The essence of pathology
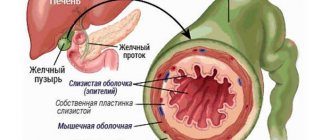
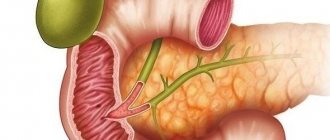
The gallbladder is a hollow organ of the hepatobiliary system.
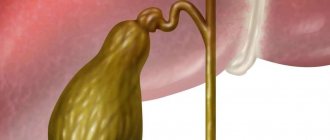
It is a pear-shaped tank. Bile accumulates and concentrates in it. Reflex contraction of the bladder leads to the release of liver secretions into the bile duct and duodenum. Afterwards, bile saponifies fats received with food, promotes their breakdown, and eliminates pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines. The role of the organ is the same for adults and children. Violations of its anatomy or loss of function leads to dyskinesia, the development of inflammation and the formation of gallstones. At the same time, the bile-producing function of the liver changes, digestion and absorption of nutrients are disrupted. A kinked bladder in a child must be monitored and treated.
Reasons for bending
A bend in a child’s gallbladder can occur during intrauterine development. Congenital deformity is provoked by problems during pregnancy and the genetic characteristics of the expectant mother. Sometimes the deformity is noticeable on ultrasound performed late in pregnancy, but it is usually diagnosed in a newborn.
Interesting! There are cases when, as the child grows and internal organs develop, the curve of the bladder straightens and the problem goes away on its own. However, if there is not just a curvature, but a bend, this usually does not happen.
The peculiarity of congenital bending is that pain rarely occurs, there are no serious disturbances in the functioning of the liver, and there are no other organs. Unlike congenital, acquired disease is more pronounced. There are many factors that can cause bending, the main ones being:
- When breastfeeding, errors in the mother's diet, taking certain medications, and infectious diseases can negatively affect the condition of the baby's bladder. Because of these reasons, organ deformation often occurs.
- At an older age, the bend can be provoked by illiterate nutrition due to the fault of the parents, especially the consumption of fast foods, fatty foods, and sweets in unlimited quantities.
- Hyperactivity. The behavior of overly active children causes pressure changes in the abdominal cavity. It can provoke a spasm of smooth muscles, which will lead to deformation of the bladder.
- Enlargement of neighboring organs. Even one enlarged internal organ located “next door” is dangerous. As it grows, pressure is exerted on the bubble, which leads to the formation of a bend.
Recently, an increasing number of children are overweight, even obese. Fat accumulating in the body can also cause deformation.
Important! Some modern parents neglect to feed their child cereals and soups, saving time on cooking. Gallbladder problems are not the only diseases that arise from this.
Signs of a bend
Congenital bending of the gallbladder occurs without symptoms or any complications. It can only be detected by ultrasound examination based on an enlarged echo sign.
The main symptoms of acquired pathology depend on its root causes and the location of the area where the bend occurred. Common signs of the disease are:
- indigestion;
- pain of a different nature in any side;
- bitter taste;
- bowel disorders;
- persistent heaviness in the stomach;
- persistent or recurring nausea and vomiting, most often upon waking;
- discomfort after eating fatty, fried, or other unhealthy foods;
- weight gain;
- heartburn, frequent belching with a bitter taste;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness, fatigue.
Since the gallbladder consists of several parts - the body, the fundus and the neck, the bend on each of them has characteristic symptoms. Most often, deformation appears at the point of contact between the bottom and the body. With such a bend, several pronounced symptoms appear:
- painful sensations in the right hypochondrium, extending under the shoulder blade or into the upper chest;
- constant nausea;
- frequent urge to vomit.
In the case of a bend between the neck and the body, which usually develops with a pathological increase in its length, sagging of the bladder or the formation of stones in it, the symptoms will be more acute. Conditions such as:
- fever;
- pain in the left side;
- increased gas formation;
- nausea;
- high body temperature.
The symptoms resemble hepatic colic:
- stabbing pain under the right ribs, radiating to the shoulder blade;
- jaundiced complexion;
- fever, heavy sweating;
- nausea and vomiting syndrome;
- loose light stools, flatulence;
- strong coating on the tongue;
- rich color of urine;
- increased anxiety;
- general weakness.
