Jaundice in a newborn: is it worth worrying about?
In Russia, viral hepatitis A (HAV) has long been called Botkin's disease, named after the doctor Sergei Petrovich Botkin. It was he who proved the infectious nature of “catarrhal jaundice”. A century and a half has passed, but this disease continues to affect huge numbers of people around the world. About ten million people are infected every year! Russia is considered a country with an average risk of contracting viral hepatitis A. In our country, every year one hundred thousand people are hospitalized in infectious diseases hospitals with this diagnosis. And 80% of the sick are children.
Viral hepatitis A: typical signs
The classic symptoms of the disease are:
- yellowing of the sclera;
- yellowing of the skin;
- stool discoloration;
- darkening of urine;
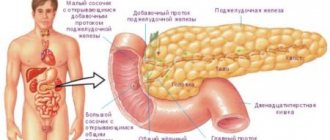
- increase in liver size;
- increase in the size of the spleen.
From the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease, ten to fifty days pass.
On average, the incubation period lasts a month. At the end of this period, the body temperature rises, sometimes reaching high numbers, a headache and a feeling of body aches appear. At this time, the disease is similar to a regular ARVI. A little later, the baby becomes lethargic, refuses to eat, constantly asks to be held, complains of abdominal pain, and scratches his skin slightly. One-time vomiting, regurgitation, and loosening of the stool may occur. A few days later, the mother notices darkening of the child’s urine and discoloration of feces. Urine looks like kvass, and feces are most similar to white (slightly grayish) plasticine. Then the sclera of the eyes turn yellow, and then the skin. The more severe the disease, the more intense the color of the skin and sclera. Interesting fact: with the appearance of jaundice, the baby’s condition improves.
He becomes more active and begins to ask for food. One to two weeks pass and all symptoms begin to disappear.
There is an asymptomatic course of HAV, when the level of bilirubin does not rise to such an extent as to stain the skin. Carrier status is also detected: the child does not get sick, but releases the virus into the environment. These cases are the most dangerous for the spread of infection.
What are the symptoms of hepatitis
All symptoms will depend on what type of hepatitis has overtaken the child. If this is a virus A, then the incubation period will stretch from a week to 7 weeks, B - from 4 to 6 weeks, C - from a couple of days to 8 weeks.
In the next phase, the child may feel unwell. The condition can be attributed to a cold, because the baby will have a fever, a cough, a stuffy nose and may experience a lack of appetite.
It is possible that the symptoms will be of a gastric type, manifested by pain in the area of the right side under the ribs.
The child will also complain about weakness and lack of desire to eat. He may experience bouts of vomiting or nausea.
Most often, no one rushes to treat a child for hepatitis, because the parents think that he only blew up his stomach. But in fact, the situation is extremely complicated by the inflammatory process in the liver organ.
There is another type of hepatitis A, in which there is pain in the joints, a rash on the skin, and the general condition will be accompanied by the urge to vomit.
At this stage, the doctor notes an enlargement of the organ and darkening of the urine.
Hepatitis A in children: causes
The disease is transmitted from person to person through unwashed hands, poorly processed food and raw water. Children are more likely to become infected in organized groups through toys and common household items. Patients are most at risk a week before the onset of jaundice. They do not yet know that they are infected, but they excrete the virus in large quantities in their feces.
A banal violation of hygiene rules (poor hand washing after using the toilet) is accompanied by the dispersion of viruses throughout the house, especially if a woman preparing food gets sick. To become infected, it is enough to “eat” just a few viruses. And they are so small that hundreds can be placed on the legs of flies that carry the infection.
The virus is very stable in the external environment. At home it will keep for several weeks, if frozen – for several years. Not afraid of short-term treatment with disinfectant solutions. Salvation is a quartz lamp. Under ultraviolet radiation, the virus dies quite quickly.
Routes of infection
Hepatitis A can develop in a child as a result of infection from a sick person. The infection is transmitted by the fecal-oral route in various ways.
