View gallery
Abdominal pain is perhaps the most common type of pain, which can appear as an independent symptom or one of the signs of another disease. Unpleasant sensations can occur both in the sides and lower abdomen, in the abdominal or epigastric region. Not so often pain occurs near the navel, namely on the right side of it. Pain that appears in the right umbilical region is a very dangerous phenomenon. After all, this may be a sign of a serious disease, for example, inflammation of the appendix.
Asymmetrical belly. Palpation of the abdomen for intestinal obstruction
On examination, the abdomen
is distended. Flatulence may be diffuse or localized. If there is limited flatulence, then in such cases they speak of the presence of asymmetry in the stomach (it can be caused not only by limited flatulence, but also by displacement of the intestinal loops).
The nature
asymmetry can sometimes suggest the level of obstruction. A “skewed” or “oblique” abdomen with a contoured, swell-shaped, swollen intestine indicates sigmoid torsion. Sometimes it is possible to see how the peristaltic wave spreads along the length of the supposed intestinal loop (if the patient is thin, then the loop itself is noticeable) and stops each time at a certain point (usually in the right iliac region or around the navel), which, as a rule, indicates the site of obstruction (Konig symptom).
As it increases
phenomena of OKN, the contractility of the afferent intestinal loop decreases and hyperperistaltism disappears and the clinical picture of peritonitis increases. In order to catch the cramping nature of the pain and not see hyperperistalsis. it is necessary to examine the patient (sit next to him and observe) not for 2-3 minutes, but for 10-15 minutes, or repeat the examination of the abdomen at short intervals.
It seems to us
the first option is more acceptable, since in this case it is possible to simultaneously examine hyperperistaltism at the height of cramping pain against a background of clear asymmetry, and sometimes even hear at a distance, without a phonendoscope, ringing intestinal sounds. When palpating the abdomen, there is no muscle tension. In the area of the abdomen where there is flatulence, an impression of elastic resistance of the abdominal wall is created, reminiscent of a balloon filled with air. In particular, with cecal volvulus, an oval or spherical swelling is detected in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen or in the navel area. And since the cecum has shifted, palpation in the ileocecal area creates the impression of emptiness (Schiman-Dans symptom).
During sigma
two swollen loops of the colon (sigmoid) colon are identified, located in parallel, often in the lower and middle parts of the abdomen. In the case of intussusception, it is possible to palpate a sausage-shaped formation, most often along the right flank and in the right hypochondrium.
Palpation of the abdomen
It is possible to identify painful points that are better identified at the height of cramping pain and can indicate the level of obstruction. Tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, as well as the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom, appear early only with nodule formation (here gangrene of the small intestinal loop quickly develops), and with other types of strangulation intestinal obstruction they appear much later.
noted here
that any type of mechanical intestinal obstruction, if treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, ultimately ends in peritonitis and severe paralytic ileus (the afferent intestinal loop is so swollen that its serous membrane cracks in places).
- Read "
Percussion of the abdomen for intestinal obstruction. Vaginal examination for intestinal obstruction"
Table of contents of the topic “Pathology of the abdominal organs”: 1. Muscular defence. Toxic and terminal phases of acute generalized peritonitis 2. General condition during the terminal phase of peritonitis. Semiology of acute intestinal obstruction 3. Mechanical intestinal obstruction. Types of mechanical intestinal obstruction 4. Dynamic intestinal obstruction. Types of dynamic intestinal obstruction 5. Vascular intestinal obstruction. Clinic of intestinal obstruction 6. Abdomen with intestinal obstruction. Signs of intestinal obstruction 7. Asymmetrical abdomen. Palpation of the abdomen for intestinal obstruction 8. Percussion of the abdomen for intestinal obstruction. Vaginal examination for intestinal obstruction 9. Gastrointestinal bleeding. Complaints and manifestations of gastrointestinal bleeding 10. Appearance of the patient with gastrointestinal bleeding. Laboratory indicators for gastrointestinal bleeding
Osteochondrosis Treatment Center
Other reasons
If you have abdominal pain in the navel area on the right, this may be a consequence of diseases of the gallbladder, pancreas or kidneys. Tingling in this area is the primary sign of inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), which precedes other symptoms of the disease. Among the pathologies that can manifest themselves in this way are the following:
- liver dysfunction;
- ulcer of the intestinal walls or stomach;
- impaired functioning of the diaphragm;
- gallstone disease – the appearance of stones in the gall bladder.
It is important to know that malignant diseases of the small intestine can also be accompanied by pain in the right umbilical area. Painful sensations in such pathologies are characterized as aching, pulling. Moreover, they are chronic and intensify if you press on the umbilical ring. If you have pain in your abdomen above your navel on the right, immediately visit an oncologist to immediately rule out the possibility of cancer.
View gallery
Symptom: protrusion of the abdomen
Such a symptom may indicate not only errors in the diet, accompanied by flatulence and bloating, but also be the first sign of serious pathologies.
Disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the digestive system, gastrointestinal tract, muscular corset - all these conditions are accompanied by characteristic signs, among which protrusion of the abdomen forward is often observed.
What diseases can it be observed in?
- Ascites (fluid accumulation) .
With this pathology, there is an increase in the size of the abdomen and its protrusion, which decreases slightly if the patient takes a horizontal position.
Painful sensations in women
If a woman has a stomach ache at the bottom of the navel on the right, then this may indicate gynecological diseases and inflammatory processes that have begun in the genitourinary system. The most common pathologies of the endometrium. Experts are confident that this is a chronic disease that cannot be completely eliminated; one can only stop its development and the division of connective tissue cells. A characteristic feature of the disease is an increase in the inner layer of the uterus and its extension beyond the boundaries of the organ.
The key reason for the development of endometriosis, according to doctors, is hormonal imbalances that occur during puberty.
Pathologies of the hormonal type can also include endometrial hyperplasia. This disease is characterized by enlargement and thickening of tissue. This pathology has specific symptoms, so identifying it is not difficult. Endometrial hyperplasia manifests itself:
- uterine bleeding that does not go away for more than a week;
- pale skin;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen and near the navel on the right or below;
- elevated temperature;
- anemic signs;
- general malaise and poor health;
- dizziness and headaches;
- low blood pressure.
Stopping bleeding in such pathologies is usually done only by curettage. This method can also be used to diagnose the disease. Using a special surgical instrument - a curette, or using a vacuum, the specialist removes the endometrium completely and sends it for histological analysis.
