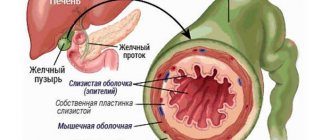
Gallbladder cholesterosis is a pathology in which lipids accumulate in this organ, which in all cases is caused by a violation of fat and cholesterol metabolism. In this case, the functioning of the bladder is disrupted, but the development of the inflammatory process is not observed.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
- Prevention
The exact cause and mechanism of development of this disease remains not fully understood, however, clinicians identify several predisposing factors, including the occurrence of gastrointestinal or endocrine system diseases, as well as the presence of excess body weight. The main risk group is young and middle-aged people. This disease is diagnosed more often in females than in males.
Establishing a correct diagnosis requires an integrated approach, which includes a physical examination and a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations. In most cases, cholesterosis of the gallbladder can be eliminated using conservative methods, but if they are ineffective, surgical intervention will be required.
Etiology
The fundamental factor in the occurrence of the disease is considered to be a violation of fat metabolism in the body. Against this background, the accumulation of lipid metabolic products - cholesterol - occurs in the walls of the bladder.
Due to cholesterosis, there is a significant decrease in the contractility of the affected organ, which is considered an additional reason leading to the accumulation of even more cholesterol.
The following factors can provoke such processes:
- Dyslipidemia is a disease that causes a slight disturbance of fat metabolism. The appearance of this disease is associated with the consumption of large amounts of fatty foods;
- diabetes;
- disruption of the functioning of the thyroid gland, which consists in low production of its hormones;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a pathology leading to increased accumulation of cholesterol in it;
- SIBO (bacterial overgrowth syndrome) is a disorder that involves an increase in the number of bacterial microflora in the intestines. This often happens due to a weak immune system or due to uncontrolled and long-term use of antibacterial medications;
- GSD - gastroenterologists often consider cholesterosis of the gallbladder to be one of the stages of such a disease;
- abdominal obesity, which is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the abdomen;
- genetic factor - a disorder of fat metabolism can be transmitted from parents to child.
Similar causes of cholesterosis of the gallbladder walls are typical for both adults and children.
Causes of the disease
Gallbladder cholesterosis, also known as lipoidosis, is a disease characterized by the deposition of lipids on the wall of the organ, caused by pathology of fat metabolism. More often the disease occurs in the fair sex, but it also occurs in men. Modern medicine considers cholesterosis of the gallbladder as one of the stages of cholelithiasis.
The main cause of this pathology is metabolic disorders, namely fats. Cholesterol in the gallbladder is deposited in the form of low-density lipoproteins, which can enter macrophages. With an excess of fat molecules, foam cells are formed from macrophages, which are filled with cholesterol esters.
Cholesterosis negatively affects the ability of the organ walls to contract, which provokes even greater deposition of cholesterol in the cavity of the bladder. Lipids can be located inside the organ in the form of fatty protrusions, or cover its wall with a dense mesh. With a massive accumulation of cholesterol molecules, hyperplastic cholecystosis develops.
Classification
There are three main forms of such pathology:
- focal cholesterosis – formation of unrelated cholesterol plaques is observed;
- polypous - characterized by the formation of benign growths that can protrude strongly into the lumen of the gallbladder;
- diffuse - deposits can be evenly distributed over the entire surface of the walls of the organ or take the form of a dense mesh.
Forms of gallbladder cholesterosis
Depending on the formation of stones, the disease is:
- acalculous - is the most common type of disease, which is characterized by the presence of general symptoms;
- combined with cholelithiasis - differs in that the formation of cholesterol stones occurs.
The tactics of treating cholesterosis of the gallbladder wall depends on the presence or absence of stones.
Depending on the disruption of the normal functioning of the gallbladder, the disease may be:
- with a slight decrease in the functions of this organ;
- with a moderate decrease;
- with pronounced functional impairments;
- completely inoperative gallbladder.
In the medical field, it is customary to divide this disorder according to changes visible only during instrumental examinations, for example, during ultrasound examination. Thus, it is possible to diagnose the asymptomatic form of the disease, as well as combined types. Gallbladder cholesterosis can be combined with:
- tumors of a malignant or benign nature;
- growth of adipose and connective tissue around the affected organ;
- the appearance of pseudoglandular structures.
Types of cholesterosis
The disease is classified according to several parameters.
