Pancreatitis is one of the most dangerous diseases that provokes a decrease in the functionality of the parenchymal gland, accompanied by an inflammatory process and all its characteristic symptomatic signs. The development of this pathology may be preceded by regular dietary disturbances, alcohol abuse, or the progression of pathological changes in the functioning of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as cholecystitis, liver failure, cholelithiasis and others. In the materials of this article, we will consider in more detail whether there can be a temperature with pancreatitis, why it occurs, what begins to happen to the patient’s body when it increases, and what to do if fever develops.
What happens when body temperature rises
One of the parts of the human brain acts as a biological thermostat - the hypothalamus. It reacts sharply to the action of pyrogenic substances, which are components of decomposition and waste products of life processes released by harmful microorganisms. The latter contribute to the formation and progression of pathological processes in the human body that are inflammatory in nature.
When foreign components are formed in the blood plasma, the hypothalamus regards this as a signal to raise the human body temperature, which is necessary to intensify the destruction of pathogenic agents of various diseases.
As the temperature level in the human body increases, the rate of metabolic processes increases, as well as the concentration and intense activity of immune antibodies that synthesize a protective protein in the form of interferon, which provides protection to the entire human body.
The rise in body temperature occurs during thermogenesis, in the processes of which both the muscular structures of the body and layers of fatty deposits participate. An involuntary contraction of muscle structures is felt by the patient in the form of trembling throughout the body, which ensures the heating of tissue structures and the breakdown of fat layers, which leads to the release of the maximum amount of energy.
High temperature during illness
The appearance of high temperature during exacerbation of pancreatitis manifests itself as a peculiar response of the human body, which has a protective type of manifestation. It is directed against the reproduction and negative effect on the health of the human body of pathogenic microorganisms and the progression of inflammation in the cavity of the parenchymal gland.
High thermometer readings, reaching febrile temperatures, indicate that the following processes have been activated in the cavity of tissue structures:
- internal reactions in tissue structures accelerated;
- the rate of regeneration of damaged cells has increased;
- and the immune defense system has also been activated, creating all the maximum necessary conditions for the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms.
High temperature and pain in the pancreas are among the first signs of the development of inflammation in the cavity of this organ.
And, if the patient also begins to be disturbed by a feeling of chills in the evening, and the thermometer rises above 37.6, then this may indicate that the pathological process has entered a more severe stage of development, accompanied by a pathology such as peritonitis, or a more serious complication in the form cancer. A low temperature can be an indicator of the development of painful shock, or as it is called in medicine - collapse, as well as internal hemorrhage and dehydration of the body, which mainly manifests itself during acute attacks of pancreatic disease of a parenchymal organ.
Causes and risk group
The appearance of pathological inflammatory disorders in the cavity of the parenchymal gland often occurs in adult men and women against the background of excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco products, as well as with frequent consumption of fatty and fried foods, salty and spicy foods. Moreover, the following factors may act as the root cause of the development of the pathology in question:
- formation of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder, or bile ducts;
- inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis);
- diet violation;
- insufficiency of kidney function, or two at once;
- In men, this pathology can be provoked by inflammation of the prostate gland;
- and in women, an inflamed ovarian or adnexal lymph node often acts as a provoking factor;
- pathological disorders of the functioning of the intestines and pathologies affecting the stomach;
- unbalanced diet and much more.
Patients who are interested in: “Is there a temperature during the development of pancreatitis?” should also be aware of the issues that the appearance of this symptom may indicate the viral and bacterial nature of this disease, and there may also be a high temperature during exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis nature of manifestation. But why do even children suffer from this pathology?
In a child, this disease can develop against the background of a hereditary predisposition, as well as congenital anomalies in the structure of the parenchymal gland.
The risk group for developing this disease, in which the overall body temperature may increase, primarily includes the following categories of people:
- with excess weight;
- in patients who lead a passive life and at the same time have a tendency to frequent overeating;
- elderly people suffering from sciatica, or inflammation of the sciatic nerve, as well as progressive arthritis in the knee joints;
- women who cannot deny themselves various culinary delights.
How long can the temperature last?
