Symptoms of liver cancer in women
In the fairer sex, the initial symptoms of liver cancer, despite their non-specificity, rarely go unnoticed. This is due to the tendency of women to be attentive to their well-being and, if any negative signs appear, to consult a doctor. This is what contributes to the timely detection of a dangerous disease.
The first symptoms of liver cancer, prompting a woman to undergo examination by specialists, are associated with an unexplained deterioration in health:
- dizziness, constant weakness and fatigue, decreased performance, apathy;
- loss of appetite and intolerance to certain foods;
- dyspeptic disorders - nausea, frequent bouts of vomiting, independent of food intake, and diarrhea;
- anemia.
In addition to these general manifestations, women in the initial stages of the disease may experience specific signs of liver cancer - heaviness in the right hypochondrium, yellowness of the skin, increased temperature. Their severity depends on what stage the transient disease has reached. Due to the fact that primary liver cancer progresses rapidly, specific symptoms can be felt quite quickly.
Liver Cancer: Signs and Symptoms Caused by Paraneoplastic Syndrome
In rare cases, in the early stages of the disease, a special type of disorder may develop, manifested by:
- changes in the blood - increased calcium, decreased sugar, increased number of red blood cells, high cholesterol;
- enlarged mammary glands (gynecomastia);
- reduction in testicular size in men.
Despite the fact that with progressive liver cancer the symptoms (manifestations) are quite well expressed, in some cases patients are not aware of the seriousness of the problem.
For example, people who abuse alcoholic beverages associate their deterioration in health with the consequences of alcohol intoxication, patients with chronic hepatitis - with errors in diet, etc.
Causes of liver cancer in women
An exact list of prerequisites that can trigger the development of a primary malignant process in the liver has not yet been identified, but scientists continue to conduct research in this area. Experts list a number of suspected factors that provoke the occurrence of abnormal changes in the cells of the largest secretory organ. They can be both internal and external.
Read here: What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Many hepatologists believe that liver cancer in women can begin to develop while taking birth control pills. These medications contain a large amount of estrogen, which provokes the formation of benign neoplasms, which can subsequently become malignant. Most often, the place of their localization is the liver tissue. Often, as clinical practice shows, the causes of liver cancer in women lie in the chronic course of certain hepatological diseases over several years.
Among them are:
- Hepatitis C. The virus that causes this pathology is considered the main provocateur of the development of tumor structures. The risk group consists of women of easy virtue.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. In 70% of cases, liver cells destroyed by alcohol begin to become malignant very quickly. This reason has come to almost first place in recent years due to the fact that an increasing number of representatives of the fair sex are becoming dependent on alcohol.
- Cholelithiasis. Stones formed in the bile ducts severely damage the surrounding tissue, which contributes to improper cell division and, as a consequence, the formation of a malignant tumor.
- Diabetes. If a woman has a history of this disease, she experiences severe metabolic disorders, which affects the functioning of the largest secretory organ.
Worth knowing! Any representative of the fair sex can herself provoke the development of a malignancy process in the liver. This happens when she begins to excessively consume dietary supplements, vitamins and mineral complexes containing iron. An excess of this substance in the body has a strong effect on the liver tissue, eventually causing its destruction and, as a consequence, the onset of malignancy.
Causes
The causes of primary liver cancer have not been studied, but doctors say that most often the tumor is detected in people who have already suffered from diseases of this organ. The main one of these factors is cirrhosis, especially the large-nodular type. Good conditions are created in the nodules for the formation of a tumor process. The majority of cancer patients had cirrhosis of the liver.
In addition to it, the following diseases can provoke the development of neoplasms:
- Viral hepatitis, which occurs in a chronic form.
- Hemochromatosis, in which excessive amounts of iron are deposited in the body.
- Gallstone disease accompanied by an inflammatory process.
- Syphilis caused by a syphilitic spirochete, which can also penetrate the liver and contribute to cell degeneration.
- Diabetes mellitus, characterized by a failure of metabolic processes.
- Parasitic pathologies in which the liver is poisoned by secretions of certain parasitic representatives.
There are also provoking factors that weaken cells, causing pathological changes in their structure and increasing the risk of malignant degeneration. Such reasons include:
- Bad habits. Substances contained in cigarette smoke and alcohol destroy cells, causing them to mutate.
- The effect of chemicals on the body, for example, arsenic, chlorine.
- Poor nutrition. Eating harmful foods leads to various disorders in cells.
- Taking anabolic steroids. This point applies to athletes who spontaneously decide to take hormonal drugs to achieve greater results in sports activities. Steroids have an adverse effect on the liver.
- Hereditary predisposition. Doctors often encounter cancer in close relatives.
