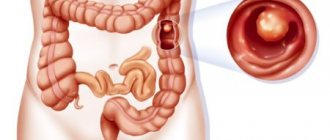
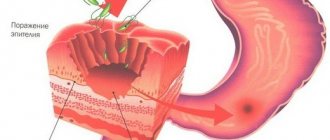
Differential diagnosis of adenomas with advanced colon tumors does not cause difficulties. Early invasive cancer may resemble a benign tumor, but has a number of characteristic features. Because Cancer invasion into the submucosal layer occurs through the stalk of the polyp, then with an increase in the volume of invasion it gradually thickens and shortens (eventually, the formation on the stalk loses it and is located on a broad base). The simultaneous disintegration of the tumor in the head region leads to its deformation and erosion (erosion is a characteristic sign of invasive cancer). Another characteristic feature is pronounced contact trauma. A retraction or “platform” on the surface of the lesion may also indicate invasive carcinoma [14].
Juvenile and Peutz-Jeghers polyps
Juvenile polyps occur primarily in children and adolescents. More often they are solitary, on a stalk and with a spherical head, have a bright red color and sometimes an eroded apex. Juvenile polyps are not lobulated. There are contradictions among morphologists regarding the nature of such polyps; a number of authors consider them as hamartromic, others point to their closeness to adenomatous polyps. Morphologically, irregularly shaped glands with cystic expansions containing mucin, exuded by cuboidal epithelium, are revealed. The stroma of such polyps is swollen, contains dilated vessels and inflammatory cells. It is believed that juvenile polyps do not become malignant.
Peutz-Jeghers polyps can either have a stalk or be located on a broad base, often lobulated and have a whitish color. Their distinctive morphological feature is the presence of branching smooth muscle bundles emanating from the muscular plate of the mucosa.
Treatment tactics
Many clinicians consider any atypical neoplasms on the mucous membranes of internal organs to be a precancerous condition. An effective treatment is surgery.
Depending on the degree of polypous lesion, the nature of the growth and the type of localization, surgical tactics are chosen.
The following methods are used for removal:
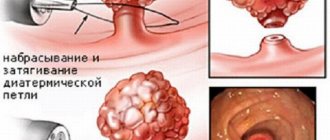
- Polypectomy . The traditional method of excision of a polyp using an electric knife, followed by cauterization of the wound surface with a laser or electrodes. The operation is performed using a rectoroscope or colonoscope.
- Transanal section . The method allows you to remove polypous lesions in the lower or middle parts of the colon using a rectoscope or colonoscope. A special loop is placed over the polyp, which is compressed and the polyp is excised. Next, the wound site is cauterized with an electric charge to prevent bleeding.
- Laparoscopic polypectomy . It is used when localizing a polypous lesion in hard-to-reach places. It involves several incisions in the peritoneum and further manipulation using surgical instruments.
- Resection . A radical method of polyp removal, prescribed for metastases and malignant tumors, may involve complete removal of the colon or part of it along with the affected mucosa.
Attention ! Unfortunately, no operation guarantees the absence of potential oncogenic risks and the formation of a new lesion. In the overwhelming majority, surgery to remove polypous tumors is an adequate prevention against intestinal cancer.
Inflammatory polyps
They represent a focus of inflammation. Often occur with nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Their size and appearance can vary widely. We observed the formation of an inflammatory polyp in the area of utero-intestinal and enterovesical fistulas. They can form in the area of intestinal anastomosis. A large number of them in inflammatory bowel diseases can create difficulties in differential diagnosis with diffuse familial polyposis. Morphologically, the formation is represented by a different combination of granulation tissue and regenerative epithelium.
Risk group
Often such neoplasms are diagnosed in people over 40 years of age, which is associated with aging of the intestines and greater vulnerability of the mucous membrane. The formation of polyps is divided into:
- Hereditary. These include:
- familial adenomatous polyposis;
- Peutz-Jigers syndrome;
- juvenile polyposis syndrome;
- Gardner's syndrome.
- Non-hereditary - Cronkite-Canada syndrome.
People whose diet consists primarily of meat and fat are more susceptible to developing such diseases. People at risk include people who are overweight, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Additional methods for differential diagnosis of colon polyps
As mentioned above, the differential diagnosis of neoplastic and neoplastic polyps, as well as early cases of carcinoma, is quite difficult, especially for small tumors. To improve such diagnostics, S. Kudo et al. proposed a method for endoscopic diagnosis of the possible morphological structure of a tumor based on the pattern of glandular pits [11]. There are 5 types of patterns of glandular pits (Fig. 8), with a clear correlation between them and the morphological structure of the formation [11].
The first type, characterized by round, regularly spaced pits of almost the same size, is a sign of an unchanged mucous membrane. The second type (regularly located pits of large size and “star-shaped” or “bulbous” shape) occurs in 69.4% of cases with hyperplastic polyps, and in 30.5% with adenomatous polyps. The third type (S) is compactly located small rounded pits in 86.3% are adenomas, and 12.3% are carcinomas. The third type (L) - large, elongated pits - adenomas in 92.7% and carcinomas in 4.2%. The fourth type - pits of the type of branches or convolutions - in 74.9% of cases these are adenomas (usually glandular-villous), and in the rest - carcinomas. The fifth type - with partial or complete disruption of the structure of the fossae - carcinoma in 93.3% of cases and adenoma in 6.7%.