In addition to the above reasons, the stomach on the right below the navel may hurt due to the development of the following diseases:
- cervical erosion;
- cystitis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- fibroid (myoma) of the uterus;
- inflammation of the appendages or ovaries;
- pyelonephritis.
Be careful and pay attention, if even after treatment of the pathology the pain is present or intensifies, immediately visit an oncologist to prevent or exclude gynecological cancer.
View gallery
Abdominal examination
In this case, the stomach “blurs” on the sides, this is especially typical for patients with weak abdominal wall muscles. In medicine, this type of abdomen is also called “frog”. When the body is positioned vertically, a large fold appears in the lower abdomen, which sags due to fluid circulation.
With constant stooping, which appears as a result of weakness of the spinal muscles, the spine bends forward, as a result of which the stomach “folds” in half, forming two (sometimes more) folds. Even with well-developed abdominal muscles, with kyphosis, a moderate protrusion of the abdomen will still be observed, since the muscle walls are in a relaxed state.
The cause of this condition is inflammatory and infectious processes occurring in the body, so if such a symptom is detected, you should go to the hospital for immediate diagnosis and treatment. In some diseases (for example, infectious mononucleosis), the spleen may rupture, so self-treatment for abdominal protrusion is unacceptable.
In the presence of tumors of various etiologies, asymmetry of the abdomen is observed, which appears as a result of protrusion of the anterior part of the abdominal wall in places where the pathogenic process is localized. If this phenomenon is observed in the lateral part, this may indicate cysts that appear mainly in the ovaries and pancreas, spreading into the abdominal cavity.
Protrusion of the abdomen occurs due to severe flatulence, in some cases it may be accompanied by the presence of peristaltic waves at the location of the pathological process.
With rickets, deformation of the shape of the legs, pelvic bones, as well as curvature of the spine can occur, which causes protrusion syndrome of the abdominal wall.
There are many other reasons that this symptom may indicate. It is impossible for an ordinary person to determine which disease caused the appearance of this symptom, since this requires a full examination and laboratory testing.
The Dolphin Clinic employs only competent specialists who will help determine the cause of the disease and also draw up a detailed treatment plan taking into account all the features of the disease.
All treatment methods used in our clinic are conservative in nature, that is, they are performed without surgical intervention.
Site Map
Home » Symptoms » Asymmetrical protrusion of the abdomen
First aid for pain
Before visiting a doctor, do not take any medications under any circumstances. If the painful sensations are not pronounced and tolerable, then you can use antispasmodic drugs one-time: “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”, “Papaverine”.
If after some time your stomach hurts to the right of your navel when pressed, you should seek help from a medical facility. If the pain is caused by poor nutrition, for example, an addiction to excessively fatty foods or overeating, you can eliminate the unpleasant symptom with special digestive enzymes. This is the drug “Mezim”. Two tablets for an adult will be enough.
View gallery
There are indeed many causes of pain that occurs in the right umbilical region: from simple overeating to serious diseases, such as appendicitis or even oncology. So, you should not ignore an unpleasant symptom or self-medicate. It is better to consult a doctor in time, undergo a full examination to make an accurate diagnosis and immediately begin competent and effective treatment. This way you can promptly eliminate the consequences of the disease and prevent possible complications.
From this article we can conclude that pain near the navel can be a symptom of very serious diseases that are dangerous to human life. Therefore, you should not take this phenomenon lightly.
Asymmetrical abdominal protrusions
Asymmetrical protrusions of the abdomen occur with tumors, cysts, inflammatory infiltrates, isolated intestinal bloating (Wal's symptom), asymmetric contraction of the abdominal muscles. Asymmetric contraction of the abdominal muscles with displacement of the white line occurs with perforated peritonitis (ulcers, appendicitis).
Asymmetry due to relaxation and even atrophy of the abdominal wall in the right half is observed in chronic appendicitis (Volkovich's symptom).
Asymmetry caused by tumors, cysts, and swelling is first differentiated by the presence of tympanitis inherent in the swollen loop.
Thus, isolated swelling in the left iliac region often occurs during volvulus of the sigmoid colon; high tympanitis is determined above the swelling.
An elastic, elastic formation resembling a ball, with high tympanitis, located in the epigastrium, is detected with acute dilatation of the stomach (Schwartz's symptom).
Causes of pain in a child
Children, due to their age, cannot clearly describe the painful sensations experienced in the body. This makes it difficult for the doctor to determine the source of the pathology.
Newborns often suffer from colic, increased gas production, intestinal blockage and other manifestations of digestive system disorders, which resolve on their own after they reach six months.
Starting from the 7th month, a child may develop gastroenteritis, which is often accompanied by diarrhea, vomiting, fever, poor health and loss of appetite.
Additional causes of pain in adolescents:
- Pneumonia.
- Urogenital infections.
- Intestinal disorders.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Constipation.
- The beginning of menstrual activity (cycle) in girls.
- Abdominal migraine. The main manifestation of this disease is the occurrence of painful sensations that are localized in the navel. Prolonged attacks are characterized by the appearance of vomiting, flatulence, nausea, and headache. Often, a consultation with a neurologist is required to make a correct diagnosis. An exacerbation of the disease occurs twice a year, and the rest of the time it proceeds as usual.
- Chronic enteritis, in which the small intestine becomes inflamed. A dull (aching) pain occurs in the navel area. After any meal, the child begins to feel heaviness, bloating, and gas.
- Intestinal volvulus. The disease is characterized by attacks of acute pain, which are localized in the right side of the abdomen and in the navel area.
Regardless of the patient’s age, one of the insidious diseases that is characterized by the appearance of pain in the navel is oncology. In such cases, appropriate therapy is required only in specialized institutions, so attempts at self-medication can lead to dangerous consequences.
READ MORE: Pain around the navel in women after eating. Pain after eating in the navel area
Abdominal asymmetry
If these symptoms are combined with urge, but no vomiting, or obstruction of the gastric tube (Borchard's triad), then they are observed with gastric volvulus.
Bloating in the right iliac region is characteristic of the cecum, and is also observed with obstruction of other parts of the colon, most often the ascending and transverse colon.
Protrusion in the epigastrium can also be caused by suprastenotic expansion of the stomach and is accompanied by a pronounced splashing noise. When the probe is inserted, liquid is released first, and then the remains of decomposing food.
A. Olshanetsky, A. Svidler
“Asymmetrical abdominal protrusions” and other articles from the section Symptoms of diseases
Additional information from the section
Prev.ContentsNext
In the coordinated interaction of the body's organs, each part of the body plays its role. All these numerous parts of the body are so interconnected that any defect in one of them affects all the others.
