In the upper third of the abdomen there are vital organs, the failure of which can lead to serious systemic disorders and even cause death. That is why unpleasant sensations in this area require attention: ignoring symptoms such as burning, tingling, stinging, bloating in the abdomen above the ribs, temperature, chills and pain in the upper abdomen, concentrated at a certain point or not having a clear localization, can play a role in a person a cruel joke - to deprive him of the opportunity to lead a full life due to suddenly developing complications, or even lead him to the grave.
Particular vigilance should be exercised if there is pain in the upper abdomen near the heart or pain between the lungs and the left hypochondrium: in this way, serious illnesses and dangerous pathologies that require urgent medical intervention can make themselves felt. The victim himself is unlikely to be able to figure out why there is pain in the upper abdomen under the ribs, what are the causes of the pain in the upper abdomen on the right, or what hurts in the upper left abdomen, since for this it is necessary to have the appropriate education. In such a situation, it is recommended to seek help from specialists - a therapist and a gastroenterologist, who will carry out an initial diagnosis and select the most effective way to solve the problem, based on the results of instrumental examinations and laboratory tests.
Relevance of the issue
At least once in their life, almost every person, having felt discomfort and pain, thought about what was in the upper abdomen in the middle. Anatomically, a person is designed in such a way that the organs of the digestive system are located in this area, but pain can be explained by problems in the functioning of not only them, but also a number of other organs and tissues. In some cases, the cause of the pain is serious enough that even during the initial examination of the patient the doctor decides in favor of hospitalization. If this is not required, the doctor will prescribe a course of therapeutic procedures and recommend medications that are effective in a particular situation. If you do not consult a doctor on time, the condition may progress, worsening to such an extent that the consequences will be irreversible, even death.
It is impossible to say exactly and immediately what is bothering a person, focusing only on the sensation of pain in the upper abdomen in the middle. Diagnostics should include a comprehensive examination using special instruments and laboratory tests.
It is known that spasms and pain can be provoked by liver, gastric diseases, pathologies of the spleen and pancreas, and intestinal tract. Sometimes pain is caused by improper functioning and malfunction of the heart, pulmonary system, and spinal column. The cause may be the esophagus, gall bladder. Soreness can be direct, but there is also a variant of radiating pain syndrome. This is detected when the source of pain is not located where it is felt.
Aching pain in the upper abdomen, causes
Continuous or paroxysmal aching pain, localized in the upper third of the abdomen, can be caused by:
1 circulatory disorder;
2 damage to internal organs due to a fall from a height, violation of the technique of performing physical exercises, or a powerful blow to the stomach or back;
3 stretching or inflammation of the muscle fibers of the abdominal cavity;
4 malfunction or disease of the digestive system, in particular gastritis, ulcers, intestinal flu;
5 acute or chronic inflammation of pancreatic tissue;
6 pathology of the reproductive organs;
7 pinched nerves in the area of the spine, in the solar plexus;
8 pathologies of the central nervous system;
9 parasitic infestation;
10 heart problems.
What happens most often?
In most cases, sharp pain in the upper abdomen in the middle is explained by perforation of an ulcerative process localized in the stomach or intestinal tract. The pathology develops in stages, each step is characterized by its own characteristics of pain. First, the patient is diagnosed with gastritis, caused by a high level of gastric acidity. The disease is characterized by an immediate course, accompanied by the formation of foci of ulceration. The patient feels weak, bowel movements alternate with the development of diarrhea and constipation. Ulcerative perforation is indicated by profuse vomiting, loss of appetite, and severe heartburn. The patient loses weight. In many ways, the clinical picture is due to the body’s inability to absorb nutritional components supplied with foods.
The most common cause of perforation is poor nutrition. At risk are people who prefer hot, spicy, fatty foods, consume excessive amounts of salt, and eat dry food. The disease can be provoked by neglect of the diet, lack of a schedule, or consumption of portions of different sizes inconsistently, without a schedule.
Causes and consequences
In addition to poor nutrition, ulcer perforation can be caused by infectious diseases. Pathological microflora, resistant to conditions of high acidity, can begin to actively develop in the stomach and intestinal tract if the patient’s immunity weakens or the patient takes certain medications. As a rule, tests show colonies of Helicobacter pylori. This pathological microscopic form of life inhibits the body’s ability to work normally, to protect itself, and stimulates the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the gastric mucosa.
A decrease in the body's ability to protect itself from aggressive factors is associated with bad habits. Among people seeking help and treatment for stomach ulcers, adults with symptoms of such a disease (the first of which is sharp pain) are most likely to smoke and drink alcohol. Stressful life situations may play a role. In order to determine in time what caused it, how to deal with the consequences, and cure the disease, you should visit a therapist. The doctor will listen to the patient and give directions for tests and instrumental studies. Even if an ulcer is suspected, it is necessary to take additional measures to exclude other life-threatening pathologies with similar manifestations.
