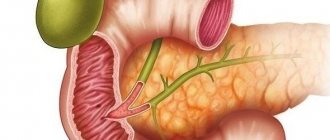
The role and functions of the gallbladder in human life
The gallbladder (GB) together with the ducts forms a single system - the biliary system. Its function is the accumulation of bile and its discharge into the duodenum (12PC).
Bile is continuously secreted by the liver. But it is only needed when food enters the stomach. Before this, the secretion accumulates and concentrates in the gallbladder. In 12PC it is released when partially digested food enters it.
Thus, the gallbladder has 2 main functions: storage (storage) and evacuation. Timely entry of bile into the 12PC is important, as it contributes to:
- further processing of food, breakdown of fats and absorption of vitamins;
- intestinal motility and mucus production;
- disinfection and prevention of infection by helminths by creating an alkaline environment;
- production of intestinal enzymes and hormones.
If bile does not enter the duodenum on time, it stagnates. Subsequently, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis develop, and the ducts become clogged. These conditions are indications for organ removal.
The gallbladder is important, but when it is damaged, relapses occur constantly, and conservative therapy is ineffective. Therefore, they prefer to remove it. How a patient will live without a gallbladder largely depends on compliance with postoperative and preventive measures.
Medicines
Drug therapy after surgery helps:
- restore normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- relieve pain, prevent diarrhea, heartburn;
- eliminate nausea and vomiting;
- get rid of PEHS;
- prevent dangerous complications, exacerbations of chronic symptoms.
The following medications will help avoid nausea and vomiting, as well as adapt the digestive tract to new working conditions:
- Hofitol – choleretic;
- Creon, Festal – enzymes;
- prebiotics and probiotics – help restore microflora in the intestines;
- vitamins.
Use drugs that help restore the functioning of the biliary system, start the movement of bile in the ducts, eliminating the feeling of nausea:
- Antispasmodics based on nitroglycerin - remove some of the pathological manifestations, but negatively affect the functions of the heart and blood vessels.
- Anticholinergic drugs – Metacin, Buscopan. Their effect is similar to antispasmodics, but there are more side effects.
- Gepabene - in addition to eliminating spasms, helps stimulate the production of bile and protect liver cells from negative influences.
- Creon - helps the body properly absorb fats, restores fermentation processes.
- Diclofenac - helps improve well-being.
- Doxycycline, Furazolidone - restore microflora, destroy pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines.
- Linex, Hilak Forte - used after restoration of microflora to normalize microbiocenosis processes.
- Almagel, Maalox - envelop the intestines and protect it from the destructive effects of bile acids.
If vomiting occurs after surgery, you should not take regular antiemetic medications. This will not allow the doctor to see the real clinical picture and will lead to loss of time, which will worsen the condition.
Reviews of hepotologists fososbuvir
Check with your doctor to see if you can take certain medications.
If symptoms bother you immediately after surgery, tell your surgeon. If inflammation is detected in the first three days, antibiotics will be required to prevent infection of other organs. The course is prescribed only by the attending physician.
How does the body work after removal?
The gallbladder is involved in digestion, and patients do not understand whether and how they can live without it. But humans have well-developed compensatory functions. Three significant changes occur in the body after removal:
- Bile does not accumulate, but continuously flows into 12 PCs.
- The pressure on the hepatic ducts increases.
- The balance of intestinal microflora changes, since the secretion is not cleared of excess water, chlorine and sodium in the gallbladder.
Removing the gallbladder leads to a number of consequences, and life changes after the extraction. Patients face:
- bowel dysfunction - due to insufficient concentration of bile, food processing worsens, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, nausea, indigestion develop;
- lack of useful elements - digestive problems lead to a lack of fat-soluble vitamins, fatty acids, antioxidants, intestinal proteins and hormones;
- early aging – absorption of antioxidants contained in vegetables decreases: carotenoid, lycopene, lutein.
In general, life expectancy without a gallbladder does not decrease. The patient is forced to eat right, say goodbye to alcohol and nicotine, and avoid mental, physical and psychological fatigue. All this has a positive effect on health.
Life without gallstones imposes some restrictions and is accompanied by discomfort, but does not cause significant problems.
