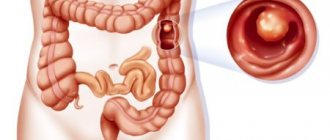
Polyps in medicine are usually called the growth of the epithelium of the mucous surface lining the internal organs of a person.
Anal polyps occur on the walls of the rectum. In the primary stages, they are completely benign neoplasms. Therefore, you should not panic when you hear such a diagnosis.
However, anal polyps are not so harmless. They must be removed because they have the ability to develop over time from a benign neoplasm into a malignant tumor.
Polyps can form in people of different ages. Most often, this disease occurs after 40 years of age, but it also occurs quite often in children.
Polyps of the so-called hereditary type are especially dangerous. In cases where the patient’s medical history reveals the presence of a similar disease in relatives, there is a high risk of rapid transformation of the formations into a cancerous tumor.
Studies show that early detection of polyps that have developed into cancer leads to patient recovery in almost 85% of cases.
The difference between polyps and hemorrhoids
It is almost impossible to determine the difference between anal polyps and hemorrhoids without the help of a qualified specialist - these diseases have too many similar signs.
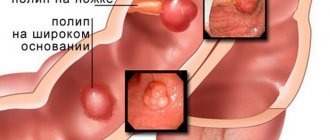
This is what polyps in the anus look like
However, hemorrhoids, unlike polyps, are not associated with the occurrence of neoplasms.
It occurs as a result of the development of inflammation and thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins located in the lower intestine.
The cause of hemorrhoids is stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis.
Falling into confusion, patients try to treat themselves, using remedies recommended for the fight against hemorrhoids.
If they make a mistake, they may deprive themselves of the precious time needed to eliminate the disease before it progresses to oncology.
The first symptoms of rectal polyps
Unfortunately, at the initial stage of its development the tumor does not manifest itself in any way. If the growths are small, single or several, but they are located at a distance from each other, then such neoplasms are often diagnosed by chance. Small growths during a routine examination or examination for another disease are detected using ultrasound, endoscopic examination, and MRI of the pelvic organs.
Despite the small volume of polyps and the absence of direct clinical signs, attentive patients may notice atypical manifestations during various vital processes.
There are several common signs of rectal polyps in the early stages of development:
- The appearance of constipation;
- Stool instability (alternating constipation and diarrhea, irregular frequency);
- Impaired excretion of intracellular mucus:
- The appearance of mucous lumps in the stool.
Considering that polyps do not appear on healthy areas of the mucous membrane, their occurrence is secondary in nature and can be combined with the symptom complex of the underlying disease:
- intestinal ulceration,
- hemorrhoidal disease,
- stomach ulcer,
- proctitis,
- paraproctitis.
Often the first symptoms of polyps “overlap” precisely the signs of exacerbation of the underlying disease.
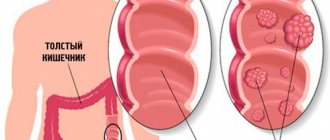
Types of formations
Polyps differ in several ways. They can be single, diffuse or multiple, and have the shape of a ball, oval, mushroom or pear. And in some cases they are able to grow in clusters, resembling in appearance a small head of cauliflower.
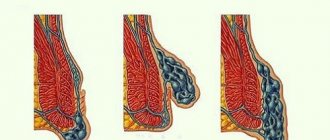
The base of the polyp can be located on a thin or wide stalk or be closely adjacent to the intestinal wall. Its color is most often similar to the color of the mucous membrane from the tissues of which it was formed.
But if there are a large number of blood vessels feeding the polyp, as well as in the case of the development of an inflammatory process, it can acquire a crimson, intense red or even crimson color.
According to their structural characteristics, polyps are divided into:
- glandular;
- villous;
- hyperplastic;
- juvenile
Separately, false polyposis is distinguished, which is a proliferation of mucosal tissue similar to polyps with the simultaneous development of chronic inflammation.
Types and Types of Anal Polyps
Clinicians distinguish two main classifications of polypous formations: according to the nature of their occurrence and structural features (histology results).
The following groups of polypous neoplasms are distinguished according to the nature of their occurrence:
- Inflammatory or infectious - the polyp is based on past inflammation;
- Neoplastic - with excessive growth of intestinal mucous tissue;
- Hyperplastic - type 3 polyp is the result of the proliferation of abnormal mucosal epithelial cells.
Thanks to the possibility of performing a biopsy, doctors can evaluate not only the structural features of the polyposis lesion, but also compare the risks of possible malignancy of the tumor. There are several types of tumors.
Causes and risk factors
To date, there is no clear opinion about the causes of polyps in the anus. It is believed that the disease can develop if the following risk factors are present in a person’s life:
- hereditary predisposition;
- bad ecology;
- poor nutrition, accompanied by the consumption of fatty foods and a small amount of coarse plant fibers;
- physical inactivity;
- bad habits, including alcohol and smoking.
