26.10.2018
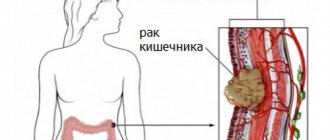
Every year, approximately 50 thousand people around the world are diagnosed with bowel cancer.
The main reason for the high mortality rate of patients with this diagnosis is too late diagnosis, when the tumor is detected at stages 3-4. Regular examinations, including blood tests, allow timely action to be taken. There are different diagnostic methods, among which one of the most common is a blood test.
There are several types of analysis for cancer of different localizations, which allow not only to confirm or refute suspicions, but, in the presence of cancer, to establish the stage and severity of the process.
It is important that a blood test for intestinal cancer will indicate the disease even at the beginning of its development. This will be a reason to undergo a more serious examination.
If the blood test is positive for cancer, you need to take another blood test to rule out a false result.
Diagnosis involves three types of blood tests:
- general analysis (clinical);
- biochemical analysis;
- analysis for tumor markers.
Bowel cancer, symptoms
Cancer is an asymptomatic disease. Specialists prescribe a blood test if bowel cancer is suspected, after certain symptoms have appeared:
- A vague symptom may simply be abdominal pain, but there is intestinal bleeding, which can be seen during a stool occult blood test.
- The occult blood test can even be performed at home. If the first test for cancer, a home occult blood test, is positive, then a colonoscopy should be performed. Now it is done under anesthesia.
- Problems with stool - this can range from frequent constipation to diarrhea.
- Gas incontinence, especially during exercise.
- Constant desire to go to the toilet “in a big way”, lack of feeling of emptiness.
- Fecal incontinence.
- Bloating.
- With partial or complete intestinal obstruction, cramping and frequent abdominal pain.
- Anemia, general weakness.
- Vomiting caused precisely by urges from the intestines.
- Nutrients are poorly absorbed, resulting in weight loss.
If you notice several of these symptoms, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. A timely blood test for colon cancer can alleviate your condition and even save your life.
Survey
Patients with suspected bowel cancer need urgent examination. During a manual examination, you can feel a pathological mass in the rectum, which may indicate rectal cancer located close to the anus. diagnostic imaging studies are required to examine segments of intestine behind the rectum or to confirm the presence of a tumor mass in the rectum
Endoscopy , which is called colonoscopy when examining the intestines, is the main test method for diagnosing bowel cancer. This is an outpatient procedure during which the rectum and colon are examined from the inside using a special probe (endoscope). An endoscope is a long, flexible bundle of quartz optical fibers approximately the thickness of a finger. This instrument is placed into the rectum. The colon is dilated with a small volume of air so that the doctor can examine the tissue lining it (the image is visible on the video monitor). If a section of the bowel needs to be assessed in more detail, an instrument is passed through the endoscope to perform a painless biopsy or obtain a tissue sample. These tissues are sent to a laboratory for analysis. Microscopic analysis of tissue biopsy is essential for correct diagnosis and staging of colon cancer.
During a colonoscopy, you can examine the entire colon, and another examination method, sigmoidoscopy, allows you to examine the lower third of the colon, rectum and sigmoid colon. For this, two types of instruments are available - a rectoscope and a flexible sigmoidoscope. A proctoscope is used for patients who are unprepared for examination, i.e. the lower intestine is not cleansed with laxatives or an enema. However, with a proctoscope you can examine approximately 20 cm of the rectum, while a flexible sigmoidoscope is more difficult to use, but allows you to image most of the descending colon and rectum. If diagnostic imaging studies indicate that more detailed testing is needed, a full colonoscopy with biopsy should be performed.
It is very important to distinguish bowel cancer from Crohn's disease and severe ulcerative colitis (it should be noted that both diseases are risk factors for the development of bowel cancer). In the case of severe nonspecific ulcerative colitis, characteristic signs can be observed endoscopically - general inflammation of the mucous membrane, swelling, fragility of the mucous membrane with hemorrhages. In Crohn's disease, repeated cycles of ulceration followed by periods of healing sometimes cause areas of the mucosa to rise and become polyp-like, called pseudopolyps or pseudopolyps . A characteristic sign of Crohn's disease during endoscopic examination is a typical appearance of the mucous membrane, similar to cobblestones.