A high level of temperature during exacerbation of pancreatic damage to the parenchymal gland may not last long, no more than 3 hours and mainly in the evening. At the same time, it can either increase or decrease throughout the day. If the nature of the inflammation is sluggish, then a similar phenomenon, when the temperature can either rise or fall, can be observed for several months a year. But, when the pathology passes into the chronic stage due to the lack of necessary treatment, or improper therapy, an increase in temperature can be observed for many years.
How and with what to reduce the temperature in diseases of the pancreas?
If an increase in temperature is observed when acute painful sensations appear, then it is allowed to take one tablet of a drug that has an anti-inflammatory spectrum of action and relieves spasms of the parenchymal gland. For these purposes, you can use regular Analgin. A qualified doctor in most cases uses antibiotics to lower body temperature as quickly as possible.
You can also make your own medicine by mixing powdered tablets of analgin, paracetamol and acetylsalicylic acid.
Subject to complex therapy aimed at treating pancreatic pathology, the temperature can be lowered with the help of medications with a homeopathic spectrum of action and healing potions prepared from medicinal herbs such as field or pharmaceutical chamomile in bags, coltsfoot leaves, greens peppermint, corn silk or rose hips.
It is important to remember that pancreatic pathology in the cavity of the parenchymal gland is a characteristic inflammation, and this, in turn, is a kind of body defense system that helps combat pathogenic processes.
Therefore, when your temperature rises, you must immediately seek qualified medical care, even if there is no acute attack of pain in the epigastric area.
What can and cannot be done at high temperatures?
A high temperature level in pancreatic disease can be brought down until it stabilizes. For these purposes, you can give the patient medications such as:
- Ibufen;
- Paracetamol in combination with Analgin;
- Nurofen.
Taking medications must be discussed with your doctor in advance.
In no case should you conduct any experiments on yourself if you have an affected pancreas or engage in self-medication with the prescription of arbitrary medications or folk remedies.
If a high temperature persists for several days, it is necessary to urgently consult a gastroenterologist, take all the necessary tests and undergo additional diagnostics to identify the true provoking factor contributing to the increase in temperature.
If the thermometer readings are above 39 degrees or below 36, then taking any medications is not recommended; you should urgently seek help from qualified doctors.
Reduced temperature in acute pancreatitis
A strong process of intoxication of the patient’s body, the development of dehydration, as well as intense manifestation of internal hemorrhage provokes the formation of collapse of the vascular system, or leads to the formation of coma.
Characteristic symptomatic signs of these conditions are a low level of the patient’s body temperature, as well as low blood pressure, pale skin, a weak level of pulsation and a sudden loss of consciousness. With such a development of pancreatic disease, urgent emergency medical care is necessary; the loss of precious time can be fatal.
Reasons for changes in temperature during remission
During periods of remission of pancreatic disease, the patient feels detached from the disease, and body temperature readings do not exceed normal limits. When an exacerbation of the underlying disease occurs, all the characteristic pancreatic symptoms begin to develop:
- begins to hurt in the epigastric area;
- the patient begins to suffer from nausea and intense vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- gas formation;
- increased body temperature;
- the trigeminal nerve may become inflamed;
- and the entire neck may also be taken away.
This indicates the development of inflammation in the cavity of the parenchymal gland.
Similar symptoms occur when you deviate from following the prescribed diet, consume even a minimal dose of alcohol-containing drinks, abuse of fatty foods, which are strictly prohibited to eat even with mild damage to a parenchymal organ, as well as improper use of medications. It is important to remember that food for pancreatitis should be hypoallergenic, light and not greasy.
What to do if signs of fever occur in chronic pancreatitis?
In situations where the level of the thermometer rises to levels above thirty-eight degrees in combination with the manifestation of other symptomatic signs characteristic of an exacerbation of a chronic process of the pancreatic type, expressed in:
- in the onset of severe pain in the subcostal area;
- in massive discharge of vomit;
- in increasing symptoms of diarrhea.
The patient may develop a very dangerous condition, which can provoke the formation and progression of pancreatic necrosis and other equally serious complications.
In this case, you should not hesitate, but on the contrary, you must urgently seek medical help. Any delay may result in the death of the patient. Therefore, no matter whether it is day or night, when these symptoms occur, it is necessary to call an ambulance or take the patient to the doctor.