Pregnancy after laparoscopic removal
Resumption, after removal of the organ, takes 2–3 weeks. In theory: it is necessary to plan fertilization, and only then conceive a child. It is possible to become pregnant immediately after hospital treatment. It is important to understand that the body has undergone a very complex procedure; it will take a lot of time to adapt to new circumstances:
- Enzymes of pancreatic secretion and bile decrease or are completely absent
- The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted
Complications after surgery are rarely observed, and the rehabilitation period lasts for several weeks. According to statistics, fertilization and normal development of the child immediately after surgery is quite possible.
If pregnancy occurs during this time interval, then it is very problematic to endure the changes.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is recommended to use safe contraceptives in the first month. When the condition returns to normal, the body and stomach are restored, fertilization can be planned.
After laparoscopic surgery, complications occur in rare cases
Doctors strongly recommend following a proper diet:
- Provide the body with the necessary amount of additional proteins and carbohydrates daily. (Meat, fish products, fresh vegetables, cereals, dairy products, fruits).
- Create a menu for every day to get the amount of highly nutritious substances your body needs. Take the rules of healthy, wholesome food as a basis.
- Carefully process, boil, steam. Use aromatic and hot spices in minimal quantities.
The gestation of gallbladder laparoscopy does not differ from the standard physical condition of an ordinary woman.
What to do immediately after surgery
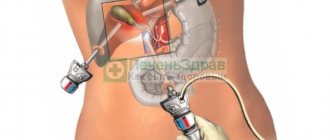
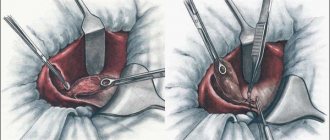
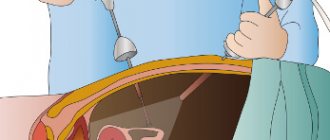
There are 2 main methods of extirpation of the gallbladder - open (cavitary) surgery and laparoscopic cholecystectomy. After the first type, recovery is difficult and takes 6-8 weeks; with the second type, rehabilitation is faster - in 10-14 days.
Regardless of the method, if the gallbladder is removed, standard consequences arise:
- temporary pain at the intervention site;
- nausea from the administration of anesthesia;
- diarrhea and increased gas formation due to lack of bile;
- fatigue, drowsiness, weakness.
If the gallbladder is excised by laparoscopy, temporary consequences appear in the form of compression of the diaphragm and radiating abdominal pain due to the injection of gas.
The first days of rehabilitation are difficult. Patients with a removed gallbladder are prohibited from eating and drinking (you can moisten your lips or rinse your mouth with a herbal decoction), get up and turn over for 5-7 hours, and wash because of the risk of wetting the sutures.
After a few hours you can get up and walk around the ward. You cannot move suddenly, bend over, or lift weights. On the second day, you are allowed to drink pure still water or unsweetened rosehip decoction - the volume of liquid is up to 1 liter. The ban on swimming is lifted on the third day, but the seams must be covered with waterproof material.
The patient spends the first day after removal of the gallbladder in the intensive care unit. During the second, he is transferred to a general ward. You need to stay in the hospital for 3-14 days.
Recovery stages
Rehabilitation after removal of the gallbladder involves normalizing physical condition, changing attitudes, rules and values of life. In addition, it is important to restore the patient’s psychological state.
The recovery period after cholecystectomy is divided into several stages
As you know, the gallbladder is an important organ that is involved in digestion. It is a reservoir for bile, which helps break down fats. Before the operation, the liver secretion had the concentration necessary for digestion. In the absence of gallbladder, bile accumulates in the bile ducts, and its concentration is low.
Despite the fact that the ducts take on the function of the removed bladder, the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract is still impaired. This happens because the body needs time to get used to new digestive conditions. To avoid or reduce the severity of negative phenomena, the patient after surgery must adjust his diet.
During the rehabilitation period, you need to help your body improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. A postoperative diet will help solve this problem. In addition, it is necessary to take medications and perform simple physical exercises. The rehabilitation period is about 2 years.
Stages of the recovery period:
- For the first 2 days after laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the patient remains in a hospital setting. At this stage, negative phenomena are observed after anesthesia and surgery.
- The late stage lasts from 1 to 2 weeks, the patient is in the hospital. Damaged tissues gradually heal, the functionality of the respiratory organs normalizes, and the gastrointestinal tract adapts.
- The outpatient period lasts from 1 to 3 months. The patient recovers his health at home.
- The patient is engaged in improving the health of the body in sanatoriums and dispensaries.