It is possible to study the action of some of the main parts of the body, such as the mind, heart, etc.
According to the teachings of yoga, the most important thing in the system is “man”. It is he who ensures the proper performance of their tasks by all seventy-two thousand nerves and arteries spreading throughout the body.
We take many precautionary measures to protect our body from all kinds of infections. These measures also include physical exercise. But if it is damaged, then all these measures will only be a waste of time and effort.
If the navel has moved out of its position, then this alone becomes the cause of many diseases that usually remain undiagnosed.
Erroneous treatment undertaken by unqualified people causes new complications, and as a result of illiterate massage, the navel may become displaced.
For our current doctors and healers, the complications caused by the displacement of the navel remain a mystery, and the patient eventually learns to endure his pain patiently. Doctors are unable to provide him with the help he needs, and he is content with an incorrect diagnosis and a course of treatment that does not bring any benefit. Those who want to get rid of diseases caused by navel displacement and also want to benefit from exercises should have their navel examined by a specialist.
Our sacred Upanishads say:
Causes of navel displacement
It is noticed that the navel usually moves from its original position after lifting something heavy or falling from a height.
This entails a displacement of the navel above its original position. If the navel has shifted to the right, left or tilted, then the cause should be sought either in the shifting of the body's center of gravity to one of the legs, or in shaking the body.
If the push falls on the left leg, then the navel moves to the right, and vice versa.
Why does my stomach hurt in the navel area{q} Types and location of pain
If discomfort in the navel area occurs for the first time and does not bother the patient much, there is no need to rush to the hospital. Moreover, if the person himself suspects that this is a consequence of overeating or eating certain foods.
A leisurely walk in the fresh air followed by rest, drinking clean drinking water without gas and unloading the digestive organs by refusing food for several hours will help alleviate the condition.
To help your intestines, you can drink unsweetened herbal tea with the addition of mint or lemon balm, brew chamomile or a gastrointestinal tea, which are freely available in pharmacies.
Many people prefer to treat themselves with tablets, because symptomatic remedies for abdominal pain, along with herbs, are available without a prescription. You can relieve pain in the navel using the following medications:
- No-Shpa - 1-2 tablets per dose up to 3 times a day;
- Buscopan - 1-2 tablets per dose 3 times a day;
- Mebeverine or Duspatalin - 1 tablet 3 times a day;
- Meteospasmil - 1 tablet 3 times a day.
All of the drugs listed above belong to the group of antispasmodics. They eliminate the most common cause of abdominal pain - smooth muscle spasm. Such drugs act simultaneously on the stomach, intestines, gallbladder muscles and bile ducts.
They are safe remedies, but can be used as self-medication for abdominal pain for no longer than 2-3 days. If after this time the problem is not solved, you need to consult a doctor.
You can get rid of unpleasant sensations with adsorbents. They help eliminate excess gases in the intestines, acid in the stomach, and eliminate harmful toxins if the pain is caused by bacteria. At home you can take:
- activated carbon - 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight 3 times a day;
- Sorbex - 1-2 capsules 3 times a day;
- Enterosgel - 1 tablespoon 3 times a day;
- Atoxil - 1 packet, dissolved in a glass of water, up to 3 times a day.
To eliminate excess gas formation, take simethicone preparations (Espuzin, Espumisan) 2 capsules 3 times a day. For children, such products are used in the form of drops.
If abdominal pain is caused by disturbances in intestinal motility, drugs from the group of prokinetics Motorix, Motilium, Domrid or Ganaton will help, take 1 tablet half an hour after a meal.
Antispasmodics, adsorbents and prokinetics are not advisable to take for symptoms of “acute abdomen” - sharp and intense pain, accompanied by stool disorders and vomiting.
Pain in the navel area when pressed can be of different types. It can be aching, sharp, dull or sudden. Just like the pain itself, the causes of its occurrence can be varied.
Pain in the navel area may be accompanied by the following diseases:
- intestinal colic;
- umbilical hernia;
- intervertebral hernia;
- stones coming out;
- appendicitis;
- gynecology.
Intestinal colic
When the stomach hurts in the navel area, pain due to intestinal colic is caused by a spasm of the small or large intestine. It may be caused by diarrhea or constipation.
Also, do not forget about dysbiosis and digestive disorders. Pain in this case occurs as a result of compression of the intestinal muscles. The stronger the pain, the stronger the muscle compression.
Intestinal colic in newborns is common.
It is impossible to name any universal methods for treating such a phenomenon as intestinal colic. To get rid of pain, you can use medication.
After the pain has subsided, you will need to seek help from a doctor.
Umbilical hernia
Pain in the navel area when pressed may be caused by an umbilical hernia. Pain is present around the navel. Very often this disease is observed in children.
The pain is very acute, since the hernia puts pressure on the stomach and when food enters it, pressure occurs on the umbilical hernia. To determine an umbilical hernia in babies, you need to undergo a course of examination.
An umbilical hernia in a child can close before he reaches 12 years of age, that is, in some cases it does not require surgical intervention.
The symptoms of this disease directly depend on the size of the hernia. Obesity can also cause an umbilical hernia. In some cases, the hernia may be represented by a fatty omentum, but there will be no pain or signs of the presence of this type of hernia.
An intervertebral hernia that occurs in the lumbar region can cause quite severe pain in the navel area. The nerve endings of the spine are located too close to the digestive tract.
During the transmission of impulses, pain will appear, which is aching in nature and occurs when a person has been sitting or walking for too long.
Since the hernia is located between the vertebrae, friction between them can create such transmitted impulses.
The body’s ability to remove stones from any organ independently or using various methods can also cause pain.
The pain when stones pass is long-lasting and accompanies a person until the stone is completely released through the genitourinary system.
READ MORE: Pain in the solar plexus (in the solar plexus area): possible causes
If the stone comes out of the left kidney, then pain will appear in the navel area on the left. If the stone comes out of the right kidney, there will be pain in the navel area on the right.
All this is due to the fact that the stone, during its release, irritates the walls of the ureters and creates an uncomfortable state for the person. In this case, it is possible to reduce the pain threshold with the help of medications, but very rarely.
Appendicitis
This disease occurs completely suddenly. It is impossible to prepare for its appearance. Appendicitis is considered the cleansing organ of the human body.
In simple words: appendicitis is a container in which various harmful substances for the body accumulate. After such a peculiar container is already overfilled, a displacement of all the organs of the digestive tract occurs.