What medications can be prescribed?
Traditional therapy can be medication or surgery. Tablets or surgery are prescribed depending on the developing disease. If there is pain in the upper abdomen, surgery is prescribed in the following cases:
- With peritonitis;
- Acute pancreatitis;
- Ulcer or cholecystitis, which are accompanied by internal bleeding;
- When cancer pathology is detected.
In other cases, drug therapy is prescribed.
Analgesics to relieve pain. They are available in the form of injections, tablets or syrups.
| Name | Description | Contraindications | Cost, rub |
| Analgin | Relieves biliary and renal colic. | Any blood diseases. | From 50 |
| Spasmalgon | Relieves mild to moderate pain. | Inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis. | From 125 |
| Name | Description | Contraindications | Cost, rub |
| Paracetamol | Recommended for both adults and children. | Chronic alcoholism. | From 16 |
| Ibuprofen | Available in light pink tablets. | Stomach ulcer. | From 15 |
| Name | Description | Contraindications | Cost, rub |
| Linex | Available in capsules. | Hypersensitivity. | From 267 |
| Mezim | Improves food digestion. | Acute stage of pancreatitis. | From 80 |
| Name | Description | Contraindications | Cost, rub |
| Torekan | Used for nausea and vomiting. | Depression. | From 100 |
| Aminazine | Used for hallucinatory-paranoid states. | Spinal cord diseases. | From 100 |
| Name | Description | Contraindications | Cost, rub |
| Aspirin | Relieves inflammation and pain. | Duodenal ulcer. | From 10 |
| Diclofenac | Relieves infectious and inflammatory diseases. | Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract. | From 14 |
| Name | Description | Contraindications | Cost, rub |
| Lactusan | Available in the form of syrup and tablets. | Lactase deficiency. | From 150 |
| Maxilac | Available in capsule form. | Hypersensitivity. | From 413 |
| Name of the disease | Name of folk remedy | Cooking recommendations | How to take it correctly |
| Gastritis or inflammation of the stomach | Agave juice with natural honey | 0.5 cups of freshly squeezed juice is mixed with 100 grams of natural honey. Stir until the lumps disappear. | Take one teaspoon three times a day. The dose should be taken fifteen minutes before meals. The course of treatment is one month. |
| Stomach or duodenal ulcer | Potato decoction | Jacket potatoes are boiled until tender. The resulting unsalted water is filtered and cooled. | Take 0.5 cups on an empty stomach three times a day. |
| Cholelithiasis | Rowan infusion | 50 grams of berries are poured with boiling water. Infuse for four hours. | Take one glass 7 minutes before meals three times a day. |
| Pancreatitis | Sprouted oats | Pour boiling water over oatmeal and simmer over low heat for two minutes. Cool and strain before use. | Take 20-30 milliliters throughout the day. |
| Crohn's disease | Sea buckthorn oil | Make your own or purchase from a pharmacy. | Take 50 milliliters daily on an empty stomach two hours before meals. |
Cholecystitis
Sometimes spasms in the upper abdomen in the middle indicate inflammatory processes localized in the gallbladder. This is often observed when stones form in this organ. The appearance of such structures can be caused by excessive accumulation and deposition of calcium compounds, excess cholesterol or bilirubin. Cholecystitis can be suspected if the pain bothers you with attacks, the duration of which varies from a quarter of an hour to several hours. The disease is associated with considerable risks, and without adequate treatment it provokes complications: peritonitis, pancreatitis, empyema. There is a possibility of an inflammatory process in the bile duct, a violation of the patency of the channels.
Diseases that accompany epigastric pain
From the liver and gallbladder:
- hepatitis;
- cholecystitis.
From the intestines:
- colitis;
- flatulence - increased gas formation.
From the small intestine:
- inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- duodenal ulcer.
From the stomach:
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer;
- food poisoning;
From the pancreas:
- pancreatitis.
From the diaphragm side:
- hiatal hernia.
From the esophagus:
- esophagitis.
Emergency conditions that are accompanied by epigastric pain:
- hepatic colic;
- acute appendicitis;
- perforation of a stomach ulcer;
- peritonitis;
- gastralgic form of myocardial infarction;
- pancreatic necrosis.
The reason is the heart
If there is pain in the upper abdomen under the ribs in the middle, the symptom may indicate a heart attack. The term refers to a pathological process in which a section of the heart muscle ceases to receive the oxygen and nutritional components necessary for functioning, which leads to death. If the cause of abdominal pain is a heart attack, additional symptoms are possible that simplify the identification of the condition. For many, the pathology is accompanied by shortness of breath, disturbing even at rest, and chills. Sometimes the patient vomits, usually only once. A sharp change in body temperature is possible: it throws you into a fever, then everything is restored.
A heart attack often occurs against the background of overstrain, both physical and emotional, nervous. If examination of the patient suggests a heart attack, the victim must be hospitalized immediately. The pathological condition is fraught with severe complications, fatal consequences, even death.