Reference. Due to strict dietary restrictions, the patient’s mental state may worsen. Therefore, the doctor must tell you how the functioning of the digestive tract is changing and what needs to be done to avoid complications.
Negative consequences of gallbladder removal
Moderate pain in the abdominal area after removal of the gallbladder is a normal consequence that can be relieved with analgesics. You should be wary if the sensations are intense, are not relieved by painkillers, and nausea and fever are added.
In addition to the primary consequences, there is a risk of second-stage postoperative complications. This condition is called PCES (postcholecystectomy) syndrome. It manifests itself:
- indigestion. Characterized by nausea, vomiting, heartburn, flatulence;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating fatty foods;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera, itching;
- blockage of bile ducts with stones or their inflammation - cholangitis;
- pancreatitis or hepatitis. They develop due to a violation of the outflow of bile.
Secondary complicated conditions after cholecystectomy develop in 5-40% of patients.
Complications after gallbladder removal in men are limited to this list. But consequences in women are still associated with pregnancy after removal of the bladder.
Surgery to remove the gallbladder does not affect the ability to conceive and bear a child, but it does impose a number of restrictions. So, the consequences may include itching during pregnancy, a high risk of stone formation due to the displacement of the peritoneal organs by the fetus, and jaundice in women and children. To avoid negative phenomena, the expectant mother needs to take multivitamins, antiallergic drugs and antioxidants. Medicines and dosage are prescribed by the doctor.
The listed complications arise with any method of cholecystectomy. But each type of operation - laparoscopic and abdominal - has its own consequences.
How is pregnancy without a gallbladder?
The majority of women who have undergone cholecystectomy claim that the operation did not affect their well-being during pregnancy. On the contrary, they noticed that if they followed a diet and a normal daily routine, their condition was much better than before the operation.
The surgical procedure does not cause disturbances in the functioning of other organs and does not affect the synthesis of hormones. However, sometimes a woman who becomes pregnant complains of discomfort associated with the removed gallstone.
Most often, in the first weeks, heaviness under the ribs on the right side bothers you. It can radiate to the scapula, left hypochondrium or shoulder. Other unpleasant sensations appear from time to time:
- bowel disorders (diarrhea or constipation);
- nausea and bitter taste in the mouth;
- increased gas formation;
- loud rumbling in the stomach;
- heartburn.
The severity of such symptoms is influenced by the time that has passed since the operation. It is believed that the hepatobiliary system returns to absolutely normal functioning within 1.5-2 years after removal of the gallbladder. In the first half of the year, there is a very high probability of stagnation of bile in the ducts, which explains the appearance of unpleasant sensations in pregnant women who were operated on shortly before conception.
In addition, the fetus growing in the womb puts pressure on internal organs: the liver, bile ducts and intestines. Therefore, the closer to childbirth, the more likely it is that pain will occur on the right side when the baby moves.
Infrequently, but still there are cases when removal of the gallstone does not solve the problem of stone formation. Stones appear in the ducts again. Therefore, pregnant women may experience attacks again even after cholecystectomy.
Gallstone disease is considered the most common female problem after gynecological pathologies. Given this fact, pregnancy planning must be approached responsibly.
And, if you have already had an attack of hepatic colic at least once or if bile stagnation makes itself felt from time to time, you need to undergo a thorough examination and consult a gastroenterologist. If a specialist insists on the need for surgery, you should not delay for long. Seizures during pregnancy can be a serious obstacle to the birth of a healthy baby.
Various diseases of the biliary system affect not only older people, but also young girls of reproductive age. A logical question arises: is it possible to become pregnant after surgery to remove the gallbladder? The body works differently than before surgery, the digestive system and the functioning of the intestinal tract suffer, and consequences are possible in the gynecological area. Cholicystectomy is quite easy to tolerate, but inferiority imposes restrictions on a woman’s diet and lifestyle. Let's look at how pregnancy proceeds without a gallbladder, how long it takes for fertilization to occur after a laparoscopic procedure, and what to do during this period.
Is it possible to carry a child to term after cholecystectomy?
The absence of one of the organs in the biliary system does not affect the reproductive function of a woman, so pregnancy after removal of the gallbladder may well occur naturally. There is a nuance when you can start fertilization after laparoscopy. The pause between conception and surgical intervention is maintained as prescribed by the doctor, who assesses the condition of the body during the rehabilitation period.
