Main symptoms:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Chest pain
- Discomfort behind the sternum
- Jaundice
- Yellow spots on the skin
- Discolored stool
- Fever
- Spread of pain to other areas
- Vomiting without relief
- Vomiting bile
- Nausea
- Heaviness in the right hypochondrium
- Frequent vomiting
Gallstone disease, which is also commonly defined as cholelithiasis or cholelithiasis, is a disease in which stones form in the gallbladder or bile ducts. Gallstone disease, the symptoms of which are observed in patients, as shown by the results of medical practice, is ineffective in treatment using conservative therapy and various types of techniques, therefore the only way to cure the disease is surgical intervention.
Online consultation on the disease “Cholelithiasis”.
Ask a question to the specialists for free: Surgeon.
- Description of the disease
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
What is the disease?
Before considering the symptoms of gallstone disease, it is necessary to find out the mechanism of its development.
The pathology can be chronic or acute. It develops gradually. Characterized by the appearance of small or large stones in the bile ducts and bladder. This process is quite long. The formation of stones begins when the bile thickens. Granules appear in it, on which molecules of undigested calcium and cholesterol settle. It should be noted that stones can be multiple or single. In addition, they have different sizes. When they begin to move, an acute attack occurs, which is accompanied by very severe pain.
Signs of gallstone disease may not appear immediately, that is, the pathology develops over time. In addition, large elements can “sit” in the ducts for quite a long time and not move anywhere. Although this also causes a lot of problems. It should be noted that this disease is very common, and the number of cases is constantly growing.
It must be said that there are several types of stones:
- pigmented;
- cholesterol;
- limestone;
- pigment-cholesterol;
- complex stones consisting of the three above components.
Symptoms of gallstone disease
Before looking at the symptoms of gallstone disease, it is necessary to understand why it happens in the first place. So, among the reasons contributing to the development of pathology, the following can be identified:
- age (after 40 years, the body’s nervous and humoral systems begin to act differently on internal organs, less effectively);
- heavy weight (especially if a person eats too fatty, spicy foods, rich in cholesterol);
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- unsuitable climate and poor ecology;
- infection of the biliary tract (cholesterol precipitates in them, which then accumulates, gets compacted and turns into stones);
- insufficient amount of acids that can dissolve lipids;
- any other pathologies of internal organs (physiological, infectious or inflammatory).
Gallstones are formed mainly due to stagnation of bile and increased cholesterol content in it. Gallstone disease can occur in anyone, but there are a number of factors that influence its likelihood:
- gender – women are more predisposed to stones than men, especially during pregnancy;
- age – the disease occurs rarely in children, it is more common in adults and especially the elderly;
- nature of nutrition;
- lack of physical activity;
- non-standard shape of the bubble, its bend;
- hormonal disorders;
- presence of overweight, obesity;
- taking medications that affect metabolism;
- accompanying illnesses.
Diet plays the most important role for the biliary system. In developed countries, where the diet of residents includes high-calorie and fatty foods, the incidence is many times higher. A high degree of obesity may be a cause of cholelithiasis. Eating vegetables, grains and fruits is much less likely to cause gallstone disease.
During pregnancy, the appearance of stones is provoked by two factors at once - the effect of progesterone (it relaxes the muscles, impairing the outflow) and the pressure of the enlarged uterus on other organs.
Diseases that impede the outflow of bile or change its composition provoke the appearance of stones:
- tumors of nearby organs;
- adhesions, scars;
- infectious inflammation of the bladder;
- chronic hepatitis;
- dyskinesia (impaired motility of the biliary tract);
- hemolytic anemia.
At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself in any way - the formation of small stones is not felt by the person, and there are no symptoms of cholelithiasis. They are not attached to the walls of the organ, but float in the bile or lie at the bottom. Before signs of the disease appear, grains of sand may periodically be released along with bile, but given their small diameter, this is also not always noticeable. When gallstone disease itself makes itself felt, it can manifest itself in different ways.
As the number and size of stones increase, they begin to irritate the walls of the bladder. Disturbances in the composition of bile also lead to its inflammation. The patient feels:
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium, especially after eating;
- periodic attacks of severe biliary colic;
- nausea, heartburn (if the outflow of bile is disrupted and bile enters the intestines);
- bloating, increased gas formation;
- poor digestion of food, especially fats, diarrhea or constipation;
- obstructive jaundice occurs.