Among the reasons, a special place is occupied by:
- disruption of intrauterine intestinal formation in the fetus;
- pathological disturbance of the intestinal environment as a result of the development of enteritis, dysentery or colitis;
- vascular diseases;
- the presence of cancerous lesions of internal organs.
Just as in the case of polyps, hereditary factors, low elasticity of blood vessels, a sedentary lifestyle, an unbalanced diet and alcohol intake can cause hemorrhoids.
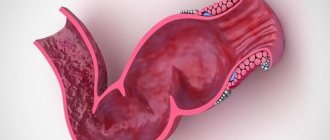
What does a polyp look like?
A polyp is a growth that noticeably rises above the mucous membrane of the rectum. It looks like a mushroom, ball or branched element located on a wide base or stalk.
On this topic
- Digestive system
Differences between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2020
The color factor is variable, depending on the nature of the neoplasm. The color can be gray-red, dark red, yellow. On the surface of the polyp there is mucus of a soft consistency. If the formation is one of a kind, it is called a polyp. If there are several of them, we are talking about polyposis.
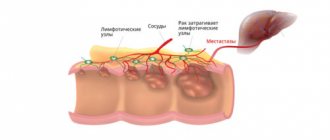
Any polyp is a harbinger of cancer. If it exists in the intestine for a long time, the risk of developing into cancer increases. Carriers of tumor processes are persons of any gender and age: the disease appears in women and men, in adults and children (more often it affects people over 50 years of age).
Symptoms of the disease
In most cases, the formation of anal polyps occurs completely asymptomatically. A person may find out that he has a disease long after its onset.
But at a certain stage in the development of the disease, symptoms still begin to appear:
- intestinal patency is impaired;
- there is pain, burning and discomfort in the anal area;
- discharge of blood and mucus appears in the stool;
- abdominal pain increases;
- there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the intestines.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence and type of disease can be determined as a result of the following diagnostic measures:
- Palpation of the anus . This simple test allows a specialist to determine whether a patient has polyps, hemorrhoids, anal fissures and fistulas.
- Sigmoidoscopy . Makes it possible to study the intestines at a distance of 25 centimeters from the anus using a special instrument. Most often, anal polyps grow in this area.
- Colonoscopy . Using the camera built into the colonoscope, it allows you to examine the mucous surface of the colon along its entire length.
- Irrigoscopy . Involves examining different parts of the intestine using x-rays. This procedure allows you to identify individual polyps that have reached a diameter of 1 centimeter.
Approach to therapy
Unlike hemorrhoids, polyps are not treated with medication. Medicines and traditional medicine methods do not have an effective effect on this disease. Anal polyps discovered during a diagnostic study are removed promptly.
If the polyp is small, it is removed during an endoscopic examination, namely colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. In this case, the electroexcision method is used.
A special diathermic loop, mounted in the colonoscope, is placed over the stalk of the detected polyp and carefully tightened, cutting off the base and removing the growth. It should be noted that the procedure for excision of polyps is absolutely painless.
Large polyps can be removed using the same method, but in parts. If the polyps are located in the lower part of the colon, they are removed using a mini-surgery.
Such surgical intervention is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization of the patient. However, before the procedure:
- the patient must adhere to the recommended diet;
- Any inflammation in the intestines should be stopped.
The tissues of the removed polyp must undergo histological examination to identify the presence of malignant cells in them. If cancer is detected, a resection of the part of the intestine in which the polyps have formed is performed.
Treatment without surgery
Unfortunately, modern medicine does not have in its arsenal such medications, the use of which would make it possible to get rid of rectal polyps once and for all. Today, there is only one effective way to eliminate unpleasant formations - this is surgical intervention, which is carried out either planned or during a diagnostic study.
However, the doctor may suggest medications that will help relieve the symptoms of the disease. Thus, gas formation in the intestines can be eliminated with the help of various simethicones, and antispasmodics will help get rid of painful sensations.
Complications and dangers of pathology
In the vast majority of cases, the disorder is successfully treated by surgical removal of nodes from the intestinal mucosa.
Complications can arise only in cases where the disease, without being promptly noticed and identified, develops to the stage at which the transformation of a benign polyp into a malignant neoplasm begins.
However, even if the polyps are successfully removed, the disease may return in the form of relapses.
Postoperative period
Any operation performed in the rectum has a favorable prognosis if pathological formations expressed by polyps are detected in a timely manner. Since after surgery there is always a possibility of recurrence of polypous processes, the patient must undergo a control colonoscopy, which will allow to establish or exclude an unwanted relapse.
In the postoperative period, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- follow a gentle diet that includes products of plant origin;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol, especially beer;
- limit physical activity;
- connect preventive measures using traditional medicine recipes.
People who have previously had problems associated with the formation of polyps in the rectum need to visit a proctologist once a year.