With open surgery, a large incision is made, and with laparoscopy, only a few punctures are made. The stitches should heal and there should be no bleeding inside the abdomen. You should also allow time for the body to adapt to the new operating mode. If a woman becomes pregnant, these processes become more complicated.
Removal of the gallbladder during pregnancy is allowed in cases of critical conditions (gallbladder stones during pregnancy) and only in the second trimester. If a pregnant woman’s term is longer, then there are ways to transform the acute stage with an emergency indication for surgery into a chronic form, when the intervention is performed after the woman has given birth.
Lifestyle changes during pregnancy after gallbladder removal
- A woman should control her eating habits, avoiding long periods of fasting. Only with this regimen is it possible to achieve normal bile secretion;
- prefer boiled or stewed dishes on the menu, steam more often;
- completely exclude from the diet all spices, marinades and salty foods, fatty foods, smoked foods, do not fry in oil;
- Any alcohol is strictly prohibited;
Lifestyle changes during pregnancy without a gallbladder
- It is necessary to take choleretic medications regularly to prevent an attack during pregnancy. A woman’s uterus gradually enlarges and in many patients, compression of the ducts begins. It is necessary to dilute the bile secretion produced in the liver with medication so that it flows without congestion even in the presence of narrowing of the lumens;
- Carrying out a tubage will cleanse the biliary system, even if there is a stone in the bile duct. To do this, take warm mineral water, after which you need to lie with a heating pad in the liver area for two hours.
These recommendations will allow you to carry a child to term without problems, even with an absent gallbladder.
Features of multiple pregnancy without a gallbladder
The presence of several fetuses will increase the load on the pregnant woman’s body. Various pathologies that arise in the biliary system often occur in expectant mothers carrying twins or triplets. In this case, the uterus stretches many times more than in a normal pregnancy. This is fraught with stagnation of bile ducts and infection of the walls of the biliary canals. If the gallbladder is not removed, it moves upward and severe cholestasis is noted.
The pressure of the uterus on the bile ducts is so strong that they are pinched and can hardly contract. This is associated with the production of progesterone, a hormone that is produced very actively in pregnant women. The substance relaxes muscles, protecting against premature onset of labor. Muscle spasms in the ducts often provoke early labor.
Gynecologists recommend supplementing therapy with a course of magnesium, which can protect the developing fetus and relax all types of smooth muscles.
Changes in the functioning of the biliary system during pregnancy
| 1 | Possible congestion in the bile ducts |
| 2 | increased viscosity of bile secretion |
| 3 | loss of billiard sludge, cholesterol or calcium crystals, bilirubin fragments, stone formation (the same thing happens with gallstones before cholecystectomy) |
| 4 | the appearance of foci of inflammation in the ducts due to infection of bile. In stagnation, there is an increase in toxic substances, which leads to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms |
How long after pregnancy can be allowed under such conditions can only be decided by the doctor who performed the gallbladder removal. This can only be done if you follow a strict diet and avoid overeating, which causes increased bile synthesis in the liver. With a successful pregnancy, fetal growth enhances changes in the biliary system.
One of the serious complications is toxicosis, which occurs in many patients with a removed biliary organ. In case of multiple pregnancy, as noted by patients who gave birth, it can last up to 16 weeks inclusive. For the first 3 months it is necessary to be kept in storage, since in a weakened state women cannot even eat. After this period, doctors allow the child to be born at home.
The nuances of pregnancy after gallbladder removal
Cholecystectomy is safe and most patients experience no complications. But you need to plan your pregnancy only a year after the operation. How important it is to meet these deadlines can be understood if you know the progress of rehabilitation after cholecystectomy:
- upset of the digestive system often occurs, dyspepsia actively manifests itself in the form of frequent diarrhea or constipation;
- the stomach is constantly bloated, flatulence is present;
- Phantom pain in the gallbladder often occurs in the liver area.
These symptoms are typical for the recovery period, but also refer to postcholecystectomy syndrome, which occurs when bile outflow is impaired. The longer the pregnancy, the brighter the symptoms.
In addition, there is constant dryness in the mouth, a bitter taste on the tongue, heaviness in the abdomen, itchy skin on the feet or palms, most often at night. Such manifestations occur in acute cholecystitis. With postcholecystectomy syndrome, a woman experiences the same sensations as before removal of the bladder, but it seems that the disease is recurrent.