Stones in cholelithiasis irritate the mucous membrane of the gall bladder, causing inflammation of the organ - calculous acute cholecystitis. With this disease, the body temperature rises (during periods of exacerbation), the person feels weakness and pain in the right side of the body. Acute inflammation is accompanied by severe pain. It may occur periodically and then go away for a long time, but this does not indicate recovery.
Severe pain in the right side can also be caused by a stone stuck in the bile ducts and blocking the exit of fluid from the bladder. A spasm occurs, and there may be a feeling of fullness caused by stagnation.
If such an attack occurs suddenly, it is necessary to call an ambulance and take measures to alleviate the patient’s condition:
- apply a heating pad to the gall area or lie in a warm bath;
- drink an antispasmodic (no-spa, papaverine, atropine), in case of severe pain - an anesthetic;
- Move less so as not to stimulate the movement of stones - this can lead to damage to the bladder or gallbladder by stones.
Causes of stone formation
At the beginning of the disease, hard formations form, which eventually turn into stones.
The most common cause of stone formation is a violation of the amount of bile components due to excess cholesterol. Cholesterol oversaturation occurs due to:
- obesity and frequent consumption of foods high in cholesterol;
- reducing the amount of bile acids that enter bile;
- reducing the amount of phospholipids that prevent the hardening and sedimentation of cholesterol and bilirubin.
The second common cause of stone formation is stagnation of bile, which occurs:
- mechanical in nature (presence of a tumor, adhesions, kinks, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes);
- functional in nature (dyskinesia of the hypokinetic type - impaired motility of the gallbladder and biliary tract).
Other reasons include:
- metabolic disorders due to diabetes mellitus, anemia, enzyme deficiency;
- hepatitis and cirrhosis;
- liver hypofunction;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- hemolytic anemia;
- congenital disorders in the formation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- presence of infection (especially E. coli).
There are factors that increase the risk of developing gallstones:
- unhealthy diet (overeating, unbalanced diet, large time intervals between meals);
- frequent consumption of spicy, fatty, seasoned foods;
- excess weight;
- taking certain medications (hormonal contraceptives, drugs with estrogens, fibrates);
- allergy;
- pregnancy;
- female gender and age over 70 years.
In children, the main causes of stone formation are:
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders;
- violations of the motor-evacuation function of the gallbladder.
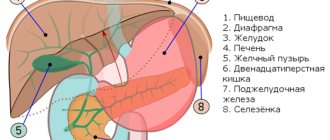
Stones can form not only in the gallbladder, but also in the pancreas. Important information about this disease and its stages:
Development of the disease
Gallstone disease in most cases begins with an increase in the thickness of bile. At this stage there are no stones yet, but the likelihood of their formation is high. If measures are not taken to reduce the concentration of cholesterol, calcium, pigments and other solids, stones begin to form from this sediment (biliary sludge).
Depending on the predominant substance in the composition, the following stones are found:
- cholesterol (in 80% of cases);
- limestone;
- pigmented;
- pigment-cholesterol;
- complex.
Most often, the first to form are cholesterol stones, which are yellow in color and contain mineral impurities, bilirubin. They come in round or oval shape. Cholesterol stones have a layered structure, diameter from 4–5 to 12–15 mm. The initial stage of the formation of such stones can be successfully treated. But the symptoms of gallstone disease at this stage may not appear, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Calcareous stones appear when calcium metabolism is disturbed or as a result of secondary stone formation due to impaired outflow. According to medical research, they can take the most bizarre shapes, consist mainly of calcium, and are light brown or dark brown in color. They are much more difficult to treat than cholesterol ones.
The occurrence of pigment (bilirubin) stones most often indicates hemolytic anemia. Bilirubin occurs as a result of the breakdown of red blood cells, and its excess is deposited in the gallbladder. Such stones are usually small and can be localized in the bile ducts and are dark in color. Usually pigment stones are present in significant quantities.
The process of stone formation develops over many years. A small grain of sand gradually becomes overgrown with an increasingly solid layer of substance and increases in diameter. Stones up to 2 mm in diameter can come out of the bladder along with bile; treating larger stones is already problematic. They are also formed in the bile ducts, helping to limit the release of bile.
