If a person is constantly bothered by pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, this indicates that pathological processes are occurring in the organ that lead to this condition and a deterioration in the quality of life. What diseases provoke pain in the intestinal area, what to do if the disease often bothers you, what methods will help you get rid of discomfort, and why should you see a doctor and not self-medicate?
Reasons for appearance
The factor that most often provokes acute painful sensations in the abdominal area on the right or left is heavy and poor-quality food. If you eat spicy, fatty and fried foods every day, your intestines will begin to give signs that something is wrong with it. A person experiences excessive gas formation, colic, pain, and problems during bowel movements. Foods to which the patient has an allergic reaction also cause pain. The substances of such food are poorly absorbed by the intestines, fermentation begins, gas formation and painful sensations appear in the left or right region of the abdomen; when a person has a bowel movement, pain bothers him, constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
Aching pain and discomfort in the intestinal area also occurs as a result of stressful situations, when there are problems with the spine, with infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, and when the patient has congenital anomalies of organ development. Malfunctions in the functioning of the organ also appear as a consequence of the abuse of alcoholic beverages, smoking, and the use of narcotic substances. Hormonal changes in women also play a role in intestinal function, and fluctuations in hormones cause intestinal upset, pain, and other uncomfortable sensations.
Acute pain and cramping in the intestinal area also appears as a result of a disease of the organ itself, when inflammatory, erosive and other pathological processes occur in it, the pain is not concentrated in a specific area, it manifests itself on both the left and right sides. If dietary restrictions have not brought results , the pain intensifies, especially aches at night, this indicates that a person is developing a dangerous pathology that requires identification and timely adequate treatment.
Pain in the intestines: causes
Experts identify several reasons that could cause pain in the intestines on the left and right side of the lower abdomen.
If the patient feels severe pain in the lower right abdomen, then these symptoms indicate problems with the small intestine. They can be caused by metabolic disorders, microflora, poor diet, long-term use of medications, and alcohol. Pain may indicate the development of dangerous diseases - enteritis, cancer, celiac disease, dyskinesia, ischemia, dysbacteriosis, the appearance of neoplasms, ulcers, polyps, cracks.
If a few minutes after eating any food a person begins to belch, acute pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, these symptoms indicate a weakness of the digestive process. Stomach pain and gastrointestinal disorders are associated with low acidity. The human body does not have enough gastric juice. As a result, the body does not properly digest food, which over time begins to ferment and cause pain.
Cutting pain in the lower abdomen may be associated with problems of the nervous system. Nervous tension causes the body to produce nonspecific ulcerative colitis. The pain goes away after a few days. If a person does not feel improvement, the disease enters the chronic stage.
- Pain in the intestines on the right and left lower abdomen in women is associated with the genital tract.
During menstruation, blood flow into the pelvis increases, so this process is accompanied by pain.
- This can provoke stagnation in girls who are prone to developing varicose veins.
Pain in the intestines can appear with decreased vascular tone and observed weakness of connective tissue. The patient begins to experience painful sensations, pain during bowel movements, an increase in the size of hemorrhoids, and gastrointestinal disorders.
The disease is accompanied by painful sensations in the intestines in the lower abdomen. Diverticulitis occurs due to inflammation in areas of protrusion of the colon. Painful sensations occur when feces and food stagnate in these areas.
- The appearance of neoplasms.
The appearance of tumors in the human body is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen on the left and right. The pain syndrome increases with changes in the size of the tumor.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by severe acute pain in the lower abdomen, and the patient has no appetite. This disease is accompanied by gastrointestinal disorders, diarrhea and constipation, diarrhea, and flatulence. Sometimes the patient notices weakness, an increase in the size of the abdomen, bloating and discomfort in the intestinal area.
- Problems with the genitourinary system
Stitching pains in the lower abdomen on the left and right indicate problems with the kidneys and bladder. The patient should visit a urologist and get tested.
In pregnant women, the size of the uterus increases. This process can affect the appearance of pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen. The enlarged uterus puts pressure on the intestinal walls, which can be accompanied by severe cutting pain, nausea, vomiting and flatulence.