Depending on the presence of stones, the disease is divided into:
- acalculous, the most common course of the disease, occurring practically asymptomatically or in the presence of general symptoms;
- a form in which cholesterol neoplasms are formed, consisting entirely of bad cholesterol (a product of lipid metabolism).
Based on signs that can be determined without microscopic examination, cholesterosis is divided into:
There are different types of cholesterosis
- focal cholesterosis, which is characterized by partial damage to the organ. Not only the walls of the gallbladder itself can be affected, but also tissues, as well as extrahepatic bile ducts;
- total, when the entire gallbladder is affected;
- total lipodiasis with damage to the extrahepatic ducts;
- polyposis, the main symptom of which is protrusion of the walls of the gallbladder due to fatty deposits on them. It is worth noting that the polypoid form requires additional diagnostics to refute the presence of malignant neoplasms;
- reticular, characterized by thickening of the walls of the bladder and can develop into a reticular polyposis form.
Based on the signs visible under a microscope, the disease is divided into forms:
- asymptomatic or hidden;
- forms in which cholesterosis is most often combined: with neoplasms (tumors), lipomatosis, adenomatosis, adenofibromatosis, fibromatosis.
Symptoms
In most cases, this pathology occurs without any signs of a clinical picture, which leads to late diagnosis of the disease and the development of consequences of late treatment. However, in some situations the following symptoms of gallbladder cholesterosis occur:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- attacks of nausea ending with vomiting are a consequence of consuming excessively fatty foods;
- stool disorder, which can result in profuse diarrhea or prolonged constipation;
- the appearance of aching pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. Soreness can spread to the entire right arm, under the right shoulder blade and to the back;
- formation of xanthoma and xanthelasma;
- dry mouth.
When a large amount of cholesterol accumulates, signs of biliary colic may occur, which include:
- sudden pain in the area under the right ribs;
- severe nausea, which ends with single or repeated vomiting. It is worth noting that gagging does not bring relief to a person;
- increased sweating;
- strong bitterness in the mouth;
- attacks of dizziness;
- general weakness.
When an inflammatory process occurs, a clinical picture similar to the acute course of cholecystitis will develop. In such cases, the symptoms will be:
- sharp pain in the projection of the gallbladder;
- severe nausea with repeated vomiting that does not bring relief;
- profuse diarrhea;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness and intense dizziness.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you must seek qualified help from a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. The doctor will prescribe the most effective treatment tactics, which will be much more successful at the early stage of the disease than in advanced forms.
How to recognize the symptoms?
If the intrahepatic ducts and gallbladder are damaged, the patient may not complain of pathological manifestations for a long time. The period without pronounced clinical signs can last several months, or even years, so the patient does not seek medical help in time. Soon, polypous cholesterosis of the gallbladder progresses and the patient complains of the following signs associated with damage to the deep tissues of the internal organ:
- soreness in the area under the right rib;
- increased pain due to non-compliance with proper nutrition;
- bitter feeling in the mouth;
- unpleasant belching;
- nausea;
- problems with appetite, the patient may completely refuse food;
- impaired bowel movement, which causes constipation and diarrhea.
When elevated cholesterol in the liver is combined with the manifestation of cholelithiasis, more acute symptoms are recorded, and biliary colic is present.
As the disorder progresses, the development of mechanical jaundice is likely, in which the sclera of the eyes and skin turn yellowish. Changes in blood tests are also observed, where a high content of bilirubin is detected. Often, blockage of the ducts leads to an inflammatory reaction in the internal organ, which causes an increase in body temperature and possible fever.
Diagnostics
The implementation of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic measures is aimed not only at establishing the correct diagnosis, but also at differentiating gallbladder cholesterosis from other ailments with similar symptoms.
Primary diagnosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist or therapist and is aimed at:
- familiarization with the patient’s medical history and life history;
- family history analysis;
- performing a thorough physical examination with palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity and the area of the right hypochondrium;
- Conducting a detailed interview with the patient.
Such activities will help not only to identify a possible etiological factor for the onset of the disease, but will also enable the clinician to find out the presence and degree of intensity of symptoms.
Laboratory diagnostics is aimed at performing:
- clinical blood test;
- blood biochemistry - to control the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the content of trace elements necessary for the body. An increase in the level of food enzymes will indicate a malfunction of the affected organ;
- blood lipid level studies;
- general urinalysis;
- microscopic examination of feces, which will detect particles of helminths or protozoan microorganisms, as well as large amounts of fat.