Prevention of complications
To prevent complications, it is necessary to support the body left without a gallbladder. To do this, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- You need to eat at least 6-7 meals per day, limiting portions to 200 grams;
- The basis of the diet should be dietary dishes, preferably table No. 5;
- for prevention, take choleretic drugs and herbal decoctions, agreed with the treating doctor;
- perform gymnastics in the morning, a complex of which can be prescribed by a gastroenterologist;
- Do tubage regularly to cleanse the biliary system of accumulated bile.
All recommended points are important and must be followed, but the most important indicator is nutrition. The balance of nutrients and the absence of violations of the regime can improve the passage of bile and normalize its composition. All junk food, processed foods, spices and fatty foods are finally excluded from the menu. The basis should be healthy food with plenty of protein and fiber; you can stick to a vegetarian menu.
From a physiological point of view, the pregnancy process in patients with and without a gallbladder is practically no different, with the exception of control not only by a gynecologist and therapist, but also by a gastroenterologist. During laparotomy, a pregnant woman needs to undergo an ultrasound to check for scars. This is especially important in the second trimester, when the formation of the fetus begins to acquire significant dimensions.
How long should I wait after surgery before pregnancy?
The gallbladder is removed, but bile continues to be produced in the hepatic system. At the same time, the digestive tract can no longer cope with fatty foods. After a year, this process improves as systems adapt to new conditions. After successful rehabilitation, the ducts widen significantly, and bile accumulates in them before being released into the intestinal tract. This is due to the lack of difference between pregnancy after cholecystectomy and normal pregnancy. A doctor can advise the time of conception based on a thorough examination of the body and a study of concomitant diseases.
Risks of premature pregnancy after cholecystectomy
It is important to know!
78% of people with gallbladder disease suffer from liver problems! Doctors strongly recommend that patients with gallbladder diseases undergo liver cleansing at least once every six months... ...
In the case of laparoscopy, the body’s readiness for pregnancy is restored after 2 months. For laparotomy, this period increases to a year. As a rule, there is enough time for the scar to finally form and for the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract to return to normal. To be safe, experts advise waiting about another six months to avoid the risk of complications:
- possible involuntary self-termination of pregnancy at the very beginning;
- development of early and severe toxicosis;
- onset of premature labor;
- the appearance of jaundice in a baby at birth.
If the recovery stage is completed correctly, complications can be avoided. At the same time, therapeutic exercises performed regularly can speed up recovery. Exercise will increase the flow of bile and prevent the formation of stones.
How does labor proceed in women after cholecystectomy?
If the patient's gallbladder was removed, this is not an indication for a cesarean section. In the absence of gynecological complications, the woman gives birth on her own naturally. Caesarean section is prescribed for immaturity or thinning, as well as failure of the scar after surgery. If the scarring is normal, then there are no risks during childbirth.
In general, removal of the gallbladder does not affect conception, pregnancy, or childbirth. Babies appear strong and healthy if the woman has passed her due date correctly. In some cases, there are complications, but there is every chance to carry the baby safely and give birth with ease.
6. How to eat after gallbladder removal?
When can you plan a pregnancy without a gallbladder?
Inna Lavrenko
Expectant mothers who have encountered pathologies of the biliary tract may wonder: is it possible to get pregnant after removal of the pyriform organ?
This article will discuss whether it is possible to conceive a child with this disease, what risks exist if the gallbladder is removed, and also about when you can get pregnant after laparoscopy.
Complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
This is a minimally invasive method and is preferred due to its high accuracy, small area of damage and quick recovery. However, the risk of complications after laparoscopic removal cannot be excluded. Possible:
- mechanical damage to tissues, organs and blood vessels;
- thermal injuries that occur due to excessive electrocoagulation lead to impaired circulation of the biliary system;
- leakage of bile as a result of damage to the ducts or gallbladder - provokes peritonitis;
- loss of stones from the gallbladder - occurs during resection of the bed or removal of the organ from the abdominal cavity.
How to prevent consequences after surgery to remove the gallbladder?
An operation is a stressful life situation for the body and unpleasant sensations in the postoperative period, in any case, cannot be avoided. However, you can prevent serious consequences after it by doing:
- strictly adhere to all doctor’s instructions, take medications prescribed by him;
- diet is the basis of a prosperous life for the rest of your life; any errors will certainly affect your well-being;
- physical exercises associated with tension in the abdominal cavity, and any physical activity only after complete healing of the suture.
