11/30/2017 Olga Migunova 2 comments
The gallbladder functions as a reservoir for bile. Normally, it accumulates bile for itself, and, if necessary, releases it into the duodenum. It happens that the process of excretion of bile slows down, which is fraught not only with disruption of the digestive processes, but also with quite painful sensations in the upper half of the abdomen. Therefore, this topic describes in detail what are the causes and symptoms of bile stagnation in adults, children and even pets. We will also look at which specialist you need to contact and how to deal with this problem.
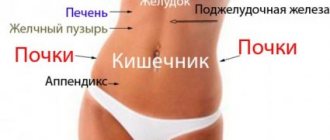
Functions of bile
Bile is a dark brown liquid with a green tint, which consists of digestive enzymes, proteins, amino acids, bile acids, salts, fats, vitamins and other substances. Bile production occurs in the liver cells, and storage occurs in the gallbladder.
The main function of bile is participation in digestive processes, namely:
- fat emulsification;
- dissolution of fat breakdown products;
- increased activity of pancreatic juice enzymes;
- stimulation of the process of bile formation in hepatocytes;
- stimulation of bile secretion by the gallbladder;
- stimulation of intestinal motility;
- neutralization of chyme acidity and blockade of pepsin in chyme entering the duodenum;
- assistance in the absorption of nutrients from the intestines;
- stopping the growth and reproduction of pathogenic organisms in the intestines.
Stagnation of bile in the liver and gallbladder: causes
All causes of bile stagnation in the gallbladder and liver are divided into 3 groups.
- Impaired functions of the liver and bile ducts.
- Diseases of internal organs.
- Harmful environmental factors.
But if we talk about specific factors that disrupt the secretion of bile from the gallbladder, then they may include the following prerequisites:
- improper and unbalanced diet. Overeating, fasting, eating dry food, predominance of fatty, fried or spicy foods in the daily diet;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the digestive system against the background of a strict diet;
- sudden changes in diet;
- severe psycho-emotional shock;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- gastritis;
- intestinal infections;
- food poisoning;
- bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking);
- taking certain groups of drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, hormonal and antibacterial drugs);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- congenital diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- food allergies;
- atopic dermatitis;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes, obesity);
- pregnancy;
- removal of the gallbladder and others.
Causes
Bile is a biological fluid with a multicomponent composition. Its main ingredient is considered to be bile (cholic) acids, which are involved in the assimilation of vitamins A, D, E, K and the emulsification of fats, stimulate intestinal motility, prevent the adsorption of bacteria, etc.
Other components are cholesterol, bilirubin, phospholipids. Part of the produced bile enters dosed into the lumen of the duodenum to digest food, the rest accumulates in the gallbladder. By the way, we recommend that you watch the video.
A disruption leading to stagnation can occur both at the stage of its synthesis in hepatocytes and at the stage of transportation to the intestine.
Depending on the location, there are two types of cholestasis:
- Extrahepatic variant - develops when the bile ducts and bladder are blocked from the inside (stones, accumulation of helminths, cholangiocarcinoma) or compression from the outside (postoperative adhesions, cysts, tumors, abscesses). This happens less often with Crohn's disease, duodenal diverticula, and aneurysm of the portal vein branch.
- Intrahepatic variant - for this type of bile stagnation, the causes are even more diverse and not always obvious. They are usually associated either with cessation of secretion due to functional failure of hepatocytes, or with impaired excretion and outflow due to blockage of the internal bile ducts. This type of cholestasis is more common and occurs more often in men.
In adults
The main etiological factors in the age category 18+ are:
- acute and chronic hepatitis - viral, drug, alcohol, toxic, autoimmune;
- severe septic conditions;
- genetic family diseases;
- malignant processes - kidney cancer with metastases to the gallbladder and liver, lymphogranulomatosis;
- systemic pathologies – amyloidosis, storage diseases;
- congenital liver fibrosis;
- cirrhosis of any origin;
- vascular disorders (shock, thrombosis);
- long-term parenteral nutrition.
Some variants of congestion in the gallbladder and liver can only appear under certain circumstances:
- with benign hepatosis in pregnant women;
- in HIV-infected people;
- in patients who have undergone organ transplantation.
In young people, cholestasis is often caused by various drugs that have a hepatotoxic effect, including paracetamol, anabolic steroids, oral contraceptives, a number of antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, cytostatics, antiarrhythmic and anticonvulsant drugs, etc.
Alcohol and drugs can worsen the situation.
In children
Stagnation of bile in a young child most often occurs due to the following reasons:
- neonatal hepatitis;
- congenital anomalies - a decrease in the number or improper formation of bile ducts (atresia, hypoplasia);
- metabolic diseases – galactosemia, cystic fibrosis, etc.;
- hereditary pathologies of a family nature;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- toxic effects of drugs.
In some cases, the etiological factors remain unknown, for example, in primary sclerosing cholangitis or biliary cirrhosis.
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder: symptoms
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder is commonly called cholestasis in medicine.
