Hardening of the gallbladder walls can be detected on an abdominal ultrasound. You shouldn’t worry too much about this, but you also don’t need to be negligent about the problem.
The normal wall thickness is about 3-5 mm. The wall itself has three thin layers; in histology they are described as follows.
- Tunica mucosa - mucous membrane.
- Tunica muscularis is a layer of smooth muscle.
- Tunica serosa - the serous membrane serves as protection for the bile sac.
The causes of this condition can be caused by various diseases directly or indirectly related to the gallbladder:
Once the cause of the pathology is established, treatment will give a good result.
Symptoms of pathology
Sometimes the symptoms of this condition do not appear at all. In chronic cholecystitis, the symptoms of the disease are blurred and do not appear as clearly as in the acute course of the disease. A person is in no hurry to see a doctor; changes in his condition are practically unnoticeable, which leads to negative consequences.
The following signs should alert you, even if they are mild:
- The occurrence of pain on the right side under the ribs, which often extends to the pit of the stomach or to the subscapular region.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting may occur frequently, but there is no relief after this.
- The body temperature reaches high levels, the person shudders.
- Sometimes icterus appears, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Thickening of the walls of the gallbladder in a child is accompanied by similar symptoms:
- There is a bitterness in the mouth.
- Nausea and vomiting occur.
- Belching and heartburn often occur.
- In some cases, the child’s skin, feces and urine change color.
If a child has symptoms of gallbladder hardening, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment for the disease. Often it is in children that an S-shaped bend of the bladder occurs, which causes disruption of the functioning of many organs.
Why do the walls of the gallbladder thicken?
The organ shell consists of three layers of tissue:
- mucous membrane lining the organ from the inside;
- a layer of smooth muscles that provide contractile activity;
- serous (outer) membrane.
Most often, thickening of the inner wall of the gallbladder (mucosa) occurs. It develops as a result of an inflammatory process - acute or chronic cholecystitis.
Inflammation contributes to the appearance of scars on the walls of the bladder, which is why they may have heterogeneous density. During chronic cholecystitis, if left untreated, new scars appear constantly. Over time, this process can lead to hardening and loss of contractility of the organ.
Thickening of the lining of the gallbladder also occurs due to the presence of cholesterol deposits. They also contribute to inflammation and swelling of the organ. The appearance of cholesterosis is preceded by excessive consumption of fatty foods and an increase in the normal amount of this substance in the body.
The wall of the gallbladder can be hardened due to benign formations (polyps) or a malignant tumor, dropsy in heart and kidney diseases. These are rarer causes that are not associated with inflammation and require separate treatment.
Possible consequences
If the bladder is contracted, and this is associated with chronic cholecystitis, then the infection can spread to other organs. Lymph tolerates microbes well. With a thickened gallbladder, dyskinesia may develop, i.e. . And since bile plays an important role in the digestion of food, the digestion process is disrupted. The composition of the bile itself also changes. If thickening of the gallbladder began due to a disorder, then liver failure and intoxication of the entire body are possible as a consequence of this.
If there are tumors in the gallbladder, they will continue to grow. If proper medical care is not provided, the tumor will grow into the walls of the organ and further metastasize. One of the complications of this condition may be a shrunken or C-shaped gallbladder, when bile is not able to penetrate into it.
The big problem with this disease is its asymptomatic course. If a person complains of abdominal pain after eating food, even if it occurs periodically, it is best to examine the entire abdominal cavity.
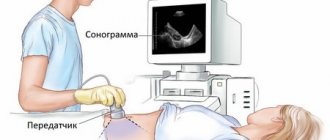
Preparing for the study
If some types of ultrasound do not require special preparation, then before examining the gallbladder you will have to carry out a number of activities. The hardest part for many patients is fasting for at least 8-12 hours before the procedure. Before the examination, you are prohibited from drinking strong tea or coffee, alcoholic beverages, as well as smoking or chewing gum. All this is recommended to ensure that there is a sufficient amount of bile in the gallbladder. Only when the bladder is full can its parameters be correctly assessed to make a diagnosis.
A shrinkage of the gallbladder may occur if you do not follow the instructions for preparing for the examination: for example, if he ate heavily at night. Then it is recommended to eat a high-fat product half an hour before the test. After this, bile is released from the liver and the bladder is filled, which allows for examination.