- Contact and household. Through direct contact with a virus carrier, through care items, personal belongings.
- Nutritional. The virion enters through food, most often poorly processed vegetables and fruits.
- Water. Common route of transmission. The virus enters water bodies and sewer systems. Infection occurs while swimming in contaminated sources or drinking raw water.
There are isolated cases of infection of children through the parenteral route; the mechanism is not natural. The virus is contracted when hygiene rules are violated.
This is interesting: What is hepatitis A, how is it transmitted, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
The child is sick: what to do?
All people sick with viral hepatitis A must be hospitalized, regardless of age. This is done to break the chain of infection and isolate the sick from the healthy.
The disease does not require special treatment. Children are given vitamins, mild choleretic agents, and are encouraged to drink more often. It is important to follow a liver-friendly diet. In the first 2-3 days - No. 5a, then, for several months, diet No. 5.
The child stays in the hospital from seven to twenty days. The length of stay depends on the severity of the disease.
After hospitalization of the patient, it is necessary to disinfect all rooms in which he has been. In a children's institution, it is carried out by employees of the disinfection station. Parents are at home. You need to take a 2% chloramine solution and thoroughly treat all surfaces with it. First, moisten thickly with the solution, wait 30 minutes and rinse several times with water. Be aware that this solution has bleaching properties and may cause respiratory irritation. Boil the bed linen for twenty minutes. If chloramine is not suitable (allergy, it’s a shame to ruin things), you can do a good wet cleaning and quartz each room for 20 minutes.
Diagnostics
A child must be strictly examined by specialists if hepatitis is suspected. Necessary tests:
- Blood biochemistry tests;
- Blood test for antibodies;
- PCR;
- Enzyme immunoassays.
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is prescribed. The study reveals the size of internal organs and blood vessels, and the pathological phenomena occurring in them. Using ultrasound, a suitable puncture area is selected for examining the liver for biopsy. The procedure is absolutely safe and is capable of identifying in detail the changes occurring in the liver.
The disease begins to manifest itself only after the incubation period has passed. For hepatitis A it ranges from 7 to 50 days; for B – from 7 to 12; for C – from 49 to 56 days.
Hepatitis A is otherwise called jaundice, but this type of virus does not always occur with signs of this disease. Symptoms depend on the form of the disease. The usual icteric form of the disease provokes a temperature that for a certain time stops at 38 - 39 degrees. A sick child feels pain in the abdomen, which is localized in different places on this part of the body.
Appear: nausea, profuse vomiting, low physical activity, poor appetite. Urine becomes dark in color, and stool loses its normal color. The liver and spleen are enlarged.
A sick child cannot always show where it hurts; this applies to newborn children. In the second week of the disease, symptoms of jaundice appear, which stains the sclera, mucous membrane, ears, and skin. After some time, jaundice reaches its maximum and gradually declines. The symptoms of the disease gradually fade away, but the urine continues to remain dark and the liver is enlarged.
- Jaundice with a holistic component has more pronounced and prolonged symptoms than the usual icteric form of the disease. Skin itching is added to the symptoms.
- An atypical icteric disease occurs in adolescents. There are no symptoms of intoxication of the body, but the form is accompanied by increased skin itching and icteric signs.
- The anicteric type of the disease provokes minor symptoms of apathy and poor appetite. The asymptomatic manifestation of the disease does not cause suspicion in the mother of the child, which leads to an advanced form.
- The hardware and subclinical form is asymptomatic. Only an enlargement of the child's liver is observed.
The duration of the disease ranges from 1 week to 2 months. Often, the disease ends spontaneously. The rehabilitation period lasts about 6 months.
Symptoms of hepatitis B in children during the period of weakening of the disease do not appear at all. When the disease worsens, the following are observed:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Poor appetite;
- Bitter taste in the mouth;
- Flatulence and pain in the epigastric region;
- Yellow coloration of the mucous membranes and skin;
- Enlargement of the liver and spleen;
- Urine becomes dark in color and stool becomes lighter.