The next cause, which is characterized by pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen and nausea, is pancreatitis. With pancreatitis, the patient experiences severe cutting pain in the upper abdomen. In some cases, the size of the abdomen increases. Gastrointestinal disorders, including constipation, accompany pancreatitis.
- Duodenal ulcer.
With a duodenal ulcer, the patient is bothered by severe sharp pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen. They are accompanied by vomiting and upset.
To determine the cause of severe pain in the intestines on the left and right side of the lower abdomen, the patient should visit a doctor. After the initial examination and consultation, the patient will be sent for testing. A general analysis of blood, urine and feces will show the internal indicators of the body and demonstrate the presence of any abnormalities in the systems of the human body.
For clearer results, the patient is referred for a bacteriological examination of stool, colonoscopy and endoscopic examination. After receiving the test results, the attending physician prescribes treatment for the patient. A medical expert prescribes medication, homeopathic or surgical intervention in advanced cases.
If necessary, to obtain information about the condition of the internal organs, the doctor refers the patient to undergo a computed tomography or ultrasound scan. These diagnostic tests are not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children under sixteen years of age. Health care professionals do not recommend these procedures for certain groups of the population. The use of radiation and contrast fluid can negatively affect healthy organs.
To make an appointment for a consultation or examination at the private clinic “KDS Clinic”, leave a request on the website and managers will contact you as soon as possible.
With appendicitis, the patient experiences severe nagging pain in the right side of the abdomen. Pain syndromes intensify during sudden movements. At first, the pain disturbs the patient throughout the middle region of the stomach, later it appears in the lower abdomen and concentrates on the right.
The pain intensifies when turning from one side to the other, when walking or coughing. Over time, tension will arise below, which is an important signal to go to the hospital. The person will constantly feel sick, the temperature and blood pressure will rise, there will be an appetite disorder, and loose stools.
With irritable bowel syndrome, the patient is bothered by acute sharp pain in the intestinal area, stool is disturbed, and the temperature rises. Symptoms disappear after a few days. If the patient's condition has not improved, it is advisable to consult a doctor. The disease has entered a chronic stage.
- Problems with the uterus and female genital tract.
In female patients, acute pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen indicates the development of the disease in the uterus and in the female genital tract. It is advisable to contact a gynecologist as soon as possible to stop the inflammatory process. Such symptoms can lead to infertility if not properly treated.
- Impaired blood circulation in other organs.
Acute pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen indicates a violation of blood circulation in other organs. Problems can be found not only in the body's gastrointestinal tract, but also in other systems.
- Functional changes in the intestines or other organs.
- Violation of cellular metabolism in the intestine.
- Crohn's disease.
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory process that is accompanied by severe acute pain in the lower abdomen.
When there is pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, the patient is also bothered by other symptoms.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Temperature increase. With severe pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, one notices weakness, fever and chills.
- Prostration.
- Lack of appetite.
- Gastrointestinal disorders, including constipation and diarrhea
- Flatulence. After eating, patients complain of severe flatulence.
- Dizziness and migraine. Concomitant symptoms of pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen are dizziness and migraine.
- Bloating. On an empty stomach and after eating, the patient's stomach swells and discomfort appears.
- Colic.
To diagnose the disease with pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, the patient should consult a gastroenterologist. The medical expert will conduct an initial examination, which consists of palpation. The patient needs to determine the nature of the pain syndromes, their frequency and intensity. After the initial examination and consultation, the patient will be sent for tests, including a general blood test, stool and urine analysis.
These procedures are prohibited for pregnant and nursing mothers, children, and people with cancer. Alternative options include other tests, such as:
- Coprogram is a stool analysis that makes it possible to judge the completeness of food digestion. This examination determines whether the patient has gastrointestinal disorders.
- Bacteriological examination of stool. Bacteriological examination of feces allows you to determine the causative agent of intestinal infection and the ratio of bacteria of normal and opportunistic flora.
- Endoscopy. In an endoscopic examination, a fiber-optic tube with a camera and light is inserted into the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. This diagnostic examination makes it possible to directly see the condition of the mucous membrane.
- Colonoscopy. The study is performed using a camera, which allows you to visually assess the condition of the intestines.
Bowel pain can be caused by many reasons. The most common are overeating, poisoning, periodic female pain, intolerance to certain substances (for example, lactose and gluten intolerance are common), as well as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If it is not possible to associate the pain with a specific event, for example, with eating stale food, then the cause may be functional disorders of the intestines.