Concretions take different shapes - they can be smooth, awl-shaped, spike-shaped, or porous. The number of stones can range from one to several hundred. Most gallstones have a mixed composition. They consist of cholesterol, bilirubin, bile acids, proteins, glycoproteins, various salts, and trace elements.
In the absence of treatment for cholelithiasis, stones fill an increasing part of the bladder space. Because of this, the outflow is disrupted, it thickens and becomes heavier, and the process of stone formation accelerates. So-called secondary stones are formed. Due to irritation of the walls of the organ, inflammation begins, the fluid released as a result of inflammation thickens and is also present in the composition of the stones.
Gall dysfunction
If the organ is full of stones, there is no free space left for bile. It stops flowing into the gallbladder and is released directly into the duodenum. Thus, at the final stage of gallstone disease, the bladder is “switched off” from the digestive process. Gradually the organ dries out and turns into a flaccid sac.
However, there is always a danger of stone passage, injury to the gallbladder and ducts, which can lead to complications including death. If the disease is detected at such a late stage, only surgical treatment of cholelithiasis is possible. The gallbladder is removed in the absence of contraindications to surgery (old age, pregnancy, concomitant diseases, etc.). In an acute condition, the operation is performed regardless of contraindications.
How do gallstones pass out?
If the stone is of a significant size, its exit from the gallbladder is accompanied by an attack of colic.
- The calculus, driven by bile, enters the mouth of the duct. Blockage and disruption of the flow of bile occurs
- Under the influence of the calculus and the pressure of bile, the mouth of the duct is stretched, which causes severe pain to the person.
- The stone is pushed through the ducts and enters the duodenum. The pain goes away and the person feels relief
- The calculus is passed along with the stool
Signs of pathology
The symptoms of gallstone disease are not specific, so it is quite difficult to recognize it at first. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. However, the disease manifests itself as follows:
Mild pain in the area of the right hypochondrium (in the early stages of development). Over time, they become stronger and acquire an aching character. This is especially noticeable after eating.
- Nausea.
- Diarrhea (especially after a person eats a fatty meal).
- Coloration of the mucous membranes (visible) yellow.
- Liver colic.
- Tension and bloating.
- Belching.
- Malaise, weakness, vomiting (and repeated), irritability.
- Slight change in body temperature.
- Itchy skin.
There are other signs of gallstone disease: allergic reactions, increased fatigue, sleep disturbances and lack of appetite, lethargy. It must be said that they can appear individually or simultaneously.
Diagnosis of the disease
The initial examination for suspected gallbladder pathology includes palpation of the right hypochondrium area. There are signs of gallstone disease such as tension and pain, and the gallbladder may be enlarged. These are the so-called symptoms of Mephri, Kehr and Ortner (manifested by tapping, exhaling, clasping the torso).
Ultrasound is usually used as the main hardware examination of the gallbladder. It helps determine the size and location of the organ, the presence of stones in it, and the inflammatory process. During an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the condition of neighboring organs can be assessed. If stones are present, their size, shape and density are visible.
At the same time, accompanying tests are prescribed - a general examination of blood, urine, and stool. In deciphering the biochemical blood test, alarming signs are an increase in cholesterol and bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase activity, ESR, and leukocytes. It is important to test for parasites in the intestines and liver, as they can cause symptoms similar to gallstones.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, one or more additional studies are sometimes prescribed with a transcript:
- cholecystography using a contrast agent is a method of obtaining an accurate picture of what is happening in the gallbladder;
- duodenal intubation of the duodenum with bile sampling - helps to determine its composition and the ratio of components to each other;
- endoscopic retrograde cholangipancreatigraphy - examination is performed using an endoscope and contrast agent for x-ray diagnostics;
- dynamic scintigraphy - conducting a radiological examination of the liver and bile with a contrast agent.
Diagnostics in modern medicine will help to see not only the condition of the bladder, but also the presence of other gastrointestinal diseases. Most often, the diagnosis of “cholelithiasis” in adults is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, pancreas, and liver. Interpretation of the results is most often performed immediately during the examination.