Pancreatitis is one of the most dangerous diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems. It can occur in long-term chronic and paroxysmal acute forms. Both are characterized by severe severe symptoms. Observed in most cases in adults, it significantly complicates, and often shortens, life.
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) limits the patient's choice of food and causes abdominal pain if the diet is not followed. Sometimes the disease worsens and dyspeptic disorders appear (vomiting, diarrhea, stool changes). Acute pancreatitis (AP) has similar symptoms. An aggravated attack has a more pronounced pain syndrome, a sharp rejection of food and fever.
The article discusses the features of the symptoms of the disease, in particular, whether there can be a temperature with inflammation of the pancreas.
Warning signs
Of course, a high temperature in itself is already a cause for concern. But there are symptoms that cannot be ignored - and if they are combined with an increase in febrile reaction during pancreatitis, urgent medical attention is required. "Warning signs" include:
- sharp increase in abdominal pain;
- the appearance of pronounced tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- convulsions;
- bleeding of their upper or lower gastrointestinal tract;
- shortness of breath with paleness and/or cyanosis of the skin, dizziness and a feeling of suffocation;
- attack of cough with moist wheezing in the lungs;
- extreme thirst or, conversely, loss of the ability to drink fluids with frequent vomiting, diarrhea and fever (this can lead to shock due to dehydration).
With severe intoxication, confusion and disorientation in space often occur. Therefore, fainting or the patient’s indifference to what is happening around him, lack of response to stimuli (questions, touching the hand, etc.) is a truly alarming symptom: the nervous system is suffering, help is needed immediately. It may also be a sign of collapse (a sudden drop in blood pressure) and shock.
Source of elevated temperature
Is there fever with pancreatitis and why? First, you should clarify the reason for this reaction of the body. The temperature of the human body must be increased in cases of inflammation to stimulate the functioning of the immune system. At temperatures above 37.2 °C, new antibodies to infection are formed faster in the blood, if this is the reason. Inflammation is also a natural reaction to any tissue damage. If such an important organ as the pancreas (PG) is irritated, then the temperature regime changes throughout the body.
Therefore, alarming readings on a thermometer are not uncommon when there is inflammation of the pancreas.
If pancreatitis is an inflammatory disease, then can a reading of 37.3-37.7 °C be considered normal? Not really. The temperature can rise only during active destructive processes characteristic of acute pancreatitis.
Can there be a temperature with chronic or acute chronic pancreatitis? The stomach will hurt at any stage of the disease, and stool disorders are characteristic of all manifestations of inflammation of the pancreas.
But temperature as a sign of organ damage processes appears only in acute pancreatitis. The following sections explain why this is being emphasized so much.
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process occurring in the pancreas. In this case, the enzymes produced by the gland do not enter the duodenum, but begin to be processed in the organ itself, gradually destroying it.
Toxic substances released during the life of the pancreas enter the blood and can cause serious harm to other organs.
The disease is accompanied by a large number of symptoms. Temperature often increases or decreases with pancreatitis.
The disease develops slowly; for a long time the patient may not even be aware of the inflammatory process occurring in the body until the disease makes itself felt with a number of characteristic signs.
Many people suffering from pancreatic disease are interested in whether there can be a temperature with pancreatitis. It is also important for them to know whether there are complications and what to do if chills and fever occur.
A high temperature, as well as sudden changes over a long period of time, always indicate that something is wrong with the body. This applies not only to cases with pancreatic disease, but also to inflammatory processes in general, when other organ systems are damaged.
It is necessary to carefully consider both the temperature indicators and the duration of its deviations from the norm. Any condition can be dangerous: a decrease or increase in numerical values, or their long stay at just above 37 degrees.
Associated symptoms
Pancreatitis has 2 forms: acute and chronic. Acute pancreatitis develops very quickly. The disease is characterized by a complex of symptoms:
- The patient feels severe pain in the upper abdomen. The pain radiates to the back and left side of the chest. As a rule, discomfort increases gradually, after a large intake of heavy fatty foods: fried meat, cream cakes, salads with mayonnaise.