Rehabilitation after cholecystectomy
The average time for full recovery after gallbladder removal is six months. But strict restrictions are imposed in the first days, when the patient’s condition is most severe.
Eating is allowed on the third day. In addition to herbal decoction and weak tea, low-fat kefir and yogurt are introduced. On the 4th day, juices, fruit drinks, liquid mashed potatoes, and light broth are added. They begin to eat food in portions of 30-50 ml and increase to 200 ml. On the 5th day you can eat rye crackers, dried bread, biscuits.
From the 6th day, ground porridge, chopped lean meat and fish, vegetable purees, and soups are added to the menu. This diet is followed for 2 weeks.
During the recovery period after extirpation of the gallbladder, adhere to the following tips:
- do not lift weights exceeding 5-7 kg for 1-2 months;
- exclude sports and heavy housework;
- do not visit the solarium, bathhouse, swimming pool, do not take a bath, avoid the sun and hypothermia;
- Intimacy is prohibited for 1-2 months;
- wear soft underwear until the seams are tightened.
People return to work not related to physical labor 1 week after laparoscopy and 2 weeks after abdominal surgery.
How quickly one recovers after removal of the gallbladder depends on the method of surgery, the presence or absence of complications, systemic pathologies, and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Postoperative rehabilitation includes taking medications. Antibiotics are taken for the first 3 days to prevent infection. The doctor prescribes analgesics and antispasmodics to relieve pain. To restore bile production, choleretic drugs are indicated - Holosas, Allochol. For normal liver and digestive function, it is recommended to take hepatoprotectors (Karsil, Ursofalk) and enzymes (Mezim, Festal).
Late rehabilitation period
After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the patient must remain in bed. After 5-6 hours he may try to roll over or sit up. If the patient feels normal, then under the supervision of a nurse he can get out of bed. It is recommended to fast for 24 hours after surgery. The patient can afford a small amount of water without gas.
After the operation, the patient can get out of bed after 5–6 hours
Postoperative nutrition involves strict restrictions. On the second day, you can drink a little broth, eat cottage cheese or natural yogurt (low-fat). The patient is prescribed table No. 5, according to which food should be taken frequently, but in small portions (200–300 g). Products with a large amount of fat, coarse fibers or that provoke excessive gas formation are contraindicated.
The postoperative period is overshadowed by minor pain or discomfort in the area of the punctures; sometimes heaviness is felt on the right side under the ribs. The pain may spread to the lower back or collarbone. The pain goes away on its own after 2–4 days. Due to artificial ventilation, the patient cannot take full breaths because the abdominal wall hurts.
Reference. In the hospital, the patient is bandaged and his body temperature is monitored to prevent inflammation or other complications.
The patient is prescribed painkillers (injections), antibacterial drugs, and enzymes. In addition, he must undergo instrumental and laboratory tests.
Immediately after laparoscopic cholecystectomy, you can take vitamins: Vitrum, Centrum, Supradin, Multi-Tabs, etc.
Diet after laparoscopic gallbladder removal
Prevention of pneumonia involves performing breathing and therapeutic exercises. Exercises are performed 5 to 8 times a day for 3–5 minutes. The patient takes a deep breath through the nose 10 to 15 times, and then exhales sharply through the mouth.
Excessive physical activity is contraindicated. It is recommended to wear soft cotton underwear to avoid damaging the surgical openings. Whether a patient should wear a bandage or not, the decision is made by the doctor for each patient individually.
The time of discharge depends on the person’s recovery time. The patient goes home after the stitches are removed and if there are no complications.
Reference. The question of how long sick leave lasts is quite relevant. A document confirming temporary disability is issued for the entire period of hospital stay plus another 10–12 days. Since inpatient treatment lasts from 3 to 7 days, the approximate duration of sick leave is from 13 to 19 days.
Many patients are interested in how many days of sick leave are written out for in the presence of complications. The doctor determines the period of incapacity for work individually for each person.
In the first days after organ removal, the patient is monitored for complications. At this time the following are possible:
- inflammation of the external sutures and the area around the drainage tube - local irritation is accompanied by pain, itching, purulent discharge - this complication is becoming less common, because removal of the gallbladder is carried out against the background of the administration of antibiotics; if any problems occur, the area is sanitized;
- cholemia is a general deterioration in the condition of the body (itching, cardiac dysfunction, drop in blood pressure, neurological symptoms) when there is an excess of bile secretion products in the blood, occurs in the first days after removal of the gallbladder as a result of an obstruction to the outflow of bile in the hepatic duct (spasm, bend, stone) requires immediate removal;
- peritonitis - internal inflammation of the peritoneum - is possible when stones from the bile ducts enter the abdominal cavity, insemination with infectious agents from places of suppuration or inflammation - a severe, life-threatening complication, rarely occurs with planned interventions.