Ultrasound is performed from various positions. During the procedure, the patient is asked to turn over to the other side or back and sit down. This allows you to examine the organ from different angles and assess the mobility of the contents of the gallbladder. When the patient moves, the stones in the bladder change position, which serves as an additional criterion for diagnosing diseases.
Using ultrasound, the wall thickness, length and width of the gallbladder are determined. The volume is determined automatically by the program in the ultrasound machine, or the doctor can calculate it independently.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
To prevent the development of gallbladder diseases, including hardening of its walls, you need to follow a special diet. Especially if there are already any violations. The menu must include the following dishes:
- Vegetable decoctions.
- Lean meat and fish.
- Dairy products.
- Porridge.
- Bread that was baked the day before.
- Juices and tea without added sugar.
Prohibited products:
- alcohol;
- soda;
- chocolate products;
- fatty and fried foods.
Treatment of thickening of the gallbladder walls should be carried out only under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. The basis of therapy is antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Initially, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease that led to the thickening of the bladder walls and eliminate foci of inflammation. If there are hormonal imbalances, they are corrected with medications. Immunotherapy is being carried out.
Wall compaction is an anomaly of the gallbladder that has developed against the background of another disease. This condition can lead to serious complications that can affect other organs. And this leads to disruption of the functioning of the entire body. Therefore, treatment for thickening of the gallbladder walls is necessary, as is timely diagnosis of the disease.
The cause of compaction is chronic inflammation. It develops as a result of the formation of adhesions or scars. This leads to disruption of the contractile function of the organ.
In addition to chronic cholecystitis, other diseases can cause hardening of the gallbladder wall. These include cholesterosis, ascites, liver cirrhosis, the presence of multiple polyps, and neoplasms.
Cholesterosis is characterized by the deposition of fats on the walls of the organ, which leads to disruption of its functioning.
The liver has a great influence on the gallbladder, since they are interconnected. With liver damage (necrosis of hepatocytes, chronic hepatitis), the gallbladder may also be involved in the pathological process.
Polyposis is characterized by active thickening of the walls of the bladder due to the formation of polyps in it. Depending on the underlying cause of the pathology, thickening of the gallbladder can lead to different consequences. This condition does not go away without treatment.
Causes and Effects
Statistical calculations show that women are much more likely to be at risk of developing biliary pathologies. This is associated with the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, changes in hormonal levels characteristic of the reproductive period. But being overweight, taking medications and contraceptives can also trigger the development of diseases. The standard length of the gallbladder in adult women is limited, in contrast to men, to 6-10 cm, with a width of 3-5 cm and a thickness of the bladder walls of 2-3 mm. These are normal indicators.
Among the numerous reasons for the development of pathological processes, the following are standardly identified:
- Pathogenic agents that initiate inflammation in the cells of a hollow organ - of bacterial origin, infectious or even viral etiology (this may also be a consequence of an infection permanently present in the body). Common ones include staphylococci, streptococci or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Parasitic infestations are a consequence of a significant spread of helminths in the body, the transfer of sexually transmitted infections to the pelvic organs and beyond, or their penetration from the gastrointestinal tract.
- The presence of modifications of a hereditary, congenital or acquired nature - transformation of the bladder, kinks, constrictions and torsions, deviations in the anatomical structure that are not pathological, but caused negative changes in functionality.
- A change from the normal composition of bile secretion to pathological, with the excessive presence of compounds leading to the formation of stones - cholesterol, bilirubin or mixed. This also includes modifications in the quantitative concentration of bile acids that occur against the background of metabolic disorders or pathology of the organ that synthesizes bile.
- Neoplasms, benign or malignant, related to the usual location of the gallbladder or directly to it.
Violation of the bile outflow can lead to a significant increase in size if acute inflammation develops or the duct is blocked by a migrating calculus. Dilatation of the common bile duct can also be provoked by wandering stones or an acute process that gives a characteristic picture. Any modification in the composition of the bile secretion, the normal state of the gallbladder or the organs associated with it, can lead to a transformation of the shape, size, or even the usual location of the hollow organ.
