Modern classification
ICD 10 presents acute (K85), chronic (K86) pancreatitis, as well as damage to the pancreas due to viral diseases (cytomegalovirus infection (B25.+), mumps - “mumps” (B26.3+)).
Chronic pancreatitis of alcoholic etiology (K86.0) is separately identified as the most common.
Section K86.1 presents other types of chronic disease:
- infectious;
- recurrent;
- repetitive.
Cysts that form as a result of exacerbation and are complications are classified in section K86.2.
How to treat pancreatic diseases
Treatment of acute conditions with pathologies of this organ often takes place in a hospital setting. Due to severe nausea and vomiting, all necessary medications are administered to the patient by injection or using droppers.
Complex therapy is aimed at reducing pain, removing intoxication and reducing enzyme activity. If a focus of purulent inflammation forms, antibiotics are prescribed.
In some cases, conservative treatment does not produce the desired effect, and surgical intervention is required.
As the general condition improves, the patient is prescribed pancreatin, a drug containing an enzyme normally produced by the gland when food enters the stomach. It is used until pancreatic function is completely restored. Some patients who have suffered severe pancreatitis, as well as those suffering from a chronic illness, are forced to take it throughout their lives.
During the recovery period, restorative therapy is prescribed, including vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants.
to contents ^
Traditional methods of treatment
In the complex treatment of pancreatic diseases, the use of folk remedies is permissible.
Home remedies based on oats have a healing effect on this digestive organ.
- Oatmeal jelly. To prepare it, pour a glass of cereal into a liter of boiled water, place it in a water bath and cook for half an hour. Cooled jelly should be drunk ½ cup 3-4 times a day before meals.
- Oat milk. You will need 100 grams of unrefined cereal, 1.5 liters of water. Boil the washed oats in water for approximately 40 minutes. When it becomes soft, it should be crushed. It is convenient to do this with an immersion blender in the same container. The resulting mixture should be cooked for another 20-30 minutes. It needs to be strained. You should drink this drug three times a day, ½ cup. Oat milk can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 3 days.
Juice from raw potatoes relieves the condition. Squeeze out the grated raw root vegetable, drink the resulting juice 100 ml 2 hours before meals.
A tincture based on dry raw materials of chamomile and immortelle will have an anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effect. For a tablespoon of herbal mixture you will need 200 ml of boiling water. The product must be infused for 30 minutes and then strained. Drink 120 ml 2-3 times a day half an hour before meals.
Ground chicory is traditionally used to treat the pancreas. It can be used instead of tea or coffee by taking a teaspoon of the product per glass of water.
In case of disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas, treatment with folk remedies should not replace the main therapy prescribed by the doctor.
to contents ^
Therapeutic diet
Dietary nutrition for diseases of the pancreas is an element of complex therapy.
During the period of acute manifestations, the patient is recommended to fast. As negative symptoms decrease, dietary dishes are gradually introduced into the menu.
Often manifestations of pancreatic diseases lead to dehydration. Therefore, it is important to maintain a drinking regime, ensuring rehydration.
- Fried, baked, fatty, spicy, salty foods, smoked foods, canned food (including home-made food), and confectionery are subject to complete exclusion.
- The basis of the menu should be porridge with water, vegetable broths and vegetarian soups, pureed vegetables, dried bread products, low-fat fish, cottage cheese, steamed omelettes, unsweetened tea.
- Meals should be fractional, in small portions.
- It is important to organize meals at the same time.
- Smoking and alcohol must be avoided.
to contents ^
What is the difference between acute and chronic process
Acute and exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis by their nature, as well as manifestations, are identical conditions associated with the advanced process of self-digestion and destruction of pancreatic cells. They are an acute surgical pathology, diagnoses must be confirmed by surgeons, treatment must be carried out in the surgical department of the hospital. If the patient’s condition is serious, complications develop - in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
The chronic process leads to a sluggish, gradual replacement of previously inflamed tissue with fibrous tissue, which loses the ability to produce enzymes and hormones. It is treated under the supervision of general practitioners or gastroenterologists. The basis of therapy is maintaining the viability of the preserved tissue, taking replacement drugs (enzymes, insulin), and preventing exacerbations.