People who are exposed to the factors listed above are at risk. Such patients should be more attentive to their health and regularly be examined by doctors.
Stages of development of liver cancer in women
Liver cancer, despite its transience, like any other oncology, develops in stages. Although with this disease very little time passes from one stage to another, each of them is characterized by its own histological and clinical manifestations, which helps in diagnosing a dangerous disease.
Experts note 4 main stages of liver cancer in women:
- I is the initial stage of development, at which the disease practically does not manifest itself at all. The patient does not experience any discomfort other than constant unexplained fatigue. There are also virtually no histological changes in the liver parenchyma.
- II – a rapid increase in the size of the oncological tumor leads to the appearance of noticeable pain in the right hypochondrium. The histological section shows cells of different structure and size, indicating the activation of the malignancy process.
- III is the last chance to carry out adequate therapy with a successful outcome. Clinical symptoms become more pronounced. Histological changes become very obvious; cells with a normal structure are almost completely absent on the histological section.
- IV – at this stage, the patient’s recovery or maximum prolongation of her life becomes impossible. The pathological process becomes irreversible, and abnormal cells spread throughout the body, provoking the development of secondary malignant foci.
Diagnosis of the disease
Symptoms of liver cancer in women at the very beginning of the development of the pathological condition are practically absent, but most representatives of the fairer sex, unlike men, take their health very seriously, therefore, when nonspecific alarming symptoms appear, they try to consult a doctor for advice. This is what saves lives, because only timely detected disease can be completely cured. Diagnosis of liver cancer begins with an initial interview with the patient about the negative symptoms that confuse her.
After collecting an anamnesis, the specialist prescribes a number of studies aimed at confirming or refuting the presence of oncological pathology:
- Lab tests. First of all, the patient’s blood is taken for tumor markers. This test almost always shows the presence of cancer cells in the body. Also, a blood test reliably shows disturbances in the functioning of the secretory organ, provoked by a previous oncological disease. But a urine test for this disease is not very informative, so it is not always prescribed.
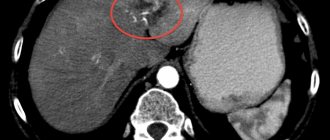
- Histological examination. The most reliable method for detecting liver cancer. Biopsy material is taken from the liver parenchyma with a thin needle under ultrasound control. The discovery of abnormal cells in it completely confirms the expected diagnosis.
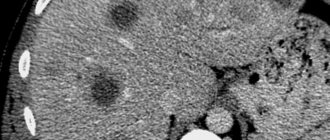
- CT, MRI and PET. These instrumental studies are prescribed to clarify the nature of the oncological tumor developing in the liver parenchyma.
Read here: What is papillary bladder cancer?
After a woman has been diagnosed with liver cancer, treatment is selected based on the main characteristics of the tumor and the general condition of the patient. A group of specialists – hepatologist, oncologist, radiation and chemotherapists – is involved in the selection of a protocol appropriate to a specific situation.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis is made based on the results of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Laboratory diagnostics include general and biochemical blood tests, urine tests, and coagulograms. The main diagnostic signs of formations are:
- decrease in specific gravity and the presence of protein in the urine;
- increased concentrations of urea, creatinine, residual nitrogen;
- decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cell content in the blood;
- decreased levels of total protein and albumin in the blood, increased fibrinogen;
- increased activity of liver enzymes.
A specific analysis for tumor markers allows one to distinguish the development of a benign formation from a malignant degeneration of tissues.
Instrumental diagnostics, including:
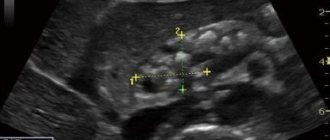
- ultrasound examination of the liver (it is possible to determine the type, size and localization of a formation in the liver by ultrasound, but it is impossible to distinguish benign degeneration from a malignant process);
- magnetic resonance imaging (an accurate method that allows you to clarify the location and nature of the tumor, determine at what distance the malignant focus is from the gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, colon);
- hepatoscintigraphy (during the study, the patient is injected with radioactive iodine ions, which tend to accumulate in pathological foci and are recorded by an X-ray machine, thus clarifying the size of the tumor and the presence of metastases);
- liver biopsy and subsequent morphological analysis of the selected material (allows us to clarify the type of tumor).
If metastatic growths are detected, it is necessary to determine which organ is affected by the primary cancer. This may require esophagogastroscopy, x-rays of the stomach and lungs, ultrasound of the mammary glands and mammography, irrigoscopy and colonoscopy (examination of the large intestine).