Possible consequences
If the cause of the compaction is chronic cholecystitis, then this is fraught with the spread of infection. In this case, pathogenic microbes can enter the underlying parts of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, the intestines, and through it through the vein system into the liver, and from it into the bile ducts.
Through lymph, the infection can spread to other organs: pancreas, gastrointestinal tract. In addition, compaction of the gallbladder leads to its dyskinesia, that is, the outflow of bile is disrupted. Bile is of great importance for the digestion of food, so the digestion process is disrupted. In addition, the composition of bile changes.
Thickening of the organ with liver damage can lead to acute liver failure and severe intoxication of the body.
If there are neoplasms in the wall of the gallbladder, the pathological process will intensify over time. If timely surgical treatment is not provided, the tumor can grow into the wall of the organ and metastasize to nearby organs, which is fraught with complications.
The thickening of the bladder wall is most often asymptomatic, but, nevertheless, a thorough examination of the entire abdominal cavity is required. Patients may complain of pain in the abdomen associated with eating food. They occur only during the period of exacerbation of the underlying disease.
Thus, hardening of the gallbladder walls is not an independent disease, but it can lead to serious consequences, affecting other organs. This pathology may conceal a more severe one.
- Hardening of the gallbladder walls - what is it and how to treat it? When considering this issue, you need to understand that this is not an independent disease, but swelling of the walls of the organ, which occurs as a consequence of the inflammatory process in the bile-forming system of the body. In addition, pathology can be caused by other ailments.
Treatment
Inflammation in cholecystitis is caused by various reasons:
- gallstones;
- bacterial infection;
- parasites;
- changes in the composition of bile;
- deposits on the walls of the organ.
How sealing of the gallbladder wall is treated depends on the cause and severity of the pathology. In adults, conservative or surgical therapy is used, aimed at eliminating the main factor causing the disease.
Medications
For drug treatment use:
- antibacterial agents – for diseases caused by infection;
- preparations – for dissolving stones and cholesterol deposits;
- antiparasitic agents – for cholecystitis caused by the activity of Giardia;
- reducing cholesterol levels - when it is excessively concentrated and deposited on the walls.
In addition, choleretic drugs are used to quickly relieve swelling and inflammation. With their help, tubage is carried out - cleansing the organ of stagnant bile. After taking the medicine, apply a hot heating pad to the right side. The procedure can only be performed if the ultrasound shows the absence of stones. To relieve pain when the walls of the bladder harden (but not as the only method of treatment), you can take an antispasmodic or painkiller.
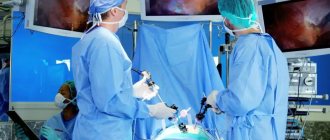
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, if the gallbladder cannot function as a result of chronic inflammation or overcrowding with stones, a procedure is performed to remove it. The diseased organ still does not participate in the digestion of food, and its constant inflammation is dangerous to life and health. Removal can be avoided if operational irregularities are detected in a timely manner. If it is possible to get rid of stones while preserving the gallbladder, more gentle methods are used - ultrasonic or laser crushing.
Diet and exercise therapy
It is important to prevent the formation of stones in the bladder before they have time to form. To do this, you need to constantly follow a diet and give yourself moderate (not excessive) sports activity. Therapeutic exercise aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles helps improve tone and normal functioning of organs.
If you have high cholesterol, you need to follow a strict diet aimed at reducing it. The diet of people with gallbladder diseases excludes fried, fatty, spicy, sour, and alcohol.
It is worth limiting the consumption of flour and sweet foods. Stewed and boiled vegetables, cottage cheese and kefir, porridge with water, lean meat and fish, fruit and berry compotes are useful. It is better to replace coffee with chicory (it promotes the flow of bile), and regular tea with decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Traditional methods
Herbal remedies provide a good healing effect with long-term use. For the prevention and treatment of gallbladder pathologies, decoctions and infusions of plants are used:
- promoting the dissolution of stones - artichoke, turmeric, milk thistle, wormwood, mint;
- anti-inflammatory – catnip, goldenseal, celandine, barberry, birch leaves, sage, chamomile;
- choleretic - immortelle, lemon balm, rose hips, corn silk, buckthorn bark, dandelion root.