With Irritable Bowel Syndrome, the motor, or motor, function of the intestines is impaired. We will tell you further how this happens and manifests itself.
For us, food is like fuel for a car. For us to be healthy, food must be well digested and absorbed, saturating the body with useful substances. The intestines play a key role in this process.
Interesting fact: the intestines are always “moving”, even when we sleep! This occurs thanks to smooth muscle cells (SMCs), which are located along and across the intestines. Thus, the intestine has longitudinal and transverse muscle layers.
Type and nature of pain
- If there is aching pain and cramping in the lower right, this may be inflammation of appendicitis.
- If the pain radiates to the left side of the abdomen, this indicates inflammatory processes in the sigmoid colon.
- If the pain is localized in the central region, extending to the navel, this indicates inflammation of the small intestine or if the patient is infected with parasites.
- When pain and cramps are not localized in one area, but can appear in different places, on the right and left, this indicates that the patient has several areas of the intestine affected. The entire peritoneum can hurt and due to inflammation of appendicitis, pain appears not only in the right side of the abdomen, but also in the lower left.
- If pain appears after eating on the left or right side, this indicates that intestinal motility and the production of specific enzymes for complete digestion of food are impaired.
- Adhesions and loops manifest themselves as painful sensations in the abdominal area after a person has eaten and taken an uncomfortable position, after physical work, after defecation. Similar symptoms also appear with malignant intestinal tumors; pain often occurs in the lower abdomen and cramps appear.
Treatment
Pain in the intestinal area is always an abnormal condition, which signals sometimes very serious problems that have arisen in the body. Anyone who has experienced pain in the abdomen has probably tried to understand what is behind this symptom. How to get rid of pain, should you immediately seek medical help, and what can you eat in such cases?
A little anatomy
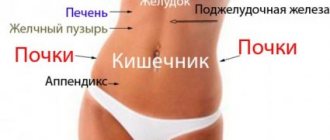
In anatomy, this is the name of the lower part of the digestive tract, starting from the bauhinian valve (which separates the small and large intestines) and ending with the anus. The length of this part of the intestine is about two meters, and it is here that water is absorbed and feces are formed from food gruel.
Disturbances in the functioning of this part of the intestine and the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen can be caused by a large number of various diseases. We will only talk about a few of them.
In its acute form, the patient feels severe cramping pain lower in the intestine or in its lateral areas. Over time, they become diffuse and less pronounced.
In addition, the pathology is manifested by loss of appetite, nausea, rumbling and bloating, bowel disorders (constipation, diarrhea), abdominal pain when palpated. With the development of an infarction of the mucous membrane of the intestinal walls, blood may appear in the stool.
It usually begins with the appearance of diffuse pain in the stomach area, and after a while the pain drops lower, concentrating on the right side, sometimes radiating (radiating) to the right leg.
It must be remembered that this symptom of appendicitis can sometimes subside. This is caused by the death of nerve cells in the appendix.
The pain usually worsens when walking, coughing, or trying to roll over in bed. Tension increases in the lower abdomen. And this is already a signal to immediately consult a doctor!
In addition to this symptom, appendicitis may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting (usually no more than 2 times), loss of appetite, increased temperature (up to 38°C), sometimes loose stools, frequent urination and increased blood pressure.
This disease occurs during an inflammatory process in places of pathological protrusions of the colon (the so-called diverticulum). Usually these protrusions do not manifest themselves in any way, but when food and feces stagnate or dysbacteriosis, inflammation begins to develop. It is accompanied by severe intestinal pain, fever, diarrhea and the appearance of blood in the stool.
Untreated diverticulitis can become chronic, which will be accompanied by the above symptoms constantly. In addition, the disease can become an impetus for the development of colon obstruction.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yl-BgI9nRKc{amp}amp;modestbranding=0{amp}amp;controls=1{amp}amp;rel=0{amp}amp;showinfo=1{ amp}amp;enablejsapi=1{amp}amp;origin=
This disease is caused by a violation of the movement of contents through the intestines. And the symptoms are cramping pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, bloating (externally this is expressed by noticeable asymmetry), repeated vomiting, loss of appetite and delayed or absent stool.