Symptoms of gallstone disease in adults cannot provide a complete picture, which is necessary to prescribe adequate treatment. Naturally, you will have to visit an experienced doctor who will carry out the entire range of diagnostic measures. They help determine the size of the stones, the degree of development of the pathology, and its type.
Various tools, both technical and clinical, are used for diagnosis. In the second case, the doctor palpates the gallbladder and ducts, during which the patient may feel discomfort and pain. In addition, colic may be accompanied by the passage of very small stones, which also indicates the presence of the disease.
When making a diagnosis, the symptoms of gallstone disease in adults and children (if there are such cases) are taken into account. In addition, the patient will need to undergo the following procedures:
- ultrasound examination of internal organs;
- blood and urine analysis (for the content of duodenal elements, cholesterol levels, bilirubin, fat metabolism indicators and alpha-amylase activity);
- a thorough analysis of the patient’s medical history and family history;
- stool analysis (in it you can often see which elements of food are not digested);
- examination of the inner surface of the stomach, duodenum and esophagus (esophagogastroduodenoscopy);
- cholangiopancreatography (examination of the bile ducts from the inside using a duodenofibroscope);
- computed tomography of internal organs;
- MRI.
It is necessary to take into account the non-specificity of symptoms, so the diagnosis must be made as accurately as possible. Otherwise, the doctor may simply treat the wrong disease, which will lead to unpredictable consequences.
Symptoms
When stones form, the first signs do not appear immediately. The asymptomatic process drags on for 10-12 years. For some people, stones form slowly and are not noticeable.
As the stones grow, they begin to injure the inner lining of the organ and interfere with the normal outflow of bile. From this moment the following symptoms begin to appear:
- Heaviness in the stomach . This is one of the first signs. Heaviness is felt in the right hypochondrium and upper abdomen. Most often it appears after eating and physical activity.
- Pain after eating in the right hypochondrium. For some people, this is the symptom that signals problems.
- Biliary or hepatic colic. This is a severe pain radiating to the right shoulder and shoulder blade. The first attacks are not as intense as subsequent ones. They are expressed in discomfort during movements, which turn into bursting pain. Most often, colic occurs after eating fatty foods or alcoholic drinks.
- Nausea, heartburn, sometimes vomiting. Also occurs after eating. This is due to the fact that in the presence of stones, the required amount of bile is not released, and food is digested less well.
- Changing the stool . Uneven secretion of bile provokes stool disorders (constipation occurs or, conversely, diarrhea). At a later stage, the stool becomes discolored in some cases. This indicates that the stones have completely blocked the bile duct.
- Jaundice. Yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes occurs in later stages. Jaundice is caused by stagnation of bile not only in the gallbladder and liver ducts. Liver dysfunction leads to the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which stains the skin.
When the body is intoxicated, the temperature may rise from subfebrile values to a febrile state.
Features of the course of an acute attack and first aid
This pathology can develop gradually, but the time will come when it will make itself felt. Therefore, you must know how to relieve an attack of gallstone disease. It must be said that a person feels worst at the moment when solid particles begin to move through the ducts and clog them.
- A heating pad or warm compress should be applied to the gallbladder. As a last resort, it is necessary to organize a warm bath to reduce pain and alleviate the condition.
- Now you need to take any painkiller that can relieve spasms (“Atropine”, “Papaverine”, “No-shpu”).
- It is imperative to call an ambulance and hospitalize the victim. Moreover, you need to go to the hospital if the pathology worsens. It is in the hospital that all necessary diagnostics can be carried out and surgical intervention can be performed (if absolutely necessary).
- Along with painkillers, it is necessary to take anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications.
It must be said that timely measures can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. Now you know how to relieve an attack of gallstone disease. However, this does not mean that the pathology does not need to be treated.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
If sand or small stones are found in the gallbladder, there is a chance to get rid of them using conservative methods. To increase the circulation of bile and dilute it, the following are used:
- medications;
- decoctions of choleretic plants;
- juices of some vegetables and fruits;
- tubage (a procedure combining the use of a choleretic agent and water with the application of a heating pad to the bladder area).
But in the presence of large stones, conservative methods will only bring harm. When released, the stone can get stuck in the bile ducts, cause them to rupture or scratch them, after which scars form. Therefore, before using choleretic drugs, it is necessary to reduce the size of gallstones as much as possible. Sometimes the disease is treated with ultrasound or shock wave therapy.
