Causes of pain in the diaphragm
Pain in the diaphragm can have several possible causes. The most common of them are listed below.
Injuries
The diaphragm is a muscular septum located between the chest and abdominal cavity.
Rough mechanical force or surgical procedures can cause damage to the diaphragm. The pain resulting from such injuries may be constant or intermittent.
Some types of injuries can tear the diaphragm. This is a serious condition that doctors usually diagnose using a CT scan or thoracoscopy.
Symptoms of a torn diaphragm include the following:
- abdominal pain;
- difficulty breathing;
- shoulder or chest pain;
- cough;
- increased heart rate;
- nausea;
- vomit.
Because the body needs to breathe constantly, the diaphragm is always in motion, which is why its tears cannot heal on their own. Therefore, surgery is sometimes performed to restore the muscle in such situations.
Musculoskeletal problems
Injury, sudden turns of the body, or intense coughing sometimes cause strain in the muscles of the ribs, which can cause a person to develop pain in the diaphragm. Broken ribs also cause pain in this part of the body.
Available treatment options in such cases include the following:
- taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen;
- applying ice for the first 72 hours after injury;
- applying heat after the first 72 hours after injury;
- breathing exercises;
- physiotherapy.
Damaged or broken ribs usually heal on their own within six weeks, but unpleasant symptoms can be eased by the following therapeutic strategies:
- proper rest;
- refusal of intense activity;
- taking over-the-counter pain medications;
- performing pain-relieving injections in the area of the nerves located in the affected area;
- performing breathing exercises.
Doctors used to advise people to wear compression bandages on their ribs, but they can interfere with deep breathing and increase the risk of pneumonia. Therefore, doctors now do not recommend using this therapeutic approach.
Intense physical activity
Heavy breathing during intense physical activity can cause the diaphragm to spasm and cause sharp or squeezing pain. This pain is often too severe for a person to breathe unimpeded. Many people feel that breathing becomes insufficient and uncomfortable. The pain usually gets worse with continued activity.
If diaphragm spasms occur during sports, then any activity should be stopped. The development of this type of pain can usually be prevented by warming up before exercise.
Gallbladder diseases
Gallbladder disease is an umbrella term for several medical conditions. Gallbladder pain can resemble pain in the diaphragm, so sometimes people confuse the source of their discomfort.
Other symptoms of gallbladder disease include the following:
- changes in bladder or bowel movements;
- fever or chills;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice).
In most cases, gallbladder diseases occur as a result of inflammation or irritation of the walls of the organ (cholecystitis). Other gallbladder problems include stones, blocked bile ducts, and cancer.
Treatment for gallbladder disease depends on the specific condition. Treatment options include medications to control pain, anti-inflammatory medications, and surgery to remove the gallbladder.
To prevent gallbladder disease, a person can make the following changes to their lifestyle:
- slowly and steadily reduce body weight (if you are overweight or obese);
- manage diabetes or other medical conditions;
- practice physical activity regularly;
- stop smoking;
- limit alcohol consumption.
Hiatal hernia
Small hiatal hernias often cause no symptoms.
A hiatal hernia is a condition in which the upper part of the stomach is pushed out through a hole at the bottom of the diaphragm. The esophagus passes through this opening, through which food passes from the mouth to the stomach.
Small hiatal hernias usually do not cause serious problems. Many people don't even know they have them and don't experience any symptoms.
However, large hernias can make themselves felt with the following signs:
- acid reflux;
- black or bloody stools;
- pain in the chest and stomach;
- difficulty swallowing;
- heartburn;
- regurgitation of food;
- shortness of breath;
- vomiting.
The most common method of managing a hiatal hernia is with medications. In addition, you can make the following lifestyle changes:
- eat several small portions of food per day instead of three or two large ones;
- avoid fatty or sour foods and any other foods that cause heartburn;
- have dinner no later than three hours before bedtime;
- stop smoking;
- maintain a healthy weight;
- When sleeping, raise your head at least 15 centimeters above the surface of the bed to prevent acid reflux.
If the hiatal hernia is very large, surgery may be required to relieve symptoms.
Pregnancy
As pregnancy progresses, the uterus expands and begins to push the diaphragm upward. This interaction between the two structures compresses the lungs and makes breathing difficult. In addition, it can lead to pain, discomfort and shortness of breath.