In this case, the pain in the navel area when pressed will be acute.
The main signs of appendicitis are high fever, nausea, and vomiting. Sometimes diarrhea or constipation occurs. It all depends on the body. The most important thing is to call an ambulance in time.
If this is not done, appendicitis may rupture, and then a series of operations will have to be performed to cleanse the organs of toxins that are located close to this organ.
No matter how paradoxical it may sound, pain in the navel area can be caused by acute diseases of the reproductive system. As a rule, women are susceptible to such diseases. The ovaries play the main role in the occurrence of such pain.
If a cyst forms on one of them or has already formed, then over time it will break through. The fluid from this formation enters the intestines.
In this case, you will need to call an ambulance. Only after a thorough examination will it be possible to determine the reason for the pain in the navel area.
A process such as pain must be approached quite responsibly. You need to go through a number of procedures:
- take a blood test for the presence of inflammatory processes;
- do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- x-ray (alternative to ultrasound);
- take a urine test.
All such tests are capable of identifying inflammatory processes in the body and in which organ they occur.
Treatment methods depend directly on the definition of the disease. It cannot be said that there are universal methods that can relieve pain in the navel area.
You can take painkillers, but their effect will be temporary. It is best to see a doctor for an examination.
The reasons why the stomach hurts below the navel are quite numerous. Soreness under the belly button is a fairly common symptom that indicates existing health problems.
Poor functioning of the jejunum is accompanied by a state of malabsorption and this has a very negative impact on overall well-being. That is why prolonged pain below the umbilical area and around is a symptom that requires urgent medical advice.
The most common causes of this pathological condition are the following diseases:
- lack of jejunal patency;
- circulatory disorders of the mesenteric vessels;
- jeunitis - an inflammatory process in the jejunum;
- umbilical hernia – pain develops as a result of its strangulation;
- enzyme deficiency;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
Each pathology, in addition to pain in the umbilical area, is characterized by certain symptoms.
Lack of jejunal patency is one of the most severe conditions. If medical care is not provided, it can cause death. A blockage of the intestinal lumen can be caused by a stone, a tumor, a lump of worms, or squeezing it from the outside, for example, by adhesions.
Jejunal obstruction most often develops as a result of intussusception.
In a child, pathology can be provoked by intussusception - penetration of an intestinal loop into the neighboring intestine. A symptom of the pathology is increasing cramping pain in the middle of the abdomen.
Uncontrollable vomiting, which also includes intestinal contents, brings relief only for a short period of time. There is also stool retention and passing of gas.
Abdominal examination. Distinctive signs of abdominal enlargement with ascites, obesity and flatulence.
Typically, in men, the navel moves to the left, and in women, to the right.
1. For men: The patient should first be placed on the ground with only the buttocks on the ground and the head and legs elevated one foot (about 30 cm) above the ground. This position is called (photo 96). Then the head and heels gradually lower to the ground. This is the “corpse pose.” The examiner then places one end of the cord on the patient's navel and applies the other end to each nipple in turn (Plate 97).
Photo 96.
Photo 97.
If the distance from the navel to each nipple is the same, then the umbilical center is not displaced. If there is even a slight difference, then the navel is displaced from its original position. Thus, this measurement examination will reveal the actual position of the navel. To return the navel to its original position, you must use the services of a specialist.
Only after this, but not before, can you begin the physical exercises of yoga.
2. For women: the patient must perform both poses sequentially - and the heels of the feet must be moved together, while the toes must be directed in opposite directions. Then one end of the cord is aligned with the navel, and the second alternately with the right, then with the left big toes. If there is a difference in distance, it means that the navel is in the wrong position (Photo 98).
Photo 98.
3. For men and women: When the patient has assumed the corpse pose after the pose, the examiner should clasp the five fingers of his hand and place them on the patient's navel (Plate 99). If it turns out that the navel is pulsating at the center of the connection of the five fingers, like a heart, then everything is in order.
If the beating of the navel is not felt in this place, it does not function normally.
The true position of the navel is where it is felt pulsating at the center of the joint of the five fingers.
Photo 99.
Objective research
Physical examination of the small intestine includes inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation.
Examination of the abdomen reveals flatulence.
When all or most of the loops of the small intestine are overfilled with gases (for example, with fermentative or putrefactive dyspepsia), uniform bloating of the abdomen is determined, especially in its central part (peri-umbilical). When gas distends one or more intestinal loops (obstruction), flatulence is usually local in nature and for the duodenum is detected in the upper part of the right half of the abdomen, for the jejunum - in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen or in the mesogastric region, and for the ileum in the right ileal region or lower abdomen.
Limited abdominal bloating due to stretching of the intestinal loop above the site of obstruction is known as Wahl's sign. In malnourished subjects, increased peristalsis of the small intestinal loops (obstruction, neurosis) may be visible through the anterior abdominal wall. With mepanic intestinal obstruction, increased intestinal peristalsis, which is accompanied by attacks of pain and in exhausted people is visible through the anterior abdominal wall, can be provoked by light tapping on the corresponding area of the abdomen.
Sometimes, with damage to the small intestine, especially with the involvement of the serous integument, superficial palpation can reveal local resistance of the anterior abdominal wall and hyperesthesia of its skin with predominant localization in the area on the left above the navel (Zakharyin-Ged zone).
With deep palpation, only the terminal segment of the small intestine is usually accessible to palpation, which is determined in the right iliac region and is located from the inside to the outside and from bottom to top to the point of confluence with the cecum.
Palpation of the terminal segment of the small intestine is carried out perpendicular to its long axis. In this case, the examiner’s right hand is at an obtuse angle to the cecum.
During inhalation, they penetrate with four bent fingers of the hand, lying with the palm, flat on the stomach, to the posterior abdominal wall, then slide along the abdomen of the psoas muscle from above and from the inside down and out, while rolling through the terminal segment of the small intestine, which is usually determined within 10 - 12 cm or, less often, 25 - 30 cm in the form of a moderately mobile smooth cylinder as thick as the little finger.
The terminal segment of the small intestine is palpable in 75 - 80% of healthy people.
When involved in a pathological process, it can be painful, spasmodic on palpation, less often stretched, rumbling or compacted, lumpy, and clearly shaped.
The remaining parts of the small intestine are inaccessible to palpation. Only in rare cases is it possible to palpate a randomly located segment of the small intestine in the left iliac region inside the sigmoid colon. However, when the small intestine is affected, palpation in the mesogastric region can reveal pain, which is often more pronounced on the left and above the navel - the Porges area.