A barium enema (or air contrast barium enema) is an X-ray examination method used to obtain images of the colon.
Two days before the barium enema test, the patient should take a light, mostly liquid diet, and in the evening before the test, take a laxative. On the day of the examination, a barium enema is administered, air is injected into the colon, and an X-ray of the abdomen is taken. Tweet
What blood test will show intestinal cancer?
Is it possible to determine oncology by blood, and what tests need to be taken for intestinal cancer? To study the problem as much as possible and find effective treatment methods, modern medicine uses three test options:
- general (clinical);
- biochemical;
- for cancer markers.
Intestinal tumor markers and their meanings
Today, more than two hundred types of tumor tumor markers are known, but only five are important for laboratory diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Based on their concentration and combination, one can judge the localization of the source of the disease, monitor the dynamics during the treatment process, make predictions and determine the likelihood of relapse. Knowing the names of intestinal tumor markers and their values within normal limits, it is possible to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, the appearance of metastatic foci and the risk of disease relapse.
Carcinoembryonic antigen
Abbreviated as CEA, it is not detected at all in a healthy person or is contained in an insignificant concentration of up to 5 ng per ml. It is produced by the body only during intrauterine development and ceases to be produced after birth. That is why its presence in the blood plasma in large volumes suggests the presence of a rectal tumor. However, an increase in the level of carcinoembryonic antigen is also characteristic of heavy smokers and people suffering from inflammatory diseases. For this reason, additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are required.
The information value of this tumor marker for intestinal cancer is very high, since it is it that is always determined in the colorectal form, that is, it is specific. Specific numerical indicators make it possible to judge the growth and size of the tumor, that is, the stage of the cancer process. Once treatment is prescribed, it allows you to monitor its effectiveness and adjust the course, and after recovery, regular studies help predict a relapse long before its clinical manifestation.
Main article: Meaning, interpretation, norms of CEA blood test
Carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9
It is a nonspecific tumor marker for intestinal diseases, since it is also detected in the blood in the case of pancreatic and esophageal cancer. Its concentrations also increase with pancreatitis, cholestasis, and cirrhosis of the liver. When the location of the tumor has already been determined, based on the results of the analysis for the CA 19-9 antigen, one can judge its operability and make predictions:
- up to 1000 units per ml – about 50% of patients can be operated on with a subsequent favorable outcome;
- above this indicator - only 5% have a chance of success of surgical treatment;
- more than 10,000 U/ml of this type of intestinal tumor marker in cancer indicates the presence of distant metastases and the futility of surgery.
Normally, the antigen content should not exceed 40 units per milliliter.
Main article: Everything you need to know about the CA 19 9 tumor marker
Tumor marker CA 242
Another carbohydrate compound characterized by a higher level of specificity. It is secreted by cancer cells of tumors of the same localization as CA 19-9, but makes it possible to more reliably detect colorectal cancer at an early stage. It is of great importance for predicting relapse of the disease after treatment, since the concentration of the antigen begins to increase several months before clinical signs.
With negative results for tumor markers for rectal and colon cancer, the values do not exceed 30 IU/ml.
Main article: What is CA 242 tumor marker; decoding and norm in women
Tumor marker CA 72-4
This substance also belongs to glycoproteins, the presence of which in the body is normal only for the period of intrauterine development. If, as a result of the analysis, its quantity exceeds the value of 6.9 units per ml, then we can judge the presence of a malignant tumor:
- intestines
- ovaries
- lungs
- stomach
Therefore, intestinal tumor marker 72-4 alone is not enough to reliably determine colorectal cancer (assessed in combination with CEA indicators). In addition, it is detected in benign formations and ordinary ovarian cysts, some liver diseases, and rheumatism.
Tumor marker Tu M2-RK
The tumor marker ptu m2-rk (tumor pyruvate kinase type m2 enzyme) does not differ in organ specificity. This test cannot determine the location of the tumor. It reflects the nature of metabolic processes in the cells of malignant neoplasms, allowing one to draw conclusions about the presence of cancerous degeneration, its metastases, and also predict postoperative relapses. A stool sample is required for laboratory testing.
What will a general blood test show for colon cancer?