With genetic predisposition, allergic reactions, individual intolerance to certain foods and the presence of chronic stress, a person may develop ulcerative colitis. It is accompanied by a dull aching pain localized in the lower abdomen or left.
In addition to pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, the pathology is accompanied by impurities of blood and pus in the stool, diarrhea, false urge to defecate, decreased appetite, increased temperature (sometimes up to 39°C), general weakness and, in severe cases, weight loss.
Due to the danger of developing benign and malignant neoplasms in the intestines during the disease, this disease requires mandatory medical intervention.
In cases of the development of such pathologies, abdominal pain is not pronounced. At the beginning of the development of diseases, mild pain sensations that do not have a clear localization may periodically occur. But in the process of growth, the tumor can block the lumen of the intestine, leading to its obstruction and, accordingly, causing the symptoms of this disease.
If a patient has persistent constipation not related to food intake, which is difficult to correct with diet or drug treatment, then the development of a cancerous tumor can be suspected. In addition, blood impurities appearing in the stool can serve as an additional warning sign.
The development of malignant tumors is also indicated by weakness, loss of appetite, fatigue and weight loss in the patient. All this requires immediate examination and observation by specialists.
Chronic pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, which transforms from mild to unbearable, occurs at any time and intensifies after eating, are symptoms of a fairly common disease. It is called irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Interestingly, no organic abnormalities are found in this disease.
The peculiarity of pain in IBS is that it disappears at night, during sleep, but can arise as soon as the person wakes up. They are usually accompanied by bloating, flatulence and bowel problems (constipation or diarrhea, and sometimes one or the other). Feelings of incomplete emptying, “coma in the throat” when swallowing, detection of mucus in the stool, as well as muscle pain and nausea are also common.
If you adhere to the right treatment, you can completely get rid of this disease. Your doctor will prescribe it for you. But do not forget about proper nutrition, which will restore intestinal flora and its contractility.
Abdominal pain can strike anyone at any age, at any time of the day or night, after eating a white roll, drinking a glass of juice on an empty stomach or a quick run behind a minibus.
Many people simply wait until it goes away on its own; those who are especially experienced help themselves with pills. However, you need to pay serious attention to pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, as it may indicate the gradual development of a severe chronic disease.
Lower abdominal pain
To identify the source of pain, it is important to analyze the nature of the sensations. By the nature of the pain, you can determine the disease that caused it:
- the causes of dull aching pain in the lower abdomen are usually chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, oncological and benign formations, intestinal obstruction or volvulus, sometimes pancreatitis can be suspected;
- colic becomes a consequence of spasms, intoxication, worms or mechanical damage to the intestines;
- acute recurring pain in the intestines can be caused by ulcerative colitis (UC), appendicitis, and infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the cause of prolonged cutting pain (cutting) in the lower abdomen is usually intestinal irritation or UC;
- pressing or bursting pain can be caused by gastritis or inflammation of the esophageal mucosa.
When the intestines hurt in the lower abdomen, its localization also plays an important role: pain can be felt on the right and left, near the ilium, closer to the navel, or radiate to the entire area of the abdomen. Depending on its location in the lower abdomen, we can talk about various diseases:
- in the lower abdomen in the navel area - suspicion may fall on enteritis, colic or worms;
- in the right iliac region - appendicitis, diseases of the cecum;
- on the left side of the iliac region - dysentery, NKY, diseases of the sigmoid colon;
- if pain spreads in the lower abdomen throughout the entire peritoneum, this may mean inflammation of several segments of the intestine or a duodenal ulcer.
You also need to pay attention to the circumstances surrounding painful sensations. If the problem occurs after eating, then the cause must be sought in the large intestine or there are problems with fermentation.
When pain in the lower abdomen in the intestines begins after a change in body position or after physical exercise, you need to check for the presence of adhesions. If pain in the intestines appears during the act of defecation, it may be hemorrhoids or neoplasms.
When consulting a doctor, be sure to point out the accompanying symptoms that accompany pain in the intestines - they will also help in diagnosing the disease:
- high temperature, chills;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- excessive gas formation and flatulence;
- bitterness in the mouth or dry mucous membranes;
- drowsiness, deterioration in performance;
- mucus or blood in stool;
- associated pain in other places.