Only tumors of the small intestine that have reached a significant size and are growing outward can sometimes be detected outside the terminal segment of the small intestine.
Neoplasms arising from the ileum are often more accessible to detection during rectal and vaginal examination.
Damage to the small intestine is usually indicated by loud rumbling in the cecum during palpation, which is associated with the filling of the intestine with gas and liquid unabsorbed contents (symptom of enteritis according to V.
P. Obraztsov).
Percussion of the abdomen over gas-inflated loops of the small intestine reveals tympanitis. With stenosis of the small intestine, the swollen overlying loops are filled with fluid and give a dull sound during percussion, which moves when the patient changes position; during succussion, a loud splash is detected - Mathieu's symptom.
When the serous membrane of the small intestine is involved in the pathological process, percussion over its corresponding parts is painful.
Auscultation of the abdomen may reveal loud rumbling and gurgling, which is mainly associated with a violation of the processes of secretion and absorption in the small intestine, as well as with increased motility.
When suppressed, bowel sounds may disappear (complete intestinal obstruction, peritonitis). Under normal conditions, periodic, smooth bowel sounds are heard.
With severe stenosis of a section of the intestine at the site of its localization, a loud rumbling is periodically heard, often even at a distance, associated with the passage of liquid contents through the narrowed area during the emptying of the stretched suprastenotic loop, the presence of which is manifested by an attack of pain and local bloating, usually preceding the rumbling and disappearing with its appearance - Koenig syndrome.
With sufficiently extensive lesions of the small intestine due to impaired resorption of most nutrients, various hypovitaminosis and trophic disorders can be observed.
Objective signs of malabsorption syndrome include emaciation, pallor of patients, decreased turgor, dryness and flaking of the skin, the presence of a kind of dermatitis of the face (wings of the nose, nasolabial folds, ears, lips), the appearance of swelling on the legs, less often in the lumbar region and other places, changes in shape, transverse striations and increased brittleness of nails, tarnishing and behavior of hair, angular stomatitis, glossitis, loosening and bleeding gums.
The gray-dirty color of closed areas of the skin is determined, especially in places of natural deposition of pigment (nipple areolas, scrotum, perineal area, linea alba) and the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue, fold lines of the palms and soles (signs of adrenal insufficiency), as well as hyperpigmentation of open skin areas - face, neck, dorsum of hands (pellagrossic dermatitis).
Pain from gynecology in the lower abdomen
Aching pain is characteristic of inflammation of a tumor and chronic nature. If there is sharp pain - this is inflammation in the acute phase, a visit to the doctor is necessary. Pain is felt near the perineum, inside the thighs and in the rectum.
Pain at the bottom of the navel during a missed period is a clear sign of an ectopic pregnancy. The woman feels severe pain just below the navel, and heavy internal bleeding begins; some blood may come out through the vagina. Treatment is to immediately remove the fallopian tube and prevent bleeding. If one tube is removed and the other is capable of patency, the woman is 100% able to give birth.
Question for doctors. What is the cause of abdominal asymmetry?
In advanced and severe cases, hemorrhages on the skin may occur - from small petechial rashes to significant bruising (vitamin K deficiency).
see also
- Primary ulcers of the small intestine
- Primary ulcers of the small intestine In 1805
Baillie was the first to describe damage to the small intestine with ulcers that superficially resemble those of gastric and duodenal ulcers.In contrast to secondary ulcers, which are the result of any disease of the small intestine (tuberculosis, tumors, ...
- Volvulus
- Volvulus Definition Volvulus is a rotation of a loop of intestine around the mesentery with subsequent necrosis of part of the intestine. Etiology and pathogenesis In the origin of volvulus, a large role is played by the condition of the mesentery, the features of its attachment, the presence of cicatricial changes that cause rapprochement...
- Sarcoma of the small intestine
- Sarcoma of the small intestine Sarcoma of the small intestine accounts for 0.5 - 0.6% of malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.
Small intestinal sarcoma accounts for 2/3 of all sarcomas of the digestive canal; they occur in 0.06-0.07% of the total number of all autopsies. Men get sick more often. They are amazed... - abdominal toad
- Abdominal angina Abdominal angina (intestinal ischemia, abdominal angina, intermittent intestinal claudication, etc.) occurs as a result of insufficient blood supply to the intestinal wall due to narrowing of the superior mesenteric artery or its branches due to atherosclerosis, obliterating endarteritis and ...
- Abdominal purpura
- Abdominal purpura Due to the increased porosity of the vessels, blood leaks into the intestinal wall and mesentery, small hemorrhages appear in the form of spots or significant hemorrhagic impregnations (hematomas).
This can lead to thickening of the intestine and narrowing of its lumen, intestinal paresis,...
Belly button pain in men: 16 main reasons for this symptom
Discomfort and pain attacks in the fart area often indicate various pathologies. To identify the cause of such sensations, the patient should consult a doctor so that a specialist can assess his general condition and analyze the severe symptoms that have appeared. The main sources of pain in the navel area:
- Unsuccessful piercing in the navel area.
- Presence of parasites.
- Intestinal pathologies, including UC (nonspecific ulcerative colitis), formed adhesions, Crohn's disease, malignant tumors. In addition, men may develop Megacolon disease with a characteristic expansion of the large intestine, causing fecal stagnation, breathing problems, and heart problems.
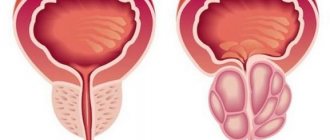
- Chronic prostatitis, which may cause pain in the umbilical area with problems with urination and hormone production characteristic of the disease.
- Diverticulosis. This disease is characterized by protrusion of the navel outward, when the intestinal mucosa erupts in some places. The pain becomes aching.
The human body is quite complex, each organ in it is interconnected. Sometimes it happens that based on the location of the pain it is not clear what disease it is associated with.
A man must understand that it is useless to treat the pain itself - it is necessary to establish why it appeared. You won’t be able to do this yourself, at home.
You will have to contact a therapist or a more specialized specialist, undergo an examination and take tests. Only then will the diagnosis be known and treatment can begin.
In most cases, pain in the lower abdomen is associated with diseases of the intestines or genitourinary system. Strong sensations that deprive you of peace and cause irritation can indicate two or three pathologies at once. Let's look at why the stomach hurts below the navel.
Intestinal pathologies
The most common cause is various intestinal pathologies or dysfunction. So, with constipation or a certain diet, flatulence may begin - increased gas formation.