Another method is to administer drugs directly into the gallbladder (based on ursodeoxycholic or chenodeoxycholic acid). The procedures are painless, they destroy large stones, and small crystals and sand are released naturally with bile. But if there are dense and hard stones, such treatment of cholelithiasis does not always give the desired effect. Stones with a high calcium content are difficult to dissolve.
If conservative methods do not produce changes in the size of the stones, or gallstone disease is detected at a late stage, when the bladder no longer functions, the only effective way to cure it is to remove the bladder along with the stones. The operation is performed in order to prevent organ rupture and relieve the patient from chronic inflammation and pain.
The main indications for surgical treatment are:
- more than 1/3 of the gallbladder is filled with stones;
- the presence of insoluble calcium stones;
- difficulty in releasing bile;
- stone getting stuck in the bile ducts;
- frequent attacks of biliary colic;
- inflammation of the gallbladder due to injury to the mucous membrane by stones, accompanied by infection;
- Emergency surgical intervention is necessary if the gallbladder ruptures or a fistula is detected.
In modern medicine, cholecystectomy is almost always performed using a gentle laparoscopic method, in which only two small incisions are made in the abdomen. However, in acute conditions (rupture of the gallbladder or bladder, peritonitis), open abdominal surgery must be performed.
Drugs are prescribed that help improve liver function and slow down the process of further formation - allochol, cholenzyme, drugs based on ursodeoxycholic acid (ursofalk, ursosan, urdoxa).
Be sure to follow a diet that minimizes the possibility of stones passing - without fried, fatty, spicy and salty foods. Such foods cause sudden bile secretion, in which stones can leave the gallbladder and get stuck in the ducts. This will provoke an attack of biliary colic and can cause unpleasant consequences, including rupture of the organ.
The quality of life does not deteriorate after removal of the gallbladder - you just need to follow a special diet. In the absence of a storage reservoir, bile flows from the liver directly into the intestines. It is advisable that meals be small but frequent. It is important to prevent the appearance of stones in the bile ducts (cholelithiasis) - their formation is also affected by diet, physical activity during the day, and taking bile-thinning drugs.
- lean meat, poultry and fish;
- fresh, boiled and stewed vegetables;
- seafood;
- fruits;
- cereal dishes - rice, buckwheat, oats;
- cottage cheese, yogurt.
It is necessary to refuse fatty foods, which in the absence of a gallbladder will be poorly digested and cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract - heavy meat, butter. Limit the consumption of spicy foods, fried foods, smoked and pickled foods, alcohol, sweets with a high content of sugar and starch, and carbonated drinks.
It is useful to drink herbal teas from plant decoctions that improve liver function:
- milk thistle;
- artichoke;
- corn silk;
- immortelle;
- mint;
- dandelion roots;
- celandine;
- turmeric.
There is no need to limit yourself in physical activity - moderate exercise is even beneficial, it promotes the outflow of bile. Sometimes massage and physical therapy are prescribed for faster recovery.
Features of treatment with folk remedies
Naturally, drug therapy is not a panacea and does not always help. Self-prepared substances can also enhance the effect. For example, treating gallstone disease with folk remedies will significantly increase your chances of getting rid of the pathology, but you should not use them without the consent of your doctor. So, the following recipes may be useful:
- Red beet juice. Long-term use of this drink will help you quickly cope with stones. Moreover, they will dissolve completely painlessly. You can use not only juice, but also beet broth. To do this, the vegetable needs to be cooked for a long time. Please note that not all people like this drink.
- Treatment of cholelithiasis, with folk remedies, in particular, can be carried out using a mixture of various plants, each of which has its own specific effect. For example, the following remedy can relieve pain, cleanse internal organs, and improve their blood supply: the roots of calamus, valerian and buckthorn, wild rosemary herbs, mint, hawthorn, chamomile, lily of the valley and rose hips mixed in equal quantities. Before this, all plants should be chopped. The maximum amount of each herb is 5 grams. Next, pour the mixture with 1.5 liters of water and put on fire. The liquid should boil for no more than five minutes. Also, give the product time to sit (about 6 hours). You need to take it several times a day, 100 ml. It is necessary to drink the remedy until complete recovery.