Possible causes of pain
Diseases of the digestive system are manifested by pain of varying localization and severity, nausea and vomiting, changes in the frequency and consistency of stool, and lack of appetite. Therefore, to find out the cause of the pathology, you need to consult a doctor, who will determine why the stomach hurts at the top and how to eliminate this symptom. We will look at the most common diseases that cause pain in the upper abdomen.
Inflammation of stomach tissue
The stomach is located at the top of the abdomen, and it is this that often provokes the appearance of unpleasant sensations. If it is full, it stretches from the xiphoid process of the sternum to the navel, with most of it located to the left of the center of the abdomen. If several hours have passed after eating food, then the stomach takes its place in the epigastrium.
On the top right of the stomach is the liver, and on the left is the diaphragm, in front is the abdominal wall, and behind it is covered by the pancreas. The stomach also comes into contact with the intestines, greater omentum, and spleen.
Stomach pain can occur as a result of poor or irregular diet. If a person has not eaten, pain appears in the pit of the stomach; it is caused by the release of hydrochloric acid and the activity of muscle tissue. Discomfort may also occur after eating certain foods, which is due to the individual characteristics of the digestive system.
Often this is the reason why a child’s stomach hurts, since the digestive system has not yet matured.
Soreness may be felt after taking:
- vegetables whose fibers are difficult to digest (carrots, turnips, cabbage, radishes);
- alcohol, as it irritates the mucous membranes;
- kvass, beer, fizzy drinks, as this leads to the accumulation of gases;
- black bread with bran, stale foods, as they accelerate fermentation processes and contribute to gas formation;
- milk or gluten, sometimes they are not digested because there are no enzymes that break them down;
- excessively cold, hot food that irritates the mucous membranes.
Pain in the upper abdomen can also occur after unusual food, since enzymes cannot quickly break it down
Acute dagger pain appears as a result of inflammation of the stomach tissue or exacerbation of an ulcer. The sensations are strong and force a person to take a forced body position. During exacerbations, the stomach can hurt so much that a painful shock occurs. It is characterized by a rapid heartbeat, decreased blood pressure, cold sweat, and a tense stomach.
Pain occurs because when an ulcer perforates, hydrochloric acid and aggressive enzymes leave the organ and affect nearby tissues, leading to inflammation of the abdominal cavity. Ulcers are more likely to develop in men than women, which is associated with diet and chronic stress.
Not long ago, scientists discovered that inflammation of the gastric mucosa is caused by a bacterium that survives in an acidic environment. It releases toxins that destroy organ tissue. Not all people who become infected with the bacterium develop gastritis; more often they become asymptomatic carriers of the infection.
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease are stress, unhealthy diet, and pathologies that affect the acidity of the stomach.
An ulcer is a complication of gastritis, so if there is chronic inflammation of the stomach and acute pain occurs, then you should urgently consult a doctor. The ulcer is treated surgically, but if it is perforated, emergency surgery is required.
An ulcer can be complicated by penetration, that is, destruction of the wall and release of contents into an adjacent organ, for example, the small or large intestine. This causes dysfunction of another organ. Destruction of a vessel by hydrochloric acid can lead to bleeding from the wound. The pain does not become more intense, but vomiting or bloody stool may occur.
To treat gastritis, drug therapy is prescribed to help get rid of Helicobacter and normalize the acidity of gastric juice.
Sphincter dysfunction
In the upper part of the tract, between the esophagus and the stomach, there is a sphincter that prevents food from passing from the stomach to the esophagus. If the muscle is weakened, belching and heartburn occur. Pain appears behind the sternum at the bottom, spreads to the back or is noted in the upper part, slightly to the left of the center of the abdomen.
Why does my stomach hurt after eating?
Between the stomach and intestines is the pylorus. If a spasm occurs, the lumen narrows and the food bolus cannot leave the stomach.
A disorder may appear due to pathological processes in the stomach that provoke pain, nervous tension or disorder.
Spasm is a functional disorder, which means that morphological changes are not observed in the muscle itself. No-shpa will help relieve the symptom. With pyloric stenosis, disturbances appear in the muscle tissue, for example, as a result of the replacement of normal connective tissue, which happens if a nearby ulcer scars and affects the muscle.
Pain due to spasm or stenosis is more intense 90–120 minutes after a meal, it is stronger if solid food was consumed. The pain is characterized as moderate intensity and is felt not in the epigastric region, but slightly lower and to the right (at the level of the pylorus projection).
Heart pathology
Nagging pain in the upper abdomen can occur as a result of myocardial infarction (gastalgic attack). Due to necrosis of the heart muscle tissue, pain is felt in the upper abdominal cavity, since they are close to the diaphragm. Necrotization of heart tissue can also negatively affect the organs of the digestive system that are nearby. Therefore, nausea and occasional vomiting are likely.