With stagnation of bile, symptoms may be as follows:
- constant bitter taste in the mouth;
- nausea sometimes with vomiting;
- periodic occurrence of heartburn;
- bad breath;
- belching bitter;
- pain in the epigastrium and right hypochondrium;
- intestinal dysfunction in the form of diarrhea;
- acholic feces The feces become light due to the absence of the pigment stercobilin;
- urine the color of dark beer;
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- skin itching;
- the appearance of skin rashes;
- yellowing of the skin, primarily the sclera and mucous membrane under the tongue;
- sleep rhythm disturbance: insomnia at night and drowsiness during the day.
Main symptoms
The most striking signs of bile stagnation are as follows:
- constant nausea and belching, bitterness remains in the mouth, a gag reflex occurs;
- a dull aching pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- the breath smells bad;
- yellowness of the skin and eye sclera is possible.
First of all, the patient should pay attention to itchy skin. This is the body's first signal about the formation of stagnation. Then the stool becomes discolored and the urine becomes dark.
Read also: How does the gallbladder hurt?
Symptoms of stagnation in children
Children may also develop cholestasis, and the pathology has the following causes:
- damage to the bile duct by roundworms, foci of reproduction block the lumen (parasites should be gotten rid of with antibiotics);
- narrowing of the nipple of Vater, a congenital anomaly in the distal duct;
- disturbances in the functioning of the sphincter of Oddi, which is responsible for the release of bile. There is a functional or organic disorder that is more difficult to remove.
If stagnation is not treated, cholecystitis and noticeable symptoms appear:
- itchy skin in the limbs and forearm, the chest and abdomen, buttocks may also be affected;
- in the upper right part of the abdomen there is pain under the ribs;
- the skin turns yellow;
- A xanthoma appears, a small bulge on the skin, soft to the touch with a yellow tint. It is found near the eyes, on the child’s palms, near the neck and on the back, under the mammary glands.
Cholestasis in pregnant women
Stagnation of bile in pregnant women is a fairly common problem, since hormonal changes occur in the body: the level of progesterone increases significantly, which relaxes all smooth muscle muscles, including the biliary tract.
Also, an important role in the development of urinary stagnation is played by an increase in the size of the uterus and an upward displacement of the abdominal organs, as a result of which the gallbladder or its duct may become kinked.
Most often, signs of cholestasis appear in the third trimester of pregnancy. The clinical picture of bile stagnation in pregnant women is the same as in non-pregnant representatives of the fair sex.
Stagnation of bile in a child
Stagnation of bile in the liver and gallbladder in pediatric patients most often occurs for the following reasons:
- ascariasis. Helminths penetrate the biliary tract and gallbladder, leading to obstruction of the main bile duct;
- congenital pathology of the biliary tract. Basically, cholestasis occurs when the opening of the papilla of Vater or the canal of the main bile duct narrows;
- biliary dyskinesia.
When bile stagnates, a child may experience symptoms such as:
- yellowing of the skin;
- dry skin;
- skin rashes;
- loss of appetite, sometimes to the point of complete refusal of food;
- nausea, vomiting;
- stool discoloration;
- darkening of urine;
- stomach ache;
- increased bleeding and others.
In principle, a child exhibits the same signs of cholestasis as an adult patient. But there is also one feature of bile stagnation in childhood - a long asymptomatic course, and obvious manifestations arise already at the stage of development of complications.
What are the dangers of congestion in the biliary system?
The gallbladder is necessary for the storage of bile and its release through the sphincter of Oddi into the duodenum. Secretion occurs when food enters the esophagus. Bile actively breaks down fats and promotes the proper absorption of carbohydrates and proteins contained in food masses.
Read also: Benefits of using celandine for polyps in the gallbladder
Stagnation in the gallbladder leads to excessive accumulation of bile (up to 300 ml), an increase in its viscosity and concentration. The process is accompanied by a disruption of metabolic mechanisms and a decrease in release into the duodenum. If the bile secretion stagnates, this leads to an increase in bilirubin. When it accumulates in the ducts, the substance is reabsorbed into the blood and bilirubinemia occurs, causing intoxication of the body.
Stagnation of bile after removal of the gallbladder: symptoms and treatment
The operation during which the gallbladder is removed is called cholecystectomy. The main indication for such surgery is cholelithiasis.
Very often, after cholecystectomy, patients experience symptoms such as:
- pain under the right rib and epigastrium, which can radiate to the right shoulder and scapula;
- yellowing of the skin;
- itching of the skin;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- stool instability;
- bloating.
This symptom complex is called postcholecystectomy syndrome.
The most common cause of this syndrome is the presence of stones in the biliary tract. After all, cholecystectomy for cholelithiasis does not exclude the appearance of new stones in the biliary tract.
Treatment of postcholecystectomy syndrome consists of strict adherence to a low-fat diet and symptomatic therapy.
If pain occurs, patients are prescribed antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Riabal).
If digestive processes are disrupted, the use of enzymatic drugs, such as Festal, Mezim, Panzinorm, is indicated.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment is indicated, during which the obstruction to the outflow of bile in the bile ducts is eliminated.