The problem also arises when intestinal obstruction occurs, which can be caused by a number of diseases and conditions:
- Ulcerative colitis. The pain is localized below the navel, usually on the left. Additional symptoms are diarrhea, fever, weakness. If a man is not treated for a long time, weight loss is observed.
- Crohn's disease. In addition to discomfort in the abdomen, it can be manifested by diarrhea, weight loss, and kidney problems. Life-threatening disease.
- Adhesions - occur more often after operations or injuries, and may be a consequence of intoxication. In many cases, they are accompanied by vomiting and fever.
Pain may also indicate colorectal cancer - the development of a malignant tumor in the colon. Cancer is detected late and can be caused by various reasons, including alcohol consumption and obesity. Mortality is quite high; on average, people live 6-10 months.
Prostatitis, as well as prostate adenoma (BPH) and prostate cancer can cause pain in the lower abdomen, including in the navel area. Acute prostatitis often occurs due to injury or hypothermia.
The chronic form is caused by various bacteria, including chlamydia, trichomonas, etc. Calculous prostatitis also manifests itself with this symptom and is caused by the accumulation of stones and sand in the ducts of the prostate gland.
Pathologies in the prostate area are manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the perineum, testicles, penis, less often - in the tailbone or in the navel area;
- urinary disorders - frequent urge at night and in the morning, sluggish stream, acute urinary retention;
- problems in the reproductive system - weak or absent erection, pain after sex, decreased desire.
If there is pain under the navel and there are the symptoms listed above, this is a reason to visit a urologist or andrologist. The doctor will listen to complaints, collect anamnesis and refer for TRUS of the prostate, blood and urine donation.
Cystitis
Another cause of pain is in the lower abdomen, more often in the pubic area, less often under the navel.
The disease is caused by various bacteria and can occur after sexual intercourse, hypothermia or other factors.
Most often, the urethra is also involved in the inflammatory process, then they talk about urethro-cystitis. The kidneys may also be affected, in which case the problem is complicated by pyelonephritis.
Pain below the navel is a problem that can occur at any age and is very common among the stronger sex. In fact, it can be caused by a serious illness, so if you often experience discomfort in the lower abdomen, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Prostatitis - this is the diagnosis that specialists make if a man has pain in the lower abdomen.
The pain can be caused by swelling and inflammation of the prostate gland, as well as the gland that lies directly under the bladder and produces sperm.
With prostatitis, pain appears in the groin area, genitals, and urination becomes painful. In especially severe cases, body temperature rises and runny nose.
Constipation – in this case there is no need to worry or panic. It hurts below the navel in men - what to do {q} Drink a glass of kefir and eat prunes, or buy a carry-on drink at the pharmacy in case of emergency.
Urinary tract infections. They affect the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. In this case, you will notice that you have begun to go to the toilet much more often, there is also a burning sensation when urinating, the urine is cloudy and smells unpleasant. In some cases, fever and chills appear.
Kidney stones are small, hard deposits that look like pebbles. Symptoms include severe pain in the side, back and below the ribs, which can spread to the lower abdomen and groin.
Other common symptoms include pain during urination, a constant urge to urinate, and cloudy and foul-smelling urine.
Interstitial cystitis, or painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic condition characterized by bladder pain and pelvic discomfort that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
Bladder spasms - this is caused by involuntary contraction of the muscles of this organ, and there is a general need to urinate. Pain below the belly button is often described as a cramping or burning sensation. This may be due to a urinary tract infection.
Inguinal hernia - a bulge appears in the groin or scrotum. Swelling, a feeling of heaviness, and a burning sensation appear in this place.
Physical or sexual abuse can cause injury in any part of the pelvis, resulting in nagging pain in the abdomen. Diagnosis depends on the patient's medical history, physical examination, and appropriate laboratory tests.
Other, less common causes of pain below the belly button in men include diverticulitis, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, ulcerative colitis, sciatic nerve inflammation, and colon cancer.
If you have severe abdominal pain, we recommend that you seek medical help and call an ambulance. With correct diagnosis, the doctor will quickly make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Any disease can have several stages of development. At the very first, initial stage, the disease is usually asymptomatic.
READ MORE: The child has pain in the left side
But the sooner a doctor diagnoses the disease and prescribes a course of treatment, the better for the patient.
The intensity and location of pain depends on the pathology causing it. Sometimes pain is felt below or above the navel, sometimes on the right and left.
When figuring out why the stomach hurts in the navel area, it is worth considering that the pain syndrome can be true, that is, associated with one or another element of our body, or it can be irradiative, when the source is located in another place, but the pain radiates to the umbilical area.
- pancreatic diseases;
- gastritis;
- obstruction of the intestines, urinary tract;
- Crohn's disease;
- inflammation of the intestinal diverticulum;
- stomach ulcer;
- problems in gynecology;
- volvulus;
- umbilical hernia;
- hepatitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
The correct solution to the problem that has arisen directly depends on understanding the causes of the pain syndrome. Severe or aching pain in the abdomen in the navel area varies in location, which to some extent facilitates the diagnosis.
The peritoneum contains many nerve endings that respond to the smallest damage to internal organs. A feeling of discomfort above the umbilical region, accordingly, indicates diseases of those systems that are located in the upper abdomen:
- The most common cause of pain is stomach disease. With gastritis, the patient complains of clear and pronounced pain, which is often accompanied by cramps, nausea, vomiting, pale skin, and a feeling of dry mouth. With a stomach or duodenal ulcer, pain is observed in the morning or in the intervals between meals.
- Diseases of the pancreas are another reason why the stomach hurts in the navel area and above. Pathologies such as pancreatitis or a tumor may well cause periumbilical pain.
- Like gastritis, stomach cancer also begins with painful conditions, but later the patient’s well-being deteriorates significantly, he loses his appetite, experiences an aversion to food, loses weight, becomes lethargic and apathetic.
Examination of the patient
Examination of patients with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract ( GIT)
) allows you to identify emaciation, pallor, roughness and decreased turgor of the skin in malignant tumors of the stomach and intestines.
But most patients with stomach diseases do not have any visible manifestations. When examining the oral cavity in patients with acute and chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines, a white or brown coating is detected on the tongue. In diseases accompanied by atrophy of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, the mucous membrane of the tongue becomes smooth, devoid of papillae (“lacquered tongue”).
These symptoms are nonspecific, but they reflect the pathology of the stomach and intestines.