With the development of myocardial infarction, in addition to abdominal pain, other signs appear, for example, shortness of breath at rest, rapid heartbeat, arrhythmic pulse, and a surge in pressure. Often the pathology is preceded by stress or ischemic disease.
If a heart attack is suspected, urgent hospitalization and intensive care are needed to restore normal blood circulation
Inflammation of the pancreas
An inflamed pancreas can cause a cutting pain in the right upper abdomen. The pain syndrome is very pronounced and can be either girdling in nature or have a clear localization. Discomfort appears during periods when the gland is overloaded, for example, after overeating, eating heavy, fatty or sweet foods, as well as after alcohol.
The pain occurs because enzymes cannot pass through the blocked ducts into the intestine. Trypsin has an aggressive effect on the gland tissue, provokes inflammation, and after some time, perforation of the parenchyma and the formation of cysts.
A painful sensation appears in the upper abdomen, under the right ribs, in the lower back, shoulder blades. Pancreatic pain is sometimes confused with a heart attack because it can radiate to the left side of the body (shoulder blade, arm, and jaw).
With pancreatitis, in addition to acute cramping pain, other signs of the disease appear. These are nausea, vomiting that does not provide relief, hyperthermia, and increased gas formation. If enzymes enter the bloodstream, the limbs, body and face turn blue, and red spots appear in the area of the gland, navel and buttocks.
If these symptoms occur, intensive care in the intensive care unit is required. If necessary, surgery is performed to restore the functioning of the ducts and remove dead tissue.
Pancreatitis
The heaviness in the upper abdomen in the middle can be explained by just such a process. The term refers to the formation of an inflammatory focus in the pancreas. The likelihood of pathology is higher if a person eats incorrectly, unevenly, and drinks alcohol frequently and heavily. Pancreatitis is a chronic disease prone to relapse. The acute phase is indicated by pain starting in the center of the abdomen, weakening if you take an antispasmodic. The condition worsens after meals, in the evening.
Exacerbation is accompanied by frequent spasmodic attacks. The patient feels sick and vomits (multiple acts). Without adequate medical care, there is a possibility of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, which provokes complications.
Myocardial infarction
During a heart attack, some area of the heart muscle is rejected. The cause of the disease is a failure in the blood flow, namely, in the nutrition of this muscle due to the development of thrombosis and atherosclerosis.
In a pre-infarction state, patients complain that the upper abdomen hurts. This is explained by the peculiarities of the location of the myocardial muscle and diaphragm.
Pain can be of varying intensity and nature. Most often there is acute pain under the ribs.
If such symptoms occur, it is necessary to urgently call a doctor, since a person’s life depends on timely medical care.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
These diseases include pathologies of the following organs:
Liver
- Hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis.
- Oncology.
The disease does not have any pronounced symptoms for a long time. With the degree of neglect of the disease, the upper abdomen hurts.
The pain begins on the right, and then radiates to the center in the abdomen and its upper part. Nausea is present.
Treatment: Therapeutic action in these cases depends on timely treatment.
If the disease is detected at an early stage, medical and surgical treatment is possible. Advanced pathology most often cannot be treated.
Stomach
- Stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach. It develops against the background of long-term inflammatory diseases, nervous experiences and other pathologies. Can cause pain in the upper abdomen, especially after eating.
- Ulcer. It is one of the most common diseases, due to which there is excessive production of gastric juice and irritation of the gastric mucosa. The disease is provoked by infections, vitamin deficiencies, bad habits, and stressful experiences. Causes severe pain throughout the stomach, including the upper part.
- Gastritis. It has the same nature as an ulcer and is in the same group of pathologies. They differ in that gastritis affects the upper layer of the gastric mucosa, and peptic ulcer disease already leaves deep lesions. With gastritis, the stomach hurts after eating heavy and unhealthy food, and there is bloating.
Treatment consists of stabilizing nutrition, eliminating the consumption of junk food, which contributes to digestive disorders and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
The second stage is to take anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics and saturate the microflora with beneficial bacteria.
Spleen
- Inflammation.
- Break.
- Cysts.
The organ is rarely exposed to disease. This mainly occurs due to serious inflammatory processes or injury. Pathologies of the spleen cause pain in the upper abdomen.
Possible nausea, both dull and sharp pain. Most often, unpleasant symptoms are localized on the left side of the abdominal cavity, but can spread under the ribs and in the middle.
Surgery, therapy and long-term observation in a hospital setting are used.
Pancreas
Pancreatitis. The disease occurs with the participation of an inflammatory process in the pancreas.
The organ is located on the left, but its features are such that with certain disorders the entire stomach hurts, especially after a fatty meal.
Abdominal pain is most often girdling, so many people mistake it for indigestion or spinal pathology.
A course of drug therapy is prescribed, which is based on taking anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics.