Causes of pain
Most often, pain in the lower abdomen is caused by gastrointestinal diseases, and each disease is characterized by its own symptoms. However, in some cases, discomfort can be caused by other reasons: urological diseases, STDs, nervous diseases, hematopoietic pathologies, etc.
In this case, the person will also feel that it is his intestines that are suffering. Only a doctor can more accurately diagnose the cause of pain.
In addition to pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, what other symptoms will help determine more or less accurately the disease that caused them:
- Gastritis is accompanied by nausea, heartburn, a burning sensation in the epigastrium, drowsiness and increased fatigue.
- Appendicitis and peritonitis are accompanied by high fever, loss of appetite, upset stool, and frequent urination.
- Intestinal obstruction is accompanied by increased gas formation, bloating, vomiting, increased heart rate and dry mouth.
- Intestinal colic is often accompanied by constipation and pale gums.
- Intoxication, in addition to pain, can be accompanied by weakness, nausea, upset stool, and fever.
- Pancreatitis is diagnosed by vomiting bile, nausea, constipation, and flatulence.
- Irritable bowel syndrome is accompanied by gas formation and flatulence, a feeling of a lump in the throat, pain in the epigastrium and under the ribs.
- Enteritis is characterized by mushy stools, a feeling of seething inside, spasms, and a light-colored coating on the tongue.
- Helminthiasis is accompanied by nausea, pallor, lack of appetite, flatulence, and itching in the perineum.
Pain can also be caused by poor diet, taking certain medications, microflora disturbances, or blockage of arteries supplying the intestines. If you experience regular or severe pain in the lower abdomen, in the absence of a connection with nutrition and a diagnosed disease, you should immediately consult a doctor to find out the cause.
- Discharge in women and pain in the lower abdomen
- Abdominal pain goes away after defecation
- Lower abdominal pain and diarrhea in men and women: causes, first aid and prevention
- Stomach hurts before menstruation: why does pain occur before menstruation?
Pain during pregnancy
If a woman has pain in the lower abdomen, this is the first sign of pregnancy. The reason for this condition is a change in hormonal levels, when the body is rebuilt and organs change their functions in order to bear the unborn child without complications. But if, during pregnancy, cramping pain appears on the right or left side of the abdomen, they are accompanied by bloody discharge from the vagina, this indicates that problems have arisen and you need to consult a doctor for help.
If a miscarriage occurs, in addition to pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding, the woman’s well-being worsens, her temperature rises, her whole body aches, and loss of consciousness is possible. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. A fragment of the fertilized egg may remain in the uterus, which needs to be disposed of; if this is not done in time, the threat of inflammation in the uterine cavity increases, and this is a serious complication that poses a threat to the woman’s life.
Diagnosis of pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen
If abdominal pain bothers you regularly, a diet does not bring any results, and a person feels worse and worse, you should not procrastinate and self-medicate. In order to exclude the diagnosis or confirm it, they consult a gastroenterologist, he refers the patient to a diagnostic test, which is selected taking into account the symptoms and nature of the disease. Diagnosis of the disease includes:
- examination and palpation of the patient’s peritoneum, asking about the main symptoms, when pain appears, whether there is a pattern;
- collection of stool and urine tests, general and biochemical blood tests;
- endoscopy of all parts of the intestine;
- X-ray of the intestine using a contrast agent.
Diagnostics involves preparatory procedures that must be followed in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician. During radiography, the patient cannot eat 12 hours before the procedure; the day before, all foods and dishes that cause fermentation and gas formation are excluded. X-rays reveal bowel movements using enemas or laxatives. All aspects and subtleties of preparing for research are voiced by the doctor. When the diagnosis is established and the cause of pain in the intestines is known, treatment is prescribed.
How to get rid of lower abdominal pain
The large intestine consists of smooth muscle. The pain is most often provoked by its spasms. In this case, a single dose of antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Buscopan, Mebeverine, Spasmomen) is acceptable. Painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are not effective for intestinal pain. They can cause harm - aggravate the inflammatory process or blur the clinical picture.