Examination of the abdomen begins with the patient lying on his back.
The shape and size of the abdomen, respiratory movements of the abdominal wall and the presence of peristalsis of the stomach and intestines are determined. In healthy people, it is either slightly retracted (in asthenics) or slightly protruded (in hypersthenics). Severe retraction occurs in patients with acute peritonitis. Significant symmetrical enlargement of the abdomen can occur with obesity, bloating (flatulence) and accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
Obesity and ascites differ in several ways. With ascites, the skin on the abdomen is thin, shiny, without folds, the navel protrudes above the surface of the abdomen. In obesity, the skin on the abdomen is flabby, with folds, and the navel is retracted. Asymmetrical enlargement of the abdomen occurs with a sharp enlargement of the liver or spleen.
Respiratory movements of the abdominal wall are well determined when examining the abdomen.
Pathological is their complete absence, which most often indicates diffuse peritonitis, but can be with acute cholecystitis and appendicitis. Stomach peristalsis can be detected only with pyloric stenosis (cancerous or scar), intestinal peristalsis - with narrowing of the intestine above the obstruction site.
Diagnostic measures
If you have a stomach ache near the navel on the right for a long time, and the discomfort regularly intensifies, then you should visit such doctors as:
- proctologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- surgeon;
- gynecologist;
- oncologist.
If there are no serious symptoms that could indicate dangerous diseases, then the examination can begin with a visit to a therapist. He will conduct a visual examination, palpate the abdominal cavity and collect all data on the patient’s general well-being.
View gallery
After initial information about the disease has been collected, the patient must undergo other diagnostic examinations. Here's what they can be:
- ultrasonography;
- abdominal x-ray;
- colposcopy or biopsy in women;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- if cancer is suspected, tests for tumor markers.
Palpation of the abdomen
The abdomen is a part of the body that is the abdominal cavity, where the main internal organs are located (stomach, intestines, kidneys, adrenal glands, liver, spleen, pancreas, gall bladder).
Two methods of palpation of the abdomen are used: superficial palpation
and
methodical deep, sliding palpation
according to V.V. Obraztsov and N.D. Strazhesko:
- Superficial (approximate and comparative) palpation allows us to identify tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, localization of pain and enlargement of any of the abdominal organs.
- Deep palpation is used to clarify symptoms identified during superficial palpation and to detect a pathological process in one or a group of organs.
Diagnosis and treatment
If there is severe pain in the navel area, it is not recommended to make any attempts at home to eliminate the symptoms. You need to call a doctor.
Taking painkillers and laxatives, compresses, using enemas, heating pads before the arrival of a specialist is contraindicated. This can complicate the diagnosis.
The source of pain is determined by the doctor based on examination of the patient, clarification of the nature, intensity of pain, and duration of attacks. Additional examinations may include urine, stool, blood tests, ultrasound, and colonoscopy.
To relieve unpleasant symptoms caused by intestinal pathologies, a specialist may prescribe drugs such as Smecta, Polyphepan, and Activated Carbon.
Doctors do not recommend using traditional medicine until the cause of pain in the navel is determined. After consultation with your doctor, you can use the following popular methods:
- Dissolve a spoonful of honey in plain water and drink the drink on an empty stomach. This method prevents the development of pain and improves intestinal motility.
- Add 500 g of rowan berries to 300 g of sugar, leave for 5 hours, and then boil for half an hour (over low heat). It is enough to take the medicine three times a day before meals (2 tablespoons each).
To prevent pain in the navel area, existing diseases should be identified and treated in a timely manner, and chronic pathologies should not be aggravated.
Changing the shape of the abdomen - crooked, gassy belly
When examining and palpating the abdomen, it is recommended to use clinical topography diagrams of the abdomen.
The principle of the superficial palpation method
Palpation is carried out by applying gentle pressure with the fingers of the palpating hand placed flat on the abdominal wall. The patient lies on his back on a bed with a low headboard. Arms are extended along the body, all muscles should be relaxed. The doctor sits to the right of the patient, who must be warned to let him know about the occurrence and disappearance of pain.
Approximate palpation begins from the left groin area. Then the palpating hand is moved 4–5 cm higher than the first time, and further into the epigastric and right iliac region.
For comparative palpation, studies are carried out in symmetrical areas, starting from the left iliac region, in the following sequence: iliac region left and right, periumbilical region left and right, lateral abdomen left and right, hypochondrium left and right, epigastric region left and right of the white belly lines.
Superficial palpation ends with examination of the linea alba (the presence of a hernia in the linea alba, separation of the abdominal muscles).
In a healthy person, upon superficial palpation of the abdomen, pain does not occur, and tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall is insignificant.
Severe diffuse soreness and muscle tension over the entire surface of the abdomen indicates acute peritonitis, limited local soreness and muscle tension in this area indicate an acute local process (cholecystitis - in the right hypochondrium, appendicitis - in the right iliac region, etc.).
P.). With peritonitis, the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom is detected - increased abdominal pain when the palpating hand is quickly removed from the abdominal wall after light pressure. When tapping the abdominal wall with a finger, local pain can be detected (Mendelian symptom).
Accordingly, local protective tension of the abdominal wall is often detected in the painful area (Glinchikov’s symptom).
Muscular protection in duodenal and pyloroantral ulcers is usually determined to the right of the midline in the epigastric region, in case of an ulcer of the lesser curvature of the stomach - in the middle part of the epigastric region, and in case of a cardiac ulcer - in its uppermost section at the xiphoid process.
According to the indicated areas of pain and muscle protection, zones of Zakharyin-Ged skin hyperesthesia are identified.
Principles of deep sliding palpation
The fingers of the palpating hand, bent at the second phalangeal joint, are placed on the abdominal wall parallel to the organ being examined and, after the formation of a superficial skin fold, which is subsequently necessary for the sliding movement of the hand, carried out in the depths of the abdominal cavity along with the skin and not limited by the tension of the skin, they sink deeply when exhaling into the abdominal cavity.
This must be done slowly without sudden movements over 2-3 inhalations and exhalations, maintaining the achieved position of the fingers after the previous exhalation. The fingers are immersed to the back wall so that their ends are located inward from the palpated organ. The next moment, the doctor asks the patient to hold his breath as he exhales and performs a sliding movement of the hand in a direction perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the intestine or the edge of the stomach.
When sliding, the fingers bypass the accessible surface of the organ. Elasticity, mobility, pain, the presence of compactions and lumpiness on the surface of the organ are determined.