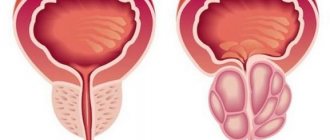
Gallbladder
Cholecystitis. It is characterized by the pathological formation of stones in the area of the entire organ. Develops against the background of reduced immunity and metabolic disorders.
The protective mucous layer of the gallbladder is very sensitive, so when the stones grow, a girdle pain appears in the upper part of the abdominal cavity under the ribs.
The disease requires surgical intervention. Without timely medical care, abdominal pain can lead to loss of consciousness and the development of a large number of dangerous complications.
In addition to the listed diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, discomfort in the stomach can be caused by food poisoning or intestinal infections.
In this case, there is an extensive effect of toxins produced by bacteria on the mucous membranes of the abdominal organs, thereby causing pain.
It is necessary to monitor the quality of food consumed. The main sign of poisoning is nausea and girdle pain in the abdomen.
Violation of the size of the lumens
One of the important elements of the gastric system is the part through which food moves from the gastric cavity to the intestinal tract. If the size of the lumen decreases sharply, obstruction occurs and normal motility is disrupted. The condition can be suspected if there is cramping pain in the upper middle part of the abdomen. The pain becomes worse after eating. The more a person eats, the more noticeable and lasting the pain will be. Most are diagnosed with belching and heartburn. The patient often feels sick, and the vomit has a pronounced sour taste.
Etiology
Unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the upper part of the stomach can be caused by the development or prolonged course of the following diseases:
- inflammation of the appendix, however, it is worth noting that such a symptom is not typical for such a pathological process;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach - often the main symptom is expressed approximately thirty minutes after eating food. Often pain torments a person at night or on an empty stomach;
- GERD – symptoms will significantly manifest themselves in a horizontal position of the body or when performing heavy physical activity;
- hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver - can sometimes be accompanied by pain in the stomach;
- oncological processes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cholelithiasis;
- hepatic colic;
- progression of cholecystitis;
- inflammation of the pancreas - the pain can be localized in the center or on the left side, but in some cases it is tingling and aching in nature;
- cystic or malignant formations in the spleen - in extremely rare cases, such pathologies are accompanied by a similar symptom;
- heart attack - a large number of patients who suffered a heart attack noted the presence of pain in the abdomen, namely at the top of the stomach;
- aortic aneurysm;
- tuberculosis;
- peritonitis;
- pathologies from the central nervous system - can manifest themselves in any part of the body, including the upper abdomen;
- pleurisy - in such cases, pain in the stomach will be felt when inhaling or coughing forcefully;
- osteochondrosis - with this disease, the process of compression of the roots of the spinal cord occurs, which entails a disruption of the innervation of organs such as the stomach, spleen and intestines;
- formation of a diaphragmatic hernia;
- chemical poisoning;
- liver rupture;
- heart failure;
- stomach dyspepsia;
- disruption of intestinal function;
- pathological influence of parasites or pathogenic bacteria.
. In addition to pathological conditions, the cause of this symptom can be:
- the period of bearing a child - the appearance of such a symptom is caused by an increase in the size of the uterus and the active intrauterine growth of the baby. This leads to compression and displacement of internal organs, in particular the stomach;
- heavy physical activity;
- intense physical activity.
Eating large amounts of food is another factor responsible for the appearance of such an unpleasant clinical manifestation. Overeating entails severe stretching of the stomach walls, which causes pain.
If a patient consults a doctor with complaints that the stomach hurts in the upper middle, then it is necessary to exclude the development of such pathologies:
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiac ischemia;
- angina attack and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The last reason for pain in the upper stomach, namely after eating, is an allergic reaction caused by food. The main allergens include:
- dairy products and milk;
- honey;
- raw fruits and berries.
Not the least important factor in the occurrence of the main symptom is excessive addiction to bad habits.
Pathologies of the spleen
If pain in the upper abdomen in the middle is associated with this cause, the sensations are localized on the right half of the body, in the hypochondrium. There are several diseases associated with the spleen. They all present with similar symptoms. Quite often, patients are diagnosed with splenomegaly and hypertrophic processes of transformation of the spleen. There is a possibility of suppuration and organ rupture. An infarction localized to the spleen is possible.
Which organ causes pain?
It is necessary to determine where the epicenter of pain is. If the symptom occurs in the upper left, then it is possible that this is a deterioration in the functioning of the stomach, pancreas, esophagus, and intestines. Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen is likely due to dysfunction of the liver, gallbladder, or colon.
The strength of the pain syndrome is also a diagnostic criterion. Acute unbearable pain overcomes with perforation of an ulcer, acute pancreatitis, biliary colic, peritonitis, rupture of the liver or spleen. With tissue necrosis, the symptom can become encircling and be felt throughout the entire abdomen.
With malignant tumors, the pain is also very strong, but it does not occur suddenly, but increases over time. It is also important whether the pain syndrome is dependent on food intake and body position. If “hunger pains” are characteristic, this indicates inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
If the symptom is more intense after eating, then an ulcer or other disorder is likely that makes it difficult to break down food. Pain in the abdomen at a certain position of the body and its disappearance after changing position indicates a pathology of the spine.