Let's summarize
Pancreatitis is a serious diagnosis that requires a similar attitude. A patient who wants to say goodbye to relapses of the disease forever must vigilantly monitor their health, undergo regular outpatient examinations with their attending physician, and strictly follow all recommendations regarding medication and diet.
Diet for patients with pancreatitis is a key point, without which recovery and normalization of well-being are impossible. Thus, the patient himself helps the doctor cure pancreatitis, carefully following all the prescriptions, not forgetting about prevention and preventing the development of complications during the course of the disease. How to stop diarrhea at home, you will find the answer in the link.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you suspect acute pancreatitis (usually a sharp girdle pain, vomiting that does not bring relief, increased body temperature), you should consult a surgeon or call an ambulance. An emergency doctor, suspecting inflammation of the pancreas, will provide transportation to the surgical department for urgent diagnosis and selection of treatment.
Chronic pancreatitis (beyond severe exacerbations) develops gradually, does not require acute care, but requires constant medical supervision.
It is necessary to consult a therapist, general practitioner (family medicine) or gastroenterologist if the following complaints occur:
- abdominal pain spreading all around, worsening after drinking alcohol or fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- bowel dysfunction (weakness or alternation of diarrhea and constipation);
- nausea, vomiting;
- dry mouth, thirst.
The described complaints may be caused by inflammation of the pancreatic tissue.
How can a person understand that he has symptoms of pancreatitis?
Above we mentioned the unique functionality of the pancreas, which is not available to other organs. The pancreas plays a vital role in the digestive process, which means that the normal existence of the human body and a high quality of life with its dysfunction is impossible.
The pancreas plays a vital role in the digestive process
The pancreas performs two main functions: it produces insulin and enzymes that break down fats, carbohydrates and proteins that come with food. With inflammation (pancreatitis), the gland begins to destroy itself due to the fact that enzymes cannot exit through the duct and simply digest the organ itself instead of food lumps. There are two types of such inflammation: acute and chronic pancreatitis. Let's consider these types of disease.
Table 1. Acute and chronic course of pancreatitis
| Type of pancreatitis | Symptoms | What measures to take |
| Spicy | Sharp destruction of pancreatic cells. Pain in the upper abdomen of a girdling nature, which is practically unresponsive to painkillers. Painful shock is possible with the rapid development of the disease. Nausea, vomiting (possibly with blood), which does not bring relief, lethargy, the skin and whites of the eyes acquire a jaundiced tint. Flatulence, bloating, fever. | Do not take painkillers, food, limit activity. Immediately consult a doctor; in case of severe pain, you need to call an ambulance. Without delay, undergo all necessary tests and diagnostics. |
| Chronic | Gradual decrease in organ functioning. Permanent moderate pain on the left in the navel area (increased by eating spicy, fatty foods, smoking, drinking alcohol), heaviness, nausea after eating, weight loss even with plenty of food, stool disorders, low-grade (jumping) temperature. Lethargy, problems falling asleep, headaches, intoxication of the body. | Make an appointment with your local therapist. Until you visit the doctor, go on a dietary diet (basis - table No. 5 P). Go through a full examination and follow the doctor’s recommendations. |
Where does the specialist meet?
General practitioners and therapists work in all outpatient and inpatient departments of medical institutions. If you suspect pancreatitis, you should contact these specialists. Depending on the diagnostic capabilities of the medical organization, these doctors either prescribe examinations themselves or refer you to a gastroenterologist.
There are gastroenterologist’s offices in clinics, private clinics, as well as in specialized multidisciplinary diagnostic and gastroenterological centers.
Do I need to be examined and what tests should I do before visiting a doctor?
If you suspect pancreatitis (as with any disease), it is better to first consult a doctor. If blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity (ultrasound of the abdomen), or stool analysis (coprogram) have previously been performed, then the results must be shown to the doctor.
Delaying time and wasting it on independent examinations can not only contribute to the aggravation and spread of the process. Expensive studies may not be informative in a particular situation and may need to be repeated after special preparation or using additional methods (for example, contrast in CT or MRI). Therefore, you first need to see a doctor and then undergo examinations.
How does a doctor's appointment work?
