Why does it hurt at night?
During the daytime, patients often feel normal, without complaining of discomfort in the abdomen. However, as soon as the person relaxes and tries to fall asleep, the discomfort returns.
The stomach hurts at night for the following reason: during the day, digestion and absorption proceed actively, and in the evening, intestinal motility gradually slows down. The autonomic nervous system signals functional disorders through pain sensations.
An acute attack provoked by sudden hunger can be relieved by eating a piece of bread. However, there are other, more serious causes of pain.
First aid
If discomfort occurs in the epigastric region at night, you should follow simple rules. Both the diagnosis and the recovery process depend on compliance with the recommendations.
General rules:
- Before the doctor arrives, you should not take medications.
- Among the pain relief remedies, you can drink warm mint tea or a few sips of cold water.
- Despite the fact that pain is often accompanied by a feeling of hunger, it is necessary to postpone eating.
- It is allowed to apply a warm heating pad. However, if the pain intensifies, the heating pad should be removed from the surface of the abdomen.
- Lying on your back with your legs raised up will help reduce pain.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
When to call a doctor
A doctor’s consultation will be needed in any case, because only a gastroenterologist can determine the etiology of nocturnal attacks and find out their cause.
Brief pain lasting a few minutes should not be too disturbing. The same applies to those cases when the condition improves after the passage of gas or the act of cleansing the intestines. More often, the malaise is explained by an excessive amount of food eaten for dinner or poor quality of the products.
The reason to call a doctor at home arises when pain manifests itself as follows:
- They torment a person for hours and do not allow him to sleep.
- They have a pulling, aching, cutting or stabbing character.
- Accompanied by spasms.
Etiology of night pain
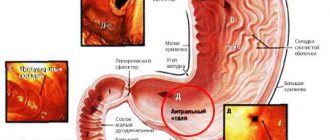
Discomfort in the stomach occurs when the organ stretches or decreases in volume. If an excess of gastric secretion is produced in it, hydrochloric acid begins to negatively affect its walls, which also leads to unpleasant sensations.
The following factors may be the culprits of discomfort:
- inflammatory process;
- abdominal wall injuries;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- intestinal infection;
- autoimmune diseases;
- peritoneal adhesions;
- endometriosis;
- flatulence;
- rapid contraction of the walls of the esophagus;
- metabolic disorders;
- acute respiratory infections;
- distension of the intestine or liver capsule;
- biliary dyskinesia.
- duodenal ulcer.
Also, discomfort in the epigastric region can be of a neurotic nature, occurring at a time of severe stress.
Among the physiological causes of night pain are the following:
- indigestion;
- incomplete bowel movement;
- excessive consumption of fatty and spicy foods;
- individual intolerance to certain products.
If night attacks are short-lived and not systematic, the cause often lies in an unbalanced diet. Reviewing your diet will help get rid of this problem.
Sometimes stomach pain can be caused by pressure from the growing fetus on the organ. In the first trimester, he may be sick due to toxicosis, in subsequent trimesters - due to an increase in the volume of the uterus.
Possible causes and treatment
There are several factors that can cause night pain in the stomach. The exact localization of unpleasant sensations, their nature, duration, frequency, and other features of the clinical picture will help determine which disease provoked the attack.
Common causes of pain are the following:
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Decreased peristalsis.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Poor nutrition.
- Frequent stress.
Ulcer
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori provokes inflammation of the intestinal or gastric mucosa, which over time becomes the cause of the development of trophic changes. The juice secreted to digest food has a detrimental effect on the walls of the organ, resulting in ulcers.
A duodenal defect appears in the same way. Hydrochloric acid aggressively attacks the protective layer, destroying the walls.
An ulcer is a chronic disease, it can be put into remission, but if preventive measures are not followed, an exacerbation occurs.
Video: Stomach ulcer: diet, recipes
Pain occurs in the upper abdomen. The attack intensifies if the patient violates the diet, drinks alcohol, fried and spicy foods, or engages in physical labor.
This clinical picture is typical for gastric ulcers that occur due to prolonged lack of treatment for gastritis. An intestinal defect manifests itself differently. Pain occurs more often when the patient is hungry. You can ease the discomfort by following a diet.
Among the accompanying symptoms, the most common are the following:
- Decreased appetite.
- Heartburn, nausea, diarrhea.
- Bitter or sour belching.
- A pressing feeling of heaviness that appears after eating.
If a person notices such signs, it is necessary to visit the gastroenterology department.
To help diagnose peptic ulcer disease:
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine.
- Examination of feces for occult blood.
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs.
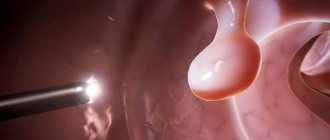
- Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is an examination of the walls of the stomach using a tube with a fixed camera to identify damage to the mucosa.
- pH-metry – determination of the acidity level of the environment.
Ulcer therapy involves complex measures. Prescribed:
- Antibacterial drugs (Amoxicillin 2 tablets three times a day).
- Agents that activate the protective functions of the gastric and duodenal mucosa (Enprostil, 1 capsule morning and evening).