The basis for confirming the diagnosis is instrumental examinations, including:
Ultrasound image of cholesterosis of the gallbladder
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - for possible detection of the presence of polypous formations;
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder with a preliminary fatty breakfast, which is aimed at stimulating the production of bile and cholecystokinin. If the ultrasound shows no contraction and release of bile, this will indicate a disruption in the normal functioning of this organ;
- conducting tests with the introduction of secretin - in order to assess the functionality of the pancreatic ducts;
- dynamic cholescintigraphy - this procedure is an x-ray technique, thanks to which you can see contractions of the biliary duct, bladder and the release of bile.
Diagnosis of gallbladder cholesterosis
The patient should not delve into the question of what cholesterosis of the gallbladder is, but it is better to immediately contact a medical institution.
When a patient approaches with suspicion of cholesterosis, the doctor, first of all, conducts a general examination and questioning for the presence of characteristic symptoms, when they appear, and whether there are other concomitant diseases: cholelithiasis, diabetes mellitus, other metabolic disorders.
They are also studying whether any of the family members have the following diseases:
- malabsorption syndrome;
- Crohn's disease;
- bacterial overgrowth syndrome;
- peptic ulcer and other diseases of the stomach and intestines.
As for laboratory diagnostics, it is mandatory to carry out:
- a general blood test, as well as a general urine test for the presence of leukocytosis, anemia;
- blood biochemistry, which allows us to identify problems in the liver, pancreas, and blockage of the bile ducts. Research on the organ must be carried out within a time frame of up to 6 hours after the last attack, as well as additionally on an empty stomach and after meals. An increase in enzyme levels in the digestive tract by 2 times or more will indicate dysfunction in the affected organ;
- examination of stool for helminthic infestation, as well as coprogram;
- study of the fat spectrum in the blood to determine indicators of lipid metabolism in the body.
As noted, this disease is difficult to diagnose and therefore cholesterosis of the gallbladder is most often diagnosed by ultrasound . To do this, an ultrasound analysis of the abdominal organs is performed, as well as a separate diagnosis of the gallbladder immediately after a hearty breakfast with a large amount of fatty foods.
In addition to ultrasound, cholescintigraphy is also performed , which allows you to study the dynamics of the gallbladder (contraction, release of bile secretion) using a special contrast agent. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis or determine the type of cholesterosis, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed.
Only on the basis of all diagnostics can a doctor make a correct diagnosis and determine effective treatment.
Treatment
The tactics for eliminating such a disease can be conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment of gallbladder cholesterosis involves:
- taking medications;
- maintaining a nutritious diet.
Drug therapy includes:
- choleretic drugs - to normalize the composition of bile and motility of the gallbladder;
- substances containing ursodeoxycholic acid - to normalize cholesterol levels;
- antibacterial agents;
- antispasmodics and antacids;
- enzymatic substances;
- prokinetics;
- vitamin complexes.
The main way to eliminate such a disease is to follow a therapeutic diet, according to which the chemical composition of dishes per day should include:
- proteins – up to 20% of the total volume of components;
- fat – up to 30%;
- carbohydrates – 50%.
Patients are advised to eat food frequently and in small portions and to control the temperature of the food - it should be warm and in no case excessively hot or extremely cold. Dishes must be prepared only by boiling or steaming, stewing or baking, but without adding fat.
The basis for therapeutic nutrition is dietary table number five, the diet of which implies the refusal of:
- fatty and spicy foods;
- baked goods and confectionery products;
- semi-finished products;
- ice cream;
- strong coffee and carbonated drinks.
Dietary table No. 5
At the same time, the diet for gallbladder cholesterosis allows the use of:
- legumes;
- dietary varieties of meat, poultry and fish;
- wheat bread;
- first courses based on vegetable broths;
- low-fat dairy and fermented milk products;
- crumbly porridges;
- fruit;
- weak tea and compotes.
A complete list of permitted and prohibited ingredients, as well as a sample menu, is provided only by the attending physician on an individual basis for each patient.
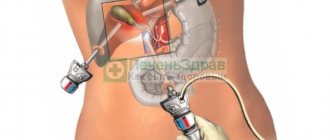
Surgical intervention is considered only in the absence of a positive effect from conservative therapy or when the disease process is widespread. The basis of this treatment is an operation to excise the gallbladder - cholecystectomy.