This pattern can be observed during a standard colonoscopy, but magnified colonoscopy provides a more accurate degree of diagnosis. Konishi K. et al compared the diagnostic yield of conventional colonoscopy and magnified colonoscopy based on 630 colonoscopies (330 with and 330 without magnification) [10]. The assessment of the pattern of glandular pits was carried out after irrigating the formation with a 0.2% solution of indigo carmine, according to the above classification. The accuracy of endoscopic diagnosis was then verified by morphological examination. This work included only patients with lesions no larger than 10 mm. Successful differentiation of neoplastic from neoplastic lesions was possible in 92% of cases with magnifying colonoscopy and only 68% of cases with conventional colonoscopy.
Reasons for the occurrence of education
A formation can form without obvious signs and not manifest itself for a long time. But a polyp in its later stages often causes unpleasant complications in the digestive system. The causes of growths can be the following factors:
- chronic diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- age group from 45 years;
- overweight;
- individual structure of the intestine.
The causes of focal formations are not fully known, since there is no single factor that can be an indicator of the development of the disease. But there is a theory that polyps are a kind of mucosal hyperplasia, proliferation and anaplasia.
Rectal polyps rarely develop into cancer, but their development should be closely monitored.
After 45 years, examination of the stomach and intestines should be carried out every 3-4 years.
What do polyps look like?
Relapse Prevention
The greatest risk of relapse occurs in the first 2 years after surgery. At this time, patients must undergo clinical observation, visiting a doctor at least once every six months. The best way to reduce relapses is a healthy lifestyle and a special diet containing plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Regular physical activity is extremely important. Hormone replacement therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs and antioxidants are prescribed.
pishchevarenie.ru
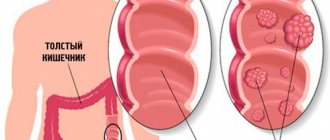
Let's draw up a morphological picture of the disease. A hyperplastic polyp of the colon is a formation on the walls of the organ, which consists of epithelial cells. It has a color identical to the surface of the mucosa. This type accounts for about 90% of all detected cases. The shape may include specimens with a stalk or a wide base, about 5 mm in size. Multiple accumulations are called polyposis.
Attention! About a third of polyposis cases eventually lead to cancer. However, it is the hyperplastic type that is practically not susceptible to this.
Similar formations are found in people of any age, however, if this is rare among children, then among the population over 50, about 40% are guaranteed to have polyps. As usual, they are small in size, so they do not cause concern to a person. However, in addition to the risk of malignancy (malignancy), some polyps are prone to hyperplasia, or, more simply, to rapid growth. Such formations can impede the functioning of the organ, block its lumen, interfering with the movement of intestinal contents. A large polyp is sometimes injured, forming a wound. By the way, hyperplastic polyps of the rectum are often found. It is in these cases that bleeding occurs, which is often confused with hemorrhoids. Polyps sometimes surround focal rectal cancer lesions.
It is impossible to say reliably why polyps appear in one case or another, but there are general reasons that provoke their formation:
- Heredity. Dysplasia - abnormal structure, development, structure of cells and tissues of the intestinal mucosa is inherited. Therefore, if one of your blood relatives has had polyposis or cancer of this organ, it is worth getting examined.
- Nutrition. Food with minimal fiber and healthy elements, a large amount of fast carbohydrates and animal fats. Overeating, fasting, lack of eating schedule.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines.
- Constipation for several years.
- Bad habits are regular smoking and systematic drinking of alcohol.
- Aging of the body.
- Lack of necessary physical activity.
Morphological signs of the presence of polyps are:
- Pain when the intestines are full and empty.
- Constipation and diarrhea, replacing each other.
- Mucus and blood in stool. By the way, the dark color of the last liquid indicates that the polyp is located in the upper part of the intestine, and the bright color is a sign of its location in the rectum.
- The abdomen hurts on the sides, radiating to the hypochondrium and anus area. The nature of the sensations is cramping.
- Anemia, exhaustion of the body.
All of these symptoms do not always manifest themselves and are dependent. Hyperplastic polyposis often occurs without the patient complaining of anything.
Pathology can be detected by resorting to the following types of instrumental studies:
- Colonoscopy. This method allows you to examine the entire internal surface of the organ using a special device.
- Retromanoscopy. An analogue of FGS only for the intestines. The downside is that only part of the organ can be examined.
- CT and MRI scans reveal any formation, even a very small one, and moreover, give an idea of its nature.
- Irrigoscopy. X-ray of the intestine using contrast. Allows you to see formations of 10 mm or more.
In addition to them, there are laboratory tests that can indicate indirect signs of the presence of intestinal polyps:
- Low hemoglobin levels in a patient's blood may be due to internal bleeding.
- This is also indicated by blood found in the stool.
Small hyperplastic formations will most likely remain under observation with concomitant symptomatic therapy and diet.
Medicines relieve sensations that cause discomfort, neutralize the inflammatory process, and get rid of pathogenic microorganisms if they are detected with the help of antibiotics.
Important information! There is no drug that will remove the formation with a 100% guarantee.
The operation to get rid of a polyp is called a polypectomy, and it is most often performed endoscopically. A special endoscope is inserted into the intestine through the anus, which not only allows you to see everything in its path, but also has manipulation tools for removal. Depending on the method, devices can eliminate a polyp by:
- Electrocoagulation.
- By radio wave method.
- Laser coagulator.
In cases of increased complexity, when due to the structure of the organ it is impossible to get close with an endoscope, the operation is performed laparoscopically. Through a puncture in the stomach.
Doctors prefer to remove polyps because of the serious risk of cancer.
There are numerous reviews about getting rid of polyps without surgery using home remedies. The main ingredients of this treatment are honey, viburnum, celandine and others. It is better to consult a doctor before use.
polips.ru