What happens during inflammation
Poor nutrition combined with functional disorders of gallbladder motility lead to the development of inflammation called. Against this background, gallstones gradually grow, which further injure the mucous membrane. What happens then?
Any inflammatory process is accompanied by swelling. Capillaries dilate to increase blood flow and provide a surge of immune cells. Leukocytes entering the tissue from the blood will actively fight the infection, which is sure to occur in this case.
With swelling, the walls of the gallbladder thicken and become denser. In case of chronic inflammation, connective tissue grows in it, resembling a scar. Because of it, the walls of the gallbladder become thicker. For this reason, the contractility of the bladder decreases, and the problems become even greater.
Video
Thickening of the walls of the gallbladder is a pathological process, most often occurring as a result of inflammation. Less commonly, this is caused by other diseases.
Thickening is not an independent disease, but a syndrome detected by ultrasound examination. Detection of such a symptom is an indication for further examination.
What can be seen on an ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is a very visual method for studying the biliary system. What can be determined by ultrasound:
- what size is the gallbladder and what is the thickness of the wall;
- whether there is a ;
- how well bile is secreted;
- what is the diameter of the bile ducts;
- whether there is damage to the liver and pancreas.
Normally, the gallbladder wall is no more than 4 mm in adults and 2-2.5 mm in children. Its structure is homogeneous, its contours are even. In the case of inflammation, the picture changes dramatically. One of the signs of cholecystitis will be uneven thickening of the gallbladder wall. The greatest increase in thickness will be in the area of the stone.
The heterogeneity of the mucosal structure appears on ultrasound in the form of increased signal and hyperechogenicity. These areas will be brighter in the photo. This means that a thickening of the gallbladder walls has occurred at this site. This occurs when the inflammatory process is chronic. And also the walls can thicken in the form of layering.
Another important sign confirming inflammation of the gallbladder is the presence of thick bile in the form of “flakes” in its lumen. What it is? With frequent consumption of fatty foods, the content of lecithin and cholesterol in the bile increases. In this state, stones begin to grow, and you need to immediately put your diet in order.
Gallbladder indicators are normal
If the size of the gallbladder is normal, and the person has complaints in the area where the organ is located, then a liver diagnosis is performed.
The volume of the gallbladder in an adult ranges from 30 to 80 ml. When conducting diagnostics, the volume of the organ is first measured on an empty stomach, then the person being examined must eat a product that stimulates the formation of bile. When an hour has passed after eating, the examination is repeated. The size of the gallbladder in an adult will be from 60 to 80% of its original state. This ratio is normal for the gallbladder.
The size of the gallbladder in an adult can vary depending on age, anatomical features, and body weight.
The normal size of the gallbladder in adults is determined by the following parameters: width, length, diameter and thickness. Generally accepted standards:
- length – 5-10 cm,
- width – 5 cm,
- wall thickness up to 0.4 cm,
- the diameter of the ducts is up to 0.3 cm, the total diameter is up to 0.7 cm.
The capacity of the gallbladder is 70 ml. If the organ becomes full, it expands to large sizes (200 ml).
Gallbladder diseases are found more often in women than in men. The risk group includes women over 40 years of age who have fair skin, white hair and excess weight. In men, problems with the biliary tract begin later, if there is no influence of negative environmental factors: excessive consumption of alcohol, foods rich in cholesterol.
A deviation in the values of a healthy organ up or down indicates the occurrence of various pathologies. An enlarged gallbladder indicates the presence of stones or the development of cholecystitis in the acute stage. A decrease in most cases indicates the presence of a hepatitis virus.
An ultrasound scan collects and analyzes general information about the gallbladder, the surface of all its walls, and the frequency and strength of its contractions.
Why does the gastrointestinal tract thicken?
Since this condition is not normal, something must cause it to develop. So, why do the walls of the gallbladder thicken:
- cholelithiasis;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis) and malformations;
- diseases of the pancreas and liver;
- cancer tumor.
Having undergone a comprehensive examination when thickening of the gallbladder walls appears and having discovered the causes, it will be possible to begin treatment. If therapy is not started in time, the disease will become chronic or complications will begin.
