant or benign neoplasms.
- Determination of violations of the anatomical integrity (ruptures) of the intestinal walls.
- Diagnosis of internal bleeding of the digestive tract.
- Determination of the presence and severity of the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane.
- Comprehensive diagnosis of functional or mechanical obstruction of the colon.
- Assessment of the quality of previously performed conservative or surgical therapy.
MRI allows you to visualize the location and structure of pathological formations, but it does not always make it possible to determine the nature and nature of the disease.
Methods for examining the stomach and intestines
In addition to MRI, there are other imaging techniques for the digestive system. The most popular is ultrasound examination. Ultrasound provides a lot of information about blood vessels and parenchymal organs (liver or spleen). Its value in diagnosing the stomach and intestines is that it allows you to detect congenital malformations, deformations and neoplasms.
A computed tomography scan is a series of x-rays that are then processed on a special computer to create a three-dimensional image. The sensitivity of the technique can be increased by introducing a special contrast that accumulates in certain types of tissue. CT allows complete visualization of the abdominal organs. Disadvantages include the presence of radiation exposure and the impossibility of performing it during pregnancy.
Endoscopic examination methods (
fibrogastroduodenoscopy , colonoscopy ) are carried out using special probes that are inserted through the mouth or through the rectum.
They allow you to visualize the inner wall of the digestive tract, detect areas of narrowing of the lumen, signs of inflammation, and neoplasms. It is also possible to biopsy individual tissues for subsequent cytological examination (if a malignant process is suspected). Disadvantages include discomfort during endoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of MRI
MRI has a number of advantages when used correctly according to its indications. These include:
- No invasion that could cause damage to mucous membranes or skin.
- Quite fast implementation.
- There is no ionizing radiation, unlike radiographic research techniques.
- High-quality visualization of even small formations and structural changes.
Disadvantages of this research methodology:
- the impossibility of performing an MRI if there are metal implants in the body;
- lack of possibility of histological examination, which is very important for diagnosing tumor pathology.
Also, during such a study, it is not possible to carry out therapeutic procedures in parallel.
How does the procedure work?
Before the procedure, the patient is asked to change into a special robe or shirt. You can keep your clothes on as long as they don't have metal fasteners. You will need to leave metal jewelry, plastic bank cards, phones and other electronics in the locker room or with the administrator.
If an MRI of the small intestine is planned, the patient is given a contrast drink, then a contrast agent is injected into the blood through an intravenous catheter.
After both contrast agents have been administered, the patient is placed inside the machine in a supine position. The patient must lie still during the entire examination.
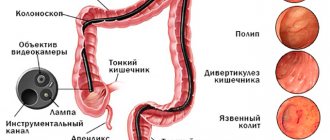
Indications for colonoscopy
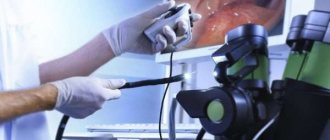
Colonoscopy is an optical technique for visualizing the intestinal mucosa. The method is based on the introduction into the cavity of the large intestine of a flexible fiber-optic tube that contains a camera and lighting. There are several main indications for colonoscopy, namely inflammatory and tumor changes in the mucous membrane that require visualization as well as biopsy:
- Crohn's disease (chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane) and ulcerative colitis, which are characterized by chronic inflammation and the formation of defects (ulcers and erosions).
- Cancer (adenocarcinoma) is a malignant neoplasm that develops from glandular cells of the mucous membrane.
- Polyps are benign tumor-like formations that form from the mucous membrane and protrude into the lumen of the colon.
- The presence of foreign bodies requiring their removal.
A biopsy is performed during colonoscopy; a section of the mucous membrane of the area of the pathological process is taken for subsequent histological examination.
Study procedure
Magnetic resonance imaging involves the use of the properties of the magnetic field and the specifics of their interaction with the nucleus of the hydrogen atom, which is located in the human body. The procedure for magnetic resonance imaging is carried out in accordance with the following scheme.
The patient is placed inside a magnetic resonance imaging machine, which has an open circuit. The device creates magnetic fields that excite hydrogen atoms in the patient's body. Radio waves appear due to radiation from cell nuclei. The image begins to form on the monitor screen.