If the consultation is primary, then after meeting the doctor conducts a survey of complaints, asks about the duration and dynamics of existing manifestations, the development of the disease, examinations performed, previous treatment (independent or as prescribed by specialists), allergic reactions, possible diseases of other organs. Next, the doctor conducts a direct examination of the abdomen (examination, palpation, tapping the abdomen and listening to bowel sounds) and issues directions for the necessary studies.
The appointment can take place in a medical facility, or maybe at home. In order for the doctor to understand the clinical picture and also to suspect inflammation of the pancreas, a medical examination at the patient’s home is sufficient.
List of mandatory examinations:
- general blood test, urine test;
- blood test for amylase, urine test for diastase;
- coprogram;
- stool test for elastase-1;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs.
To clarify the cause and nature of the damage to the pancreas, retrograde cholecystopancreatography may be performed. This method determines the localization of stones in the bile ducts that obstruct the outflow of bile and pancreatic secretions, which causes inflammatory changes in the pancreatic tissue. Cysts and areas of necrosis in acute or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis are detected using computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (CT) with or without the introduction of contrast, depending on the specific clinical situation.
The doctor also determines the place of treatment (hospital or home conditions under supervision), selects medication treatment, individual dosages, and duration of treatment. Writes prescriptions for medications if necessary (dispensed at the pharmacy only by prescription).
Chronic pancreatitis: we act according to the situation
Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) refers to diseases of the digestive system. When the disease occurs, two of its main functions are disrupted: the secretion of enzymes for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the secretion of hormones that affect glucose metabolism. To find out exactly which doctor treats pancreatitis in your case, you need to determine the form of its course.
ICD 10 presents acute (K85), chronic (K86) pancreatitis, as well as damage to the pancreas due to viral diseases (cytomegalovirus infection (B25.), mumps - “mumps” (B26.3)).
Chronic pancreatitis of alcoholic etiology (K86.0) is separately identified as the most common.
Section K86.1 presents other types of chronic disease:
- infectious;
- recurrent;
- repetitive.
Cysts that form as a result of exacerbation and are complications are classified in section K86.2.
Acute and exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis by their nature, as well as manifestations, are identical conditions associated with the advanced process of self-digestion and destruction of pancreatic cells.
They are an acute surgical pathology, diagnoses must be confirmed by surgeons, treatment must be carried out in the surgical department of the hospital.
If the patient’s condition is serious, complications develop - in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
The chronic process leads to a sluggish, gradual replacement of previously inflamed tissue with fibrous tissue, which loses the ability to produce enzymes and hormones. It is treated under the supervision of general practitioners or gastroenterologists. The basis of therapy is maintaining the viability of the preserved tissue, taking replacement drugs (enzymes, insulin), and preventing exacerbations.
If you suspect acute pancreatitis (usually a sharp girdle pain, vomiting that does not bring relief, increased body temperature), you should consult a surgeon or call an ambulance. An emergency doctor, suspecting inflammation of the pancreas, will provide transportation to the surgical department for urgent diagnosis and selection of treatment.
Chronic pancreatitis (beyond severe exacerbations) develops gradually, does not require acute care, but requires constant medical supervision.
It is necessary to consult a therapist, general practitioner (family medicine) or gastroenterologist if the following complaints occur:
- abdominal pain spreading all around, worsening after drinking alcohol or fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- bowel dysfunction (weakness or alternation of diarrhea and constipation);
- nausea, vomiting;
- dry mouth, thirst.
The described complaints may be caused by inflammation of the pancreatic tissue.
General practitioners and therapists work in all outpatient and inpatient departments of medical institutions. If you suspect pancreatitis, you should contact these specialists. Depending on the diagnostic capabilities of the medical organization, these doctors either prescribe examinations themselves or refer you to a gastroenterologist.
There are gastroenterologist’s offices in clinics, private clinics, as well as in specialized multidisciplinary diagnostic and gastroenterological centers.
If you suspect pancreatitis (as with any disease), it is better to first consult a doctor. If blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity (ultrasound of the abdomen), or stool analysis (coprogram) have previously been performed, then the results must be shown to the doctor.
