Gastrointestinal disorders are almost always accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea. These symptoms may indicate either an intestinal infection or more serious diseases. Fortunately, most often everything ends well and no doctor’s help is required. In order not to miss serious health problems, you need to listen to the signals of your body.
Main causes of abdominal pain
Sharp abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea are the most common symptoms of various pathologies of the abdominal organs. During his life, a person faces similar problems more than once.
Painful sensations appear due to irritation of receptors that are located in the muscles, serous membrane and skin. They arise due to inflammatory changes and poor circulation. The mucous membrane of the intestines and stomach does not contain pain receptors. It does not react to irritations, like skin does. Therefore, a mucosal biopsy does not cause any discomfort at all. Stretching of their walls or a sharp contraction can provoke pain in hollow organs. Spasms can be caused by various reasons, for example, ischemia.
The nerve endings of parenchymal organs are located on the capsule. Pain occurs when this membrane is sharply stretched. If the organ and its capsule increase gradually, irritation of the receptors does not occur.
The outer lining of the vessels is also covered with nerve fibers. Sudden stretching of their walls, for example with an aortic aneurysm, will lead to pain. A growing tumor can irritate nerve endings.
The higher parts of the central nervous system are responsible for the formation of pain. How intense they will be depends on the emotional background, environment and individual properties of mental activity.
Visceral abdominal pain has no clear boundaries. Diarrhea and nausea are often its companions. The lack of strict localization significantly complicates diagnosis.
Somatic pain is very intense. Its location is usually easy to determine. It is felt strictly in the place where the affected organ is located.
Referred pain is not associated with the peritoneum. It is observed with severe irritation of the affected organ. It can occur with pneumonia, heart attack and diseases of the meninges.
What to do and how to treat associated symptoms
If you experience abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting, consult a doctor.
If you suspect diseases of the abdominal organs, you should not resort to independent treatment; incorrect assistance will lead to aggravation of the situation. In case of exacerbation of gastrointestinal pathologies, urgent surgical intervention is required.
You can eliminate unpleasant symptoms using certain medications.
- Toxins are removed from the body by taking sorbents. Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Enterol, Smecta, Sorbex, Atoxyl are considered effective.
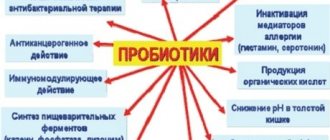
- Antidiarrheal drugs are used to treat diarrhea - Nifuroxazide, Levomycetin, Imodium, Loperamide, Hilak forte, Diaremix. Depending on the cause of the disorder, it is necessary to use antibiotics, probiotics, agents to reduce intestinal motility, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Diazepam, Lorazepam, Motilium, Betagistin, Pipolfen stop vomiting.
- Abdominal pain is relieved with analgesic drugs. No-Shpa, Paracetamol, Nurofen (Ibuprofen), Spazmalgon, Festal, Diclofenac, Ranitidine, Cerucal, Omez will help relieve pain spasms.
- To improve intestinal function, it is recommended to use bacterial preparations - Yogurt, Linex, Lactovit, Enterozermina, Bifidumbacterin, Lactulose, Lactofiltrum.
Taking medications is possible after consultation with a doctor. If abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting occur in a child, self-medication is strictly prohibited.
To prevent dehydration, a person should be provided with adequate fluids. If a patient has diarrhea and vomiting at the same time, the body loses a lot of fluid, which is quite dangerous. The condition needs to be treated. Drink warm boiled mineral water without gas. During treatment, adhere to a food diet. Give preference to rice dishes.
A person needs to understand that the development of symptoms is dangerous to health and life. The use of drugs and therapeutic actions must be discussed with a doctor. Otherwise, the person takes responsibility for possible negative consequences upon himself.
Intestinal infection
Intestinal infections are one of the most common pathologies. Diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever and nausea are characteristic signs of the disease. Intoxication and dehydration often develop. This condition is especially dangerous for infants.
