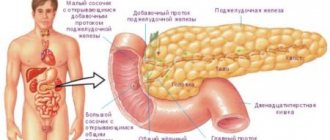
Dyscholia is a mysterious concept for parents, because in most cases they do not know what this name of the disease hides. In simple language, the term stands for a violation of the composition of bile. There is much more of it in the gallbladder than in the liver. In healthy children, bile contains acids, bilirubin, phospholipids, cholesterol (C) and biologically active substances. The normal ratio of bile acids and cholesterol is 2: 1. Exceeding the permissible levels of cholesterol creates the prerequisites for the formation of stones.
What affects the composition of bile?
There are quite a lot of factors that disrupt the physicochemical characteristics of bile. The main ones are:
- relocation of harmful flora from the intestines to the gallbladder;
- hematogenous/lymphogenous infection of the body;
- infection with E. coli, staphylococci and other microorganisms.
Additional factors include problems of metabolism and hepatic-intestinal transport of bile components. Deviation in children is often genetically determined if the parents suffer from dyscholia.
Worm infestations, a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, neuropsychiatric disorders and obesity also provoke changes in bile.
For reasons of occurrence, pathology occurs:
- nutritional, provoked by external factors (for example, poor diet);
- metabolic, associated with faulty metabolic processes.
Prevention
To avoid the development of ADHD, it is necessary to follow a number of preventive rules:
- If possible, feed your baby natural and healthy foods.
- Avoid long intervals between meals.
- Avoid stressful situations for your child.
- Regularly undergo helminthiasis prevention.
- Treat gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner.
Biliary dyskinesia is a fairly serious disease, which in the absence of timely treatment often leads to all sorts of complications (digestive upset, risk of gallstones, etc.). Therefore, if there are suspicious symptoms, the child must be shown to a gastroenterologist and undergo an examination. Treatment in the early stages allows you to completely get rid of the symptoms of this pathology.
How to recognize dyscholia
The clinical picture of gallbladder dyscholia is characterized by pain.
Discomfort occurs in a child after eating spicy, fatty and fried foods.
The pain can be dull and sharp, radiating to the right shoulder, shoulder blade, and right side of the neck. If the syndrome cannot be controlled with antispasmodics and warming procedures, it means that the inflammation has left the boundaries of the bladder.
An important sign of changes in bile is a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. Sometimes it is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric zone. And nausea and vomiting are considered quite rare phenomena in children.
Intestinal disorders as symptoms of dyscholia are expressed in different ways. The baby may experience:
- diarrhea, sometimes too foul;
- constant release of gases;
- atrophy of the gastric mucosa;
- the release of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach, which causes a bitter taste in the mouth.
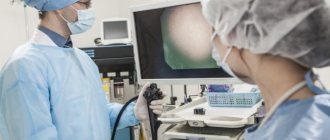
To assess the condition of the biliary tract, young patients are referred for esophagogastroduodenoscopy and ultrasound. Doctors extract some useful data from the answers of a biochemical blood test. The diagnosis is facilitated by family history, neurological status and individual characteristics of the body.
Specialists develop therapeutic measures based on diagnostic information. Parents receive dietary recommendations and prescriptions for the purchase of medications that improve the flow of bile and increase the secretion of acids.
Causes of biliary tract diseases in children
Biliary dyskinesia does not manifest itself in structural changes in internal organs - liver, gall bladder, ducts. Its cause is a violation of their function, which is caused by malfunctions in the central nervous system and the autonomic system of the body. The causes of the disease should be sought much deeper than it might seem at first glance - in the vast majority of cases, in the emotional state of the child.
Stressful situations, increased emotionality, nervous breakdowns - all this affects the state of the child’s body and leads to excessive involuntary contractions of the gallbladder. Because of this, excess bile accumulates in the area of the bile ducts, which begins to thicken, losing its antibacterial properties and functionality. At the same time, the formation of stones and blood clots begins inside the biliary tract, which interferes with the natural movement of bile to the duodenum. As a result, the disease itself develops and its complications become probable.