- The patient feels heaviness in the stomach and nausea.
- Vomiting can be very frequent, every 2-3 hours. The patient may suffer from severe diarrhea, attacks of which recur after 2-3 hours.
The temperature during pancreatitis in the acute stage reaches 39...40°C. If an attack of acute pancreatitis recurs, this means that the disease has transitioned into a chronic form, which lasts for years, especially in the absence of treatment and poor lifestyle (systematic food excesses, alcoholism), leading to surgical intervention or dangerous complications.
Symptoms in the chronic form are almost the same as in the acute form. The pain is not so severe and is constant. If the head of the pancreas is affected, the patient feels discomfort in the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs. If the tail part of the gland is affected, the pain radiates to the left and is often mistaken for a heart attack.
Reasons for temperature changes
The inflammatory process in the pancreas is not always accompanied by changes in temperature. Its fluctuations depend on the form in which pancreatitis occurs - acute or chronic. It may remain within normal limits if the disease manifests itself in a mild form.
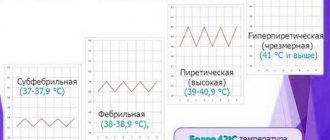
The so-called low-grade fever, at which there is a slight increase (up to 37-37.5 degrees), accompanies a pathology of moderate severity.
High values indicate the existence of severe pancreatitis with accompanying purulent inflammation.
An exacerbation that causes acute pancreatitis is accompanied by pain in the upper abdomen. At the same time, vomiting occurs. It usually bothers the patient after eating, 20-30 minutes later.
The abdomen becomes hard and pain occurs in the pancreas area. Pallor of the skin of the face and a bluish tint to the lips appear.
Often the temperature balance is disturbed due to non-compliance with the recommendations prescribed by the doctor and the prescribed diet. Eating fatty, spicy or smoked foods, as well as overeating, can cause temperature disturbances.
As a rule, this occurs in the chronic form of the disease, when the patient complains of a constant feeling of nausea and general weakness of the body. An increase in temperature (no more than 38 degrees) usually occurs in the evening or at night.
For chronic pancreatitis
At this stage of the disease, the temperature is usually normal; with exacerbation and no complications, the temperature does not exceed 37 degrees. Any change in temperature during the chronic stage of the disease indicates the occurrence of complications.
There may be cases when there is a sharp jump in temperature, while the person experiences chills and falls into a feverish state.
Fever is a clear sign that an abscess has begun in the body, that is, pustules have appeared in the damaged tissues of the pancreas . Further progression of the condition in the absence of proper treatment can lead to infection of nearby tissues.
For acute pancreatitis
An increase in temperature is the first sign that an exacerbation of the disease has occurred. Moreover, the temperature balance is disturbed from the first day of illness.
If the thermometer readings reach a critical level of 39 degrees, you should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe an examination of the body and identify existing complications.
In some cases, with an advanced form of the disease and prolonged neglect of the treatment process, surgical intervention may be necessary, otherwise there is a risk of death.
Reasons why temperature deviates from the norm during acute inflammation:
- The course of the inflammatory process is accompanied by the formation of substances that cause an increase in body temperature.
- Decay products poison the body.
- The inflammatory process is accompanied by complications.
In a febrile state, a patient with acute pancreatitis may experience other symptoms:
- Weakness and malaise.
- Dizziness, headache.
- The person feels muscle weakness.
- The pulse quickens, the pressure drops.
- As a result of a sharp decrease in appetite and its absence for a long time, the patient loses a lot of weight.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract appear: vomiting, nausea, problems with stool.
Characteristic
Exacerbation of pancreatitis is accompanied by high fever: 39-40 degrees. If there is a combination of fever and aching pain in the left side of the abdomen, call an ambulance. Acute damage to the gland poses a threat to human life. It must be treated in a hospital setting.
Thermometer for measuring body temperature
It’s not a good idea to take an antipyretic before seeing a doctor; it can complicate the diagnosis. If a diagnosis has already been made, the doctor may prescribe antipyretic medications. When treating indolent lesions, a person does not need to be given antipyretic drugs if the therapy regimen has been drawn up correctly and the diet is followed.