The cells begin to return to their original state without experiencing damage. Using a computer, the obtained data about organs and blood vessels is processed. A three-dimensional image (high resolution) is created. The duration of the organ examination takes about 25 minutes. As a rule, medium-field and ultra-high-field machines are used for diagnostics.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is an invasive technique for imaging the large intestine. During the insertion of a colonoscope into the intestinal lumen, there is a risk of damage to the mucous membrane of varying severity, as well as infection with pathologies with a parenteral transmission mechanism (HIV AIDS, viral hepatitis).
The procedure itself is quite unpleasant and brings a feeling of discomfort to the patient. The main advantage of colonoscopy is the ability to perform a biopsy, as well as perform a number of therapeutic procedures, which include:
- direct removal of small benign formations and polyps;
- stopping bleeding from the walls of the colon;
- elimination of minor damage to the mucous membrane;
- removal of foreign bodies from the lumen of the large intestine.
Due to these advantages, colonoscopy is often used as a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure.
Useful properties and uses of angustifolia fireweed
Botanical characteristics of fireweed angustifolia
Angustifolia fireweed is a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the fireweed family. The straight, unbranched, succulent stem reaches a height of 75 to 200 cm. The creeping rhizome is well developed, has numerous shoots and can reach a length of 100 cm. The leaves are alternate, sessile (very short petiole), elongated, with a pointed apex.
The flowers are wide open, purple or bright pink, and are collected in a conical raceme at the top of the plant. The fruit is an elongated capsule with numerous small seeds inside. A characteristic feature of fireweed seeds is the presence of a tuft (consists of fluff), thanks to which the seeds can scatter a considerable distance from this medicinal plant.
Narrow-leaved fireweed blooms in the summer - from mid-June to mid-August, and bears fruit in late July - August.
The natural distribution area of angustifolia fireweed is almost the entire territory of Russia. This medicinal plant grows abundantly along roads, in forest clearings, burnt areas and embankments.
Useful properties of fireweed
In folk medicine, both the above-ground part of fireweed - leaves and flowers - and the underground part - rhizome - are used. The collection of leaves and flowers occurs during the flowering period of the medicinal plant, and the flowers should not be fully open, since there is a high probability that they will turn into seeds during the drying process. Before drying, the leaves are separated from the shoots and laid out under a canopy in a thin layer.
The roots are harvested after flowering (in autumn). After digging, the rhizome is cleared of soil and washed well under cold water, after which it is dried in the oven at a temperature of 70 ° C.
The chemical composition of fireweed leaves contains a number of useful organic compounds: flavonoids, tannins (up to 20%), mucous substances (up to 15%), tannin of the pyrogall group (up to 10%), alkaloids (0.1%), coumarins, sugars, ascorbic acid (vitamin C), iron, manganese, provitamin A (retinol acetate).
The chemical composition of the roots contains carotenoids, flavonoids, tannins, starch, and mucous substances.
The chemical composition of flowers contains flavonoids, tannins, mucous substances, ascorbic acid, coumarins, sugars and essential oils.
Healing infusions and decoctions of fireweed are used in folk medicine as an effective enveloping, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, sedative, hemostatic and laxative agent.
Application of fireweed
Decoction and infusion of fireweed are used for a number of diseases of various organs and organ systems. In their chemical composition, fireweed leaves contain a significant amount of mucus and tannin, which is why the infusion is successfully used for various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract characterized by high acidity (stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis). In addition, the infusion helps to cope with the negative consequences of intestinal dysbiosis and normalize the flora.
The presence of ascorbic acid, iron and manganese in the chemical composition of this medicinal raw material characterizes the healing infusion as an effective remedy in the fight against iron deficiency anemia (low hemoglobin as determined by a general blood test). In addition, the infusion can be used by women during heavy menstruation, as well as during the postpartum period.
Infusion and decoction of fireweed stimulate cardiac activity and have a mild effect on the nervous system. They are used for insomnia, nervous overexcitation, increased irritability and headaches.