These symptoms usually do not cause any serious problems and disappear after childbirth.
However, a woman should consult a doctor if she observes the following:
- intense or constant pain;
- persistent cough;
- severe breathing difficulties.
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is inflammation of the pleura, that is, the layer of tissue located on the inside of the chest cavity around the lungs.
Pleurisy causes sharp pain in the chest along with shortness of breath. In some cases, this condition leads to cough and fever, and pain sometimes reaches the shoulders and back.
Treatment of pleurisy involves taking pharmacological products to control pain and eliminate the cause of the underlying problem. This may include infections, autoimmune disorders, and sickle cell disease.
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bronchial tubes, through which air enters the lungs and returns back. Bronchitis can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
Bronchitis causes pain that people often mistake for diaphragm pain. Other symptoms of bronchitis include the following:
- chills;
- cough;
- fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- thick colored mucus.
Acute bronchitis usually develops from a cold and goes away on its own in about a week. Cough suppressants and pain relievers help relieve symptoms until the infection goes away.
Chronic bronchitis requires medical attention. Treatment options for this condition usually include inhalers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and pulmonary rehabilitation to help the person breathe easier.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia can cause difficulty breathing and pain in the diaphragm
Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation of the alveoli in the lungs. It can be of bacterial, viral or fungal origin. Symptoms of pneumonia include the following:
- difficulty breathing;
- chest pain;
- chills;
- cough with phlegm or pus;
- fever.
In some cases, pneumonia can be life-threatening, especially if the disease occurs in young children, older adults, or those with other health problems.
Treatment for pneumonia is aimed at eliminating the infection and preventing complications. It involves taking antibiotics, cough suppressants and painkillers. Sometimes patients with pneumonia require hospitalization.
Other possible causes of pain in the diaphragm
Less common causes of pain in the diaphragm include the following:
- lupus;
- pancreatitis;
- nerve damage.
Pain associated with the diaphragm can also be caused by heart surgery or radiation therapy.
Why does my stomach feel heavy after eating?
Why might there be a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and belching, why run to consult a doctor?
Very often, even completely healthy people can experience a feeling of squeezing in the abdomen, when something is pressing on the stomach. The causes of such abdominal pain are very often associated with poor-quality food consumed and stress experienced.
But in some cases, heaviness in the stomach after eating and even pressing pain in the stomach may appear due to the development of certain types of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
If there is a tug in the stomach and pressure after eating, then such symptoms may appear due to lazy stomach syndrome. A problem called lazy stomach syndrome occurs in humans due to a lack of certain pancreatic enzymes.
This condition affects the quality of digestion and in some cases can lead to abdominal pain. It should be noted that the cause of lazy stomach syndrome may be a consequence of long-term use of certain types of medications.
Often, abdominal pain, a feeling of heaviness, pressing discomfort in the abdomen are associated with a late dinner. It is recommended to have dinner and eat before bed, at least three to four hours before bedtime.
It is highly recommended not to overload the stomach with heavy food before bed, or to eat foods that are difficult to digest, which can delay the process of digestion of food by the stomach for many hours.
Often, heaviness in the stomach after eating can appear in those people who like to wash down their food. With frequent sealing during meals or immediately after eating food, the secreted gastric juice is washed away, due to the lack of which the process of digesting food is delayed and leads to the appearance of painful symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, and even abdominal pain.
One of the common symptoms, which occurs almost as often as a headache, is pain in the lower left or right side of the abdomen.
Such a rather unpleasant sensation may be evidence of pathology of the pelvic organs or gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, pain in the lower abdomen in women can be one of the clinical signs of gynecological pathology.
Before you understand what to do if the lower abdomen, its left or right area hurts, you need to understand the possible causes.
Types of pain and factors that provoke it
Pain in the lower abdomen, on the left or right side, may be evidence of an inflammatory, infectious process or many other pathologies.
In order to understand why it hurts, you need to determine the specific area and form of pain. Pain syndrome in girls can be divided into several main types:
- Dull or sharp;
- Drawing, aching;
- Paroxysmal, constant;
- Intense, weak.