Treatment of liver cancer in women
All therapeutic measures to remove a malignant tumor from a secretory organ are possible only after its presence is confirmed by diagnostic studies. Moreover, the main role in their selection is played by histological signs of liver cancer, which are similar in women and men. They show whether surgical intervention is cost-effective and to what extent it should be performed.
The main therapeutic complex consists of the following activities:
- The first step is to remove the liver cancer. In women, as well as in the stronger sex or children, it is possible only if the tumor is small in size. Surgery for liver cancer can be of two types - partial resection or organ transplantation. The latter is performed infrequently, since in medical clinical practice there is a problem with selecting a donor that is suitable for a cancer patient in all respects.
- Chemotherapy for liver cancer is only permissible through intra-arterial administration of drugs. Systemic chemistry does not produce tangible results in liver pathology, so it is almost never used.
- Until recently, radiation therapy for liver cancer was not prescribed, since radiation can cause great harm to healthy liver cells and lead to death in the patient. But research in the field of oncology does not stand still, and not so long ago the latest systems began to appear in large specialized centers, making radiation therapy for oncological lesions of the liver effective and safe.
Important! Timely and adequate treatment of liver cancer in women can save life at least until the five-year critical period. Oncologists strongly recommend that all representatives of the fair sex who have been diagnosed with this terrible disease do not abandon traditional treatment and accurately follow all the oncologist’s recommendations. Only this gives a chance for a future life.
General symptoms
Liver cancer is a terrible disease in which the first symptoms are nonspecific and do not appear so quickly. Since the pathology is formed under the influence of the above ailments and deterioration of the condition, the patient experiences a number of symptoms that bring general discomfort.
The patient notes general signs of illness:
- lethargy and weakness;
- abdominal enlargement;
- heaviness in the liver area;
- jaundice;
- increased body temperature;
- vomit;
- nausea;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of diarrhea;
- swelling of the limbs;
- anemia;
- nosebleeds.
The patient feels severe pain in the lower back, in the right hypochondrium and upper abdomen. In the first days, attacks of a periodic nature appear under heavy loads, and then develop into constant pain.
How and where does liver cancer metastasize in women?
The extensive blood supply to the liver contributes to an increased supply of nutrients to the malignant focus, due to which it grows at a rapid pace and begins to metastasize in the early stages.
Liver cancer spreads:
- With the lymph flow, first regional and then distant lymph nodes are affected, which is expressed in their severe enlargement and pain.
- With blood flow. Through the hematogenous route, metastases from liver cancer penetrate into distant internal organs, the brain and bone structures. This leads to the appearance of additional symptoms that are directly related to the site of the lesion.
- By penetration. Such metastases in liver cancer in women appear most often, since the growth of the primary tumor occurs into the tissues of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis surrounding the liver parenchyma.
The tendency of hepatic malignant neoplasms to early and extensive metastasis leads to the fact that secondary malignant foci can be diagnosed in a wide variety of areas of the body. This significantly complicates the treatment of liver cancer in women and worsens the prognosis for their lives. Oncologists believe that only early detection of the pathological process increases patients' chances of long-term remission.
Important! The main consequences of liver cancer are associated with the process of metastasis. If metastases have spread throughout the body, after therapy the tumor will return in a short time. In this case, patients are prescribed repeated surgery and a course of combined treatment.
Treatment
Recently, the government has set medicine the task of early diagnosis of cancer. At the initial stage, it is possible to treat with drugs and techniques that destroy cancerous nodes or at least stop their growth. Modern research methods, such as PET (positron emission tomography) and PET in combination with CT and MRI, make it possible to detect the presence of a tumor at the molecular level, specifically determining the location of the smallest nodules.
Methods for treating liver cancer at an early stage:
- Small formations (up to 3 cm) without metastasis are subjected to percutaneous ablation, which is an injection with ethanol or acetic acid, or thermal exposure to heat or frozen gas. There is also a technique for processing nodes with microwave or high-energy radio radiation. The procedures are carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine.
- Larger nodes with a diameter of 3-5 cm are destroyed by vascular embolization. This is achieved by inhibiting their blood supply by introducing special drugs or radioisotopes into the hepatic vessels.
- Targeted radiation therapy involves focusing X-ray beams precisely on the tumor, while sparing healthy tissue. The method is applied at all stages.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma can be treated with the anticancer tablets Sorafenib or Nexavar (sorafenib tosylate). This is a modern medicine that affects tumor cells and suppresses their growth. This chemotherapy has many severe side effects.
- A single tumor of no more than 1/3 of the liver volume without metastases, vascular growth, or beyond the contours of the organ is surgically removed, giving patients a chance to completely get rid of cancer. Modern techniques allow the operation to be performed laparoscopically with minimal trauma to the patient. The liver is a self-healing organ, so a complete recovery is possible. At later stages, in the presence of a larger tumor, abdominal surgery is performed using donor material or a complete organ transplant.