Low
During active treatment of chronic inflammation, the value may be within the normal range: 36.6-36.8 degrees. Gradually, other manifestations of the disease cease to be felt. The absence of fever is a good sign, meaning that the correct therapy is being carried out.
Why does the temperature rise with pancreatitis?
Almost any inflammatory process is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Pancreatitis can be asymptomatic for a long time. The appearance of symptoms of the disease is associated with the destruction of pancreatic tissue. The stronger the lesion, the higher the fever and the brighter the other signs of pathology. In the remission stage, a person feels much better. With the right lifestyle and timely treatment, manifestations of pancreatitis do not bother you.
Low-grade fever
During a period of minor exacerbation of sluggish pancreatitis, the thermometer may show 37-37.5. This temperature is called subfebrile. It causes slight discomfort, so there is no need to knock it down. Chills and general weakness are typical symptoms. The value is normalized with the use of digestive enzymes and proper nutrition. The basis of therapy is reducing the load on the pancreas through medications and diet.
Duration of high fever
Hyperthermia can persist for varying periods of time. If an attack occurs, a high temperature occurs as a reaction of the body to severe pain and can persist for several hours.
With a sluggish inflammatory process, the temperature is unstable, changing either up or down during the day. This condition can be observed for a month or even a year, when pancreatitis becomes chronic and is not treated or therapy is prescribed incorrectly.
Additional events
In addition to taking medications, you must follow general rules.
- Drink as much liquid as possible (warm, not hot).
- Cool compresses on the head. If the temperature is high with pancreatitis, then prepare a vinegar compress.
- Humidify the air in the room (with a humidifier or light cleaning).
Always remember - improper treatment of pancreatitis will lead to serious complications. Therefore, before taking medications on your own, consult your doctor.
Features of treatment
Drug therapy is considered effective. In acute forms of inflammation, accompanied by high fever, fever, chills, and unbearable pain, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve tension and pain in the affected areas of the body.
If the pain does not stop, the temperature remains at the same level for a long time or rises higher, and medications do not provide adequate relief, you must seek urgent medical help.
In the chronic form of pancreatitis, in addition to basic therapy, homeopathic medicines and various herbal decoctions are effective. Decoctions and tinctures that contain components such as:
However, you should not abuse traditional medicine. Any changes in temperature, especially if a chronic form of the disease is diagnosed, is an indicator that the inflammatory process in the body is progressing and destruction of the diseased organ is occurring.
If your pancreas hurts, it is important to consult a doctor in time to make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment.
The patient must be provided with complete rest and a properly organized diet, excluding the consumption of fatty, spicy foods. In medical practice, a special diet has been developed for people with inflammation of the pancreas.
With this disease, the functioning of not only the gland, but also the entire digestive tract is disrupted. It is important to change your diet so that the food entering the body does not irritate damaged organs, but contributes to the normalization of their vital functions.
Patients, regardless of the form of the disease, benefit from porridge cooked in water or steamed, and dried fruit compotes. It is necessary to reduce the amount of sugar, as there is a risk of organ irritation due to increased acidity.
Mineral water is useful, neutralizing acidity and dissolving fats. This will help relieve the work of the pancreas and bring down the temperature. A special diet takes into account all the features of this disease.
Treatment of pancreatitis
Doctors, speaking about what to do at high temperatures with pancreatitis, note the undesirability of self-treatment. If hyperthermia develops, the patient is advised to call an ambulance. Specialists will conduct the necessary examination and determine further treatment tactics.
If the temperature does not exceed 38°C and is not accompanied by severe abdominal pain, the patient is allowed to take antipyretic drugs: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, etc. They help cope with hyperthermia and alleviate the person’s condition.
In case of chronic pancreatitis and symptoms of its exacerbation (severe pain, vomiting), antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs cannot be used. Eliminating pain will prevent the doctor from examining the patient and determining the cause of the discomfort.
To alleviate the condition, the patient can independently use the following groups of medications:
- antispasmodic medications (“No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”, etc.), eliminating spasm of the pancreatic duct and ensuring the removal of active enzymes from the pancreas. This will reduce pain and prevent the development of pancreatic necrosis;
- enzyme agents if symptoms develop after ingesting large amounts of food or fatty foods. Doctors recommend using Festal, Gastal and their analogues.