With prolonged hepatitis B in children, bleeding from the nose or gums is observed.
Signs of hepatitis C in a child largely depend on the nature of the disease. It is chronic, acute or protracted. The illness lasts for at least three months and ends up to six months. During illness, a child feels:
- Nausea, possible vomiting;
- Apathy;
- Poor appetite;
- Dyspeptic symptoms in the epigastric region;
- The temperature increases to 39 degrees;
- Urine darkens and feces lose their usual color;
- Painful enlargement of the liver.
Only in some of the sick, a yellow tint of the skin and mucous membranes is observed. In the chronic course of the disease, there are often no signs, but the disease directly has a destructive effect on the child’s liver, which provokes cirrhosis and other severe disorders of the liver and kidneys.
The method of therapy depends on the cause of the disease. Treatment of hepatitis in children occurs in combination with diet. The doctor selects medications to maintain liver function. Choleretic and antiviral agents and vitamins are prescribed. To eliminate intoxication, sorbents and mineral water are used. With the permission of the doctor, a course of herbal medicine is carried out.
Viral hepatitis A and breastfeeding
The hepatitis A virus does not pass into human milk. There is nothing stopping you from continuing to breastfeed if you carefully observe the rules of hygiene. Just remember that a baby can get viruses by licking them from the skin of the mother’s breast if she didn’t wash her hands well and didn’t treat her breasts enough.
Do not forget about the mandatory hospitalization of the mother in an infectious diseases hospital. It is a rare medical institution that has the opportunity to provide a separate room for mother and baby to stay together.
The good news: if a woman has had viral hepatitis A before, when breastfeeding she transfers her antibodies to the baby and protects him from HAV infection for at least a year.
First signs in children and adults
The incubation period of the disease is 8-50 days (on average 14-28). At this time, the patient is already considered infectious and dangerous to the people around him. However, the first signs of hepatitis A have not yet been observed in him.
For your information. Acute hepatitis in some cases resembles influenza and acute respiratory infections in its course, the main symptoms of which are muscle pain, headache, and hyperthermia.
What should I do to prevent my child from becoming infected with viral hepatitis A?
All children under 1 month of age have temporary immunity to HAV received from the mother (if, of course, the mother has antibodies to this infection). Then they can become infected, like all other people. Only breastfed children are protected, as we mentioned above. Contagiousness is 100%: when the virus enters the body, a person who has not been sick before will definitely get sick.
There are simple tips to help minimize hepatitis A infection.
- Wash your hands often. Mandatory - before eating and after visiting the street or toilet.
- Drink only clean water. If you're on a trip - bottled.
- Handle food correctly.
- Be sure to wash fruits and vegetables before eating. Get in the habit of rinsing them after washing with boiling water.
- Swim only in permitted places.
- In the summer, actively fight flies and prevent their contact with finished products.
How does hepatitis C manifest in a child?
In babies under one year of age, the disease almost immediately becomes chronic, since the immune system has not yet strengthened and reacts late to the presence of viruses in the blood. It depends on the state of immunity how hepatitis C manifests itself in a child, in acute form or asymptomatically.
Carriage of HCV in a newborn is very dangerous. If the disease was not diagnosed in time, then already at the age of 1 year, half of the patients have pathological changes in the liver. By the age of 5, the gland is almost completely affected.
Symptoms and signs
With a powerful and timely immune response, severe symptoms of hepatitis C in children, also characteristic of influenza or ARVI, are pronounced:
- sharp pain in the right hypochondrium (complains of a sore stomach);
- headaches, joint pain;
- high body temperature;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- increased excitability, tearfulness;
- sleep disturbance.
In addition, darkening of the urine with simultaneous lightening of the stool may occur. Based on this feature of the disease, hepatitis C can be suspected, since other symptoms may be the result of other pathologies.
Infection can be recognized in a timely manner by characteristic signs that, in combination with each other, point specifically to HCV.