- Antisecretory medications (Misoprostol 200 mcg 2-4 doses per day).
Symptoms
Stomach pain can occur regardless of the time of day. If the pain suddenly started and stopped after a couple of minutes, then there is no reason to worry.
If your stomach hurts for more than an hour, then during the day it is better to consult a gastroenterologist or call an ambulance.
Often, pain at night is not the only symptom of a malfunction in the body.
You should pay attention to other signs:
- Changing the position of the body, the pain intensifies.
- There is a urge to vomit.
- Sweating increases.
- There is intense rumbling in the stomach.
Intestinal infections or problems with the biliary tract are manifested not only by pain and spasms.
In addition to the main symptoms, you need to monitor for other signs of disease. They may indicate the following:
- With an increase in temperature and chills, there may be pelvic diseases: gonorrhea, chlamydia, and other diseases.
- If you lose your appetite, feel nauseous, vomit, that is, gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Fainting and shock, with a sharp change in pressure, indicates bleeding inside the abdomen.
- Painful urination, cloudy urine, and temperature indicate kidney and urinary tract problems.
Additionally, you need to know the nature of the pain that occurs in the lower abdomen. This will allow you to correctly describe your condition to the doctor to establish an accurate and correct diagnosis.
So if discomfort appears suddenly, then the cause may be exacerbations or acute diseases.
There is no need to joke with such symptoms, otherwise a perforation may appear, bleeding will occur, or a certain organ will rupture.
Why do you feel soreness in the stomach area in the morning? There are different causes of abdominal pain. However, you should not self-medicate; you should visit a doctor for advice.
The following morning symptoms require immediate consultation with a medical specialist:
- vomit;
- increased body temperature;
- flatulence;
- bloody diarrhea;
- swelling of the limbs.
Correct treatment of night pain in the stomach involves the use of antispasmodics. They are aimed at effectively relieving muscle spasms and act locally.
Other principles of correct treatment include the pathogenetic approach. This is an item that is part of an emergency project and involves the use of antibacterial agents. Such drugs are effective against night pain in the stomach because Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium that causes many stomach problems, is susceptible to them.
The main symptom is pain, which can have different characteristics: intensity, frequency, localization. It may be accompanied by additional symptoms:
- Heartburn;
- Bitter or sour belching;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Possible flatulence and bowel dysfunction;
- Insomnia;
- Weakness and sweating;
- Fever, chills;
- Loose stools, mixed with blood or modified (black, or, conversely, light).
Of course, these signs are not observed all at once, but according to the disorder that occurs in the stomach or gastrointestinal tract.
First aid for stomach pain
If the attack is isolated and bothers the patient for the first time, and the sensations are not acute, then you can provide help yourself. To do this, first of all, the patient should lie in bed so that no one disturbs him.
If you have complaints of heartburn, then Renia or Almagel will help relieve the burning sensation in the chest area. If you don't have medicine on hand, you can use baking soda. It is dissolved in water (half a teaspoon per 200 ml) and drunk.
Metoclopramide or its analogues will help relieve cutting pain in the abdomen.
If the performed manipulations do not bring relief to the patient, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Diagnosis of the body
To make a correct diagnosis, specialists prescribe a comprehensive examination. Recommended examination methods include the following:
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- FGDS;
- General analysis of blood, urine and feces.
In addition, the doctor palpates the abdominal cavity and collects a detailed medical history.
FGDS - fibrogastroduodenoscopy involves inserting a probe with a built-in video camera through the esophagus, which allows you to assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. If necessary, short-term anesthesia is given. The most informative method for diagnosing gastric diseases.
The main causes of nighttime abdominal pain
The painful sensations may not last long – up to a couple of minutes. These spasms are usually not a cause for concern. But hours and whole nights in the claws of tearing or aching pain can rightfully be called serious signs and signals for an early visit to a medical facility and examination. Despite the fact that these signs can appear at completely different times, they become most stable at nightfall, when the body relaxes and the nervous system requires some rest. At such a time, the autonomic nervous system comes into action, which is characterized by the manifestation of all the most significant symptomatic pathologies. Considering a variety of causes of abdominal pain at night, clinicians identify the following main and most important:
- The appearance of abdominal pain that forces you to wake up can occur on an empty stomach due to excessive production of gastric juice.
- Painful cramps immediately after eating, when indigestion occurs due to an imbalance in the acid-base balance.
- Due to insufficient bowel movements or immediately after defecation.
- A consequence of irritable bowel syndrome, possibly with biliary dyskinesia.
- Eating unbalanced food. This could be salty, excessively hot or cold food.
- Dishes made from foods rich in cholesterol, which provokes the formation and active movement of gallstones.
- Physiological intolerance to certain products: milk, lactose and other dairy products.
Determination of the main causes can occur exclusively in a medical institution after carrying out diagnostic measures prescribed by the doctor.
Severe abdominal pain at night can be a sign of many conditions and diseases. Sometimes it’s difficult to understand: either it’s just increased gas formation, or it’s something much more serious.