Billions of different microorganisms enter the human body every hour. To neutralize them, nature has created many methods: bactericidal saliva, deadly gastric juice, bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Despite powerful protection, there are always a few microbes that cannot be neutralized.
The main cause of the disease is non-compliance with hygiene standards: unwashed hands, flies and improper storage of food. The most common causative agents of the disease are:
- dysentery bacillus;
- staphylococcus;
- various viruses;
- salmonella;
- shigella;
- typhoid fever sticks;
- some viruses;
- clostridia.
Penetrating into the body, pathogens begin active reproduction. As a result, the digestion process is disrupted and the intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed. Severe abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea are the most common accompaniments of infection.
The worst consequence of diarrhea is the loss of fluid and salts. The human body can survive without food for quite a long time. But with a shortage of water, sodium and potassium salts, the clock counts. Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea in a child are especially dangerous. All this contributes to rapid fluid loss in the baby and can be fatal. After all, the reserves of salts and water in his body are small.
Only a doctor can correctly determine the danger of infection. But few people seek help from doctors for every diarrhea. Therefore, it is necessary to know the most dangerous symptoms, and if they appear, you should call a doctor as soon as possible:
- High temperature, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain.
- Inability to replenish fluids due to vomiting.
- Prolonged absence of urine.
- Sunken eyes.
- The appearance of blood in the stool.
- Dry tongue.
- Changing normal skin tone to gray.
You should not take antibiotics without a doctor's prescription. Most often, diarrhea is caused by viruses, and these medications have no effect on them at all. Antibiotics are used for dysentery. Even less common with salmonellosis.
Many doctors suggest using eubiotics. These are intestinal bacteria that are beneficial to humans and must destroy pathogenic ones. In addition, to combat salmonella or dysentery bacillus, it is proposed to use special viruses that are safe for humans. They are called bacteriophages.
Despite numerous developments by modern pharmaceutical companies, the use of new-fangled drugs is not able to heal the patient faster than drinking plenty of fluids and dieting. Even in a hospital, the basis of treatment is infusion therapy. To quickly compensate for losses, the patient is given intravenous fluids and salts. For the treatment of one of the most dangerous infections - cholera, such therapy is the most important.
High fever and diarrhea
These indicators may be indirect evidence of an infection that has entered the stomach. Such conditions are treated in a hospital. The following diagnoses can be made:
- Stomach flu. This disease is caused by certain viruses entering the stomach. Rotaviruses, adenoviruses and noroviruses often cause illness. The situation is complicated by cutting pain, the patient is plagued by nausea and weakness.
- A patient with dysentery feels cramping pain, the doctor diagnoses pallor of the skin, and tachycardia may appear. To avoid making an incorrect diagnosis, you should wait until the doctor arrives and not take any pharmaceuticals. You need to drink more water.
Food poisoning
Sharp abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea - all this is the body’s reaction to eating low-quality food. The risk of poisoning exists everywhere: at a party, at home, at a picnic, in a restaurant. The likelihood of consuming low-quality products increases for people traveling to hot countries.
There are two main types of food poisoning:
- Microbial. This type is caused by food that contains pathogens or their metabolic products.
- Non-microbial. Poisoning is caused by poisons of animal, plant or synthetic origin that enter the body with food. For example, inedible plants or mushrooms, some types of shellfish, sprouted potatoes.
The consequences of poisoning can be very serious. A person’s health and even life depends entirely on how adequate and timely the assistance provided to him will be.
The time when the first symptoms appear depends on what caused the poisoning. He will be able to understand that a person has consumed low-quality food within two to three hours. Symptoms of poisoning from poisonous plants or mushrooms may appear after half a day.
Weakness, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea are signs of toxic infection. Its mild degree can be treated at home. You cannot let the disease take its course. Otherwise, the situation may worsen.
If nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea and chills are accompanied by headache, rapid pulse and bluish skin, this is a sign of acute intoxication. This condition threatens human life. It requires immediate medical attention. If the patient consumed canned food, mushrooms or alcohol the day before, he must inform the doctor about this. In such circumstances, hospitalization will most likely be required.
