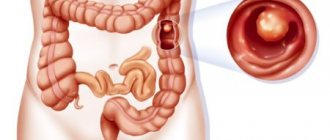
Any person at any age can develop colon polyps. People aged 50 or over, who have bad habits and are overweight are most at risk. Typically, polyps do not cause a person much discomfort, but in rare cases they turn into cancer. What causes this condition and what ways can you get rid of it?
- 8.1 Removal
Classification
By histology and origin
Colon polyps are divided according to histology (structure and quantity) into:
- tubular, villous, tubular-villous;
- single, multiple, diffuse (more than 15 pieces).
Polyps in the large intestine, depending on their origin (morphology), have the following classification:
- inflammatory (grow in the intestinal mucosa in response to an acute inflammatory disease);
- adenomatous (true tumors, considered a precancerous condition);
- hyperplastic (appear as a result of excessive growth of healthy mucosa);
- neoplastic (the most dangerous, such a polyp can degenerate into a malignant tumor).
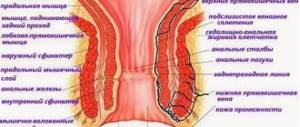
General concepts
The size of polyps can vary from a few mm to 2 or more cm. They can be single, group, or intertwined with their legs. Their surface also varies: it can be completely smooth or villous.
Their consistency is soft, they can have a spherical shape, some of them are mushroom-shaped and branched. Their favorite localization is the lower part of the large intestine and the ampulla of the rectum.
In other sections they grow very rarely: in particular, in the duodenum they occur in only 0.1% of cases. The color of such polyps varies from burgundy to reddish-gray with a hint of yellow. Often, polyps are covered with mucus on top.
Despite the fact that polyps do not cause concern to their owner at the beginning of their development, they are very dangerous due to the increased risk of malignancy, especially with its hereditary etiology.
Many researchers consider polyps to be an intermediate link between inflammation and intestinal cancer. Therefore, if they are detected, only surgical removal is performed.
The difference between hemorrhoids and polyps in the colon
Some symptoms of hemorrhoids and polyps are very similar to each other, but still these are not the same diseases that are treated differently. Hemorrhoids are associated with thrombosis, inflammation, pathological expansion of hemorrhoidal veins and occur in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Its main symptoms are: discharge of blood and mucus from the anus, prolapse of nodes. Polyps form on the walls of the intestine or in the anal canal, forming nodules similar to hemorrhoids, which never fall out of the anus (the exception is a large anal polyp). Very often, only with the help of a diagnostic method can diseases be distinguished from each other.
Root causes of polyposis
The exact cause of the occurrence is not always determined, since polyps sometimes do not show any symptoms. Often they are discovered by chance, during complaints of a completely different disease. The development of intestinal polyposis depends on the following factors:
- improper nutrition and diet (eating large amounts of fatty foods, lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet);
- excess body weight (which is also often a consequence of poor nutrition);
- chronic constipation;
- bad habits;
- age factor;
- disease through genes (genetically).
Risk of degeneration
The likelihood of malignancy depends on the age of the polyp, its type, quantity and size. The greatest danger is posed by adenomatous villous polyp, as already mentioned. Hereditary multiple polyposis is also dangerous.
Large polyps speak their age themselves: in this case the prognosis is also not particularly good. If the polyp is more than 2 cm, the risk of degeneration increases by 20%, and with further growth – by 40%.
A small polyp less than 1 cm has a risk of malignancy of only 1%. Only hamartomas, inflammatory and hyperplastic polyps are not prone to cancer.
Symptoms of the disease
Often, small polyps do not cause any symptoms and the person is not even aware of their existence in the colon. Only with the help of a certain study can a specialist identify them. When the polyps grow, then the following symptoms begin to appear:
- Bloody discharge from the anus. You may notice traces of blood on toilet paper after defecation. Although bleeding is not only caused by polyps, but also by conditions and ailments such as cancer, hemorrhoids, and anal fissures. If such a sign appears, you should consult a doctor and determine the exact cause of the bleeding, so as not to make a mistake in the diagnosis.
- Presence of blood in stool. Blood can stain the entire stool and make it black, or is present in it as impurities.
- Stomach upset such as diarrhea or constipation. It is worth paying more attention to this sign, since the longevity of this condition is a signal of the growth of a large polyp on the mucous membrane of the intestinal walls.