It is impossible to relieve pain with any painkillers or antispasmodics. An urgent emergency call and hospitalization of the child is necessary.
Multiple bends of the gallbladder are very rare and, as a rule, with a significant increase in the organ itself due to the presence of stones or prolapse of nearby organs. This pathology is accompanied by acute pain and constant nausea.
All the symptoms described above can be observed in children 3 years of age and older. In infants, the presence of any of these pathologies is indicated by constant crying during or immediately after meals, especially when complementary foods are introduced.
The presence of a deformity in a child may not manifest itself in any way, especially in the case of a functional bend. Symptoms begin to appear when the bladder enlarges or the outflow of bile is disrupted. A kink is often discovered accidentally during a routine ultrasound examination.
Symptoms appear when the biliary system malfunctions. In this case, symptoms such as:
- pain, feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea, possible vomiting after eating;
- light stool and dark urine;
- itching and yellowing of the skin;
- increased gas formation in the intestines.
The symptoms are due to stagnation of bile, which is caused by an excess. Information that states that symptoms depend on the location of the constriction is not reliable. Only a doctor using medical equipment can accurately determine the location of the pathology.
Treatment
A recurved gallbladder rarely requires surgery. In most cases, after timely contact with specialists, complex treatment is selected, combined with diet therapy. It can also be supplemented with physiotherapy, and, if desired, with folk remedies.
A common method of physiotherapy is therapeutic gymnastics, consisting of a set of exercises. Doing them correctly every day helps speed up the flow of stagnant bile. What is dangerous about this stagnation is the occurrence of obstructive jaundice, when the bile produced by the liver accumulates in the bladder and does not have time to be evacuated.
Important! The main goal of therapy is to restore the natural shape of the gallbladder and normalize its function.
Drug therapy
It is not easy to select drugs suitable for treating the gallbladder in children; many of them have age-related contraindications.
Usually one of two common ones is prescribed:
- Hofitol. It has an active choleretic function and has a plant base. Recommended for children aged 6 years and older, available in several dosage forms: tablets, solution.
- Holosas. Syrup for oral administration, also having a plant base. It has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes occurring in the liver.
The following groups of drugs are also prescribed:
- anticholinergic;
- antispasmodics;
- cholekinetics;
- vitamin complexes.
Children's doctor Komarovsky advises the use of herbal medicine, which can relieve the manifestations of gallbladder bending. In pharmacies you can purchase a ready-made herbal mixture that has a choleretic effect. It contains calendula, mint, tansy, chamomile, and yarrow. However, herbs cannot replace full-fledged drug therapy, so you must first consult a doctor.
Why does this happen in children
A bend formed in the mother's womb is called congenital. The reasons for the phenomenon are not fully understood. Doctors do not rule out a genetic factor, developmental abnormalities, or adverse effects on the mother’s body.
Acquired excesses occur in children more often than congenital ones. This is triggered by the anatomy of the developing gallbladder. In adults, it is pear-shaped or funnel-shaped. In babies, the organ is narrower and more elongated. Its shape is closer to fusiform. Due to the rapid growth of a child’s body, the gall muscles develop and “strengthen” unevenly. As a result, stretching and bending occur.
The risk of deformation is increased by inflammation of the liver and gall bladder (hepatitis, cholecystitis). They provoke the formation of fibrous fibers in the smooth muscles of the organ.
In childhood, excesses develop against the background of poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, and regular carrying of heavy objects. Violation of the outflow of bile provokes stagnation and stretching of the bladder in certain places.
Causes of gallbladder bending: congenital and acquired
The reasons for the bending of the gallbladder, which occurs during embryonic development, are associated with a disruption in the formation of this organ, which occurs in the fifth week of pregnancy (simultaneously with the formation of the liver, bile ducts and duodenum). The future gallbladder is formed by strands of glandular epithelial cells of the abdominal (ventral) part of the embryo - from a diverticulum common to the liver. The fetus is most sensitive to various adverse effects on the formation of the biliary system during this period. And it is at this stage that a congenital bend of the gallbladder may occur, associated with a violation of the proportions during the growth of the organ.
The disease is most often permanent, which doctors define as either persistent or fixed inflection of the gallbladder. But, since the bladder is a hollow organ with a muscular shell (that is, quite mobile), the deformation can change its location and shape. And then the so-called labile inflection of the gallbladder is diagnosed.