There are two types of pain, which contain several more subtypes.
Convulsive (spastic) pain, which is also called colic. More often, such pain is characterized by wave-like attacks, the brightness and intensity of which varies. Pain appears due to various intestinal deformations: compression, stretching, etc.
The most dangerous subtype of these pains is “acute abdomen,” when the pain is severe, cutting, and the person’s condition sharply worsens. This happens, for example, with peritonitis or pancreatitis. The pain can also be dull and constant, as with acute appendicitis.
Abdominal constant pain, which is characterized by a stable and constant course, often accompanies serious inflammatory diseases of the internal organs. Patients often complain of a burning sensation. Such pain can occur due to ulcerative lesions, attacks of cholelithiasis. A subtype of these pains are chronic pains, which may or may not accompany gastrointestinal diseases or are pains of a neurotic nature.
The main diseases that can cause abdominal pain:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, any organ of the abdominal cavity;
- intoxication;
- circulatory disorders in the abdominal cavity;
- diseases and inflammation of the peritoneum;
- pathological processes that occur in the chest (pericarditis, pneumonia, etc.).
Often the pain is accompanied by other manifestations of malaise: sweating, rumbling,... Moreover, the degree of activity of these symptoms changes with changes in body position. It is these manifestations that indicate disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, intestines, pancreas, or are a sign of cholelithiasis.
If fever and chills appear, then abdominal pain indicates intestinal infections or that there is a blockage of the bile ducts. All this can occur at any time of the day. But at night, these symptoms usually manifest themselves more strongly because we are in a relaxed state and are more sensitive to changes occurring in the body.
If the pain is short-term, low or moderate in intensity, and the intervals between painful sensations are from one to several hours, then most likely the situation does not require immediate medical attention. But a consultation with a therapist is still necessary.
Abdominal pain at night should alert you if it begins to manifest itself as unpleasant symptoms, or the pain simply lasts too long - several hours, or the pain is sharp and very severe. In this case, you should not wait, but call an ambulance.
If the pain went away after the intestines cleared (you went to the toilet) or after the release of gases, and began to subside after a few minutes, then, most likely, nothing serious is developing.
It should be remembered that in case of intense acute abdominal pain, you should not take any medications on your own (especially laxatives and antipyretics), but you should seek qualified help. Taking medications can suppress symptoms, making it difficult to determine the cause of pain, and can also cause a worsening of the patient’s condition.
A heating pad applied to the area of pain can cause especially great harm.
The location of pain is the main factor in suspecting a certain disease. This will be the first question your doctor asks you about the pain you are experiencing.
If the pain is localized in the upper abdominal cavity, then it may indicate disorders in the esophagus, pancreas, upper intestines, liver, and biliary tract.
Pain on the right often occurs during inflammatory processes in the liver and biliary tract. It may be a sign of acute appendicitis.
There are two most common types of pain.
Spasmodic or convulsive pain, also called colic, makes itself felt in wave-like attacks of varying intensity. Its causes are compression or stretching in the intestines, which occur due to hyperactive peristalsis, for example, excessive gas formation in the intestines, infectious inflammation or stress.
Constant abdominal pain is characterized by a relatively stable and constant manifestation. Patients may complain of a “fire in the stomach” and describe cutting, sharp, or “hungry” pain. This type of pain can occur due to ulcerative lesions, abscesses and other dangerous inflammations of the abdominal organs, attacks of cholelithiasis or acute pancreatitis.
Accompanying symptoms
Abdominal pain at night may be accompanied by rumbling, which becomes more pronounced when changing position or taking a horizontal position. These symptoms must be taken into account, since they indicate disturbances in the activity of the stomach, intestines, bile ducts, or the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the stomach. Chills and fever usually accompany dangerous intestinal infections or blockage of the bile ducts. Changes in the color of urine and feces are also a sign of blockage of the bile ducts. In this case, the urine predominantly darkens, and the feces become lighter, even white.
Moreover, if intense and cramping pain is additionally accompanied by black or bloody stools, internal bleeding should be suspected and immediate hospitalization should be performed.
Kinds
Pain at night has the following types:
- Visceral. This type of pain is the result of irritation of the nerve endings that are located on the wall of the abdominal cavity. The pain resembles hepatic or intestinal colic and varies in intensity.
- Parietal. Occurs when the peritoneum is irritated and has a clear location. Parietal pain is acute and is accompanied by pain that intensifies with breathing or movement.
- Psychogenic. A painful syndrome occurs as a result of increased anxiety and suspiciousness. It represents a reaction to stressful situations.
- Neurogenic. The appearance of this type of pain is a consequence of neurological diseases. The painful sensations are shooting in nature and can suddenly go away or reappear.
The intensity of the pain depends on the nature of the injury and is of the following types:
- "dagger";
- cramping;
- intolerable;
- pulsating;
- permanent;
- aching;
- burning;
- moderate intensity;
- stupid;
- shooting;
- twitching;
- reflected.
Painful sensations can increase and progress or have a monotonous, decreasing character. Based on their duration, they are divided into acute and chronic.