- The appearance of pain and cramps in the abdomen. Large polyps can block the intestinal lumen, thereby complicating the process of defecation, which leads to pain.
Tests and diagnostics
Medical clinics diagnose colon polyposis by performing a stool occult blood test. This is a classic test that is used for the early diagnosis of malignant tumors of the colon and rectum. Its implementation includes preparatory procedures: before the analysis, it is forbidden to use toothpaste or take certain medications. This diagnostic method is not considered accurate, since polyps in the intestines may not have symptoms at all, in which blood appears in the stool.
The next common method of diagnostic research is computed tomography, which can be used to detect the presence of polyposis and tumor formations in the intestine. Well, the most important thing is to conduct a colonoscopy to examine the intestinal mucosa; it will help not only to detect, but also to remove the existing polyp. Colonoscopy is performed under anesthesia, so the patient will not experience any pain or discomfort when removing the formations.
Types of operations
If diffuse (familial) polyposis is diagnosed, the affected area of the intestine is completely removed under general anesthesia (resection), and the anus is sutured to the ileum. Removed polyps can recur after a year or 3, so observation by a coloproctologist with periodic colonoscopy is mandatory.
Transrectal excision of the polyp - it is used when the polyp is located close to the entrance to the anus - no further than 10 cm. Local anesthesia - novocaine. After its exposure, the ampulla of the rectum is expanded with scissors and the polyp is removed. If the polyp has a stalk, it is clamped with a clamp. The site of its removal is sutured. The sutures are made of catgut and dissolve on their own within a month.
If the polyp is located further than 10 cm, use a rectal mirror to stretch the intestinal wall to the desired diameter and stretch it with your fingers until completely relaxed. The patient is asked to push to bring the polyp closer, it is additionally anesthetized and then excised.
Endoscopic polypectomy – it is used for polyps in the upper and middle intestines. The patient is euthanized with medication; An endoscope or colonoscope is inserted transanally, the polyp is first identified and then removed endoscopically. The doctor performs additional electrocoagulation of the polyp site to prevent bleeding.
Photocoagulation is also used - it is carried out with an anoscope, which has fiber optics and with the help of it the formation is coagulated and then removed with a laser. The method is good for children with a single small polyp. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and medicated sleep.
If the polyp is large, it is not removed immediately, but in parts, using biopsy forceps, which has its own name - biting. Due to its complexity, this technique requires a qualified doctor, since burns of the intestinal wall can cause perforation and release of gases into the abdominal cavity.
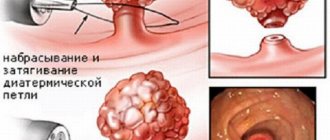
Electrical excision is performed with a proctoscope inserted. At the same time, they bring the electric loop to the polyp and throw it over it. The loop is then heated by passing electric current. The epithelium of the polyp dies as a result of the resulting burn. Gradually the noose is tightened, the polyp is cut off and pulled out. There is no bleeding with this method.
Colotomy or intestinal resection - it is performed when polyps are localized in the sigma or for villous polyps with wide bases. Under anesthesia, a section of the affected intestine is removed through an incision in the left iliac region. The tumor is excised and sutures are placed. The abdominal wall is sutured in layers.
Enterotomy is the excision of small mushroom-shaped polyps. From the localization of the polyp, the following are performed: duodenotomy (duodenum), incision of the ileum (ileotomy), removal of the polyp in the small intestine (jejunotomy).
Resection of the small intestine by segment – performed for large polyps; the area of growth is excised and the healthy ends of the intestine are sutured - an interintestinal anastomosis appears. Such a patient subsequently experiences digestive problems due to shortening of the intestines. Cure is 90% guaranteed with early treatment. The relapse rate is 30%.
Treatment options
Removal
Treatment of polyposis with drugs will not bring any results, so only a surgical operation in a clinic can save a sick person from an unpleasant disease. The main thing is to carry out a timely operation, including the removal of small polyps, in order to prevent the development of malignant tumors. Endoscopic surgery is performed (an operation performed using an endoscope, loop electrode, electrocoagulator). If colon polyposis is accompanied by multiple growths, then endoscopic surgery is performed in conjunction with excision of the polyp using a rectoscope (polypectomy), or the polyp is specifically removed (laparoscopic resection). After the operation - polypectomy, the eliminated polyp is sent for examination to the laboratory to determine the presence of dangerous neoplasms.