Acquired bending of the gallbladder in an adult can be a consequence of such reasons as:
enlargement of the gallbladder, liver or right kidney;
increased mobility of the gallbladder (due to its atypical location outside the right longitudinal groove on the lower surface of the liver);
constant violation of the diet (alternating prolonged fasting and overeating);
lifting heavy objects, sudden movements, or sitting for long periods of time (functional bending of the gallbladder);
significant prolapse of internal organs relative to the anatomical norm in old age (physiological inflection of the gallbladder);
obesity.
In this case, the bend can occur in different parts of the bladder - in the area of its body, bottom or neck. And according to localization, when conducting diagnostics, gastroenterologists distinguish between the inflection of the lower third of the gallbladder, the upper third, the bottom, wall and duct of the gallbladder. More often than other varieties, a bend in the neck of the gallbladder is diagnosed, and the most dangerous consequences are caused by a bend in the gallbladder in the body.
The forms taken by the gallbladder as a result of deformation are very diverse and depend on the location and degree of pathology. So, it can be a hook-shaped bend, in the shape of an arc or an hourglass. Moreover, there may be a double bend of the gallbladder, which doctors define as S-shaped and consider it the main cause of biliary dyskinesia in young children.
In rare cases, a woman may develop a bend in her gallbladder during pregnancy - when the uterus enlarges to such a size that it begins to affect the liver and gall bladder. But more often it is simply a congenital pathology, which did not bother the patient in any way and was discovered only when examining the woman for pregnancy.
Diagnostic procedures
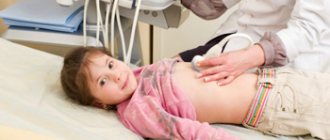
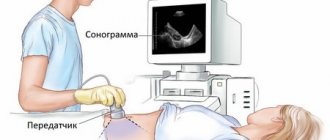
The standard for diagnosing kinks is ultrasound. During the examination, the specialist analyzes not only the condition of the deformed bladder, but also other adjacent organs. This allows us to give an unambiguous answer to the question about the cause of the bend.
To diagnose inflection in children, the following technique is used:
- Ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach;
- Next, the child is offered to have breakfast with food with a high concentration of fats - yolks, sour cream;
- After 15 minutes, repeat the procedure;
- The functional inflection disappears. The permanent one does not react in any way to provocation.
Additionally, laboratory tests indicate problems with the movement of bile. The most obvious indicator will be an increase in bilirubin. This is a breakdown product of hemoglobin, its increased content in the blood indicates a violation of utilization.
In the case of bile duct inflection, there is an increase in direct bilirubin due to a deterioration in its release into the intestine for excretion from the body. The child may experience an increase in the size of the gall bladder.
Conservative treatment
Drug treatment is aimed, first of all, at eliminating the causes of illness. In addition, during therapy, the symptoms of both the gallbladder bend itself and the accompanying diseases: gastritis, colitis, ulcers should be relieved.
Most often, the treatment regimen for a pathological condition includes:
- Nicodin - improves bile formation and promotes the outflow of bile into the duodenum;
- Allohol, Odeston - enhance the excretory function of the liver, stimulate the motility of the biliary tract and gastrointestinal tract, eliminate putrefaction and fermentation in the intestines;
- Gepabene - a combined herbal product improves the separation of liver secretions;
- Ursosan, Hofitol - have choleretic, hypocholesterolemic and immunomodulatory effects, facilitate the breakdown of stones;
- Flamin - improves the functioning of the gallbladder, has analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity.
- medicines that improve digestion - enzymes Mezim forte, Pancreatin, Festal;
- antispasmodics - relax the smooth muscles of the bile ducts and relieve spastic pain - Papaverine, Drotaverine, No-shpa.
If the development of an inflammatory process is suspected, the patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs.
Treatment for an irregularly shaped gallbladder can take months. All medications should be taken in courses of 12–14 days. The duration of therapy and the set of medications is determined by a specialist after diagnostic measures.
To eliminate the symptoms of bending of the bile organ, the patient is prescribed physical therapy: electrophoresis with novocaine, magnetic therapy, ultrasound. The procedures provide excellent pain relief, improve the separation of liver secretions and relieve inflammation.