Diet
Without a special diet, treatment will be ineffective, since everything depends on nutrition. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, your weight will normalize and your digestive system and metabolism will improve. Cholesterosis of the gallbladder walls in its initial development is often treated with a special diet.
You will need to eat fractionally about five times a day and in small portions. It is necessary to chew food thoroughly, then there will be good digestion. You need to eat food at the same time. The diet should include dairy products, yoghurts and kefir. You need to eat lean meats, fresh vegetables and fruits. Completely avoid fatty, spicy, smoked foods. Avoid alcoholic drinks and smoking.
If you follow the diet for a long time, it will help normalize digestion. Thanks to proper nutrition, the inflammatory process in the liver and gallbladder goes away. The organ begins to recover faster, and the patient feels better. A diet for gallbladder cholesterosis should be followed throughout your life. If food is introduced that provokes an exacerbation, then all the symptoms will return and medications will need to be used.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the development of such a disease include:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- rational and balanced nutrition;
- performing therapeutic exercises;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases;
- regular preventive examination by a gastroenterologist;
- taking vitamins and mineral components.
Due to the fact that cholesterosis does not cause serious disturbances in the functioning of the gallbladder, the prognosis of the disease is often favorable. Normalizing metabolic processes and following a diet significantly improves a person’s condition. However, the outcome of the disease worsens significantly with the development of complications, namely cholecystitis, which can occur in a purulent form.
Reviews and results
Treatment undertaken in the early stages of the disease and proper nutrition can reduce cholesterol and restore gallbladder function, in addition, the risk of stone formation is minimized. The diet is easily tolerated, and following it has a positive effect on health: nausea and heaviness in the right hypochondrium, constipation . Constantly following it gets boring, so some people switch to their usual diet while undergoing drug treatment.
- “...I did an ultrasound. Conclusion: signs of cholesterosis, moderate deformation of the gallbladder. Previously there was sludge and dyskinesia. The doctor advised me to follow a proper diet, which will help normalize metabolic disorders. You need to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits, avoid spicy and fatty foods, and stick to your diet. I stick to Table No. 5 and have studied it thoroughly. It’s convenient to cook all dishes in a slow cooker - it doesn’t take much time. I understand that I will have to eat this way all the time, but this is associated with certain inconveniences - cooking separately for myself”;
- “... This diagnosis was made two years ago. Ursosan was immediately prescribed, I took it for six months and switched to medical nutrition. It is complete, you can eat all foods, but exclude fatty and fried foods. I started eating more vegetables, introduced bran and seaweed. I can’t say that I follow it very strictly - there are deviations, but then I switch back to medical nutrition. I feel good, I’ve lost weight, but the most important thing is the positive changes on the ultrasound”;
- “... Cholesterosis didn’t bother me, I didn’t know about it until cholecystitis came along. These two diseases force you to constantly be on a diet. In principle, a normal diet without fatty, smoked, fried and too salty foods. I eat mostly fish and chicken, sometimes turkey. I cook it in a steamer or oven. I completely eliminated animal fats - sometimes just a little butter in porridge. I switched to vegetable oils and add them to soups, porridges, and potatoes. Since my bladder is “lazy,” I can drink a tablespoon of oil before meals. I chose flaxseed and wheat germ oil - I alternate between them.”
Treatment options
For a long time, there were no options for treating cholesterosis with conservative methods, and therefore patients were offered removal of the gallbladder. With the use of highly accurate diagnostic methods, the likelihood of identifying pathology before the need for surgical intervention has increased.
Treatment involves a wait-and-see approach with dietary adjustments and symptomatic therapy.
The course of medications is compiled individually for each patient. The following groups of drugs are used in therapy:
- Antispasmodics. They relieve pain and help reduce the severity of biliary colic (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Riabal). Used sporadically.
- Choleretic drugs. Helps improve the outflow of bile and normalize its composition (Gepabene, Magnesia, Ursohol). Prescribed for long-term use lasting up to several months.
- Enzyme-containing products. Help restore the digestion process (Creon, Allochol, Mezim).
- Antacid drugs. Prescribed in the presence of heartburn and increased acidity of gastric juice (Rennie, Gastal).
- Antibiotics. They are used in cases of microbial infection to prevent cholecystitis. Selection is carried out individually.
If there is no response to traditional treatment, rapid progression of the disease, or extensive damage to the gallbladder tissue, surgery is performed to remove the organ.
Gall tissues are sent for histological examination. Removal is carried out mainly laparoscopically; in rare cases, abdominal surgery is required.