This surgical method of treatment (removal of the formation) is usually easily tolerated and is absolutely painless, although it is performed without painkillers and anesthesia. The patient is not kept in the clinic for a long time and is allowed to go home after a day. But if part of the intestine is removed, the patient is left for treatment in a hospital until the end of the recovery period. If a large polyp and its multiple growths have been removed, re-treatment (surgery) must be carried out a year later, and a diagnostic examination - colonoscopy - must be carried out for several years after the operation, since in rare cases the secondary appearance of polyps in previously affected areas is possible. places.
Folk remedies
The best folk remedies are considered to be enemas with a decoction of celandine and herbs. Let's start with the first recipe: to prepare a decoction of celandine you need to take 1 tsp. herbs, pour 100 ml of boiling water. Enemas must be administered within 10 days. At the end of the course, take a break of 7 days and repeat the course again. The second recipe for treatment with folk remedies: to prepare the collection you need to take 3 tsp. celandine, 2 tsp. chamomile and 2 tsp. St. John's wort. Mix all the herbs and pour a glass of boiling water. An enema must be done before bed every day for a whole month.
An excellent traditional medicine is juice therapy made from fruits and vegetables. Fruits such as kiwi, apples, pears; vegetables - beets, carrots, cucumbers are great for making fresh juices. Therapy with fruits not only prevents the formation of polyps, but is also beneficial for the whole body; such a diet will have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Possible complications
Depending on the choice of surgical procedure, the possible risks associated with surgery should also be taken into account. The occurrence of complications depends not only on the lack of professionalism of the doctor, but also on the nature of the tumor, and on patients who do not fully comply with doctors’ instructions.
The main complications are considered:
- Rectal bleeding (usually disappears after 7 days);
- Copious mucous discharge from the colorectal lumen, which wets the underwear;
- Perforation of thin mucous tissues;
- Postoperative infection;
- Inflammatory process;
- The appearance of a new polyp with potential cell malignancy.
Unfortunately, relapses after surgery do occur and are not uncommon. The likelihood of such complications occurring is minimized, however, even with minimally invasive methods, all medical prescriptions should be followed, just as with abdominal surgical interventions.
Possible consequences
Unwanted complications and danger can arise at any time. Possible bleeding from the colon, end-to-end disruption of one of the intestinal walls, intestinal obstruction, the appearance of enterocolitis, anemia, dense formations from feces. Often, after surgery to remove polyps or resection, they reappear in the intestines. The danger is that polyps turn from benign into malignant formations and can be inherited genetically.
Prevention
The best prevention to prevent the appearance of polyps in the colon will be the following recommendations: diet and proper nutrition - eat more fresh fruits and juices from them; products containing fiber - fruits (apples, pears) and vegetables (cabbage, zucchini, pumpkin); in the diet, introduce restrictions on the consumption of animal fats (replace with vegetable fats); refusal of alcohol and low-alcohol drinks, which lead to the formation of malignant intestinal tumors. If a person follows a diet, proper nutrition, and does not abuse alcohol, then the disease will not affect him at all, or the existing one will not lead to dire consequences.
Diet after surgery
The patient’s recovery after surgery depends on his compliance with a certain diet. Rehabilitation takes place in several stages. Stage 1 lasts 3 days. On the first day, food and drink are completely excluded.
The next day, you can only quench your thirst, and the volume of liquid you drink is no more than 50 ml. The same volume of compote, rosehip decoction or vegetable broth is allowed.
After the next 12 hours, lean meat broth, jelly and rice broth are given. All these efforts are aimed at limiting as much as possible any intestinal peristalsis and reducing the production of enzymes. The secreted digestive juices can damage unhealed sutures and surgical sites.
Stage 2 – occurs on the 4th day after surgery. The diet is already expanding and the patient can eat thin porridges and slimy soups. At this stage, bowel loading is carefully increased to help form normal stools. This stage lasts until discharge.
After 2 weeks, stage 3 begins, when the patient is allowed a gentle diet. He will comply with it for 4 months. The rules for such nutrition are as follows: eat fractionally, at the same hours, eat at least 6 times, but in small portions. Fermentation should not occur in the intestines, so nuts, legumes and mushrooms are excluded. Sour, spicy, fatty and fried foods are prohibited. Products are pureed or baked.
Protein should be included in the diet daily, as it builds repaired tissue. The presence of first courses on the menu is mandatory. The daily volume of liquid consumed should not be less than 3 liters.