Additional factors of psychosomatic causes of the development of the disease may be:
- irregular meals;
- excess fat in food;
- a large amount of spicy, salty, smoked foods in the diet;
- consumption of junk food - nuts, crackers, soda;
- food allergies;
- intestinal parasites. Giardia is especially dangerous;
- side effects of certain pharmacological drugs;
- intestinal diseases and poisoning.
Frequency of meals and healthy foods are very important for children. This should be given the closest attention to anti-parasitic prevention. A specialist will help you adjust your child’s diet.
Diet rules for dyscholia
Having told mom and dad what dyscholia is, the gastroenterologist should explain to them the importance of the baby following a diet. During the first five days, he should eat often and in small portions. The baby will have to be protected from smoked, fried and fatty foods.
Wheat bran helps improve the functions of the gallbladder. 30 g will be enough for one day. The product lowers the level of cholesterol in bile. It is introduced into the diet of children as follows:
- the bran is doused with boiling water and the liquid is drained;
- the mass is added to food in a single dosage of 0.5 - 1 tsp. (only 3 rubles per day);
- with the beginning of the 3rd week, the volume is doubled and the bran is given to the baby for another 2 weeks.
To restore bile, it is useful for the baby to take olive oil (1 tablespoon on an empty stomach). The product can be added to all dishes and replaced with sunflower oil. In the summer, the secretion of bile is well accelerated by salads of fresh cucumbers and cabbage with the addition of dill, basil, and cilantro.
How to improve the contents of the gallbladder
To adjust the composition of bile in children, doctors prescribe choleretic drugs:
- choleretics with natural bile – Allochol;
- choleretics with lektravas - Holosas, Flamin, Holemaks, Chofitol, Febichol;
- synthesized choleretics – Osalmid, Nikodin, Oksafenamide;
- cholespasmolytics - Spasmonet, No-shpa, Atropine, Drotaverine, Spazoverine, Metacin, Ple-Spa, Platyfillin;
- cholekinetics – Magnesium sulfate, Cormagnesin, Valerian, Magnesia, Valerianahel.
Their dosage is calculated based on the body weight of the small patient. Drugs for dissolving stones are given to children for a long time - up to 8 months.
Among the folk remedies, the condition of the bile ducts quickly improves with tea made from wild strawberry stems. The twigs are collected during the flowering period of the crop. The raw material is brewed fresh or dry and given to children as regular tea.
Functions of bile and its composition
The main function of bile is to participate in the digestion process. It is carried out in the following directions:
- breakdown of fats, absorption of cholesterol in the intestines;
- activation of enzymes for subsequent absorption of proteins;
- stimulation of pancreatic enzymes.
Its other functions are no less important:
- regulation of motor activity of the small intestine;
- stimulation of mucus formation in the intestines;
- reducing the aggressive action of gastric juice.
The composition of bile is represented by the following components:
- bile acids (cholic, deoxycholic, chenodeoxycholic);
- bile salts (glycocholic and taurocholic compounds);
- bile pigments (bilirubin, biliverdin);
- cholesterol;
- water.
What is gallbladder dyscholia?
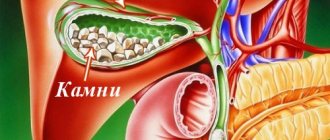
A change in the composition of bile leads to a pathological condition. First of all, the ratio of bile acids and cholesterol is disrupted (in favor of the latter), the content of pigments increases, and the amount of water decreases. Due to this, the bile thickens - this process is called dyscholia. The thicker the bile, the higher the risk of stone formation.
Dycholia is provoked by the following factors:
- an infectious process in the gallbladder (its source can be any source of infectious inflammation in the body);
- excess nutrition (abuse of fatty, fried foods, overeating);
- alcohol;
- lack of physical activity;
- liver diseases (fatty hepatosis, hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- liver parasites (giardiasis, opisthorchiasis);
- disruption of the activity of internal secretion organs (thyroid gland, pancreas);
- hereditary causes.
Discholia #8212; Why do abnormalities develop in the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is an important organ of the digestive system that receives bile from the liver and continuously distributes it into the duodenum in a certain amount, which depends on food intake.