The development of a tumor in the intestine may be indicated by the following results of a general blood test:
- Anemia may indirectly indicate intestinal cancer if there is a rapid decrease in hemoglobin levels, which occurs with prolonged bleeding from a tumor. If the presence of anemia is confirmed, the patient is immediately sent to a gastroenterologist for consultation.
- At risk for anemia are women during menopause and men over 45 years of age.
- Anemia is caused by colorectal cancer and malignant tumors.
- Leukocytosis - specialists should be alerted to high levels of leukocytes, which indicate long-term inflammatory processes in the body, and the likely presence of a malignant tumor.
- You need to be especially careful when detecting myeloblasts or lymphoblasts.
- ESR - if the level of erythrocyte sedimentation rate is elevated and does not decrease with antibacterial or anti-inflammatory therapy, then there is a suspicion of cancer.
Diagnostics
To accurately diagnose this disease, you need to take blood tests. These include:
- biochemical;
- clinical;
- analysis for tumor markers.
Each of them separately will not be able to give a person a complete picture of what is happening. Together, when comparing the available data, specialists can accurately identify the presence of cancer cells. In addition, this approach makes it possible to determine their location. There are cases that patients are forced to take tests several times to obtain a more reliable result.
Biochemical
Such a laboratory test does not provide one hundred percent confirmation of the presence of intestinal cancer. However, data obtained with deviations from the norm may be the first signal for subsequent diagnosis. Biochemical analysis shows:
- Hemoglobin. When deviations downward to 70-80 units and below are observed, this may indicate malignant processes in the intestines.
- Protein. If its concentration, which depends on the number of amino acids, is underestimated, this is one of the manifestations of oncology in the organ.
- Urea. The presence of its high level indicates incomplete patency inside the intestine due to the possible presence of a tumor.
- Haptoglobin. An increased level of this substance usually increases with the appearance of bowel cancer.
Clinical
Conducting this type of research helps to identify various pathological processes in the human body. Typically, a general blood test is prescribed during preventive examinations. However, it also helps to detect malignant tumors of any organ.
You need to pay attention to the following parameters:
- In this disease, leukocytes are usually enlarged, and the structure of white blood cells is changed.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). Increased levels of these compounds indicate inflammatory processes. When the level does not decrease after taking antibacterial agents, this may indicate oncology.
- A decrease in hemoglobin levels may indirectly indicate the development of intestinal cancer.
Blood for tumor markers
One of the reliable tests for detecting a malignant tumor is a blood test for tumor markers.
This is how proteins that are waste products of cancer cells are identified. These substances are observed when there is a tumor in the body that is constantly growing. If a person is healthy, they will not appear.
A blood test for oncology markers allows you to:
- determine the type of education;
- calculate the size of the tumor and the stage of its development;
- find out the body's reaction to the tumor;
- monitor treatment.
There are 2 groups of tumor markers indicating bowel cancer:
- Carcinoembryonic antigen. It increases rapidly at the beginning of the disease, and then its rate remains unchanged. In cirrhosis of the liver and in smokers, there is no active growth of this antigen.
- Antigen CA-19-9. It indicates the development of, in addition to intestinal cancer, also a tumor in the pancreas. The analysis makes diagnosis easier by speeding up the discovery of the actual location of the tumor. When the level of antigen constantly increases, it means that intestinal cancer is progressive. If the indicator decreases, one should judge the good effect of organized treatment.
Although diagnoses are often made based on cancer markers, they are sometimes present in healthy bodies.
It is necessary to perform a full examination, since it is unacceptable to prescribe treatment after receiving the result of only one test. It is worth noting that a blood test for intestinal cancer is usually classified as an additional research method. Along with them, it is necessary to undergo other diagnostics, in particular, a stool test for occult blood. In addition, the following procedures are recommended:
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- irrigoscopy.
What does a biochemical blood test say about cancer?
Biochemical studies are taken into account in many diseases, and malignant tumors are no exception. Important indicators of biochemical analysis that you should pay attention to:
- urea - may indicate intestinal obstruction, which is a sign of colorectal cancer;
- total protein - a reduced level indicates intestinal diseases;
- Any fluctuations in hormones, deviations from the norm of elements indicate diseases or inflammatory processes within the body.