The upper right side of the abdomen may become painful during the initial stages of appendicitis.
During pregnancy, chronic diseases worsen, and the risk of stone formation and passage also increases. In addition, the uterus puts pressure on adjacent organs, and the child can “hit the neighbors,” so the occurrence of pain in the upper abdomen does not always indicate obstetric pathology.
Hernia
This condition is often observed against the background of a weakening of the muscular skeleton responsible for the normal functioning of the esophagus. The lumen of the diaphragm is disrupted, resulting in a displacement of the internal structures. This condition is indicated by pain that comes after eating. After some time, the sensations go away on their own. Belching and heartburn are considered additional symptoms of a hernia. Many people vomit severely, the rhythm and speed of the heartbeat is disrupted. Possible loss of appetite and sudden weight loss. As a rule, the pathology is accompanied by severe shortness of breath.
What else is possible?
Sometimes the pain is caused by a previous injury. This is possible, for example, in the event of an accident, a conflict that leads to a fight, in which a person is hit. Even a relatively weak physical impact can cause injury to an internal organ. Sometimes the reason is strong shaking. Due to this influence, the spleen and liver may rupture, there is a risk of rib fracture, internal hemorrhage may appear, and hematomas may form. As a rule, after an injury the painful sensations are dull.
However, most often pain indicates the need for treatment of a stomach ulcer. Symptoms in adults and children occur in most cases precisely because of an acute peptic ulcer, which requires immediate medical attention. Without adequate support with procedures and medications, perforation is possible with the penetration of gastric and intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity.
In some cases, pain indicates poisoning, poor nutrition, or porphyria. Soreness is possible with systemic overeating, hepatitis and vertebral disorders. There is a possibility of pleurisy and pneumonia. Sometimes abdominal pain is a sign of osteochondrosis.
Stitching pain - why does it sting in the upper abdomen?
Dagger lumbago in the upper or lower third of the abdomen, right or left side, occurring during movement, when lifting heavy objects, while riding in public or private transport, may be a consequence of:
1 recent stress;
2 parasitic infestations (in particular, helminthiasis);
3 violations of the technique of performing physical exercises, resulting in muscle rupture or damage to internal organs;
4 diseases of the digestive or reproductive organs of inflammatory or infectious origin;
5 appendicitis;
6 perforation of the walls of the stomach or intestines.
Check and clarify everything
Having become a victim of pain, you should figure out which doctor to contact. Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle can be examined by a gastroenterologist to determine the reason for its occurrence. Sometimes the therapist will refer you to a surgeon or cardiologist. In especially severe cases, the patient is admitted to intensive care. If the cause of pain is an infection, an infectious disease specialist will come to the rescue.
The doctor knows exactly what to do. Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle requires a preliminary examination of the condition, since many diseases manifest themselves as such symptoms. First of all, at the initial appointment, the doctor palpates the painful area and assesses what the patient’s skin looks like and what the general state of health is. The patient is given directions for tests of urine, feces, and blood. It is necessary to check biochemical parameters and the content of individual blood elements. To assess the condition of the heart, an electrocardiogram is taken, and an x-ray is taken to check the internal organs. Many are prescribed ultrasound and FGDS.
It is necessary to realize that pain is often provoked by dangerous factors that threaten a person’s health and life, so it is impossible to independently treat pain at home by taking antispasmodics. To avoid complications, you should come to your appointment as soon as possible. In some cases, the doctor will consider that gentle treatment will be sufficient; in others, emergency surgery may be prescribed.
Features of pain syndrome
If the pain in the upper abdomen in the middle is localized in the fourth space between the ribs, most likely the cause is gastric pathologies. Sharp sensations usually indicate the penetration of chemically aggressive substances into the digestive system. Poisoning exhibits a similar symptom. Heaviness and distension may be signs of decreased activity of the pancreas. Pyloric stenosis indicates similar phenomena. If the pain is dull and there is an aching in the stomach, the reason is probably different, because such sensations rarely accompany a disruption in the secretory ability of the organs.
Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle can be very strong, moderate in level, or quite weak. The latter option in most cases indicates gastritis. Many people do not go to the doctor, so the disease progresses without treatment and the condition worsens. In some cases, mild pain indicates an ulcer. Sometimes cancer processes initially manifest themselves as just such a symptom. The longer the discomfort persists, the more important it is to get an appointment as soon as possible.
Possibilities and cases
If the pain in the upper abdomen in the middle is severe, we can confidently speak of a severe peptic ulcer. There is a possibility that foci of ulceration are simultaneously observed in both the stomach and intestinal tract.
A state of increased danger includes pain described as dagger-like. The sensation in most cases indicates a perforation of the ulcer, in which the contents of the gastric system end up in the abdominal cavity. If you suspect such a condition, you must urgently call an ambulance.