A rare complication that occurs after any abdominal surgery is vascular thrombosis. Blood thickening is a reflex phenomenon in the vascular bed in response to a violation of the integrity of body tissues. This phenomenon is aimed at closing the wound and preventing extensive blood loss. However, blood viscosity arising in the wrong place can cause blockage of vital vessels.
This rapidly developing condition is prevented by elastic leg bandaging before surgery and in the postoperative period until all threats disappear. If a complication occurs, a complication is eliminated by administering thrombolytics (heparin), which thin the blood. This increases the likelihood of postoperative bleeding, but may prevent vascular embolism.
Another nonspecific complication after cholecystectomy is pulmonary problems. Difficulties with breathing and even pneumonia occur occasionally due to lack of active movements (prolonged bed rest). Therefore, even in the hospital, they recommend that all recovering patients get up early after surgery, and if this is not possible, do daily breathing exercises.
All early complications are treated in the hospital. Therefore, the timing of discharge from the hospital is not the same. The discharge document indicates the features of the recovery phase.
After discharge from the hospital, it is important to follow the recommendations of the inpatient surgeon and outpatient doctor.
At this stage, some consequences are possible after removal of the gallbladder from the gastrointestinal tract - dyspeptic symptoms (changes in taste, belching, nausea, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, stool disorders). A restructuring of digestion occurs against the background of a change in the composition of bile entering the intestines; over time, these troubles pass - the body adapts to new conditions.
Eating without gall - diet, menu and individual recipes
When the gallbladder is removed, in order to avoid consequences, adhere to dietary table No. 5. Eat 5-7 times a day in small portions at regular intervals. Food temperature is 20-60°C, consistency is soft or puree.
The diet is strictly limited. The list of permitted and prohibited products is outlined below.
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Dietary meat – chicken, beef, veal, turkey, rabbit, fish | Fatty meat and fish, offal, eggs |
| Soups with light meat or vegetable broth without frying | Rich broths |
| Boiled, baked dishes cooked in a slow cooker | Fried, smoked, spicy, pickled |
| Sweet fruits, baked vegetables | Sour fruits and berries, raw vegetables, mushrooms |
| Fermented milk products without sugar | Raw milk, sweet yoghurts and curd mixtures |
| Marmalade, honey, marshmallows, jam | Baking, confectionery, chocolate |
| Rusks, biscuits, day-old or dried bread | Fresh baked goods, black bread |
| Herbal infusions, weak black or green tea, juices, fruit drinks, compotes | Strong tea, coffee, cocoa |
| Porridge | Semolina |
They consume limited amounts of sugar (25 g/day), vegetable oil (50 g/day), and butter (20 g/day).
Examples of ready meals:
- Cottage cheese paste. 80 g of cottage cheese are ground, mixed with two tsp. sour cream and honey, add a quarter of an apple.
- Lazy dumplings. Add an egg, 15 g of sugar, a pinch of salt and 30 g of flour to 200 g of cottage cheese. Knead the dough and form dumplings.
- Cream soup of chicken and vegetables. Chicken fillet and any vegetables are boiled in water until tender. The cooked ingredients are crushed with a blender, diluted with broth, salt and sour cream are added, and brought to a boil.
The diet is strict, but it is possible to live on it after extirpation of the gallbladder. After a few months or a couple of years, it can be diversified. For diseases of the digestive system, the diet must be followed constantly.
Prevention of complications
If there are indications, it is safer to remove the gallbladder as planned. A detailed examination before surgical treatment of pathologies will help predict the course of the intervention and hypothetical difficulties. In this case, the threat of complications is significantly reduced.
Gallstones occur due to systematic gastronomic errors - an abundance of fatty foods, large portions entering the body at once. A low-active lifestyle is important in provoking pathology - it provokes a stop in the movement of bile and its compaction, and therefore stone formation.
Smoking cessation is of great preventive importance. This habit is accompanied by periodic spasms of blood vessels, which for some time are compensated by their subsequent expansion. But over time, spasms become constant, not only the blood vessels narrow, but also the hepatic ducts, including the bile ducts.