The sequence of deep palpation is: sigmoid colon, cecum, transverse colon, stomach, pylorus.
Palpation of the sigmoid colon
The right hand is placed parallel to the axis of the sigmoid colon in the left iliac region, a skin fold is collected in front of the finger, and then, during the patient’s exhalation, when the abdominal muscles relax, the fingers gradually sink into the abdominal cavity, reaching its posterior wall.
After this, without weakening the pressure, the doctor’s hand slides along with the skin in a direction perpendicular to the axis of the intestine, and rolls the hand over the surface of the intestine while holding the breath. In a healthy person, the sigmoid colon is palpated in 90% of cases in the form of a smooth, dense, painless and non-rumbling cylinder 3 cm thick. In pathology, the intestine can be painful, spastically contracted, lumpy (neoplasm), strongly peristaltic (obstruction below it), motionless during fusion with mesentery.
With the accumulation of gases and liquid contents, rumbling is noted.
Palpation of the cecum
The hand is placed parallel to the axis of the cecum in the right iliac region and palpation is performed. The cecum is palpated in 79% of cases in the form of a cylinder, 4.5–5 cm thick, with a smooth surface; it is painless and slightly displaceable. In pathology, the intestine can be extremely mobile (congenital elongation of the mesentery), immobile (in the presence of adhesions), painful (in inflammation), dense, lumpy (in tumors).
Palpation of the transverse colon
Palpation is carried out with both hands, i.e.
e. by the method of bilateral palpation. Place both hands at the level of the umbilical line along the outer edge of the rectus abdominis muscles and palpate. In healthy people, the transverse colon is palpated in 71% of cases in the form of a cylinder 5–6 cm thick, easily dislocated. In pathology, the intestine is palpated dense, contracted, painful (with inflammation), lumpy and dense (with tumors), sharply rumbling, increased in diameter, soft, smooth (with narrowing below it).
Palpation of the stomach
Palpation of the stomach is very difficult; in healthy people it is possible to palpate the greater curvature.
Before palpating the greater curvature of the stomach, it is necessary to determine the lower border of the stomach using the ausculto-percussion method or the ausculto-affriction method.
- Ausculto-percussion
is carried out as follows: a phonendoscope is placed over the epigastric region and, at the same time, quiet percussion is performed with one finger in a direction radial from the stethofonendoscope or, conversely, to the stethoscope.The border of the stomach is located by listening to a loud sound.
- Ausculto-affriction
– the percussion blow is replaced by a light intermittent glide over the skin of the abdomen. Normally, the lower border of the stomach is determined 2–3 cm above the navel. After determining the lower border of the stomach using these methods, deep palpation is used: a hand with bent fingers is placed on the area of the lower border of the stomach along the white line of the abdomen and palpation is performed.The greater curvature of the stomach is felt in the form of a “roller” located on the spine. Pathology reveals prolapse of the lower border of the stomach, pain on palpation of the greater curvature (with inflammation, peptic ulcer), and the presence of a dense formation (stomach tumor).
Palpation of the pylorus
Palpation of the pylorus is carried out along the bisector of the angle formed by the linea alba and the umbilical line, to the right of the linea alba.
The right hand with slightly bent fingers is placed on the bisector of the indicated angle, a skin fold is collected in the direction of the white line and palpation is performed. The pylorus is palpated in the form of a cylinder, changing its consistency and shape.
Intestinal pathologies
Half of all cases where a patient has abdominal pain to the right of the navel is the result of problems with intestinal function. The cause may be diseases such as:
- irritable bowel syndrome is a functional type of intestinal disorder that periodically worsens, then goes into remission, and then takes a chronic form (the disease is diagnosed if the intestines do not function as they should for more than 3 months, and this is not accompanied by infectious or organic causes) ;
- colitis is an inflammatory process of the outer epithelial layer of the intestinal wall;
- intestinal obstruction - a condition that is characterized by a disruption in the transport of food through the digestive tract due to the fact that the intestinal walls stop contracting;
- enteritis is a pathology in which the absorption of nutrients by the walls of the small intestine is disrupted, and the cellular layer of the mucous membranes atrophies;
- diverticulitis is an inflammatory pathology in the intestines, which is characterized by the appearance of special pouch-like formations in the organ cavity, similar to hernias. For all these reasons, the stomach to the right of the navel may hurt.
Poor nutrition, large amounts of salt and harmful chemical additives in the daily menu, smoking, consumption of large quantities of ethanol, disturbed intestinal microflora - all this also greatly contributes to the occurrence of discomfort in this area. In some cases, if the patient has recently undergone a long course of treatment with antibiotics and other antibacterial drugs, pain may be an adverse reaction to the medications.
It is also worth saying that in women who regularly torment themselves with various diets and significant dietary restrictions, abdominal pain becomes chronic. To avoid this, you need to plan your diet wisely. The daily menu should include foods such as meat, poultry, fish, chicken or quail eggs, milk, berries, fruits, nuts and herbs.
View gallery
Percussion of the abdomen
The value of percussion in the diagnosis of gastric diseases is small.
Using it, you can determine Traube's space (the area of tympanic sound on the left in the lower part of the chest, caused by the air bubble of the fundus of the stomach).
It can be increased when there is a significant increase in the air content in the stomach (aerophagia). Percussion allows you to determine the presence of free and encysted fluid in the abdominal cavity.
With the patient positioned on his back, quiet percussion is performed from the navel towards the lateral abdomen. Above the liquid, the percussion tone becomes dull.
When the patient turns on his side, free fluid moves to the lower side, and above the upper side the dull sound changes to tympanic. Encapsulated fluid appears with peritonitis limited by adhesions. Above it, during percussion, a dull percussion tone is determined, which does not change localization when changing position.
Preventive measures
For chronic diseases of the internal organs, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity at least once a year to monitor the state of health. Some autoimmune diseases are hidden, so it is almost impossible to detect them without patient complaints. The same applies to malignant neoplasms.
It is recommended to do antiparasitic prevention once a year using herbal preparations or herbal collection. The course is at least 21 days.
The infection can be acquired by drinking dirty water, unwashed vegetables or fruits, exotic foods or raw eggs. It is recommended to wash store-bought vegetables or fruits with soap and water before consuming them.
- Pain in the abdomen on the right at the level of the navel
- Abdominal pain above the navel: causes, treatment. What to do if there is pain above the navel?
- A woman's lower abdomen hurts, causes are on the right
- Abdominal pain above the navel: causes, treatment. What to do if there is pain above the navel?