When finding out what caused the pain, the doctor will definitely ask the patient about the connection between the sensation and food intake. For example, if discomfort comes when a person has not eaten for a long time and goes away after a meal, a high level of gastric acidity can be diagnosed. If you experience discomfort after eating, the cause is likely to be gastritis, which has become chronic. With a stomach ulcer, pain appears a couple of hours after a meal, with an intestinal ulcer - if the pauses between meals are long. In addition, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease is observed with physical overexertion, strong anxiety, and stress.
Features in women
If it hurts in the upper abdomen, this may be a consequence of inflammatory processes in the internal reproductive organs - the uterus, tubes, ovaries. Unpleasant manifestations are felt in the upper or lower abdomen in the iliac regions. May be accompanied by intoxication syndrome in the form of:
- Chills;
- Weaknesses;
- Loss of appetite;
- Dizziness;
- Fevers.
The localization of pain occurs above the womb, upper and lower abdomen.
Purulent discharge with blood clots that have an unpleasant odor is formed. Unpleasant sensations can radiate to the perineum, sacrum and lower back. Pathologies include:
- Intra-abdominal bleeding;
- Ovarian rupture;
- Ectopic or ectopic pregnancy;
- The stomach hurts during critical days, after blows, falls, complications after a tubal abortion.
The presence of painful spasms below the ribcage and in the center of the esophagus can occur for the following reasons:
- The muscles that grip the passage into the cardia - the stomach - relax abnormally; this occurs when the nerves are damaged. This happens, for example, during surgery.
- Abuse of dry foods.
Increased dryness of the mucous membrane in the esophagus or the growth of a fibrous structure with prolonged gastroreflux disease (when the movement of stomach acid back into the esophagus), causing a hard passage of food. This can, in rare exceptions, cause systematic sclerosis.
A gastric hernia affecting the esophageal opening in the diaphragm and thereby causing an abnormally closed passage to the stomach. Signs of pathology are pain below the chest and in the larynx, which radiate to the central or upper part of the stomach. The main symptom is the presence of an unpleasant acidic taste in the mouth.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ycZGO-BiJrI
Inflammation of the inner layer of the gastric mucosa is gastritis. The following are considered signs of gastritis: individually or collectively:
- Pain in the chest, center or upper abdomen, worse after eating.
- Dark chair.
- Nausea, sometimes followed by vomiting.
- Abdominal cramps, accompanied by wave-like spasms under the stomach.
- Fast saturation.
- Heartburn (burning in the larynx or chest).
- Temperature increase.
- The disease gastroparesis is a slow process of emptying the stomach due to the fact that the muscles are unable to relax enough due to nerve damage. The reasons that provoke the occurrence of gastroparesis: atherosclerosis, hormonal imbalances, psychological troubles, the formation of fibrous tissue on healed ulcers and after gastric surgery. Symptoms of this disease include a convulsive state after or during food intake, rapid satiety, heartburn, bloating, and severe belching.
- Gastric ulcers are open sores inside the stomach. Characterized by an aching burning pain after or during eating in the upper abdomen.
- Inflammatory processes of the small intestine (duodenum) are characterized by dull pain, mainly at night and in the intervals between meals; pain is felt under the ribs and in the center of the abdominal cavity. With inflammation, blood may be detected in the stool and it may darken.
- Cancerous formations provoke not only unpleasant pain in the center and upper abdomen, but also nausea, loss of appetite, excessive weight loss, and extremely dark stools.
- Pancreatitis. The acute form of the disease is an inflammatory process in the pancreas due to cholelithiasis or long-term alcoholism. The pain is predominantly felt on the left in the upper part and in the center of the abdomen, sometimes encircling (it hurts both in front and behind). Appetite worsens, nausea appears, white, thin stools appear, and the patient loses weight sharply.
- An injury that results in a tear in the abdominal muscle due to a blow or exercise can cause severe abdominal pain. The hematoma that appears later can accumulate in the muscles, causing a noticeable bulge that is blue in color and soft to the touch.
- The small intestine, or rather, a small fragment of it, protrudes into the muscles of the abdominal cavity through the clefts. Symptoms are pain and a noticeable bulge that is soft to the touch.
- Vertebral fractures, spinal arthritis, and other disorders in the lumbar spine or chest manifest themselves, causing pain in the middle of the abdomen and above. Exacerbation of pain usually occurs when moving.
- Aneurysm (protrusion of the walls of the aorta) and dissected layers inside the aorta are characteristic of predominantly elderly people, especially if atherosclerosis is present. The pain is dull, continuous, intensifies during and after eating.
- The onset of a heart attack also provokes pain in the upper or middle abdomen. High cholesterol levels and smoking are recognized as well-known factors for the occurrence of a heart attack.
- If the pain is localized predominantly on the right side of the upper abdomen, it is most likely inflamed appendicitis. May cause fever and nausea.