Many girls also report throbbing pain. It should also be noted that modern experts identify the factors that provoke the development of pain:
- functional group of factors - painful menstrual periods, complicated ovulation;
- organic variety - various kinds of inflammatory pathologies, formations in the pelvic organs, diseases of the genitourinary and gastrointestinal systems.
Please note that if the lower abdomen hurts very much or the discomfort does not subside for a long period of time, then you need to consult a specialist as soon as possible.
In some cases, pain in the left, lower or right abdomen is a warning sign of serious problems that can lead not only to complications, but also to death.
Possible reasons
As mentioned earlier, abdominal pain is an extremely common symptom that can indicate many diseases.
In order to understand exactly what pathological process is occurring, it is necessary to know additional signs of a particular disease.
The stomach may hurt due to:
- gynecological disorders;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- use of contraceptive methods.
In each group of diseases, modern experts identify the most common ones.
Gynecology
One of the most common reasons why a woman has pain in the lower abdomen is pathological processes in the reproductive system.
These diseases include: endometritis, endometriosis, cystic neoplasms, fibroids, ectopic pregnancy.
In addition, pain on the left or lower side can appear during menstruation and in some cases, if the discomfort is moderate enough, then this phenomenon is the limit of the norm.
It should be noted that acute, intense and prolonged pain before or during menstruation may be signs of the development of diseases. You need to contact a gynecologist.
Hiccups as a symptom of diaphragm spasm
A fairly common and harmless phenomenon in the human body is hiccups. It is a spasm of the diaphragm and can occur as a result of prolonged laughter, hypothermia, or fast eating. In medicine, there is another definition of hiccups - a short reflex breath with sound, which occurs as a result of narrowing of the glottis during diaphragmatic spasm. Basically, a person stops hiccupping within a few minutes or immediately after taking measures to get rid of hiccups.
However, if hiccups continue for a long time, then you should worry, since in this case it may indicate the presence of a serious illness in the body. The patient needs to see a doctor to find out the cause of prolonged hiccups. After the diagnosis, the specialist will make a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
What causes stomach pain in women?
Unpleasant sensations often occur under the left rib, and can sometimes radiate to the lower back, lower abdomen and heart area. In addition, the pain varies in the nature of its course - intense, cutting, pulling, dagger-like, cramping, stabbing. Depending on the cause of painful spasms, you may also notice the presence of other symptoms. The most common are:
- nausea with vomiting;
- belching of gastric juice;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- bowel dysfunction - diarrhea or constipation;
- weakness;
- heat;
- bloating;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Based on the intensity of pain attacks, doctors can judge the presence of a particular disease. For example, chronic gastritis is always accompanied by aching pain and heaviness that occurs after eating. Burning, unbearable pain indicates increased acidity and activity of hydrochloric acid of the mucous membranes.
Sharp changes in hormonal levels, a general decrease in immunity - all this in women during pregnancy carries the risk of exacerbation of pre-existing chronic diseases. Among the most common causes it is worth highlighting: gastritis, ulcers, colitis. In addition, during this period, a woman’s sensitivity to allergens and foods increases. Even relatively fresh food can cause poisoning, nausea and vomiting.
Causes of spasm
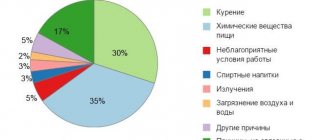
Most people are concerned with the question, why does diaphragm spasm occur? There are many reasons for this, the main ones being:
- Binge eating. After a heavy meal, the stomach increases in volume and puts pressure on the diaphragm, causing hiccups.
- Eating hot or, conversely, chilled food or peppery dishes provokes irritation of the mucous layer of the esophagus. The irritation is transmitted to a nerve that is nearby and through it enters the brain, where a response to the stimulus is formed in the form of a spasm of the esophagus.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol-containing drinks have a negative effect on the esophageal mucosa, burning it. As a result, intoxication occurs, which disrupts the functioning of nerves, including the diaphragmatic one. For this reason, people often hiccup after drinking a lot of alcohol.
- Hypothermia often causes shivering throughout the body, which is defined as a convulsive contraction of muscles aimed at retaining heat. Hiccups are a tremor of the diaphragm.
- Drug poisoning. Diaphragmatic spasms in this case are a side effect of medications. The components in the medicine disrupt the functioning of the nervous system, causing involuntary inhalations with sound.