Classification
Bladder bends are classified according to several criteria. By nature of occurrence:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Curls can form during intrauterine development and after birth. The symptoms of the anomaly depend on the nature of its occurrence. If congenital abnormalities occur, therapy is not required; it is enough to undergo the necessary examinations in a timely manner to monitor their growth or reduction. Acquired bending of the gallbladder in a child must be treated so as not to cause complications.
Bladder bends are divided into congenital and acquired. According to the degree of stability, labile and fixed deformations are distinguished. The first type is typical for children. These are “temporary” changes that resolve themselves as the child grows and develops. They are rarely accompanied by the formation of dense fibrous “strands” in the muscles and disappear without a trace.
Fixed (stable) kinks are more often a congenital pathology. The change in the shape of the organ is pronounced. Depending on the location of the bend and the quantity, double, triple and even multiple bends are distinguished. The bubble can take the shape of a boomerang or hourglass. Double bends with a pronounced curvature are called S-shaped. This deformation is considered the most dangerous. It rarely goes away on its own.
Doctors classify the bends of the bladder according to their location. More common are curvatures between the fundus and body, neck and bile duct. Less commonly diagnosed are curvatures of the body of the bladder, the area between the body and the neck.
How dangerous is bending for a child?
A bend of the gallbladder in children of more than 45° is considered clinically significant. Very often the pathology goes unnoticed. The unfavorable consequence that this anomaly leads to is bile stagnation. This phenomenon, when it persists for a long time, causes the formation of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder with the development of cholelithiasis.
In addition, prolonged and frequent existence of a bend can lead to the following conditions:
- disruption of food digestion;
- pathology of the duodenum and pancreas;
- imbalance of intestinal microflora;
- deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins;
- hemorrhagic syndrome caused by a lack of vitamin K;
- cholestasis, if the bile duct is blocked;
- ischemia, necrosis, amputation of part of the gallbladder;
- perforation of the gallbladder wall with the development of peritonitis.
Dietary errors, physical activity, stressful situations or other emotional shocks provoke the occurrence of bending.
Obesity and diabetes mellitus can be both a cause and a consequence of the decline. Due to a violation of the breakdown of fats, their excess appears in the blood. The rate of glucose utilization slows down, which leads to an imbalance in carbohydrate metabolism and the development of diabetes mellitus.
Disease prognosis
Since accumulated bile interferes with the process of breaking down and digesting food, over time the level of fatty acids in the blood will begin to increase and, conversely, the rate of glucose oxidation will slow down. As a result, the following pathologies may begin to develop:
- Deterioration of vision.
- Dysfunction of the digestive organs.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Formation of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder.
- Lag in general development.
With correctly defined therapy, the prognosis of the disease has a positive trend, and in many cases, as the child grows older, he gets rid of all the symptoms of the disease.
In the video, doctor Komarovsky explains what to do if a child has a deformed gallbladder.
When a persistent deformation of the gallbladder develops in a child, the disease progresses. Stagnation of bile increases the load on the organ, disrupts the digestion of food, and intoxication of the body occurs.
If a bend develops in childhood, this can subsequently lead to the formation of gallstones. However, in general, the prognosis for the inflection point is favorable. In the absence of other unfavorable factors, even persistent constriction of the gallbladder in a child may not affect the functions of the biliary system.
If the gall bladder is bent, the child should be under the supervision of a pediatrician. It is important to ensure that he strictly follows all the specialist’s recommendations.
▼We RECOMMEND YOU TO STUDY▼
Why do kinks occur?
As mentioned earlier, this pathology can be congenital or acquired. Birth defects occur under the influence of a person’s genotype and negative factors during intrauterine development. Typically, congenital abnormalities do not cause additional discomfort to a person, and may disappear on their own in childhood. Acquired kinks in the bladder in children can occur for the following reasons:
- prolonged emotional stress in a child;
- excessive physical activity;
- severe obesity;
- violation of proper diet;
- backbreaking physical labor;
- exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis.
Read: Finding vitamin B12 in food
In childhood, there is no need to lift excessive weight, as this can provoke prolapse of internal organs and affect the appearance of kinks in the gallbladder. Acquired kinks cause discomfort and must be treated.
Gallstone disease that develops in childhood can also lead to twisting of the bladder. In this case, the gallbladder begins to sag under the influence of gravity of the formed stones and, as a result, an inevitable bend of the cervical part of the organ occurs. In case of this pathology, you should immediately seek advice from a medical institution, otherwise a violation of the outflow of bile formed in the body in most cases leads to problems in the functioning of all digestive organs.