As an external remedy, an infusion of leaves is successfully used for diseases of the oral cavity, such as stomatitis, sore throat, and sore throat. Dry powder from the leaves of the medicinal plant is used as an adjuvant in the treatment of infected wounds and ulcers. It is used as a poultice for otitis (including acute) and soft tissue bruises.
Infusion of fireweed angustifolia
Recipe No. 1: 15 g of crushed medicinal raw materials (aerial parts of the medicinal plant) are poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left for 60 minutes, then filtered into a clean container and taken 1 tablespoon (15 ml) 3 times a day.
Recipe No. 2: 1 tablespoon of medicinal raw materials (roots and rhizomes) is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left for 45 minutes, then filtered into a clean container. Take 15 ml infusion 3 times a day for headaches and insomnia.
Recipe No. 3: 1 tablespoon of medicinal raw material (leaves) is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left for two hours, then filtered into a clean container. Take the medicine 1 tablespoon (15 ml) 3 times a day for anemia and 1/3 cup three times a day for chronic cystitis.
Recipe No. 4: 2 tablespoons of medicinal raw materials are poured into 400 ml of boiling water and left for 6 hours, then filtered into a clean container. This infusion is used as an external remedy for otitis media; for this, a tampon is well moistened in the infusion and inserted into the ear hole.
Decoction of fireweed angustifolia
10 g of dry medicinal raw materials (flowers) are poured into 200 ml of water and placed in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes. Take a decoction of 1 tablespoon (15 ml) 3 times a day.
Fireweed tea
Several hundred years ago, tea was an extremely rare and very expensive drink in Rus', which only noble people and the rich could afford. That is why ordinary people were looking for a worthy replacement for it from what grows on Russian soil. As a result of lengthy searches, fireweed tea, which later received the name “Russian tea,” became very popular.
For the first time, the aerial part of the medicinal plant was harvested in the village of Koporye, which is why tea was called Koporye tea. The drink gained great popularity among the ordinary population of Russia, because its cost was several times cheaper than English and Chinese tea, and in taste it was in no way inferior to them.
The technology for preparing real Koporye tea includes several sequential steps:
- collection;
- wilting;
- crushing (either lightly crush or “tap” in a bag);
- fermentation;
- drying
There is a second, simpler and faster method of brewing Koporye tea; it consists of simply pouring boiling water over the dried leaves and flowers of fireweed and letting the composition brew for 10–15 minutes, but in this case most of the beneficial properties of the medicinal plant will be lost.
The collection of the aboveground part of fireweed occurs during the period of active flowering of the plant. Leaves and flowers are collected and laid out separately from each other. Only the upper and middle leaves are plucked (without the lower leaves), while the plant material is immediately separated from the stem (without tearing it out).
The next stage is wilting. To do this, the leaves are laid out in a thin layer under an awning and left to dry slightly for a couple of hours, after which the medicinal raw material is rolled by hand until the juice is released.
Then comes the time of fermentation. To do this, the medicinal raw materials are placed on a baking sheet, in a pan, in a jar and left for several days at a temperature of 25 ° C. The container must be covered with a damp cloth and carefully ensure that it does not dry out; to do this, you will either have to moisten it regularly, or promptly replace the dry cloth with a damp one.
The final stage of preparing Koporye tea is drying. Typically, the leaves are dried in the oven at 70°C for 40 minutes.
Ultimately, the leaves should dry completely and acquire a dark (almost black) tint.
Dried fireweed leaves should be stored in a glass jar with a tightly closed lid. To brew fireweed tea, you need to pour 2 teaspoons of the resulting tea leaves with boiling water and let them brew for 15 minutes.
Flowers do not require such a long and labor-intensive drying procedure. To dry flowers, simply spread them out in a thin layer and dry them in a dark place.
Fireweed leaves
The main medicinal raw material of angustifolia fireweed is its leaves, which have a number of unique healing properties. Healing infusions of fireweed leaves have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, soothing and enveloping effect. In addition, the biochemical composition of medicinal raw materials allows us to consider the healing infusion as an additional remedy in the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, reduced immunity and dysbiosis. An extract from the leaves of a medicinal plant is also successfully used in modern cosmetology as a natural tightening component.