How to get rid of the problem
If the disease was detected at an early stage, then a wait-and-see approach is used to begin with. For six months, a specialist monitors the condition and functioning of the gallbladder, based on which he selects a method and treatment regimen. Treatment for cholesterosis can be surgery or medication in combination with a special diet.
If the patient develops severe symptoms of cholesterosis, gallstones, cholestasis, then surgical intervention is indicated.
Surgery to remove the gallbladder is a last resort: it is used in advanced stages or complications of the disease.
Drugs from the pharmacy
The main purpose of using medications in the treatment of cholesterosis is to reduce cholesterol in bile and have a choleretic effect. To solve these problems, drugs such as Cholenzym and Allochol are prescribed.
Bile acid can be used to reduce cholesterol levels in the bile.
To restore lipid metabolism and reduce the content of bad cholesterol in the body, the doctor may prescribe:
- Drugs whose active ingredients bind bile acids and promote their excretion from the body. Due to the resulting bile deficiency, the liver begins to produce bile acids from cholesterol. Such drugs include Cholestyramine, Colestipol.
- Products with nicotinic acid that help eliminate excess fatty acids. These include Acipimox, Enduracin.
- Drugs aimed at removing cholesterol along with bile (Probucol).
- Medicines that improve the properties of bile and the quality of the bile wall, so that it can prevent the sedimentation of cholesterol. Among such drugs: Ursosan, Ursofalk and others.
Tubazh
Tubing of the gallbladder is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision. The procedure is carried out using a substance that has a choleretic effect. This could be Essentuki or Borjomi mineral water, sorbitol or magnesium sulfate. The liquid is drunk in small sips in a volume of 200-300 ml for 20-30 minutes. At this time, a heating pad with warm water is applied to the liver area. If the procedure is carried out correctly, the feces during subsequent bowel movements should have a yellow-green tint.
Diet food
Diet for gallbladder cholesterosis is a prerequisite for effective treatment. It involves eating food in fractions (a little, but often). The disease requires adherence to dietary table number 5, which excludes baked goods, fatty fish and meat, coffee, fried foods and many other foods. The diet should be supplemented with plant foods containing dietary fiber (whole grain cereals, bran). Along with healthy food, it is necessary to take vitamins E, K, A, D, iron, B12.
Is it possible to use folk recipes?
Treatment with folk remedies can be used as an additional measure to the main treatment of cholesterosis and must be agreed with a doctor. Beetroot juice, infusion of dandelion roots, infusion of St. John's wort and immortelle, and strawberry tea help well with the disease.
How to diagnose the disease?
Without additional examination, no doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. First, the specialist is obliged to collect data on the patient’s condition, how long he has been bothered by alarming symptoms, whether the person has undergone operations on the gastrointestinal tract, whether he has suffered from hepatitis and gallbladder diseases.
The doctor must examine the patient, determine the location of pain and its intensity. By palpating, the specialist can easily determine the enlargement of the patient’s liver and spleen.
The list of required studies includes:
- Laboratory analysis of blood, urine and feces.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder.
- Cholescintigraphy (it will help determine the level of contraction of the gallbladder).
- Tests using secretin to determine the patency of the bile ducts.
The specialist takes into account everything: the patient’s previous illnesses, predisposition to diseases such as obesity and diabetes, the presence of thyroid disorders, and the patient’s complaints. Based on the results obtained, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions, determine the form of the disease and select the optimal treatment.
Treatment of gallbladder cholesterosis
Please note that in most cases, treatment for gallbladder cholesterosis is carried out comprehensively.
First of all, you need to establish your diet. You should eat in small portions, at least 5 times a day, adhering to a certain diet, which will be discussed below.
In addition to special nutrition, gallbladder cholesterosis also requires certain drug therapy, including:
In addition to special nutrition, gallbladder cholesterosis also requires certain drug therapy.
- antispasmodics to relieve spasms;
- painkillers;
- cholesterol-lowering drugs;
- medications that improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- antibiotics;
- enzymes to improve the digestion process;
- medications to increase bile flow.
In addition to drug treatment, you can also treat with folk remedies. The choleretic properties of some herbs (dandelion, St. John's wort, immortelle, strawberry) will improve the flow of bile secretions and prevent the appearance of stones.
Surgical intervention is considered a last resort method of treatment, in case of a negative result with traditional treatment or when the affected area is too large and it is not advisable to continue medical treatment.