What is the pathology fraught with?
A change in the shape of the bladder leads to disruption of the outflow of bile and chronic stagnation within the organ. Sometimes flakes and dense stones form in it. This threatens the development of:
- cholecystitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- organ blockage;
- blocking of its ducts;
- abscesses;
- wall ruptures;
- peritonitis.
The latter complication can be fatal.
Excesses of the gallbladder provoke dyskinesia of the bladder and bile ducts. Violation of the outflow of bile is the cause of stagnation of secretions, a provocateur of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, fat metabolism, and the development of dysbiosis. The secreted bile is not enough to fully process the food bolus.
Complications of kinks are manifested by moderate symptoms of damage to the hepatobiliary system. Unpleasant sensations occur every day after every meal. Periodic increases in nausea and vomiting can cause loss of appetite. As a result, the child develops anorexia.
Methods for diagnosing bending of the gallbladder
After symptoms of bending appear, the child should be shown to a gastroenterologist. He will conduct a diagnosis using ultrasound. There is no other way to determine the bend.
Using this method, the doctor will determine the size and position of the bubble and determine what type of inflection he is dealing with - congenital or acquired.
If the bladder does not change size after taking choleretic drugs, this is a congenital defect. Otherwise, they speak of an acquired bend.
How to determine the inflection
Labile bends of the gall bladder in children rarely provoke significant disturbances in well-being. The pathology may remain undiagnosed for years. Congenital abnormalities also do not always manifest themselves. Symptoms may be absent for several years, appear periodically, or disappear. The disease is characterized by a variety of symptoms:
- weak appetite or lack thereof;
- digestive disorders (bloating, heaviness);
- aching or nagging pain in the abdominal cavity that the child cannot characterize;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea);
- bitterness in the mouth;
- coating on the tongue;
- yellowness of the sclera and mucous membranes;
- nausea and vomiting (usually after eating);
- weakness, fatigue, nervousness of the child.
Signs of pathology become pronounced against the background of complications: dyskinesia, chronic bile stagnation, development of cholelithiasis. There are no symptoms that clearly indicate organ bending. Pathology is most often diagnosed during preventive examinations.
Types of gallbladder kinks in children
The gallbladder vaguely resembles a pear. The organ consists of a neck, body and fundus.
A bend in the gallbladder in a child can be observed in any part of the pear:
- Bottom. The bending of the gallbladder here is the cause of severe pain in the abdominal area. The sensation may radiate to the scapula or sternum. The child develops a feeling of nausea. Possible vomiting. Nausea after a meal, especially a fatty one. In addition, a sign of a bend in the bottom of the bubble ─ cracks in the corners of the lips. A specific coating forms on the tongue. The disease is usually diagnosed in children under one year of age.
- Neck. Here the bend is characterized by the appearance of pain in the left hypochondrium. A bend in the neck of the gallbladder in a child is accompanied by gas formation. It is caused by the entry of liver secretions into the digestive system. Bile acids have a negative effect on the mucous membranes of organs. The child feels sick and vomits. A fever may develop. Temperature contributes to the development of peritonitis ─ inflammation of the peritoneal tissue.
- Combined type. An inflection of the gallbladder in a child can be observed in the body, fundus or cervix at the same time. In this case, the entire digestive system is at risk. The child experiences pain in the abdomen and becomes capricious and irritable. A gag reflex is observed with every meal. The combined type of bend is rare.
A labile bend of the gallbladder, characteristic of a congenital type of disease, can also be diagnosed in a child. It has a second name - unstable. The deformity shifts. When examining an organ using an ultrasound machine, doctors diagnose a bend in one place, and when examining it again, it is in another part of the organ.
There is also a permanent form. It has a name – fixed inflection of the gallbladder. It is permanently fixed on the child without changing the shape or location of the deformation.
Both fixed and labile bending of the bile duct cannot be treated. If the organ does not straighten on its own, only supportive therapy is possible. It is designed to prevent the development of complications.
Is it possible to get rid of the disease?
For a long time, the child has no symptoms of a bent gallbladder. If the disorder occurs immediately after birth, most likely there will be no complaints. The acquired bend appears against the background of some deviations in the functioning of the biliary system. Listen carefully to your baby's complaints.