The main signs of HCV in childhood:
- yellowing of the sclera, mucous membranes and skin (jaundice);
- frequent regurgitation in infants;
- poor appetite, refusal to eat;
- spider veins on the skin (especially many on the stomach or shoulders);
- muscle weakness, weight loss;
- reduction of the liver against the background of an enlarged spleen;
- changes in normal blood parameters (general, biochemical tests) positive ELISA, PCR tests.
In advanced conditions, glossitis may develop, which is noticeable by a bright red tongue or anastomosis (bright red palms and feet).
If you suspect an infection in your baby, you should immediately report this at a regular appointment with your pediatrician.
Diagnostics
If the doctor suspects a child has HCV, he will prescribe all the necessary tests to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnosis of hepatitis C in newborns and older children is practically no different from studies carried out for adults. However, after birth, infants may retain antibodies from the infected mother, the presence of which does not indicate illness. Anti-HCV should disappear by 3–5 years.
The main diagnostic methods are:
- general blood test to detect inflammation;
- blood biochemistry to determine levels of liver enzymes and bilirubin;
- enzyme immunoassay that detects antibodies to HCV;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies: genotyping and determination of virological load;
- Ultrasound examination (US) showing pathological changes in the gland.
Only after undergoing a complete examination is it possible to make a final diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy.
Hepatitis A vaccination
If the risk of contracting viral hepatitis A is too high, it is better to get vaccinated. Before vaccination, it is necessary to determine the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis A virus. If they are present, the baby has already had contact with the virus and has developed immunity. If not, vaccination is carried out. The following vaccines against HAV are registered in Russia:
- The hepatitis A vaccine “GEP-A-in-VAK” is produced in Russia and is approved for children from three years of age;
- Avaxim is produced in France and is approved for children over two years of age;
- "Havrix"-720 is produced in Belgium and is approved for children from one year of age.
Vaccination is carried out twice, with an interval of 6-12 months. Russian and Belgian vaccines form immunity for twenty years, French - for ten.
Have you encountered viral hepatitis A or perhaps been vaccinated against this infection? Tell us about your experience!
Hepatitis B, C, D, etc. - know to protect the child?
Vulvitis (vulvovaginitis) in a girl: what to do? Read our next article.
Hepatitis in infants
Infection of an infant often occurs through the blood, and such an illness is severe for the baby. Infection occurs in utero from the initiated mother or father of the baby. Infection of the expectant mother in the early stages of pregnancy leads to complications of childbirth and pathology of fetal development. The intrauterine development of the virus leads to the fact that the child is born as its carrier.
In newborns, the anicteric type of congenital hepatitis is characterized by an increased increase in liver enzymes and dilation of the liver and spleen. Congenital hepatitis has a subacute or chronic form. It is extremely rare for newborns to experience cirrhosis of the liver and blockage of the bile ducts.
Viral hepatitis in a child occurs in an infectious and microbial form. Often tests during examination show a staphylococcal infection. The development of the disease in children occurs in latent, anicteric or with mild manifestations of jaundice.
The following signs should raise suspicions in the baby's mother:
- Dark urine, which can be seen by dark marks on the diaper;
- Anxiety;
- Profuse regurgitation;
- Refusal to eat.
Often, the disease in infants is diagnosed already at the acute stage. Viral hepatitis in newborns differs in the nature of the disease. Pre-icteric signs of hepatitis in children may be absent. The acute period of the disease begins with a sharp increase in temperature, and catarrhal phenomena are possible. The icteric period lasts about a month: tests show an increase in bilirubin, the liver and spleen are sharply enlarged. The course of the disease provokes inflammatory complications in the body in the infant.
Vaccination schedule
The most reliable prevention of this disease is vaccination. Currently, the National Vaccination Calendar includes vaccinations against hepatitis B.
The first vaccination is carried out in the first 24 hours for both healthy children and children at risk. The first revaccination is carried out at the age of 1 month, and the second at 6 months, provided that the child is healthy.
If the child is at risk (was born from an infected mother), then the first revaccination is carried out at the age of 1 month, the second at 2 months, and the third at 12 months.