Possible consequences
Increased body temperature and chills indicate that pathological processes in the tissues of the organ have accelerated. If measures are not taken, it may happen that the human body will be unable to take food.
There is a risk of developing diseases of the digestive system. In addition, there is a high probability of failure of the digestive process, which affects the cells of the pancreas. In this case, not only the gland itself is destroyed, but also nearby organs.
A common complication of untimely treatment of pancreatitis is cirrhosis of the liver. There are disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system, which lead to the development of diabetes mellitus.
If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, this may be an indication that pancreatitis is becoming more severe. There is a danger of developing peritonitis when the entire abdominal cavity becomes inflamed.
Low temperature is no less dangerous . If the indicators significantly deviate from the norm to a lesser extent, the situation is fraught with the development of painful shock, internal bleeding or dehydration of the body is possible.
Pancreatitis is a serious disease that requires immediate medical treatment. Self-therapy is unacceptable. The course of medications is prescribed by the doctor taking into account the patient’s health status, the characteristics of his body, and individual intolerance to the substances included in the medications.
All medications have contraindications and side effects. It is important to read the instructions for use and strictly follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas accompanied by inflammation.
It develops due to poor nutrition, unhealthy lifestyle or anatomical features of the body.
Changes in temperature in pancreatitis act as a consequence of the inflammatory process. We will find out further why the temperature rises during pancreatitis.
Can there be a temperature with pancreatitis and why?
When both the pancreas and any other organ become inflamed, toxins are released into the blood , resulting from the death of body cells. The brain perceives these substances as a signal to activate the immune system. Metabolism accelerates, cells become more efficient. Because of this, a large amount of energy is released, which heats the body and increases its temperature.
Considering the mechanism of the disease and the results of examination of patients suffering from pancreatitis, gastroenterologists argue that changes in temperature may accompany inflammation of the pancreas. However, with different forms of the disease, the temperature varies.
In acute
With the development of an acute form of pancreatitis, swelling of the gland and obstruction of the ducts of the organ indicate the disease. The destroyed tissue begins to become inflamed, which is accompanied by a change in body temperature. Temperature allows us to judge the purulent-inflammatory process in the body and its severity:
- Easy. With this degree of disease, the gland suffered minor damage and the inflammation was mild. Therefore, the temperature either does not rise at all or rises slightly. The maximum time the fever lasts is three days.
- Medium-heavy. This degree is characterized by significant damage to pancreatic tissue, widespread inflammation and the onset of the formation of necrotic foci.
The patient complains of severe pain, vomiting that does not bring relief, and an increase in temperature to 39 degrees. This is due to serious intoxication of the body and activation of the defense system. With moderate pancreatitis, the fever continues for up to ten days, while on the fourteenth day the patient recovers.
Severe degree and complications. With this variant of the development of the disease, the patient experiences extensive damage to the gland, involving the entire organ or almost the entire organ in the process.
In addition, a purulent abscess begins, and inflammation spreads to nearby organs and tissues. In addition, cysts, fistulas and internal bleeding form as complications. The combination of these signs leads to extensive intoxication of the body and the spread of infection. The temperature reaches forty degrees and is difficult to lower.
Separately, cases of decreased temperature during pancreatitis should be considered. Extreme intoxication, profuse internal bleeding and dehydration observed in extremely severe cases of the disease cause vascular collapse. This condition leads to a sharp drop in blood pressure, heart rate and body temperature. The patient loses consciousness.
Without timely assistance from a doctor, the patient dies, therefore, if the temperature drops during an attack of pancreatitis, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance.
For chronic
In the chronic course of pancreatitis, without exacerbations, the disease is not accompanied by any symptoms . By following a diet and leading a healthy lifestyle, the patient is able to significantly delay or completely avoid the development of an attack.
An indicator such as body temperature in the chronic form of the disease usually remains normal or increases slightly, but not more than 37 degrees.
Patients are advised to measure their temperature regularly and note any changes.
So its sharp increase indicates the following complications:
- tissue necrosis;
- sepsis and abscess;
- paranephritis.