Delaying time and wasting it on independent examinations can not only contribute to the aggravation and spread of the process.
Expensive studies may not be informative in a particular situation and may need to be repeated after special preparation or using additional methods (for example, contrast in CT or MRI). Therefore, you first need to see a doctor and then undergo examinations.
You need to take medical documentation with you: pictures, conclusions of tests and studies performed earlier, a medical card (if you have one). No special preparation is needed.
However, it is better not to eat for 2-3 hours before the examination.
And if further studies are planned, for example, after an examination by a doctor, it is likely (as prescribed by him) to perform a FEGDS or ultrasound, then you need to be on an empty stomach and take a towel with you.
If the consultation is primary, then after meeting the doctor conducts a survey of complaints, asks about the duration and dynamics of existing manifestations, the development of the disease, examinations performed, previous treatment (independent or as prescribed by specialists), allergic reactions, possible diseases of other organs.
The appointment can take place in a medical facility, or maybe at home. In order for the doctor to understand the clinical picture and also to suspect inflammation of the pancreas, a medical examination at the patient’s home is sufficient.
List of mandatory examinations:
- general blood test, urine test;
- blood test for amylase, urine test for diastase;
- coprogram;
- stool test for elastase-1;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs.
To clarify the cause and nature of the damage to the pancreas, retrograde cholecystopancreatography may be performed.
This method determines the localization of stones in the bile ducts that obstruct the outflow of bile and pancreatic secretions, which causes inflammatory changes in the pancreatic tissue.
The doctor also determines the place of treatment (hospital or home conditions under supervision), selects medication treatment, individual dosages, and duration of treatment. Writes prescriptions for medications if necessary (dispensed at the pharmacy only by prescription).
There are differences in the clinical picture and causes of the disease depending on gender. In men, pancreatitis more often occurs with regular consumption of alcoholic beverages, in women - as a complication of bile outflow disorders due to stone formation in the gallbladder.
In old age, depending on the state of health, there may also be features of manifestations. If the cardiovascular system is damaged (atherosclerosis), metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus) with damage to nerve endings, pain can be significantly reduced.
Such patients do not seek medical help in a timely manner, more often when complications develop associated with the body’s general reaction to local inflammation in the pancreas (a sharp drop in blood pressure, liver and kidney dysfunction, the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the digestive tube, hemorrhages or blockage of small vessels ( thrombosis)).
When pancreatic cells that secrete hormones that regulate sugar metabolism are destroyed, blood glucose levels increase and fat metabolism suffers. If there is a disturbance in glucose metabolism or the development of diabetes mellitus, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary, and subsequently treatment under his supervision.
- Suspicion of acute or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is an indication for urgent consultation with an abdominal surgeon (specializing in surgical interventions on the abdominal organs).
- For a patient with a chronic course of the disease, in some cases it is necessary to consult an oncologist.
- Symptoms of a long-term disease that cause concern:
- gradual weight loss;
- reduction of pain with a simultaneous increase in general weakness;
- chronic stool disorders with a tendency to diarrhea;
- increased fragility of blood vessels, tissue bleeding;
- pain in the bone area.
The described signs occur not only with pancreatic pathology, but are also likely to occur with malignant neoplasms. In addition, long-term chronic pancreatitis itself can lead to degeneration of pancreatic tissue and the development of tumors.
The main question, in addition to timely treatment, is “how to change lifestyle and nutrition in order to further prevent exacerbations of pancreatitis and its further progression?”
To cope with this task, you should ask your doctor:
- Is it possible to smoke and drink alcohol?
- What to do if pain suddenly appears?
- What foods, in what form, can be consumed after the exacerbation of the disease subsides?
- Should I stick to a diet for the rest of my life?
- How often should control examinations of the pancreas (ultrasound) and laboratory tests be done?
In Russia, in Moscow and St. Petersburg, the best doctors of both therapeutic and surgical profiles work for the treatment of pancreatitis. Scientific achievements, as well as extensive practical experience, determine their high qualifications.
Anna Sanno, general practitioner of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, 12 years of experience.
The development of chronic pancreatitis can develop according to two scenarios:
- Invisible development of the disease without an acute form.
- Acute pancreatitis, developing into chronic.