- Cholesterol analysis, despite all the benefits of “good” cholesterol, its high levels can be caused by malignant tumors in the intestines.
- Problems cannot be ignored; it is better to immediately contact a competent specialist. In this case, you can not only find out your diagnosis, but also begin timely treatment.
Determining the signs of bowel cancer during diagnosis
Symptoms of diseases of the digestive tract can hide serious pathologies. Therefore, there are additional signs that accompany malignant formations. If possible manifestations of cancer occur, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis.
To prevent the tumor from reaching a dangerous stage, the following clinical picture is revealed:
- loose stools;
- constipation;
- inclusion of undigested food, mucus or pus in the stool;
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
- bloating;
- increase in body temperature to 38-39°C;
- vomit;
- flatulence;
- bleeding from tumors.
Symptoms of bowel cancer include weakness. The patient complains of increased fatigue and dizziness. Because of these symptoms, test results may reveal anemia.
The progression of cancer is accompanied by pale skin and weight loss. The patient often gets tired even with little physical activity.
With a malignant formation in the intestines, the patient experiences pain in the anus. Body temperature rises for a long time. The cause of the symptom cannot be determined. Only after differential diagnosis is carried out, the manifestation factor is determined based on the results. Oncological neoplasms are accompanied by reduced absorption of nutrients.
The stronger sex is at risk of cancer in the intestines. By age – over 45 years old. Pathology often occurs in smokers.
Tumor markers for colon cancer
Correctly selected blood tests for cancer markers can accurately diagnose or refute suspicions of intestinal cancer.
- The waste product of cancer cells and specific proteins are cancer markers. Their appearance in the blood and growth indicates the presence of cancer and the development of this disease within the body.
- There are situations when the active development of these proteins does not indicate cancer, but a serious inflammatory process inside the intestine.
- A blood test for cancer markers determines not only the presence of a tumor, but also:
- its type (benign or malignant);
- stage of development;
- dimensions;
- the body's response to cancer cells;
- allows you to monitor and control the effectiveness of treatment.
Oncological markers that specifically indicate the development of intestinal cancer:
- Antigen CA-19-9 indicates not only the development of intestinal cancer, but also pancreatic and stomach cancer.
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) - at the beginning of the disease, indicators increase rapidly and do not decrease over time.
Detection of tumor markers in the blood
The third method is most specific for colon cancer. Indicators of blood tests for tumor markers change only if there is any tumor in the body.
Tumor markers are proteins that are specific to certain tumors. They enter the bloodstream as a result of metabolism of cancer cells. However, this method is also not absolutely specific for cancer, since their increase can also be observed with severe inflammatory processes in the intestines.
There are a large number of markers that are specific to a particular organ. But in addition to the source of the tumor, it is also possible to determine the nature of its growth (benign or malignant), the stage of the disease, and monitor the effectiveness of anticancer therapy.
Among the oncological markers characteristic of colorectal cancer, the most common are CA-19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
CA-19-9 increases both in malignant neoplasms of the intestine and in tumors of the stomach and pancreas. At the same time, it increases in the case of inflammatory processes in the digestive organs and in diseases such as cystic fibrosis.
CEA is also not specific to colon cancer. Its increase is also possible in case of oncological diseases of such organs as the cervix, bladder, lungs, liver, prostate gland, etc. A slight increase in CEA is observed in cirrhosis of the liver and in people who smoke.
Oncological pathology is characterized by a sharp significant increase in the concentration of markers. Their concentration also increases in the early stage of the disease. A further increase in their level over time is also typical. With properly selected anticancer therapy, CEA and SA begin to decrease, which indicates a favorable prognosis for the treatment of this disease.
Who is recommended to take these tests?