The main clinical manifestations of a bent gallbladder:
- pain in the right hypochondrium and abdomen;
- decreased appetite due to constant nausea;
- increased gas formation, noticeable bloating in the child, especially after eating;
- the appearance of a permanent white or yellow coating on the tongue, which may indicate malfunctions in various organs of the digestive system;
- periodic bowel irregularities, tendency to diarrhea;
- weakness, general malaise;
- deterioration of complexion, appearance of sallow or yellow skin.
Symptoms of a bent gallbladder in a child can be varied and inconsistent. As a rule, children complain of abdominal pain of various localizations. Usually it hurts in the navel area, with obvious flatulence present. The general well-being of children often does not suffer. But with a significant violation of the recommended diet, intense paroxysmal pain may appear in the area of the right hypochondrium, which is accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting.
A child in this state is very frightened, cries, and his body temperature may rise. To exclude the development of dangerous complications, it is necessary to urgently hospitalize the baby and conduct an ultrasound examination of the liver, gall bladder, and other abdominal organs.
The reversibility of a bend depends on its shape and complexity. Minor deformities disappear on their own, even if they are congenital. Labile bends almost always heal themselves. Proper nutrition and treatment contribute to this.
If a child experiences symptoms of liver disease, you should immediately contact a pediatrician or gastroenterologist. The doctor will order an examination, establish a diagnosis, and give recommendations for treatment (if necessary). In the future, regular monitoring of the condition of the gallbladder will be required. Scheduled ultrasounds are needed for timely detection of bile stasis and prevention of complications.
How to detect a bend in the gallbladder in a child
The bending of the gallbladder in children is accompanied by a feeling of discomfort and pain, which is localized at the site of development of the pathology.
For the doctor, this becomes the basis for making a diagnosis. The pain can radiate to the back or collarbone, gradually moving to the hypochondrium on the right side. The pain may intensify or subside. The process is stool disturbance, bloating, and fever.
Diagnosis is based on stool and blood tests, as well as ultrasound examination. Based on the results obtained, a conclusion is made about the presence of pathology, as well as its stage and causes of occurrence.
Treatment Basics
To get rid of deformation, you should create optimal conditions for regular and complete outflow of bile. This is important for the prevention of stagnant processes and additional stretching of the walls of the organ. Diet therapy plays a key role. A proper diet and a rich diet with healthy foods ensures the optimal composition of bile and improves its rheological properties.
Regular meals contribute to the timely contraction of the bladder walls and the full release of secretions into the duodenum. It is important to prevent excessive synthesis of bile acids by liver cells. Accumulation of bile increases the risk of stone formation, dyskinesia, and blocked ducts.
Drug therapy consists of prescribing antispasmodics, cholekinetics, and hepatoprotectors. Medicines are selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the pathology and the age of the patient. Self-medication is unacceptable.
It is possible to use phytotherapeutic measures. The synthesis and outflow of bile is favorably influenced by the use of rosehip decoction, tansy infusion, chamomile, and mint. Any herbs, the method of their use and dosage are also prescribed by the doctor.
To normalize the functioning of the gall bladder, physiotherapy and exercise therapy are prescribed. The procedures prevent the development of inflammation and relieve spasms of the ducts. Gymnastics are selected taking into account the shape of the bend. Regular exercise improves the flow of bile from “hard-to-reach” places and prevents the formation of flakes in the organ.
Treatment of bile duct in children
A bend formed in the mother's womb is called congenital. The reasons for the phenomenon are not fully understood. Doctors do not rule out a genetic factor, developmental abnormalities, or adverse effects on the mother’s body.
Acquired excesses occur in children more often than congenital ones. This is triggered by the anatomy of the developing gallbladder. In adults, it is pear-shaped or funnel-shaped. In babies, the organ is narrower and more elongated. Its shape is closer to fusiform. Due to the rapid growth of a child’s body, the gall muscles develop and “strengthen” unevenly. As a result, stretching and bending occur.
The risk of deformation is increased by inflammation of the liver and gall bladder (hepatitis, cholecystitis). They provoke the formation of fibrous fibers in the smooth muscles of the organ.
In childhood, excesses develop against the background of poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, and regular carrying of heavy objects. Violation of the outflow of bile provokes stagnation and stretching of the bladder in certain places.