- Stressful situations and fear. These phenomena put a strain on the central nervous system, which is responsible for contracting the diaphragm. As a result, excitation occurs and is transmitted to the muscles.
- Swallowing air. Eating or drinking quickly causes air to be swallowed, which puts pressure on the abdomen.
- Laughter. Strong laughter is accompanied by deep breaths along with sharp exhalations, which leads to a malfunction of the respiratory center.
- Certain foods. Various foods that contain large amounts of air, such as yeast bread, can provoke hiccups.
- Narrowing or sore throat. These manifestations can occur as a result of exposure of the throat to irritants such as cigarette smoke or seasonal allergies, a cold, or hairs getting into the throat.
Various diseases can cause diaphragm spasm:
- stroke;
- inflammation of the brain;
- malignant formations;
- myocardial infarction;
- concussion and severe bruises;
- cholecystitis;
- pneumonia;
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- bronchitis;
- diabetes;
- heartburn.
Spasm treatment
Therapy for hiccups caused by diaphragmatic spasm is based on taking medications and performing special actions that are aimed at calming the diaphragm. You can do the following:
- Drink a glass of water in small sips, taking the “swallow” pose, or drink from the opposite side, while tilting your head.
- You can deal with hiccups by using something that is difficult to swallow. For example, eat a spoonful of honey or a handful of sugar, peanut butter, wasabi or jam.
- The most common way to combat hiccups is to hold your breath. It is enough to simply inhale air and not exhale it for several seconds. This will increase carbon dioxide levels and calm the diaphragm from any spasms that may occur.
- You can get rid of hiccups by applying pressure to the eyeballs, by plugging your index fingers into your ears and making small rotational movements with them.
- Most people claim that they stop hiccupping if they hold their breath three times.
- If you hold your breath as you exhale before the spasm begins, and then breathe shallowly and hold your breath again, then after two or three times after such movements there will be no trace of hiccups.
- You can calm the diaphragm from spasms by drinking a glass of water, lying on your side, or lying on your back with your arms raised up. It is necessary to take your left hand at the wrist and make up and down movements, providing a slight vibration to the chest. After a short period of time, the hiccups will pass.
- If the hiccups do not go away for a long time, you can put a mustard plaster on the neck or apply a cold compress; a rubber heating pad with cold liquid applied to the diaphragm will remove the spasm.
- In some cases, switching attention may help. You should focus on some object or situation and distract your thoughts from the hiccups.
- You can take 200 ml of water and add a small spoon of apple cider vinegar to it. Drink the liquid without delay in large sips. Water with lemon juice also has a good effect. Squeeze a few drops of lemon into water and drink quickly.
- If a person hiccups due to hypothermia, the spasm will go away if he is allowed to warm up.
- Hiccups can go away if you lie on the bed and hang your head so that it is below the level of the diaphragm. To do this, some stand on their hands.
- By soaking the tip of your tongue in salt and pressing it to the upper palate, you can get rid of annoying hiccups. Just to do this, you should sit more comfortably and relax.
- You can stop hiccups by sniffing pepper, which will cause irritation of the nasal mucosa and sneezing.
- Not the most pleasant method is to provoke vomiting. To do this, press on the root of the tongue so that the urge to vomit begins.
Medications
If most simple methods of dealing with hiccups do not remove the spasm of the diaphragm, then you should resort to medications. In this case, the patient should consult a doctor and undergo treatment according to his recommendations. The doctor may prescribe anticonvulsants and sedatives, which will stop the cycle of spasms and return the diaphragm to its previous function. Medicines used to combat hiccups are as follows:
- "Finlepsin";
- "Cerucal";
- "Corvalol";
- "Scopolamine";
- "Difenin";
- "Motilium";
- "Pipolfen."
The diaphragm performs important functions in the human body; it is a fairly wide plate shaped like a dome. In the center there is predominantly tendon tissue, and at the edges there is direct muscle tissue. The diaphragm divides the body into the abdominal and thoracic cavities. Important blood and large lymphatic vessels, as well as the esophagus and nerves pass through it. The vessels literally permeate it.
It is worth noting that most vessels pass through the diaphragm exclusively in the muscular section, except for the inferior vena cava, which seems to penetrate the diaphragm in its tendon section. Let us add that the inferior vena cava has fairly thin walls. If it intersected with the muscle tissue of the diaphragm, it would be constantly pinched during contraction. When the pressure in the chest begins to decrease, blood flows up the heart. Although the main function of the diaphragm is to provide breathing.