At the last stage of cancer, the prognosis is poor. A tumor with numerous metastases is not operated on; only supportive treatment, radiation or chemotherapy is performed.
Traditional healers offer treatment with herbs and bee products. They can be considered as additional methods in consultation with your doctor.
Relapse in liver cancer in women
The greatest danger of this type of oncological lesion is that it tends to recur within a short time after therapeutic measures. The main reason for the re-development of cancer in the liver is the presence of abnormal cells in the body left after treatment.
Read here: What is fibrosarcoma?
Recurrence of liver cancer can be:
- Local. A new tumor appears in the same place where the previously removed one was located.
- Regional. Despite treatment for liver cancer, women still have malignant cells in the perihepatic lymph nodes.
- Metastatic. The main tumor process affected distant organs and bone structures.
In modern oncological practice, liver cancer that recurs almost immediately after treatment is very common in women. Mandatory post-treatment monitoring of their condition is considered the best way to increase the survival rate of cancer patients. If a repeated tumor structure localized within the hepatic parenchyma is detected in a timely manner, then the chances of adequate treatment and a favorable outcome of the disease increase significantly.
The first signs at an early stage
The insidiousness of cancer lies in the fact that at an early stage it does not show any signs. A first-degree tumor is characterized by the fact that it is solitary, does not extend beyond the liver, and is not entangled with blood and lymphatic vessels. Only slight weakness, increased fatigue and uncomfortable sensations in the right hypochondrium can be the first signs at an early stage of a malignant neoplasm. Often the initial stage is detected by chance during an ultrasound or SCT examination of internal organs.
People prone to bad habits, working with toxic substances, suffering from hepatitis, cirrhosis, diabetes, should regularly examine the liver using ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. This should also be done when there are no signs of illness.
If the first symptoms appear that indicate possible disorders in the liver, especially regular discomfort under the ribs on the right in combination with increased fatigue, you should monitor other signs characteristic of diseases of this important organ.
Symptoms of liver disease:
- loss of appetite, nausea (sometimes with vomiting);
- weight loss;
- fever, a persistent increase in temperature that is difficult to bring down;
- when palpating the abdomen in the liver area, there is a feeling of a hard and lumpy surface of the organ, pain;
- change in color of stool (urine dark, feces light);
- yellowness of the skin and eye sclera;
- an increase in the volume of the abdomen, a feeling of bloating and tightness of the skin, often combined with the appearance of a tortuous pattern of blood vessels and a protrusion of the navel (abdominal dropsy);
- nosebleeds.
A low red blood cell count is an indirect symptom of liver cancer. Also indirect, but quite accurate, signs are tumor markers. In liver cancer, indicative markers are AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), CA15-3, CA19-9. For women, it is advisable to determine the tumor antigen CA72-4, the excess of which indicates cancer of the gastrointestinal tract (including the liver), or tumors of the ovary, endometrium and cervix.
In the later stages of the disease, internal bleeding is possible, which causes such obvious symptoms as severe discoloration of the skin and weakness, even fainting. In this case, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
The main causes of tumors lie in disruption of the formation of organ cells, metabolic disorders or mechanical damage to the parenchyma. Disruption of the process of healthy cell division and tissue generation can be caused by various external and internal phenomena.
External influences include human exposure to a toxic atmosphere, abuse of nicotine, alcohol, narcotic substances and certain medications, consumption of foods contaminated with fungus, worm-infected raw fish and other foods containing poisons and carcinogens.
Statistical analysis shows that there are families in which a predisposition to cancer is passed down from generation to generation due to an inherited mutation.
In addition, the cause of pathology can be the presence of the following diseases:
- Cirrhosis. The disease is characterized by the formation of nodes in the liver tissue; there is a high probability of degeneration of hepatocytes in the nodes into malignant cells. In the later stages of cirrhosis, the disease is aggravated by the oncological process.
- Hepatitis (usually B and C). When the disease occurs, the parenchyma of the organ is affected. Many forms are very difficult to treat. As a result of the long chronic course of the disease, tissue scarring occurs, cirrhosis occurs and cells degenerate into cancer. The main prevention is to use condoms during sexual intercourse, disposable syringes and other means during medical interventions, individual or properly processed instruments during cosmetic procedures (manicure, pedicure, eyebrow correction).
- Cholelithiasis. The resulting large mechanical particles clog the bile ducts and injure their walls; damaged areas tend to transmute into malignant growths.