Many parents perceive the bending of the gall bladder in children as a dangerous disease, which, in their opinion, must necessarily lead to dyskinesia, cholecystitis and the formation of stones. But with the right approach to treatment and organization of the diet, this disease disappears safely and no longer bothers the child in adulthood. It is important for you to figure out for yourself how to treat a bend in the gallbladder in a child, but not from information on forums, but with the help of the attending physician.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kmtTv4C7tOA
The following groups of drugs may be prescribed:
- antispasmodics (no-spa);
- choleretic drugs (chofitol);
- antibiotics;
- probiotics (bifidumbacterin).
In specialized medical institutions and sanatoriums, when the gall bladder is bent in children, tubages are performed. Sorbitol is most often used, as it combines softness and high efficiency. It is not recommended to carry out such procedures at home, since parents cannot be sure that there are no stones in the child’s gall bladder.
But most often, experts recommend limiting yourself to following a therapeutic diet. If the child's gallbladder is bent, diet No. 5 is prescribed. It must be followed in any case, even if there is no chronic pain or signs of impaired functionality of the biliary tract.
Principles of nutrition
The therapeutic diet for a bended gallbladder in a child involves excluding the following foods and drinks:
- fatty meats, chicken and chicken skins;
- all fried foods;
- sparkling water;
- sauces and marinades;
- smoked meats, all sausages, including frankfurters;
- fast food, semi-finished products;
- margarine;
- garlic, onions and other vegetables that irritate the mucous membranes;
- sour berries and juices.
Additionally, it is recommended to limit foods that increase gas formation in the intestines. Avoid simple carbohydrates. They promote the processes of fermentation and decay, and negatively affect the functioning of the gallbladder. Of course, a child cannot completely stop eating sweets and baked goods, especially if previously he often allowed himself such products.
Healing herbs
When a child’s gallbladder is bent, it is important to prevent thickening of the bile. To prevent the development of dyskinesia and stone formation, you can use soft choleretic herbs. Chamomile is in first place in children's practice for diseases of the biliary system. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, promotes mucosal regeneration and stimulates the flow of bile without increasing the risk of colic.
In pharmacies today you can buy special choleretic preparations based on common herbs. They include tansy, peppermint, yarrow, and corn silk. Such preparations are taken in long courses, achieving a mild choleretic effect.
You may be interested in the following articles: Features of the course of biliary dyskinesia in children Why a bend in the gallbladder occurs in a child Features of the diet for biliary dyskinesia in children
From this video you will learn what Komarovsky thinks about the treatment of a bent gallbladder in a child and how parents should behave in the event of such deformities.
Life with a Bubble Kink
Even if all recommendations are followed, the pathology may remain with a person forever. The patient will need regular monitoring by a doctor and adherence to a diet.
The regimen corresponds to the basic provisions of the diet, which is prescribed immediately after diagnosis of the disease:
- fractional meals (up to 6 times a day) in small portions;
- exclusion of secretion stimulants (fatty, fried, hot, cold);
- limitation of extractive substances (broths, fatty meats, mushrooms);
- compliance with the drinking regime (60 ml/kg per day);
- saturating the diet with vegetables, fruits, and dairy products;
- consumption of easily digestible protein (steamed and boiled minced meat and fish);
- cereals are the basis of the diet;
- limiting marinades, pickles, sweets, industrial products, spices.
A child diagnosed with kinks needs moderate physical activity. Increased loads provoke spasms of the bladder muscles and acute bile stasis.
If a child’s gallbladder is bent, parents should not panic. With such a diagnosis, you can live carefree, never encountering unpleasant symptoms. It is important to fully undergo diagnostics, determining the degree of danger. To create conditions for the disappearance of pathology, it is enough to provide the child with dietary nutrition and control his lifestyle.
What it is
The normal shape of the gall bladder in a newborn baby is elongated, fusiform. As a person grows, the shape changes until it reaches a pear shape. This is how it should be in a healthy person.
Did you know? The importance of bile has been known and understood since ancient times. The Hippocratic Oath contains words about the danger of undergoing surgery for stone disease. The Tibetans believed that each organ has its own bile, responsible for the functions of the organ, and that bile is responsible for the production of energy.
A bend (kink) of the gallbladder is a violation of the shape of the organ for any reason.