The diaphragm constantly relaxes and contracts; during contraction, it turns from a dome to a flat surface. The chest cavity seems to “inflate”, and the pressure in the lungs decreases significantly. Due to the difference in pressure, air begins to enter the lungs. Air fills microscopic bubbles, which are called alveoli. When the alveoli become full, the nerve impulses that control the contraction of the diaphragm begin to slow down. After which it again takes the shape of a dome, exhalation occurs. If we compare the diaphragm with car parts, we can say that it acts as a “piston,” constantly pumping air into the lungs.
Diaphragm spasm: causes
There are many reasons for the reflex contraction of the diaphragm. If hiccups continue for a long time or occur several times a day, then there may be some serious illness. Hypothermia can lead to spasms. Often infants suffer from this, since their heat exchange processes have not yet been fully established. Therefore, parents periodically panic when the child has a spasm. For this reason, your child should be dressed according to the weather. The causes of diaphragm spasm are always different.
Gastric distension is another option when stomach spasms occur. Most people suffer from this after overeating. Moreover, spasm can occur both in adults who do not know how to stop, and in children whose parents are trying to feed the child as satisfyingly as possible. It is worth noting that pediatricians advise feeding children more often, but in smaller portions, this way you can avoid the icon. Also, some young mothers have a lot of milk during lactation. A baby who is trying to swallow a lot of liquid may experience spasms.
Additional possible reasons:
- fright, shock;
- being in an uncomfortable position;
- intoxication.
In some cases, psychogenic factors may influence. The fact is that involuntary contraction of the diaphragm often occurs during critical nervous tension. Mostly sensitive people, as well as pregnant women, suffer. Some doctors explain hiccups in children by saying that they are often influenced by the modern education system, which overloads the psyche.
But remember that if hiccups occur frequently in you or your child, then it may be caused by some kind of disease:
- meningitis;
- pneumonia;
- encephalitis;
- damaged vagus nerve;
- impaired brain activity;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- osteochondrosis;
- scoliosis;
- pre-stroke condition.
Diaphragm spasm: treatment
There are a large number of ways to cope with diaphragm spasm. The effectiveness of some is difficult to explain, but they really work. Some people like to use traditional methods. And if the spasm persists, the doctor may prescribe special medications.
Options to get rid of the problem:
- Hiccups can be suppressed by reflex. To do this, you need to put your finger in the throat as if you were inducing vomiting. As a rule, it is enough to simply do this, but without making yourself vomit. The rhythm of the spasm will be disrupted, and the unpleasant symptom will stop.
- You can drink a glass of water while leaning over the sink.
- Some people use something sour or bitter. Lemon helps to get rid of this problem.
- Of course, they mostly resort to sudden fright. But if the spasm occurs precisely for this reason, then you should not further frighten the person, especially a child, he may simply cry.
Medications
Treatment of diaphragm spasm, if it occurs due to a serious illness and does not go away for a long time, must be carried out with the help of drugs, but they should only be prescribed by a specialist. Previously, the patient is prescribed an examination, as well as some tests. Medicines are usually taken orally, that is, by mouth. But in some cases injections are used.
Common drugs:
- "Cerucal" - helps empty the stomach.
- "Omeprazole" - accelerates the movement of food.
- "Baclofen" - can reduce the excitability of the diaphragm.
- "Aminazin" - helps with stress.
Homeopathic medicines, which should also be prescribed by a specialist, help very well. The doctor prescribes the regimen; some homeopathic medicines can be prescribed to children. The drugs calm the nervous system and relieve tension, including the diaphragm. You can get rid of a harmless diaphragm spasm at home using a decoction of dill seeds. It is very simple to prepare: take a teaspoon of raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water. The decoction should steep for half an hour. After this, you can drink a third of a glass three times a day.