Bile performs an equally important function, because it contributes to the normal digestion of coarse and fatty foods that enter the human body, crushing large particles for normal absorption. If for some reason a certain malfunction occurs in the biliary system, unpleasant diseases arise, fraught with some complications.
There are several diseases associated with the biliary organ, one of which is dyscholia. This term characterizes provoked disturbances in the composition of bile, which can occur due to an incorrect lifestyle, as well as due to developed diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
If any abnormalities in the functioning of the gallbladder are detected, you must urgently seek help from a gastroenterologist! Treatment in the early stages of the disease is more gentle and short-lived, and in case of advanced disease, surgical intervention and sometimes death cannot be ruled out.
Causes of dyscholia
Bile contains different components: phospholipids, bilirubin, biological compounds, cholesterol, bile acids and other elements. With normal organ functionality, the amount of cholesterol and bile acids is in a 1:2 ratio.
Any negative changes can lead to an increase in cholesterol levels several times, and this phenomenon provokes favorable conditions for the formation of gallstones.
When the level of cholesterol in the biliary system increases, dyscholia occurs. As a rule, several factors contribute to this, for example, excessive consumption of fatty foods, obesity, and advanced diabetes mellitus.
In some cases, dyscholia occurs against the background of hemolytic anemia, which provokes a sharp increase in the level of bilirubin in the bile. The action of pathogenic microorganisms in the bile organ negatively affects lithocholic acids, which can also cause the development of dyscholia.
Symptoms
Thickening of bile may not manifest itself in any way for a long time. Even over time, when this process intensifies and sand, suspension and sludge appear, painful symptoms may not bother you. This happens if the outflow of bile from the bladder is not impaired.
In some cases, the appearance of symptoms is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile from the bladder.
The main signs of this disease are as follows:
- pain under the ribs on the right (aching or sharp), can radiate to the collarbone, scapula, shoulder;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- nausea;
- periodic vomiting;
- tendency to constipation;
- loss of appetite;
- fatigue.
If the patient has the listed complaints, an examination by a gastroenterologist is necessary. The following additional examination methods are recommended:
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- biochemical blood test for liver tests;
- Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder and liver.
After confirming the patient’s diagnosis, it is advisable to immediately begin treatment measures.
Causes of the disease
The disease is a dysfunctional disorder that appears for a variety of reasons. With pathology, the regulation of the sequence between contraction and relaxation of the gallbladder and sphincters is disrupted. If there are malfunctions in the functioning of the biliary system, then bile does not fully enter the intestines.
In infants, the pathological process develops with perinatal damage to the central nervous system. A common cause of pathology is hypoxia. Biliary dyskinesia in children develops due to birth injuries. Newborns who are diagnosed with asphyxia are at risk. The disease occurs when there are abnormalities in the bile ducts, which leads to difficulty in the normal outflow of bile. If the sphincter apparatus is disrupted, this becomes the cause of the disease.
The occurrence of biliary dyskinesia in older children is observed with various infectious diseases:
- salmonellosis;
- hepatitis A;
- dysentery.
The disease can develop in children with a variety of chronic pathologies. Children who suffer from sinusitis are at risk. In case of chronic tonsillitis, biliary dyskinesia is diagnosed in children. The disease can appear in childhood with giardiasis. The provoking factor is ascariasis. The disease appears with neuro-atritic diathesis.
In adolescence, the main cause of the disease is vegetative-vascular dystonia. If a patient has psycho-emotional disorders or neuroses, this leads to pathology. If gastritis or duodenitis occurs, this becomes the cause of the disease. It develops in adolescence against the background of enterocolitis and pancreatitis.
There are many causes of biliary dyskinesia in children, which are recommended to be identified in order to prescribe effective treatment.
Treatment
If gallbladder dyscholia is diagnosed, treatment includes:
- adherence to a diet (exclude the consumption of fatty, fried foods, overeating);
- physical activity mode to prevent stagnant processes;
- psycho-emotional peace;
- drinking alkaline mineral waters (Essentuki No. 4, No. 17, Naftusya);
- use of medications.
Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating unpleasant and painful symptoms and normalizing the composition of bile. It is recommended to prescribe drugs from the following drug groups:
- stimulants of bile formation (Allohol, Cholenzym, Holosas, Flamin, Hofitol);
- antispasmodics (Papaverine, Drotaverine, Platiphylline).
In the presence of dyscholia, eating wheat bran has a positive effect. One teaspoon of bran should be poured with boiling water, left for 10 minutes, drained and consumed three times a day before meals. The course of treatment is one month; after a ten-day break, treatment must be repeated.
Drinking rosehip infusion, tea from berries and strawberry leaves also helps normalize the composition of bile.
Useful video
For more information about what symptoms are the result of gallbladder problems, watch the following video:
Dear readers, due to the widespread prevalence of cholelithiasis, many would like to learn as early as possible about the increased risk of stone formation, and the detection of dyscholia is precisely the alarm bell that deserves special attention.
The basis of this disease is a change in the physicochemical properties of the composition of bile, in which there is 3-5 times more cholates. This contributes to their deposition on the walls of the bladder and ducts, the development of inflammation and the formation of stones.
Many people find out about the presence of sediment in the lumen of the gallbladder by chance, during an ultrasound examination. If you or your child have been diagnosed with gallbladder dyscholia, do not be upset and think that this will definitely lead to the formation of stones. If at this stage you pay attention to the nature of your diet, start using soft tubes and do not let the bile stagnate, you can avoid complications. Who is predisposed to dyscholia?
At-risk groups
Dyscholia of the gallbladder occurs in children and adults. If parents have liver and gallbladder diseases, in particular gallstone disease, then the risk of bile sediment formation and changes in its composition in the child increases sharply.
It is recommended to immediately contact a pediatric hepatologist immediately after detecting this disorder. The doctor will tell you what dyscholia is in children, why it occurs and how to prevent the formation of stones.
Among the predisposing factors are the following:
- any chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially bends and curvatures of the gallbladder;
- underweight or, conversely, a tendency to obesity;
- increased cholesterol levels;
- abuse of fatty and fried foods;
- previous intestinal infections;
- the presence of worms;
- taking certain medications (ceftriaxone, hormonal contraceptives);
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases;
- poor diet;
- rare meals;
- lack of regular physical activity.
It is worth noting that biliary dyscholia presumably occurs under the influence of several unfavorable factors. But it is impossible to say exactly what affected the composition of bile. Experts can only guess by studying the patient’s medical history, lifestyle and complaints.
Symptoms in a child
Symptoms of biliary dyskinesia in a 3-year-old child in general will differ little from biliary dyskinesia in a 5-year-old child, only if the individual characteristics of the body.
The nature of the manifestations of the syndromes depends on the form of development of the disease. If a child has hypermotor dyskinesia, the symptoms are as follows:
- sharp pain in the right hypochondrium;
- duration of pain – short-term;
- nausea, vomiting;
- appetite decreases;
- diarrhea;
- constipation.
In the hypomotor form, there are the following signs of dyskinesia:
- dull pain in the right hypochondrium;
- duration of pain – long;
- feeling of heaviness;
- diarrhea;
- appetite decreases;
- belching;
- bloating;
- enlarged liver.
In some cases, when bile is difficult to drain, biliary dyskinesia in children has the following symptoms:
These signs disappear after taking choleretic drugs.
Symptoms and signs of dyscholia in children and adults
The characteristic signs of dyscholia in children and adults are often absent. This is the reason for late diagnosis. Complaints about well-being appear when the walls of the gallbladder become inflamed and concomitant disorders occur—cholecystitis.
Possible clinical manifestations of dyscholia in children and adults:
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- abdominal pain after eating;
- nausea, possible vomiting, especially after fatty and fried foods;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth, heartburn;
- excessive gas formation.
It is most difficult to identify the first signs of gallbladder dyscholia in children who, due to their age, cannot clearly talk about their sensations and the location of the pain. Pay attention to your child's mood, especially after eating.
If children are capricious after eating, put their hands on their stomach, or complain of pain, it is imperative to undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract.
Parents should also be wary of increased gas formation in the intestines. In the absence of helminthic infestations and dysbacteriosis, one can suspect pathologies of the biliary tract, which are often accompanied by flatulence.