Even with a sluggish course of the disease and unexpressed pain syndrome, a sharp regression can still occur. In this case, the patient will feel symptoms characteristic of acute pancreatitis. In this case, you need to act as described above - call an ambulance. Doctors will collect anamnesis and decide whether the patient needs emergency hospitalization, or can visit a gastroenterologist at the clinic the next day.
Emergency doctors will decide on hospitalization
In fact, the methodology for diagnosing and treating chronic and acute pancreatitis is the same, the only difference is in the efficiency of these measures, which is important for preserving the life and health of the patient. Therefore, a gastroenterologist, to whom a person turns with symptoms of chronic pancreatitis, will prescribe the same tests, but in a smaller volume and in a less urgent manner:
- General blood test and biochemistry.
- Coprogram.
- Urine analysis, in particular for amylase.
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs.
- MRI or CT.
Features of the disease depending on age and gender
There are differences in the clinical picture and causes of the disease depending on gender. In men, pancreatitis more often occurs with regular consumption of alcoholic beverages, in women - as a complication of bile outflow disorders due to stone formation in the gallbladder.
In old age, depending on the state of health, there may also be features of manifestations. If the cardiovascular system is damaged (atherosclerosis), metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus) with damage to nerve endings, pain can be significantly reduced. Such patients do not seek medical help in a timely manner, more often when complications develop associated with the body’s general reaction to local inflammation in the pancreas (a sharp drop in blood pressure, liver and kidney dysfunction, the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the digestive tube, hemorrhages or blockage of small vessels ( thrombosis)).
How does the pancreas work?
The gland is conventionally divided into 3 sections: the head (located inside the bend of the duodenum), the body (consisting of the anterior, posterior and lower surfaces and the tail (directed upward and to the left towards the spleen).
The structure of the organ is determined by two main functions performed in the body.
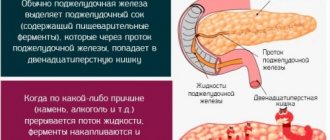
1. Exocrine function , which is provided by tissues formed by small lobules - acini. Each of these lobules has an excretory duct. All these ducts connect into a common excretory canal running along the entire length of the gland. It enters the duodenum, ensuring the delivery of pancreatic secretions to this digestive organ.
The pancreas produces enzymes:
- Amylase , which promotes the breakdown of carbohydrates;
- trypsin and chymotrypsin, which affect the process of protein digestion, which begins in the stomach cavity;
- lipase responsible for the breakdown of fats.
Enzymes are produced by the gland in an inactive form. When a bolus of food enters the duodenum, a series of chemical reactions are triggered, activating them.
The production of pancreatic juice is directly related to food intake: the content of certain enzymes in it depends on the type of food components.
2. Endocrine function , which consists in the release of insulin, glucagon and other hormones into the blood. Insulin regulates carbohydrate and fat metabolism and reduces blood glucose levels. Glucagon increases this indicator, being an insulin antagonist.
to contents ^
Which related specialist can the doctor refer you to?
When pancreatic cells that secrete hormones that regulate sugar metabolism are destroyed, blood glucose levels increase and fat metabolism suffers. If there is a disturbance in glucose metabolism or the development of diabetes mellitus, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary, and subsequently treatment under his supervision.
Suspicion of acute or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is an indication for urgent consultation with an abdominal surgeon (specializing in surgical interventions on the abdominal organs).
For a patient with a chronic course of the disease, in some cases it is necessary to consult an oncologist.
Symptoms of a long-term disease that cause concern:
- gradual weight loss;
- reduction of pain with a simultaneous increase in general weakness;
- chronic stool disorders with a tendency to diarrhea;
- increased fragility of blood vessels, tissue bleeding;
- pain in the bone area.
The described signs occur not only with pancreatic pathology, but are also likely to occur with malignant neoplasms. In addition, long-term chronic pancreatitis itself can lead to degeneration of pancreatic tissue and the development of tumors.
Who is doing the treatment?
Which doctor treats inflammation of the pancreas if the patient has a long-term chronic phase of inflammation of the pancreas?