Hiccups - spasm of the diaphragm
It is perhaps difficult to find a person or child who has never suffered from hiccups in his life. Of course, it is mostly harmless to the body, but it causes some inconvenience in everyday life and interferes with eating. What is hiccups? Hiccups are a reflexive and short inhalation, which is accompanied by a characteristic sound. Due to the fact that the glottis narrows during a spasm of the diaphragm, such an interesting sound arises. Hiccups - a spasm of the diaphragm can occur due to prolonged laughter, as well as fast eating. As a rule, it goes away on its own within a few minutes. Remember that if this symptom continues for a long time, it may indicate the presence of a serious illness. In this case, you need to contact a specialist.
The causes of diaphragm spasm are always different. Sometimes spasms occur due to disturbances in the functioning of the diaphragm, and here self-medication will be powerless. When these roots are pinched, not only lower back pain can occur, but also breathing spasms due to disturbances in the functioning of the diaphragm.
The diaphragm performs important functions in the human body; it is a fairly wide plate shaped like a dome. The diaphragm divides the body into the abdominal and thoracic cavities. It is worth noting that most vessels pass through the diaphragm exclusively in the muscular section, except for the inferior vena cava, which seems to penetrate the diaphragm in its tendon section.
If it intersected with the muscle tissue of the diaphragm, it would be constantly pinched during contraction. Although the main function of the diaphragm is to provide breathing. The diaphragm constantly relaxes and contracts; during contraction, it turns from a dome to a flat surface.
When the alveoli become full, the nerve impulses that control the contraction of the diaphragm begin to slow down. What is a spasm? A spasm is a convulsive state of muscles that is completely uncontrollable. When a spasm occurs, problems with blood circulation, breathing, and digestion may occur. There are many reasons for the reflex contraction of the diaphragm. Hypothermia can lead to spasms.
Treatment of esophagitis reflux gastritis
If pain when inhaling does not appear so often, then stress or physical activity may be the cause. It's enough to just relax.
Causes
Reflux esophagitis is a disease of the digestive system in which the esophagus receives the main blow. The disease manifests itself when the proper functioning of the stomach is disrupted and its contents rise to the esophagus. This contact is unfavorable, since the walls of the esophagus are not adapted to such a concentration of acids, and causes irritation, and over time, inflammation.
Treatment of esophagitis reflux gastritis is carried out after a complete examination.
The disease is accompanied by a jump in secretion (increased acidity), which means that pain in the lower part of the esophagus and almost constant heartburn will be characteristic. You should not prolong and endure this illness, as it can get worse and will lead to even greater discomfort, pain, and, over time, aggravation.
- 1 Causes and consequences of the disease
- 2 Symptoms of the disease 2.1 Course of the disease in children
- 2.2 Course of the disease in adults
- 5.1 Diet and nutrition rules
Causes and consequences of the disease
The disease is bad because in the initial stages of development it is hardly noticeable, and the symptoms are barely felt. Because of this, few people immediately consult a doctor only with the appearance of the first symptoms, and meanwhile the disease is gaining momentum. As practice shows, patients seek help from specialists already at the stage of inflammation development and the appearance of the first erosions.
Esophagitis reflux gastritis in its advanced form leads to ulcers of the lower esophagus, causing acute pain and bleeding. According to research, the disease may be the cause of a hiatal hernia in the diaphragm. This hernia is a part of the stomach that has fallen into the esophageal opening, which clearly does not belong there.
It all started with this diaphragm
And if the spasm persists, the doctor may prescribe special medications. But if the spasm occurs precisely for this reason, then you should not further frighten the person, especially a child, he may simply cry. Treatment of diaphragm spasm, if it occurs due to a serious illness and does not go away for a long time, must be carried out with the help of drugs, but they should only be prescribed by a specialist. The doctor prescribes the regimen; some homeopathic medicines can be prescribed to children. The drugs calm the nervous system and relieve tension, including the diaphragm.
Norms and deviations in IAP indicators
To determine whether the pressure inside the peritoneum is increased or decreased, special measurement methods are used. Then the data obtained is compared with normal values. Normal parameters include a figure of 10 units of mercury. Art. and less.
Deviations in a large direction allow us to draw a conclusion about the development of pathologies:
- Moderately elevated IAP is considered to be between 10 and 25 mmHg. Art.;
- moderately high – from 25 to 40 mm Hg. st;
- high – from 40 mm Hg. Art.
By palpation and assessment of symptoms, it is impossible to determine exactly what pressure the patient has. To identify the exact characteristics, an instrumental examination is required.