Enzyme deficiency or overeating
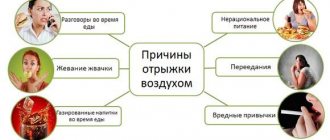
A deficiency of enzymes produced in the gastrointestinal tract leads to inadequate digestion. Proteins and other substances are not completely broken down. This causes a complex of symptoms: belching, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, heartburn, boiling and flatulence.
This condition is not an independent diagnosis. In this way, one or more pathologies may appear. Enzyme deficiency can result from:
- Binge eating. The enzymes produced by the body are not physically sufficient to process large quantities of food. Especially if she's fat.
- Impaired outflow of pancreatic juice into the intestines. Such conditions can occur if the duct is blocked by parasites, stones or a tumor.
- Any form of pancreatitis.
- Inflammation of the small intestine.
- Pathologies of the biliary system.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Crohn's disease and other autoimmune disorders.
- The result of surgery. For example, removing part of the intestine.
- Congenital disorders. For example, the lack of enzymes to break down milk sugar. It accumulates in the intestines and fermentation begins. After drinking milk, a person may experience mild abdominal pain, rumbling, nausea, diarrhea and even vomiting. For some people to experience these symptoms, they need to drink several glasses of milk. But there are people who experience such problems after drinking a small cup of coffee with cream.
- Irrational diets.
A long-term lack of enzymes is accompanied not only by abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea. The patient's physical endurance and performance decrease, sleep deteriorates, headaches become more frequent, and irritability appears. Frequent diarrhea leads to dehydration. And impaired absorption of iron results in anemia.
It is impossible to get rid of congenital enzyme deficiency. The first symptoms - nausea, abdominal pain and diarrhea - may appear in the baby immediately after eating. In order to compensate for this condition, you will have to adhere to a strict diet throughout your life and regularly take enzyme preparations.
Acquired enzyme deficiency has a more favorable prognosis. The patient has a chance of complete recovery. The exception is cases where the intestinal wall or pancreas has suffered irreversible damage.
The main goal of therapy is to facilitate the digestive process. Since the resulting disorders constantly damage the intestinal mucosa, further aggravating the course of the disease. And also the general condition of the patient is negatively affected by nutritional deficiency. Treatment can only be prescribed by a specialist after a thorough examination. Enzyme preparations are most often prescribed. The patient must also follow a strict diet and avoid overeating.
When to see a doctor
There are situations in which self-treatment is prohibited:
- symptoms appeared in a newborn;
- diarrhea and vomiting do not stop for more than 2 days;
- pain increases sharply;
- the patient lost consciousness;
- neurological signs;
- suspicion of botulism, poisoning by mushrooms, household chemicals or industrial poisons;
- there are impurities of blood and pus in the stool or vomit;
- The causes of the disorder are not clear.
It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor if the victim, in addition to general symptoms of illness, has an elevated body temperature. A clear sign of the inflammatory process and the fight of the immune system against foreign microorganisms. No less dangerous symptoms are disorientation and vision problems, complemented by discomfort in the abdomen. The symptom appears with the development of botulism, which is fatal to humans.
To prevent the situation from worsening, it is advisable to visit a doctor regardless of the severity of the illness. If the disorder is minor, the doctor will recommend the necessary medications and bed rest. If the severity of the condition is high, the patient may require urgent hospitalization.
source
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix is most often diagnosed in people under 30 years of age. According to statistics, women get sick more often. The exact reasons why inflammation of the appendix occurs is unknown. The most popular hypothesis is infectious.
Quite often, with appendicitis, Staphylococcus aureus, pyogenic bacteria and other pathogens are found. Moreover, they are also present in healthy people. Some experts believe that under favorable conditions, these bacteria begin to multiply rapidly, which becomes the cause of inflammation.
The main factors that stimulate the growth of pathogenic microflora in the appendix:
- Blockage of the appendix with fecal stones, tumors and other foreign bodies.