Parameters for assessing the condition of the gastrointestinal tract
- The thickness of the wall of the gallbladder in a normal state is about 0.4 cm. It is lined by three membranes (mucosal, muscular, adventitial). All layers are thin.
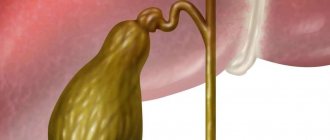
- In its shape, an empty gallbladder resembles a pear. When filled with bile, the organ takes the shape of an oval or cylinder.
- When monitoring the functioning of the gallbladder, the size, diameter and patency of the bile duct are taken into account. In an adult, the total diameter of the duct is about 7 mm.
- When the condition of the gallbladder is examined, the condition of the membranes of the gallbladder walls is taken into account. Deformation can occur when the organ is twisted, bent or constricted. This pathology can develop congenitally and under the influence of unfavorable external factors. Violation of the form of the gallbladder affects the formation of bile and the development of diseases.
- The neck of the gallbladder is one of the three components of the organ. Normally it is smooth and up to 35 mm long. Problems with the cervix can arise even at the stage of embryonic development in the womb. Most often, this is a congenital abnormality that causes digestive disorders. As the child grows, the bend may straighten out.
- The biliary tract consists of two ducts - right and left, which unite into the common bile duct. The normal size of the common duct is up to 70 mm in diameter. In medical practice, dyskinesia of the bile excretory pathways (disorder of the contraction function) is observed.
How does this condition manifest?
At the initial stages of the formation of inflammatory changes in the gallbladder, there may be no obvious complaints. A person may not pay attention to periodic heaviness in the right side or tingling sensation. This is usually associated with fatigue or stress at work.
Serious symptoms will appear when acute inflammation begins. And then it will no longer be possible to miss it. What may concern:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste, dark coating on the tongue;
- nausea and vomiting;
- heat;
- weakness, increased blood pressure.
With calculous cholecystitis, a stone can get into the bile duct and disrupt the flow of bile. Then the leading symptom will be biliary colic. In this condition, you may notice that your skin and eyes have turned yellow. Vomiting may be uncontrollable.
Symptoms
Chronic processes in the gallbladder usually manifest themselves as pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium from time to time. In addition, nausea, indigestion, heartburn, and bitterness in the mouth may bother you. Blockage of the bile ducts with a stone leads to a sharp pain, the appearance of obstructive jaundice, vomiting, and fever.
In the absence of exacerbations, the patient may not attach importance to the signs and symptoms of thickening of the gallbladder wall, which is detected only on ultrasound.
During the procedure, the doctor detects thickening of the walls of the gallbladder to a size of more than 5 mm. Heterogeneity of the mucous membrane may be visible - the consequences of scar formation, thickening of bile and the presence of flakes, stones (stones) in the gall bladder. Normally, the organ has a cone-shaped shape, but the inflammatory process leads to changes and deformation.
What complications can there be?
If cholecystitis is not treated, it can lead to serious complications. These may include the following conditions:
- perforation (appearance of a hole) in the bladder wall;
- purulent inflammation (empyema);
- peritonitis;
- pancreatitis if a stone gets into the pancreatic duct;
- hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver.
Treatment in these situations will be long and not always successful. Therefore, try to consult a doctor when the first signs of illness occur. He will prescribe additional examination and a course of drug therapy.
The essence of pathology
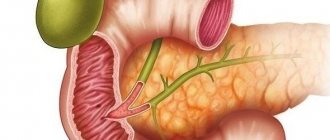
The gallbladder is a kind of reservoir in which bile accumulates, which then flows through the bile ducts into the duodenum. It takes an active part in the digestion process, being responsible for the dissolution of fats. The process of bile outflow depends on the correctness and strength of contractions of the gallbladder.
The organ wall consists of 3 layers:
- mucous membrane covered with epithelium, which provides metabolism and blood supply;
- smooth muscle , which causes contractile movements to evacuate bile;
- serous membrane , which provides protection to the organ.
What is it - thickening of the gallbladder walls?
Normally, the thickness of the organ wall should not exceed 3-4 mm. Under the influence of pathological factors, the walls and bile ducts of the gallbladder thicken and become denser, becoming thicker than 4 mm, and the contractile functions of the organ are impaired. As a result, bile stagnates, which leads to a deterioration in the digestive process.