In order to protect yourself and save yourself from a terrible diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo a systematic (once a year) full examination. Those at risk for a disease such as intestinal cancer are:
- people over 60 years of age;
- who in the family has had such a problem as cancer, a hereditary factor;
- people suffering from frequent colitis, diarrhea or constipation;
- heavy smokers and alcohol drinkers;
- patients with a deficiency of B vitamins, especially
Endoscopic methods for diagnosing colon cancer
Diagnosis of intestinal cancer can be done using different methods, but endoscopic examination methods are the most accurate for diagnosing intestinal cancer. The most commonly used research methods are:
- video colonoscopy, with biopsy;
- high-resolution narrow-spectrum video colonoscopy with 136x optical zoom function, with biopsy;
- a new method is swallowing a capsule instead of a colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy
- Endoscopic research methods - video colonoscopy and high-resolution narrow-spectrum video colonoscopy with an optical zoom function of 136 times, differ mainly only in the quality of optical zoom and review.
- Typically, the colonoscopy procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
- The world standard stipulates that during the colonoscopy procedure, polyps and other neoplasms, if any, are immediately removed.
- The removed biomaterial must be submitted for cytological examination or biopsy to determine whether the formation is benign or malignant.
- The colonoscopy procedure requires special preparation, which the doctor must tell you about.
Minimally invasive methods to replace colonoscopy
Some of these methods have been used for many years and are not particularly pleasant, others are promising and gentle, but even they will not replace the uncomfortable procedure of a colonoscopy. These include:
- capsule endoscopy;
- irrigoscopy with barium or air;
- endorectal ultrasound diagnostics.
The colon or sigmoid colon can be studied using a method that has enviable prospects - this is an electronic tablet (video tablet). This method of capsule endoscopy is considered the most gentle and at the same time the most expensive. After the patient has swallowed the electronic device, after some time the device begins recording.
The doctor takes photographs of the mucous membrane of the area being examined. But he must use only the received images, while colonoscopy is an online method. That is, a specialist, if some area seems suspicious to him, can examine it more carefully.
Irrigoscopy is a method tested over the years, but also not very pleasant . It comes down to giving a barium enema or straightening the intestines by pumping air, after which an x-ray is taken. This method also has contraindications (pregnancy, allergy to barium, etc.). It requires a lot of experience to decipher the image and is insensitive to small polyps. The method is good when you need to see the location of the intestines in the abdominal cavity. It perfectly identifies elongation of the sigmoid colon (dolichosigma) and volvulus.
Rectal cancer is confirmed using endorectal ultrasound. In this procedure, a probe is inserted into the rectum through the anus. This research method is usually used to verify the diagnosis of an oncological process in the rectum. It is needed to determine which surrounding tissues and lymph nodes are affected by the process.
New method, swallowing capsules instead of colonoscopy
A new method has been invented for examining the small and large intestines using a capsule that is swallowed.
- Unlike colonoscopy, the capsule swallowing method is less traumatic and very accurate for diagnosis.
- During the colonoscopy procedure, most of the large intestine is viewed, and only a small part of the small intestine.
- The capsule swallowing method allows you to see the small and large intestines.
- This examination is carried out using a highly sensitive micro-camera, which is enclosed in a very small capsule.
How the capsule works
- It is enough to swallow the capsule, and as it moves, a sensitive microscopic photo camera in the capsule takes 20 to 30 frames per second.
- A person swallows the capsule, then it enters the stomach, then the duodenum.
- Then it moves through the small intestine and passes into the large intestine.
- The capsule comes out of the large intestine on its own.
- After exit, the capsule is opened, and the images taken by the microcamera are viewed and analyzed.
- The capsule remains in the patient’s body for approximately 15-16 hours.
- Additionally, a recording device is attached to the patient on a special belt, which operates while the capsule moves.
- After the capsule comes out, it is removed, and the data from this recording device is also decrypted and analyzed on the computer.
- Special preparation is carried out for the procedure, and the patient is under the supervision of a doctor throughout the entire examination process.
Instrumental methods
A neoplasm can be detected using tomography, endoscopic examination (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy), irrigoscopy and radiography.
For pain in the anus and bleeding, sigmoidoscopy is required.
Literally, this study is translated as an examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon. Preparing the patient for the procedure includes giving 2 enemas on the eve of the study.
The intestinal mucosa is examined with a rigid endoscope. During sigmoidoscopy, the condition of the intestinal mucosa is assessed at a distance of 25-30 cm from the posterior opening. If the tumor is localized in the upper parts of the large intestine, then a colonoscopy is necessary. In this situation, a flexible probe is used, which is inserted deep into the intestine through the anus. During the examination, the doctor sees everything on a computer monitor connected to the device.