- Impaired blood supply. If the nutrition of small vessels suffers, necrosis may develop.
- Deterioration of peristalsis. Disruption of innervation often leads to increased mucus formation. This further stimulates the development of inflammation.
Doctors' observations indicate that pathology most often develops in people suffering from constipation, amebiasis, and intestinal tuberculosis. In men, inflammation of the appendix often occurs due to bad habits. In women, gynecological pathologies can become a provoking factor.
The main symptoms of the disease are severe abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea. Vomiting often occurs. At first, pain may vary in intensity and location. Gradually, colic concentrates in the appendix area. The pain becomes constant, but moderate. May get worse when changing body position or coughing.
Pain that subsides on its own for several hours does not bode well. Most likely, this is due to a rupture of the walls of the appendix. The pain will definitely return, but with even greater intensity.
Vomiting with appendicitis occurs once. It may consist of mucus, food debris, fluid and bile. A situation in which frequent vomiting is not able to bring relief is considered dangerous.
Constant companions of pathology are severe abdominal pain, diarrhea and nausea. Appendicitis rarely occurs without fever. It can be either high, reaching 40 degrees, or drop to critically low levels.
If you suspect appendicitis, it is prohibited and deadly to use heating pads on the abdominal area or do enemas. You should also not take laxatives or painkillers. When the first symptoms appear, you should call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Gastritis
Poor nutrition, smoking, long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs and alcohol can provoke inflammation of the gastric mucosa. It can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Damage to the stomach lining, which doctors call gastritis, is accompanied by symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn and bloating.
Acute inflammation does not last long. With adequate and timely treatment, complete recovery occurs. Chronic inflammation can cause mucosal atrophy. Healthy cells will gradually begin to be replaced by atypical ones. This process can lead to the formation of ulcers or cancer.
One of the first signs of pathology is heartburn. This is the result of an imbalance in acid-base balance. Gastritis can occur hidden. But more often this disease is characterized by a wide variety of different symptoms. The main one is abdominal pain. Nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, flatulence and vomiting are important but not permanent signs of gastritis.
The chronic form is more difficult to determine. For a long time, the disease can manifest itself only as rumbling in the stomach, flatulence, coating on the tongue, drowsiness, and bad breath. Diarrhea may alternate with constipation.
Gastritis can become an impetus for the development of serious pathologies. Self-medicating or ignoring its symptoms is dangerous. It is very important to contact a gastroenterologist as soon as possible, who can correctly diagnose the form of the disease and select adequate treatment.
Inflammation of the duodenum
Inflammation of the duodenum, or duodenitis, can cause symptoms such as bloody vomiting, severe belching, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Reasons provoking the development of the disease:
- Ischemic intestinal disease.
- Cholecystitis.
- Crohn's disease.
- Severe stress.
- Gastritis.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Dyspepsia.
- Chronic infections.
The acute form of duodenitis most often develops as a result of ingestion of poor quality food. Products that cause irritation to the mucous membrane, alcohol or the ingestion of toxic substances injure the intestines. The acute form of duodenitis may resemble poisoning in its symptoms. In some cases, complications may develop. For example, bleeding or damage to the intestinal wall.
Periods of remissions and exacerbations alternate in the chronic form of duodenitis. The disease develops against the background of an irregular diet, with the consumption of large amounts of spicy, fatty and fried foods. In addition, duodenitis can progress against the background of other pathologies.
According to statistics, this disease most often affects men. Its development often begins in childhood. Statistics show that acute inflammatory processes affecting the duodenum become chronic in 95% of cases.
Causes of symptoms
Each disease is characterized by certain symptoms and the order in which they appear. The causes of poor health may be inflammatory or infectious. At the first stage, it is important to exclude severe pathologies through a thorough diagnosis of the digestive tract.