How can this be cured?
If there are no complaints, and an ultrasound scan accidentally reveals only a thickening of the gallbladder without stones, then the likelihood of a complete cure is very high. It is enough to follow a diet and take choleretic drugs. If there are stones in the lumen of the gallbladder, there are two treatment options:
- Crushing stones using laser or ultrasound ().
- Laparoscopic removal of the gallbladder ().
If it is not possible to perform lithotripsy, then surgery is recommended for the patient. This is the only radical treatment method, after which you will forget about problems with the gallbladder.
Diet and exercise therapy
The most significant methods of therapy remain diet and physical therapy. Especially if the stones have not yet formed. This will also be an excellent prevention for those who have a hereditary predisposition to gallstone disease. By following the principles of proper nutrition, you can forget about health problems for a long time.
Lean foods containing a minimum of plant and animal fats will normalize the composition of bile and prevent the growth of stones. It is recommended to eat vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish. Products can be boiled, stewed, steamed and baked in the oven. These gentle cooking modes will preserve maximum vitamins.
Try not to use a lot of seasonings and various spices. And also in diet No. 5 there are restrictions on the consumption of flour and confectionery products with fatty cream. It is better to bake a pie or cake at home: this way it will contain less harmful trans fats. Do not forget to drink enough clean water, about 1.5–2 liters per day.
Therapeutic exercise is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and improving the outflow of bile, for which it is necessary to perform a certain set of exercises daily. The only thing that is not recommended is the starting position on the right side, in which bile flows poorly from the gallbladder.
Medications
Thickening of the walls of the gallbladder is caused by inflammation. Therefore, drug therapy will be aimed at relieving swelling and improving bile secretion. Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- antispasmodics to relax the gallbladder and ducts;
- choleretic drugs, if there are no stones;
- Ursosan or Ursofalk, which dissolve cholesterol stones;
- Magnesium preparations also have a good effect on the smooth muscles of the biliary system;
- herbal medicine to relieve inflammation.
Tubage is considered an effective method of treatment during remission. This procedure allows you to establish the outflow of bile and open the bile ducts. The patient drinks a choleretic agent (for example, mineral water with magnesium), applies a warm heating pad to the gallbladder area and lies on his right side. This takes about an hour.
Diet No. 5
This diet, called “Healing Table No. 5,” is an integral element of successful therapy for any pathology of this internal organ. Its compliance is mandatory. Otherwise, all other therapy will be a waste of money and time.
The basic principle of this diet is fractional nutrition, which means eating small portions at regular intervals, five to seven times a day. You can prepare dishes with this diet only by steaming, boiling or baking. You will have to forget about fatty, fried, hot, spicy and smoked dishes. Also prohibited are alcoholic and carbonated drinks, sweets and baked goods, some and strong tea.
Products allowed for consumption on this diet:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | weak tea |
| 2 | low-fat cottage cheese |
| 3 | milk (in the absence of individual intolerance) |
| 4 | low fat fermented milk products |
| 5 | dried fruit compotes |
| 6 | decoctions, jellies, jellies and mousses based on sweet berries and fruits |
Read also: How to do gymnastics for the gallbladder?
- one chicken egg per week;
- lean meat (veal, chicken, rabbit, turkey);
- low-fat types of sea and river fish;
- yesterday's white bread or crackers based on it;
- vegetables (both in the form of soups and purees, and fresh);
- porridges based on buckwheat, oatmeal and semolina;
- pasta;
- low-fat and non-spicy hard cheese;
- vegetable oils (linseed, sunflower and olive);
- butter (in very limited quantities).
Inna Lavrenko
auto RU
All food should be warm, in no case cold or hot.
The same diet is indicated after surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Diagnostic methods
If you notice any disturbing symptoms, you should consult a gastroenterologist. After a conversation with the patient, a physical examination and anamnesis, he establishes a preliminary diagnosis. Next, diagnostic measures are prescribed aimed at identifying the disease that caused the thickening of the walls of the gallbladder.
Ultrasound is one of the most effective diagnostic methods. Using ultrasound, epithelial compactions are detected, the degree of wall thickening is determined, and the cause that caused this syndrome is identified.