If the pain is frequent, regular, intense, but has arisen for the first time, you should consult a doctor yourself or call an ambulance. Intestinal pathologies are treated depending on their nature. In case of infectious lesions, you will need to take antiparasitic, antibacterial or antiviral drugs (Vormil, Levomycetin, Nifuroxazide, Isoprinosine). In parallel, regulators of intestinal flora (Subalin, Enterozermina, Canadian yogurt) are prescribed.
For inflammatory lesions, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes sorbents (Atoxil, Smecta, Enterosgel), enveloping and astringent agents (for example, flaxseed infusion), herbal remedies (intestinal infusions, homeopathic medicines), hormonal and immunosuppressive drugs. For neoplasms, surgery, chemotherapy and radio wave therapy may be required. In case of obstruction and intestinal volvulus, surgical intervention is performed, the cause of the obstruction is eliminated, and the pathological loop is straightened.
Diet is a necessary part of intestinal healing. It is important to eat enough food, fiber in the form of vegetables and cereals, and easily digestible meat and fish dishes. Refractory fats, coarse dietary fiber, sour, sweet and gas-forming foods are excluded from the diet.
The intestines are a vital organ for humans, so a pain attack is a reason to consult a specialist. Treatment of intestinal diseases is more effective in the early stages of pathology development. In advanced forms, surgical removal of the affected parts of the colon may be required.
source
The intestines are a vital organ for humans, so a pain attack is a reason to consult a specialist. Treatment of intestinal diseases is more effective in the early stages of pathology development. In advanced forms, surgical removal of the affected parts of the colon may be required.
What to do when treating an illness?
When test results show the root cause of pain in the intestines, the doctor prescribes treatment. If the cause of pain in the intestines is inflammatory processes with the addition of a bacterial infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed, it lasts 5-7 days, after which repeated tests are taken and the doctor draws conclusions about the success and cure, or the therapy is extended until complete recovery.
If a painful symptom occurs as a result of an imbalance in the intestinal microflora, prebiotics and a special diet are prescribed, aimed at normalizing beneficial microorganisms in the intestines. In case of inflammation of appendicitis or acute intestinal obstruction, surgery helps, which eliminates the root cause of the disease.
For severe pain, you can use No-shpa.
For pain that cannot be tolerated, the doctor prescribes medications that can relieve pain and spasms, No-Spa copes well with this. But you need to remember that eliminating painful spasms does not solve the root cause; if pain and cramping in the abdominal area appear frequently, you cannot endure it, but seek help from a medical facility. To improve intestinal function, the doctor prescribes enzyme medications; they help digestion and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The cause of pain in the intestines can also be stomach disease, such as ulcers, gastritis, reflux esophagitis. These diseases affect intestinal motility, interfere with its normal functioning, and suppress beneficial microflora. To eliminate discomfort and symptoms, the root cause of the disease is eliminated, and the accompanying manifestations disappear along with it.
Treat the intestines effectively using traditional methods. Leafy green tea, which contains many antioxidants and microelements that can improve intestinal function, will help get rid of the disease. You can drink green tea with honey and lemon if your stomach acidity is normal. An infusion of raisins will also help improve intestinal function. To prepare it, take a handful of raisins, add boiling water and leave for 15-20 minutes. You need to drink the infusion 2-3 times a day before meals. A mixture of honey and aloe is also used to relieve painful symptoms. To prepare it, the fleshy parts of the flower are taken, crushed in a meat grinder or blender, and mixed with honey. This mixture is taken 3-4 times a day before meals.
Diet therapy
For diseases of the intestines and digestive organs, it is necessary to follow a therapeutic diet, in which irritating foods are excluded, and preference is given to gentle food, which helps restore the mucous membrane and stimulates peristalsis of the intestines and stomach. Food is steamed or boiled, a small amount of salt and spices is used, and the consumption of black tea and coffee is limited.
From the menu you need to exclude fresh white bread, baked goods, sweets with butter creams, chocolate, and sweet soda. For drinks, it is preferable to drink fresh juices, herbal teas and infusions, fruit drinks, compotes. Fermented milk drinks - natural yogurt, fermented baked milk, kefir - will help improve the functioning of the intestines and populate it with healthy microflora. Depending on why and how the intestines hurt in the lower abdomen, the doctor will help you create the right diet.