Fireweed seeds
The seeds of angustifolia fireweed are very small and numerous. One plant during the growing season can produce about 20,000 seeds. A distinctive characteristic of fireweed seeds from other medicinal plants is the presence of a white tuft (fluff), which contributes to the instant dispersal of the seeds to a considerable distance from the plant.
At the same time, the seeds retain the ability to germinate and grow for many years. In their chemical composition, fireweed seeds contain up to 45% fatty oil.
From a medical point of view, fireweed seeds are of no value, therefore they are not used for medicinal purposes.
Mountain fireweed
Mountain fireweed is a perennial herbaceous plant of the fireweed family. Its stem is single, erect, pubescent, usually branched in the upper part, height is 25–60 cm. The leaves are short-petioled (sessile), ovoid in shape, with an unequally toothed edge. The flowers are approximately 5–10 mm in diameter and are pink, purple or white (rarely). The flowers are collected in terminal racemes.
The fruit is a pubescent capsule 5–7 cm long. Mountain fireweed blooms in June-July, bears fruit in July-August.
The natural distribution area of mountain fireweed is almost the entire territory of Russia, Europe, Siberia and the Caucasus. This species grows in shady, damp places, in coniferous and mixed forests, as well as among shrubs.
In their chemical composition, the aboveground and underground parts of the medicinal plant contain tannins, which makes it possible to use the healing infusion of mountain fireweed as an effective hemostatic agent.
Mountain fireweed infusion
2 tablespoons of crushed medicinal raw materials are poured into 200 ml of boiling water and infused for two hours, then the resulting infusion is filtered and used for bleeding 1/3–1/2 cup 3 times a day.
Willowweed marsh
Swamp fireweed is a perennial herbaceous plant of the fireweed family. A single, erect, cylindrical stem is covered with hairs in the upper part. The length of the stem of the marsh fireweed can reach 80 cm. The leaves are short-petioled (sessile), opposite, entire, their length is 2–9 cm. The small flowers of the plant are located at the ends of the stem and form a small brush. The petals are colored pink or white.
The fruit is a short pubescent capsule 4–8 cm in length. The seeds are small, spindle-shaped.
Swamp fireweed blooms from July to September inclusive, bears fruit from July.
Natural distribution area - Europe, the Caucasus, Scandinavia, Eastern and Western Siberia, the Far East, Central Asia, Mongolia, China, North America. Swamp fireweed grows in damp, swampy places, along the banks of reservoirs, peat and sand quarries.
The medicinal raw material is the aerial part of the plant, which contains tannins, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and flavonoids in its chemical composition.
An aqueous infusion of marsh fireweed is used in folk medicine as an effective remedy for bleeding of various etiologies, diarrhea, nervous overexcitation and insomnia. Externally, an infusion of a medicinal plant is used for various skin diseases (for example, scrofula).
Tincture of marsh fireweed
20 g of dry medicinal substance is poured into 200 ml of 40% ethyl alcohol, then left in a dark and cool place for 10 days, after which it is filtered and taken 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. Alcohol tincture is used for various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Infusion of marsh fireweed
1 tablespoon of the medicinal substance is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and infused for two to three hours, after which it is filtered into a clean container and taken 1/3 cup 3 times a day. A water infusion is used for bleeding, nervous disorders and insomnia.
Fireweed hairy
Hairy fireweed is a perennial herbaceous plant of the fireweed family. The branched, erect, cylindrical, strong stem is covered along the entire length with long soft hairs; the length can reach 150 cm. The leaves are short-petioled, finely serrated along the edges. In the lower part of the plant the leaves are opposite, in the upper part they are alternate. The flowers are solitary, the petals are dark pink.
The fruit is a pubescent capsule, 4–10 cm long. The seeds are small, ovoid and numerous. The plant blooms in summer, from June to August inclusive.
Natural distribution area is the European part of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Western Europe, Central Asia, Western Siberia, Asia Minor, North Africa, India, China, Mongolia. This species grows in damp places, in flooded meadows, marshy areas, along the banks of reservoirs and in reed thickets.