A quiet course of the disease with mild symptoms can be treated on an outpatient basis. The attending physician (therapist) constantly monitors the course of the patient’s illness and prescribes medications that alleviate the patient’s condition.
If insulin deficiency syndrome develops with pancreatitis, an endocrinologist begins treatment. Problems with the production of this important hormone can lead to diabetes, which will have its extremely undesirable consequences.
The use of medications for this disease makes it possible to stop its progression and relieve symptoms. All medications included in the standard course of therapy can be divided into two conditional groups:
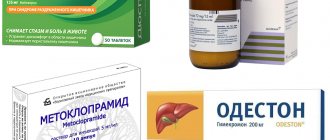
- Antispasmodics. This group includes “pure” medications (“No-shpa”) and drugs containing painkillers (“Analgin”, “Paracetamol”).
- Enzyme agents. Their action is aimed at improving the digestion process. In this group, drugs are divided into two categories: those containing enzymes (Mezim, Pancreatin) and those containing bile (Festal, Ferestal). There is no need to abuse medications, because the body can get used to such artificial help. Drugs from the second group provide a good therapeutic effect, but their use is contraindicated in case of cholelithiasis and exacerbation of gastritis.
To enhance the therapeutic effect of medications, doctors recommend additionally taking antacids. They help reduce stomach acidity, thereby increasing the beneficial effect of medications.
Reactive pancreatitis in a child cannot be cured without the use of medications. However, to relieve symptoms, you can resort to the help of recipes from traditional healers. Before starting a course of therapy, you should consult your doctor.
One of the popular products in the treatment of pancreatitis is royal jelly. It can only be used if the child is not allergic to honey. The duration of the course of therapy is 2-3 months.
Then you need to take a short break for a few days. It is recommended to take royal jelly one teaspoon three times a day. It is better to slowly dissolve the sweet treat rather than swallow it whole.
You can also make homemade kvass from celandine. To prepare it you will need 3 liters of whey. If you cannot find it, you can replace it with plain water. The liquid must be poured into a vessel, add a teaspoon of sour cream and sugar.
Pour half a glass of celandine herb into a gauze bag and place it in a jar of water or whey. You need to stir the kvass daily for two weeks. If you strictly follow the instructions provided, on the 10th day the drink should begin to foam. Take kvass for a week, a tablespoon three times a day.
Pediatric pancreatitis requires a serious approach to treatment
Carrying out therapeutic actions in relation to children with manifestations of acute inflammation of the pancreas, or exacerbation of chronic inflammation, is carried out in an inpatient setting of a medical institution.
In this case, first of all, strict bed rest is established. Two treatment methods are used, which depend on the severity of the disease:
- conservative;
- surgical.
We suggest you read: Glycated hemoglobin test: how to take it
The meaning of the conservative method of therapy is to fulfill the following conditions:
- guaranteeing functional peace of the diseased organ;
- protecting the gastrointestinal tract from mechanical and chemical effects;
- finding and eliminating the sources of the disease;
- relief from painful symptoms.
During the course of treatment, food rest is prescribed for a period of 1 to 3 days, depending on the well-being of the sick baby.
During this period of time, frequent small sips of warm alkaline natural mineral water are allowed, after releasing gases from it. The most common are: “Borjomi”, “Nagutskaya”, “Essentuki”.
In addition, treatment is used with antispasmodic and analgesic medications:
- No-shpa;
- Voltaren;
- Papaverine;
- Mebeverine;
- Baralgin;
- Tramal;
- Pentalgin;
- Platyfillin;
- Analgin.
In cases of too strong pain in young patients, special narcotic analgesics are prescribed, such as Promedol, Omnopon, Tramadol.
The following must be used using intravenous drip:
- saline;
- glucose;
- blood plasma;
- Ringer's solution;
- trisol;
- protease blockers (“Aprokal”, “Kontrikal”, “Trasilol”, “Kontriven”, “Gordox”).
These medications are provided as a source of energy for a sick child, as well as to relieve intoxication in the body.
The following medications are prescribed as parenteral administration:
- Octreotide, Proxium are medications designed to reduce the formation of pancreatic enzymes.
- Pentoxifylline, Vazonit, Persantine - with an antianginal effect, to improve the quality of microcirculation and blood properties.