- Female causes of pain in the abdominal region are often a possible miscarriage, rupture of a cyst in the ovary, or ectopic development of the fetus. This is characterized by cutting sensations and nagging pain.
- Completed course of antibiotic treatment.
- Heatstroke.
- Typhoid fever is an acute intestinal infection. A distinctive feature is roseola rashes, accompanied by fever, general intoxication of the body, and specific lesions of the lymphatic system in the small intestine.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Heart failure is a decompensated disorder of myocardial function. At first, this disease does not reveal itself, but then it manifests itself in shortness of breath, pain in the left upper abdomen, increased fatigue, and swelling.
- Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs. Symptoms are similar to the flu or a cold, but are accompanied by severe chest pain, sometimes pain under the chest, radiating to the upper abdomen, cough with reddish or greenish thick phlegm, increased sweating, fever, rapid breathing and rapid heartbeat.
- Hepatic or renal colic. Characterized by sharp, severe pain (stronger than labor pains), which is often accompanied by hemorrhage.
- Herpes zoster, or shingles, is a viral infection with characteristic rashes. Older people are most susceptible to infection, mainly in autumn or winter.
- Lead poisoning.
- Animal bites (snakes, insects).
- Cholecystitis.
- Hepatitis.
- Infarction, rupture or abscess of the spleen.
- Chills;
- Weaknesses;
- Loss of appetite;
- Dizziness;
- Fever;
- Intra-abdominal bleeding;
- Ovarian rupture;
- Ectopic or ectopic pregnancy;
The stomach hurts during critical days, after blows, falls, complications after a tubal abortion.
How serious is it?
Doctors say that pain in the upper abdomen in the middle has occurred at least once in the life of any person. If the sensations are strong and sharp, the duration of the attack reaches half an hour or continues even longer, it is necessary to call a first aid team. If possible and the patient’s condition allows this, you can take the patient to the nearest clinic. There is a possibility that the person needs surgery.
If pain bothers you, you should not massage the pathological area. If there is internal bleeding, the condition can worsen significantly. For the same reason, you should not apply a heating pad to a sore stomach. However, sometimes the pain factor is excessive food consumption. There are foods that are difficult for the human body to digest. If there were a lot of them in the food or the food was saturated with fats, the likelihood of stomach pain is higher. A similar symptom can result from eating foods containing gluten or lactose if the human body does not tolerate these substances. Sometimes the pain is caused by eating food that causes increased gas formation. The symptom is relatively mild and disappears after an hour or two.
Oncology as a cause
Sometimes aching pain in the upper middle of the abdomen signals cancer. Among other reasons, this particular one is relatively rare, but almost always the patient is referred for specialized tests in order to exclude such a development of events. Cancer is one of the most terrible diagnoses. If there is a suspicion of cancer, it is necessary to undergo all tests as quickly as possible to make the most accurate diagnosis and begin treatment, following the program developed by the doctor. Malignant formations can metastasize to unpredictable, distant parts of the body. Without proper and timely treatment, the likelihood of death increases significantly.
Many rightly believe that cancer is the worst explanation for pain in the stomach. Recently, malignant neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract have become more common; some classify this system as one of the three most common variants of localization of atypical cells. Around the world, the number of cancer victims is growing every year. Esophageal cancer, among other malignant pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, is relatively rare. The risks are higher if a person eats incorrectly. The more red, fried, fatty meat is consumed, the greater the danger. The danger of a malignant process and the frequency and volume of alcohol consumed by a person correlate.
It has been suggested that the likelihood of developing esophageal cancer may be associated with carcinogenic food additives, but at present there are no reliable studies on this issue. Coloring, aromatic substances, and preservatives are found in almost any food that is on store shelves. Doctors recommend consuming as little food processed in this way as possible. If the body works normally, such substances are soon eliminated, but if the functioning of internal organs fails, accumulation is possible, associated with the risks of malignant degeneration of cells.
When to go to the doctor?
In many ways, the manifestations of cancer are determined by the localization of the process. If atypical structures grow in the esophagus, in addition to pain in the upper center of the abdomen, the patient notices problems with swallowing. There may be a feeling of weakness in this part of the body. Sometimes there are problems with stool. If esophagitis is diagnosed, it is necessary to especially carefully evaluate any painful manifestations and other questionable symptoms. Conditions such as stomach and intestinal polyps and peptic ulcers are potential precursors of cancer.
As can be learned from medical statistics, many patients do not pay attention to the primary manifestations of the disease, and come to the doctor when the pathology has already progressed to the third, sometimes fourth stage. One of the problems of the cancer process in the esophagus is the high rate of progression of the pathology. Doctors recommend that at the first signs of discomfort or stable unpleasant symptoms, you undergo a comprehensive examination, which will help eliminate any suspicions or confirm the disease. This means it will be possible to start treatment in a timely manner.