Low-grade fever, which persists for a long period, acts as a signal of possible oncology .
Chronic pancreatitis and hyperthermia
Fever in chronic pancreatitis is a rare symptom. A disease with a similar course is characterized by mild dyspeptic symptoms and a feeling of discomfort in the upper abdomen.
Hyperthermia may indicate several conditions:
- exacerbation of pathology that developed due to the use of alcoholic beverages or errors in diet;
- the addition of a purulent infection with increased inflammatory changes and the formation of pus;
- purulent complications: abscesses or phlegmon in the tissues of the pancreas with melting of the organ;
- breakthrough of purulent masses into the abdominal cavity against the background of pancreatic necrosis with the development of diffuse peritonitis;
- complications from the biliary tract, gallbladder or liver, which are inflammatory in nature.
What happens?
Depending on the severity and form of the disease, the temperature in patients varies:
- Low (about 35 degrees). In case of vascular collapse due to acute pancreatitis with severe intoxication and complications.
- Subfebrile (37–38 degrees). This temperature is observed in patients with a mild acute form of the disease or with a chronic form.
- High (38–40 degrees). A significant increase in this indicator in a patient indicates a moderate to severe degree of the disease in acute form. Such heat often accompanies the development of complications and damage to nearby organs and tissues by the inflammatory process.
It is important to note that fever is not necessarily a symptom of pancreatitis . So, in children suffering from the disease, it rarely rises above 37 degrees.
Why is it dangerous?
Changes in temperature during pancreatitis in themselves are not so dangerous. However, the reasons for this change are dangerous:
- Thus, a significant and sharp increase in it is promoted by an extensive inflammatory process with possible suppuration or tissue necrosis, as well as damage to nearby organs.
- A drop in temperature below 36 degrees indicates the onset of vascular collapse due to severe intoxication and the need for urgent medical attention.
- Subfebrile values over a long period of time allow us to judge the possible onset of oncology.
Overheating of the body itself poses the following dangers:
- cardiopulmonary failure;
- convulsions;
- blood viscosity increases;
- dehydration;
- folding of proteins in the structure of cells.
Changes in temperature help indirectly monitor the patient’s condition and the development of his disease. This is why it is so important to quickly respond to all temperature fluctuations.
What to do and how to reduce the fever?
If a patient with pancreatitis has a fever, then, regardless of the form of the disease and the magnitude of the indicator, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
Such changes most often accompany worsening of the inflammatory process in the body.
With a slight increase, if it does not cause discomfort, the temperature is not reduced at all or resort to the help of herbal remedies. So, decoctions of rosehip or mint can reduce fever. However, traditional medicine recipes are not suitable for all patients, as they cause allergies.
When the thermometer reaches 38 degrees, it is recommended to begin antipyretic therapy . Drugs such as Paracetamol and Aspirin help with this. The drugs are not intended for self-administration, and therefore the patient waits for the doctor to assess his condition and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Until the doctor arrives, keep the patient quiet and drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Fever is an optional symptom of inflammation of the pancreas. At the same time, any change in the body temperature of a patient suffering from pancreatitis indicates the development of the disease, its aggravation or the appearance of complications. Therefore, it is important to monitor how the temperature changes and, at the slightest suspicion of a worsening condition, consult a doctor.
What to do if hyperthermia occurs
When the victim's hyperthermia increases, regardless of the stage of the disease and its magnitude, urgent help is needed. When hyperthermia is accompanied by other signs of pancreatitis, this indicates the development of an infectious course and other pathologies. The presence of chills, fever, weakness and muscle pain are symptoms of severe intoxication.
If the increase is insignificant and does not cause inconvenience, herbal remedies are used. They use a decoction of rose hips and mint, which perfectly reduce fever. It is worth considering that traditional methods of treatment are not suitable for all patients, as they cause an allergic reaction.
When the reading reaches 38 degrees, it is recommended to take a fever-reducing medicine - Paracetamol, Aspirin. Self-administration of medications is unacceptable; wait for a doctor to assess your well-being and prescribe the required therapy. Until the medic arrives, the patient needs to rest and take fluids to prevent dehydration. The disease is treated only by a gastroenterologist.