During a colonoscopy, it is possible to remove a fragment of the intestine affected by the tumor for laboratory testing. The relief of the colon, its length and elasticity can be determined using irrigoscopy. This is an additional research method. It cannot replace colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy. During irrigoscopy, a dye (barium suspension) is injected into the intestinal lumen. The condition of the intestines is assessed by how it is distributed.
Layer-by-layer images of internal organs can be obtained using tomography. This is the most modern method for diagnosing diseases of internal organs. If there are problems with other organs (bladder, pancreas, liver), an ultrasound scan is performed. This is a safe diagnostic method that is suitable for people of any age. Examination of the small intestine is difficult. With the help of FGDS it is possible to assess only the condition of the duodenum.
Additional cancer diagnostic methods
Colon cancer can be diagnosed using different techniques. Most often used:
- Ultrasound, X-ray, digital examination.
- Endoscopic examination methods, video colonoscopy with biopsy.
- Laboratory tests are also necessary.
- Additional PCR blood test to exclude intestinal tuberculosis.
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging.
Analysis of feces and urine for occult blood
Screenings and test samples are used to determine the presence of occult blood in stool and urine. Two methods are considered the most effective and informative:
- An immunochemical test is prescribed to identify pathological processes in the lower parts of the digestive system. Most often used in colorectal oncology;
- The benzidine test or Gregersen test is carried out chemically to detect blood clots in all structures of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
How is blood tested?
Investigation for suspected bowel cancer is complex. The following tests are taken for intestinal cancer - general, clinical and for tumor markers, which make it possible to identify the development of a neoplasm in the intestine at the initial stage.
- First of all, a clinical general blood test is taken to check for anemia, as a primary symptom of the development of a tumor in the colon. With anemia, there is severe bleeding in the rectal walls of the intestine, while the patient has constant constipation and the passage of feces with blood. In addition, when examining blood, the composition clearly showed an increased level of leukocytes and decreased hemoglobin in blood cells. A general blood test is not enough to confirm the diagnosis of cancer. Next, the patient is redirected to undergo a biochemical blood test.
- Biochemical analysis involves taking blood to examine a sample to determine the level of proteins, urea, and hepatoglobin in the blood. If there are problems with the intestines, the indicators have obvious deviations from the norm. It is the biochemical test indicators that will indicate the possible operation. Often the test is taken during treatment. If the dynamics are positive, then the blood counts should soon return to normal.
- The third and most reliable indicator for the presence of a cancer tumor in the intestine are tumor markers. This is a specific test for RNA modifications in the cells of the body, in particular in the intestines. With the development of the pathological process, the following is observed:
- decreased hemoglobin levels
- signs of anemia
- the appearance of antigenic cancer cells in the blood
- high percentage of microorganisms in the intestinal structures.
The main indicators used when testing blood for tumor markers are REO and CA19-9, which make it possible to identify antigens in the blood.
- To establish an accurate diagnosis, feces and urine are additionally examined. If there is blood in the urine, there is a suspicion of hematuria and the development of cancer cells in the intestines. The presence of blood in the stool is a clear sign that the rectum is susceptible to inflammation or polyps.
People over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo these tests annually. A course of antibacterial or chemotherapy may be prescribed.
Home cancer tests
Occult blood test
Cancer tests can be done at home. Test kits are available freely in pharmacies, there are more than three types. Everything you need to carry out the test is included in the kit, and there is a description. Types of cancer tests you can do at home:
- Blood tests. You can take blood from your finger yourself by purchasing a kit at the pharmacy.
- Urine tests.
- Fecal tests for occult blood.
For example, tests for three common cancers:
- PSA test - for common prostate cancer.
- Test for colon cancer.
- Test for bladder cancer.
How to read test results:
- If there is 1 line on the indicator, it means there is no cancer.
- If there are 2 stripes on the indicator, this means there is cancer.
- If something is wrong, then you need to urgently look for a good doctor.
- Cancer tests are done at least once a year.
Bladder Cancer Antigen Test
It must be remembered that the presence of bleeding always indicates intestinal cancer. And, if you are careful about your health, do a home test. It's not difficult at all!