Causes
Prevention of such pathologies is very important, so it is imperative to exclude negative factors leading to gallbladder dyscholia.
The disease develops due to the following reasons:
- Inflammation in the gallbladder due to infection from a nearby organ or bloodstream.
- Improper diet, abuse of spicy, fatty and fried foods, constant overeating.
- Inactive lifestyle, overweight and lack of exercise.
- Severe liver pathologies: hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, various types of cirrhosis.
- Damage to the organ by parasites, intoxication by their waste products.
- Malfunctions of the secretory organs (pancreas, endocrine system).
- Regular alcohol abuse.
- Hereditary predisposition to this type of disease.
- Pathologies of muscle activity of the gallbladder walls.
- Hormonal disorders caused by age-related changes in the body, lack of sexual activity, and thyroid dysfunction.
It is not possible to eliminate absolutely all factors, but reasonable restrictions on food, as well as feasible physical activity, will help improve the functioning of internal organs, and will also have a positive impact on overall well-being.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method for dyscholia is ultrasound. The use of ultrasound does not allow assessing the composition of bile. But this method helps to detect indirect echo signs of dyscholia. Typically, during the study, specialists identify bile flakes, its stagnation and a clear increase in lithogenic properties.
Dyscholia is often combined with dyskinesia and gallstone excesses. Such developmental anomalies contribute to stagnation of bile and the inflammatory process. And it is impossible to say for sure, for example, when a doctor identifies chronic cholecystitis with dyscholia: what was the root cause of the disease - inflammation of the walls of the gall bladder against the background of violations of the principles of a healthy diet, curvature of the bladder, or initially the bile became more lithogenic and flakes began to form.
Additional examination methods:
- general blood test, blood biochemistry (with dyscholia, an increase in alkaline phosphatase is observed, hypercholesterolemia may be detected);
- stool analysis for worms, including Giardia, stool for dysbacteriosis;
- FGDS, ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract (if there are complaints of pain, discomfort, bloating, stool disturbances).
According to indications, probing of the gallbladder is prescribed with further study of the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of bile. If dyscholia is detected, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Sometimes a violation of the composition of bile is only a consequence of other concomitant diseases of the digestive tract.
To treat or not to treat?
Dycholia, like gallbladder deformation and dyskinesia, usually do not require complex and specific treatment. The main emphasis is on diet. But she is not very strict either.
It is advisable to treat gallbladder dyscholia in adults and children in the presence of severe pain, signs of inflammation and bile stagnation. According to indications, choleretic agents and antibiotics are prescribed. At home, you can use mild choleretic preparations, make tubage using magnesia and sorbitol. It is recommended to carry out preventive ultrasound diagnostics several times a year to monitor the functionality of the gallbladder and detect possible complications in a timely manner, including the formation of stones.
Any medications for dyscholia are prescribed by a doctor. Do not experiment with medications, especially if you are not sure that there are no stones in the bladder. Otherwise, it may lead to acute colic and other adverse effects.
How to treat dyskinesia in a child
To prevent the child from having problems with the gastrointestinal tract in the future, gallbladder dyskinesia in children must be treated in a timely manner. Otherwise, the disease will lead to a chronic inflammatory process and an increased risk of stone formation. It is very important to correctly determine the form of the pathology, since it is dangerous to treat biliary dyskinesia in children without preliminary diagnosis. The wrong choice of medications can lead to the opposite effect.
Principles of treatment of gastric dyskinesia in a child:
- constant adherence to diet No. 5, which is the basis for effective treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia in children of all ages;
- complete split meals (up to 5-6 times a day) with a complete rejection of fatty, fried and spicy foods, carbonated drinks, sour juices;
- avoiding constant snacking;
- control over the amount of nutrients in consumed products, prevention of vitamin deficiency;
- the use of antispasmodics for pain in the right hypochondrium and deterioration of health;
- the use of medications only in consultation with the attending physician, who prescribes medications depending on the type of biliary dyskinesia (hypomotor, hypermotor);
- moderate physical activity, swimming, yoga.