Fireweed small-flowered
Small-flowered fireweed is a perennial herbaceous plant of the fireweed family. The stem is single, erect, simple or branched, covered along its entire length with small soft hairs, its length is usually 100 cm. The leaves are oblong-ovate, narrowed upward, short-petiolate (sessile). The upper leaves are alternate, the lower leaves are opposite. The flowers are small (length 5–10 mm), the petals are colored light pink.
The fruit is a pubescent capsule up to 8 mm in length. The seeds are small, numerous, dark brown in color.
Small-flowered fireweed blooms from June to September.
The natural distribution area is the European part of Russia, Europe, India, the Himalayas, Iran, the Caucasus. This species grows along the banks of various bodies of water (rivers, lakes, reservoirs), in swampy areas, and in ditches.
The medicinal raw material is the above-ground part of the plant (grass), which is collected during the budding period (beginning of flowering).
In its chemical composition, the grass of small-flowered fireweed contains alkaloids (up to 1%), tannin, mucus, pectin, sugar, ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
Decoction, infusion and tincture of the medicinal plant are used with great success in folk medicine as an effective remedy in the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system, namely prostatitis, cystitis and kidney diseases. In addition, the use of a healing infusion helps in the treatment of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, headaches, insomnia and sore throat.
Infusion of small-flowered fireweed
1 tablespoon of dry medicinal raw material is poured into 250 ml of boiling water and left for 15 minutes, then filtered and taken 1 tablespoon (15 ml) 3 times a day.
Tea from small-flowered fireweed
1 teaspoon of medicinal raw material is poured into 250 ml of boiling water, infused for 10–15 minutes and filtered into a clean container. Take the resulting infusion for chronic prostatitis, adenoma and cystitis, 200 ml 2 times a day on an empty stomach.
Phytoapplications of small-flowered fireweed
Leaves of small-flowered fireweed are steamed in boiling water, and after they have cooled, they are applied to areas of localization of inflammatory processes on the skin and acne.
Fireweed extract
The chemical composition of fireweed extract contains tannins, triterpene acid, flavonoids and phytosterols.
Alcoholic and aqueous extracts of fireweed have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and are used in folk medicine for chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, such as acute and chronic prostatitis, adenoma, chronic inflammation of the ureters and inflammation of the bladder (cystitis).
Fireweed root
The root system of fireweed is powerful, creeping, and can reach a length of one meter. Along the entire length, the horizontal roots are strewn with buds, from which an ankle stem grows.
Fireweed roots are used both in folk medicine and in cooking. Plant materials are harvested in the fall; after digging, the roots are washed in cold water and then dried, first in the open air and then in the oven.
In the chemical composition, fireweed roots contain from 10 to 20% tannins, carotene, sugar, mucus, pectin substances, alkaloids and ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
Contraindications to the use of fireweed
As a rule, healing infusions and decoctions of fireweed are well tolerated (except for cases of individual intolerance), so there are no contraindications or restrictions in its use.
What is better to choose for diagnosing intestinal diseases?
The choice of diagnostic procedure, namely colonoscopy or MRI of the intestine, primarily depends on the indications. If a tumor process is suspected, for further histological examination, as well as in the presence of foreign bodies or bleeding that requires emergency stopping, it is better to perform a colonoscopy. To identify and determine the localization of a pathological formation, especially if it is located outside the mucous membrane (which does not allow visualization using colonoscopy), an MRI is performed.
The final choice of diagnosis, MRI of the intestine or colonoscopy, is made by the attending physician, depending on the results of the clinical examination, as well as the digital examination of the rectum. A clinical examination includes interviewing the patient, palpation of the abdomen, and identification of symptoms of pathology of the lower intestine (abdominal pain, pathological discharge in the form of blood, mucus or pus).
Preparation for the procedure
The presence of gases and food in the stomach and intestinal contents in the intestines can significantly complicate the examination and make images of organs unclear and uninformative.
In this regard, before the procedure it is recommended to carry out special preparation:
- the last meal should be no later than 6 hours before the examination;
- From the diet for a couple of days before the examination, it is necessary to exclude any foods that provoke increased gas formation in the intestines (legumes, carbonated drinks, cabbage, etc.);
- on the recommendation of a doctor, you can take activated charcoal or other enterosorbents, a laxative, or do a cleansing enema.