- Antibiotics - act as an antibacterial agent when purulent phenomena occur.
The method of surgical intervention is resorted to in certain cases. Among them:
- development of various kinds of complications;
- disease progression;
- lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment therapy.
Surgery for pancreatitis in children involves performing certain actions:
- resection of the affected part of the organ;
- necrectomy (removal of the dead area of the pancreas);
- drainage of suppuration.
Adults should remember that it is possible to avoid the development of pancreatitis in children or the exacerbation of an existing disease, but they should make every effort to achieve a positive effect.
First of all, this concerns strict adherence to the diet established by specialists and compliance with all medical prescriptions.
This form of pancreatitis is characterized by sharp, stabbing, and sometimes burning pain in the abdominal area, which can put a person into a state of shock. When acute inflammation develops, the patient experiences severe pain and needs urgent medical attention.
The only correct solution for such symptoms is to call an ambulance. An ambulance specialist will conduct an examination and provide first aid outside the hospital. The patient is then hospitalized to diagnose the disease.
In a hospital setting, acute forms of inflammation of the pancreas are diagnosed, differential diagnosis with other diseases whose symptoms may overlap with signs of pancreatitis. Correct diagnosis requires collecting all the necessary tests:
- Blood test (biochemical, clinical);
- Urinalysis (general and amylase);
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- ECG, MRI, CT;
- Retrograde cholecystopancreatography;
- Angiography of the pancreas.
The diagnostic procedure is determined individually, based on an analysis of the patient’s complaints, examination and palpation results. Next, the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed or refuted and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
With proper treatment, the exacerbation of pancreatitis goes away or the disease is cured completely. In both cases, the specialist prescribes special medications and a diet. Afterwards, the patient’s condition is monitored by a general practitioner, who will also refer the patient to a highly specialized doctor who treats concomitant diseases.
When the exacerbation passes, chronic inflammation of the pancreas is characterized by symptoms such as dyspeptic disorders and mild pain in the abdominal area. If such signs bother you, the patient can contact his local general practitioner, who will analyze the patient’s complaints and refer him to a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, oncologist or surgeon.
Which doctor treats pancreatitis? Based on statistics, the most common disease of the organ is its inflammation, called pancreatitis. Most often this is due to a lack or excessive production of enzymes that are aimed at processing food. Treatment can be carried out by several specialists at once.
Each doctor will have his own work plan to eliminate the consequences of pancreatitis:
- The therapist carries out treatment if pancreatitis has not acquired a chronic form and occurs in a mild stage.
- If the disease is acute and accompanied by attacks of pain, you will need to consult a surgeon, and sometimes a resuscitation surgeon. All acute attacks of pancreatitis are an indication for hospitalization of a person.
- If acute inflammation during pancreatitis can be relieved without surgery, through drug treatment, then a gastroenterologist gets down to business. In addition, the same doctor prescribes a special diet for the patient.
- It is also necessary to consult an endocrinologist, who must refer the patient for additional examination. This is due to the fact that against the background of pancreatitis, the production of insulin and glucagon may be disrupted. If this is true, then hormone replacement therapy is prescribed. If this treatment is neglected, diabetes mellitus will subsequently develop as a complication of pancreatitis.
What questions to ask your doctor
The main question, in addition to timely treatment, is “how to change lifestyle and nutrition in order to further prevent exacerbations of pancreatitis and its further progression?”
To cope with this task, you should ask your doctor:
- Is it possible to smoke and drink alcohol?
- What to do if pain suddenly appears?
- What foods, in what form, can be consumed after the exacerbation of the disease subsides?
- Should I stick to a diet for the rest of my life?
- How often should control examinations of the pancreas (ultrasound) and laboratory tests be done?
Who treats the pancreas
If there is a suspicion of pathology of this organ, you should contact a gastroenterologist. Considering that the pancreas also performs an endocrine function, observation by an endocrinologist is often required.
In the treatment of such diseases, a therapeutic diet plays an important role, so a consultation with a nutritionist may be additionally recommended.
Pancreatic diseases are easier to prevent than to cure. This can be done by making a choice in favor of a healthy diet and an active lifestyle, giving up smoking and drinking alcohol.