For the hypermotor form of dyskinesia, choleretics, cholespasmolytics, and dry bile-based agents are used. It is recommended to carry out a course of electrophoresis with antispasmodics and massage the cervical-collar area. Psychotherapy is also helpful. For hypermotor dysfunction, herbal sedatives can be prescribed.
Hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder requires the use of choleretic drugs with cholekinetic action (sorbitol, magnesium sulfate). But such drugs are allowed to be used only if hypomotility of the gallbladder is confirmed. It is possible to use herbal remedies with a choleretic effect, such as corn silk, calendula, and rose hips. Under the supervision of a doctor, regular tubing using sorbitol can be performed.
Dysfunction of the gallbladder and other organs of the biliary system at any time can result in acute cholecystitis or the development of cholelithiasis. Self-medication in such situations often leads to serious consequences for the health of children.
Diet for dyscholia
For dyscholia, treatment table No. 5 is prescribed. But there is no need to follow a strict diet if there is no pain or other complaints about your health. The main thing is to give up fatty and fried foods, which, even in a person without signs of dyscholia, cause pathological changes in the gall bladder and liver.
But remember that the composition of bile and its lithogenicity can be influenced by other factors, for example, taking contraceptives causes the formation of sludge (sand) in many women. Pregnancy also contributes to this. But nutrition still plays a key role in the timely outflow of bile and maintaining the functionality of the biliary tract organs.
Basic principles of nutrition for dyscholia:
- try to eat at least 4-5 times a day, but in small portions;
- do not drink immediately after meals so that there are enough digestive enzymes and bile to digest food;
- avoid overeating;
- limit not only fatty fried foods, but also spicy foods, marinades, and sour juices.
The diet should be as varied as possible. For dyscholia, fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and all dishes that contain plant fiber are useful. It cleanses the intestines, stimulates the growth of beneficial microflora, and prevents constipation, which plays a key role in the development of cholelithiasis and cholecystitis.
Prohibited Products
A diet for dyscholia requires limiting the following foods:
- fatty fish and meats;
- alcohol;
- smoked meats, sausages;
- spices, marinades, all canned foods;
- sour juices;
- extractive substances contained in garlic, onions, radishes;
- gas-forming products (cabbage, corn, legumes);
- carbonated drinks.
To prevent complications of dyscholia, it is recommended to steam, boil or bake food. It is not advisable to fry, even if there are no complaints. With this diagnosis, you can quickly and deliciously cook in a slow cooker.
The daily diet must include porridge with water or milk, vegetable and fruit salads, low-fat fish and meat. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day, preferably, in addition to clean water, use infusions and decoctions of rose hips, which have a mild choleretic effect.
Nutritional Features
To get rid of this condition, it is very important not only to eat right, but also to follow the correct drinking regime - drink at least two liters of clean water a day, this will clear the bile ducts of accumulated bile and remove cholesterol.
With dyscholia and its treatment, daily nutrition must be adjusted. In this case, the treatment will produce more results and recovery will speed up.
The diet is adjusted regardless of age. All dishes must be steamed, boiled or baked.
It is best to eat fractionally, in small portions 5-7 times a day. There should not be more than 3-4 hours between meals, and the last meal should be taken 3 hours before bedtime.
It will be useful to eat porridge with water every day, to which 30 grams of wheat bran are first added.
Such food will reduce harmful cholesterol in the blood, which will speed up treatment. Prohibited foods and drinks include:
- Any alcohol.
- Rich meat-based first courses.
- Any spices, especially hot ones.
- Sodas.
- Fried and smoked products.
- Fatty meats and fish.
- Canned food, semi-finished products, products with stabilizers and other additives.
A patient who has been diagnosed with gallbladder dyscholia must remember that he is unlikely to achieve much success in treatment if he does not adhere to simple rules:
- The patient must eat properly.
- Follow a certain diet.
- Monitor the breaks between meals and develop a separate regime for yourself.
- Eliminate a number of foods that can be harmful.
- Don't worry and don't get stressed.
- At the first manifestations of the disease, get examined.
- Once a year, be sure to do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs for the sake of prevention.
If you follow these simple rules, the prognosis for recovery will be favorable.