- Diabetes. Disruption of metabolic processes in the liver is a provoking factor for improper cell formation and the occurrence of oncology.
- Syphilis. The disease occurs when infected with pathogenic bacteria, which, when multiplying, destroy liver tissue, which is a risk factor for cancer.
More often, long-term use of contraceptives leads to the appearance of benign formations (cysts, polyps, fibroids), but in their presence there is always a threat of malignancy. It should always be remembered that artificial influence on the female body can disrupt the mechanisms of regulation of the reproductive system created by nature. No one gives a 100% guarantee that undesirable consequences will not occur.
In most cases of liver cancer, it is affected by metastases of tumors of the genital organs, adrenal glands and intestines.
Recently, the government has set medicine the task of early diagnosis of cancer. At the initial stage, it is possible to treat with drugs and techniques that destroy cancerous nodes or at least stop their growth. Modern research methods, such as PET (positron emission tomography) and PET in combination with CT and MRI, make it possible to detect the presence of a tumor at the molecular level, specifically determining the location of the smallest nodules.
Liver cancer in women: how long do patients live?
The likelihood of a favorable outcome for cancer that affects liver tissue is very low. The reason is that liver cancer, due to its transience, is most often diagnosed in the last stages. In this regard, the life expectancy of patients is significantly reduced and in some cases can be several months or even weeks.
The life prognosis for liver cancer in women is directly related to what type of cancer develops in it:
- with fibrolamellar carcinoma, the life expectancy of patients can range from 2 to 5 years, and if the pathological condition is identified before the metastasis process begins, a complete recovery is possible;
- for cystadenocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, five-year survival is possible only with timely and successful liver resection;
- with sarcoma and angiosarcoma, the prognosis is the most disappointing - from several months to 2 years after the onset of tumor development.
Oncologists divide all malignant tumors of the secretory organ into operable and inoperable. In the first case, after a successful surgical intervention, patients have a real chance of living well for several years, and in the second, the count goes on for months.
Symptoms of stage 4 cancer
The last stage of the pathology is characterized by a sharp deterioration of the condition. The patient feels severe pain in many internal organs. Liver damage and the spread of metastases to other organs are diagnosed. The patient's symptoms of previously acquired diseases worsen. At this stage, any therapy is powerless and doctors only try to keep the patient alive, relieving the patient’s pain.
It should be noted that if the above first signs of liver cancer appear, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Prevention of liver cancer
The question of how to prevent the development of a terrible disease worries many patients who are at risk. According to the unequivocal statement of hepatologists, this is not at all difficult to do.
Prevention of liver cancer, both in women and men, consists of following some simple rules:
- if there is a possibility of contracting hepatitis C, you should get vaccinated against this disease;
- before you start using dietary supplements or mineral complexes, the main component of which is iron, you must consult with your doctor about their need;
- It is strictly not recommended to abuse alcohol. Even low-alcohol drinks are prohibited for the prevention of liver cancer.
By following these simple rules, the risk of developing cancer in the liver is significantly reduced.
Be healthy!
What liver formations can be identified by ultrasound?
During an ultrasound examination of an organ, when cancer is detected, benign neoplasms are detected:
- adenomas with and without the inclusion of vessels;
- cysts with liquid contents;
- lipomas – lipid capsules;
- hemangiomas - tangles of overgrown veins;
- hepatosis – fatty degeneration of cells;
- cirrhosis – replacement of functional connective tissues;
- hepatitis C, it manifests itself as a blurred outline of the organ, its enlargement;
- calcification - compaction saturated with salts.
This is interesting: Is liver cancer curable or not: is it possible to cure cancer in the later stages?
Foci of tuberculosis, candidiasis, and other diseases are detected. The inflammatory process is detected by liver enlargement.
All pathologies require periodic monitoring, as they can develop into cancer. It is recommended to do examinations at least once a year. The doctor looks to see if the lesions have increased and how homogeneous they are. All ultrasound data are entered into the patient’s card. He automatically falls into the risk group and must be more attentive to the appearance of symptoms characteristic of the initial stages of cancer.
In addition to benign neoplasms, anomalies in the development of the organ are detected: a deficiency or excess of lobes, their incorrect location. They have little effect on the functioning of the organ; the cells do not degenerate.
Cancer detected by ultrasound can be of different nature. Types of malignant neoplasms:
- sarcoma - consists of connective tissue and blood vessels;
- carcinoma is a primary cancer formed by the degeneration of hepatocytes;
- hepatoblastoma arises in utero from undeveloped functional cells and is diagnosed at an early age, up to five years;
- hemangiosarcoma is a pathological proliferation of blood vessel tissue, no less dangerous than sarcoma.