Sweets and fats are excluded from the diet, alcohol is limited. Nutrition is distributed throughout the active part of the day at approximately equal intervals in small portions.
Over time, the digestion and well-being of the patient who has undergone removal of the gallbladder returns to normal. The new way of life is accepted by the body and becomes familiar to the operated person, and an almost complete recovery occurs.
Important Tips
After cholecystectomy, lifestyle changes. This applies to diet, physical activity and daily habits. Patients need:
- pay attention to stool consistency and regularity of bowel movements every day;
- women should not plan children in the first year after surgery;
- take multivitamin complexes.
Enzymes and hepatoprotectors are faithful companions. They are taken in courses under the supervision of the attending physician. On the advice of a gastroenterologist, include herbal supplements: corn silk, decoctions of immortelle, rose hips.
Is it possible to drink alcohol
Alcoholic drinks are a taboo for patients with a removed gallbladder. Normally, ethyl alcohol is processed by the liver. She secretes it along with bile into the gallbladder, where it is neutralized.
When the gallbladder is removed, ethyl alcohol, along with bile, immediately enters the 12PC and provokes indigestion. In addition, alcohol consumption leads to complications: the formation of stones, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, inflammation of the bile ducts.
Doctors recommend completely abstaining from alcoholic beverages during the first year after surgery, or better yet, forever. A person can live without alcohol, especially since patients with a removed gallbladder develop intolerance to ethyl alcohol.
Pregnancy after open removal
Resection by direct removal involves free access to the abdominal cavity by cutting the layers of the abdominal wall. Rehabilitation continues for 2-3 months.
It is necessary to wait until pregnancy until the scar has completely healed. Doctors will conduct diagnostics and determine the strength of the seam. When the gynecologist gives permission, it is allowed to plan children.
It is important to adhere to proper nutrition and daily routine. Such patients are examined more often than other expectant mothers. The strength of the scar is systematically checked using ultrasound equipment. Every 3 months, be sure to be examined by a gastroenterologist.
Gymnastics and physical activity
How long people live without a gallbladder largely depends on exercise therapy. The first 1-2 months of exercise are prohibited. Then walking is recommended, increasing the distance every day. After a couple of weeks, breathing exercises and exercises to warm up the joints are added.
Patients are prescribed therapeutic exercises. It is carried out at home or in a rehabilitation center. The complex normalizes the outflow of bile and peristalsis.
Classes last 10-15 minutes. They are performed in the morning before breakfast and in the evening an hour before bedtime. Gymnastics consists of warm-up, breathing exercises, and a complex to strengthen the abdominal muscles. Exercise therapy is done smoothly, in the first days 2-5 approaches are performed, increasing the number of repetitions every week. After a few months, weights, race walking, and skiing are added. Stair walking is a great addition to your daily exercise routine.
It is very important to monitor your well-being. If during exercise you experience pain, discomfort, nausea, or a fever, stop exercising and consult a doctor.
Patients without a gallbladder who do exercises live well for many years. The main thing is to practice every day.
There are pros and cons to living without a gallbladder. You will have to limit your diet, give up pleasant but bad habits, and reduce physical activity. But a proper diet and healthy lifestyle will help you lose weight and improve your health and appearance.
The main advantage of the operation is the elimination of relapses of diseases of the biliary system. The gallbladder is not vital, so removing it will not take years off your life. How long people live without an organ depends on the presence of other chronic pathologies, the presence/absence of addictions, and excess weight.
Nutrition rules in the postoperative period after gallbladder removal
After cholecystectomy, a diet is necessary. It must be observed not only for a certain time after surgery, but also for the rest of your life. The absence of a bladder promotes the flow of bile without delaying it to accumulate, which, if not eaten properly, can cause stagnation in the bile ducts and lead to the formation of stones. Therefore, for preventive and therapeutic purposes, doctors prescribe diet (table) No. 5, it involves:
- 5-6 meals a day with the same interval between meals at the same time;
- eating only fresh foods;
- meals should be taken in small portions, but the feeling of hunger should not be present, just as it is not permissible to overeat;
- all dishes must be exceptionally warm;
- Food should be chewed well before swallowing;
- All daily menu dishes must be prepared exclusively by boiling (in water or steamed), stewing or baking in the oven, but without crust. Frying even without oil or with a small amount of it is completely excluded.