Nausea and vomiting can be caused by overeating, and diarrhea can be caused by alcohol abuse or intolerance to certain foods. Inflammation in the digestive tract is accompanied by stool disorder for a long period, and requires diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
What is important to tell your doctor
Treatment of nausea, diarrhea and abdominal pain can only be effective if the diagnosis is made correctly. If the cause of your illness is not simple poisoning, which can be treated at home, you should consult a doctor. Already during the initial examination, it is important to provide the doctor with as much information as possible about your health condition.
The most valuable information will be:
- Localization. The doctor needs to talk in detail about where exactly the negative sensations are concentrated. Perhaps the pain radiates to the back or arm. It happens that it changes localization. You should tell your doctor about all this.
- Intensity. The severity of the sensations can vary, from mild to painful. Sometimes the pain is so intense, for example with appendicitis, that it is impossible to take a deep breath.
- Duration. The painful attack may last only a couple of minutes. Sometimes, it persists for several weeks.
- Character. The pain can be pulling, cutting, sharp, dull, cramping. This information will make it easier for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
- Time of onset of pain. It is recommended to remember and tell the doctor about those events that, in the patient’s opinion, could have caused the development of the pathology. For example: eating, drinking alcohol or taking medications, experiencing stress or trauma.
Prevention
To avoid pathologies that cause unpleasant symptoms, it is important to follow some rules:
- You should wash your hands thoroughly with soap after using the toilet.
- Avoid crowds during epidemics.
- Choose food products carefully, paying attention to the production date and shelf life.
- Consume meat and fish only after heat treatment.
- People with chronic diseases need to undergo a complete examination at least once a year.
- Carefully monitor the foods you eat; it is better to exclude foods with a high content of preservatives and food colorings, giving preference to natural ones.
Stool upset, weakness and nausea may not be taken seriously by a person. Sometimes, indeed, the reasons that caused such reactions in the body are banal - stress, overeating. But sometimes the pathology that is accompanied by symptoms can be so serious that untimely treatment can lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, the first thing a sick person should do is consult a doctor to find out the causes of the pathological processes.
source
Treatment
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to understand the reasons. For example, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, diarrhea and nausea often occur in women during menstruation or a few days before it. Unpleasant sensations are explained by spasms in the uterus. Irritation from this organ can spread to neighboring ones, for example, the intestines. This provokes increased peristalsis and leads to the development of diarrhea. Painful periods are often accompanied by weakness, headache and diarrhea. In this case, it is recommended to go to bed and drink herbal tea with mint. In addition, you can take two tablets of no-shpa or papaverine.
In the event that the cause of the illness is poisoning, first of all it is necessary to rinse the stomach. To do this, prepare a weak saline or soda solution. For two liters of water you need to take no more than a tablespoon of powder. After drinking the solution, immediately induce vomiting. Repeat the procedure several times. Preferably until the vomit is clear.
After this, you should take sorbents. Ordinary activated carbon, familiar to everyone since childhood, gives excellent results. It can be replaced with “Smecta” or “Enterosgel”.
Regidron will help replenish the lost water balance. On the first day you should stop eating altogether. But significantly increase the amount of water. You need to drink at least three liters per day. This can be clean water or homemade fruit drink.
If the above methods do not produce results, you should consult a doctor. It is important not to miss the development of a dangerous disease.
What to do if your stomach hurts and diarrhea
You can give yourself first aid yourself if you suddenly feel constricted. What to do if your stomach hurts and diarrhea:
- Drink plenty of clean water, unsweetened tea or mineral water.
- Take Regidron.
- To remove toxins from the body, drink Enterosgel, Smecta.
- Do a gastric lavage with potassium permanganate.
- Loperamide and Furazolidone are good for poisoning.
- To get rid of cramps, drink No-Shpu, Bral or other local anesthetic.
- Stick to a diet for some time, give up foods rich in fiber, dairy products, juices, salty and sweet foods.
- Indomethacin, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is good for diarrhea.
- If you do not feel better within 24 hours or become even worse, be sure to call an ambulance.
Find out what sigmoid colon diverticulosis is - symptoms and treatment of the disease.