- In order to eliminate stagnation of bile in the ducts, use a decoction of wild strawberry berries and leaves. Take it three times a day, a glass.
- Regular dill is also considered useful. To prepare the decoction you will need two large spoons of seeds and 2 cups of boiling water. Next, the mixture must be put on fire. It should boil for no more than 12 minutes. Try to drink half a glass of the product daily. Moreover, the liquid should be warm. It will take you several weeks to heal.
- Chicory root infusion will help you effectively dissolve stones and remove them from the body. To prepare the drink, take 60 grams of crushed raw materials and pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. The decoction should sit for at least 20 minutes. Next, take the drink in small portions throughout the day. It is best if the broth is fresh each time.
- Black radish juice and honey will help you cleanse your gallbladder and dissolve stones. Try to drink 1 tablespoon of the mixture on an empty stomach in the morning. After this you can eat only after a quarter of an hour. Please note that this procedure is lengthy and takes at least six months.
In addition, try to improve bile secretion. To do this, take carrot and cabbage juice every day.
Complications
The most dangerous consequence of the formation of gallstones is perforation (rupture) of the gallbladder. It can occur at any time when the stone presses on the wall of the organ during its contraction. Bile and other contents of the bladder enter the abdominal cavity, which causes complications including death. The inflammatory process, the presence of microbes and pus in the organ further increase the risk of peritonitis.
Sometimes injury to the walls of the gallbladder occurs gradually. A fistula is formed, through which the contents gradually leak into neighboring organs.
Stones can cause blockage of the bile ducts by getting stuck in them or causing mechanical injury, which is why scars and adhesions form. Large gallstones completely block the exit of bile from the organ, leaving no room for it - the consequence of this is the “switching off” of the organ from the digestion process. Over time, bile stops flowing into the bladder altogether, and it dries out. If there are small stones, there is a high risk of them exiting into the bile ducts.
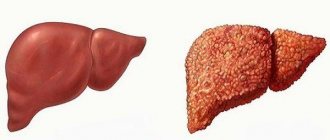
The liver also suffers when the gallbladder malfunctions. If the exit of bile from the liver itself is difficult, the consequences can be chronic hepatitis, death of organ cells and cirrhosis. Therefore, it is important to identify the symptoms of cholelithiasis in time and begin treatment.
Diagnostic methods
Only highly qualified specialists can diagnose cholelithiasis. First of all, these are gastroenterologists, and surgeons will help cope with the disease.
In a clinic with good technical equipment and diagnostic equipment, you are guaranteed to receive the correct diagnosis. To accurately determine your disease, you will need to undergo an ultrasound examination. This method is the main one in diagnosing cholelithiasis. During an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, it will be possible to accurately determine whether stones are present in the gall bladder, as well as accurately determine their size and quantity, evaluate their shape, determine the size of the gall bladder itself, the deformation of its walls, and the condition in which the bile ducts are located.
Another effective method is computed tomography with contrast. This will allow your doctor to identify the key signs of inflammation of the gallbladder, evaluate its functionality, and notice if there is a blockage of the bile ducts.
Experts also advise that you definitely undergo general and biochemical blood tests. This will make it possible to identify other signs of inflammation, if any. In-depth and comprehensive diagnostic studies help to establish concomitant diseases and determine the individual characteristics of patients. Only in this case will the doctor be able to prescribe the optimal and effective course of treatment.
Indications for surgery and types of operations
There are cases when it is impossible to use medications for gallstone disease or traditional recipes simply do not help. In addition, acute attacks require surgical intervention. In this case, surgical removal of stones is performed. There are certain indications for intervention:
- large stones in the gall bladder, which prevent the organ from working properly and cause severe pain;
- intestinal obstruction;
- gangrenous lesion of the gallbladder;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- eliminating the possibility of gallbladder cancer.
There are also contraindications to surgery: the patient’s serious condition, any oncological diseases of other organs, severe inflammatory processes in the body, as well as individual characteristics.
Gallstones are removed in several ways:
- Traditional (laparotomy). To do this, the doctor must open the anterior abdominal wall and remove the bladder along with all its contents. Such an operation is performed if the stones are too large or the organ will no longer perform its assigned function.
- Laparoscopic. To do this, you do not need to cut the peritoneum. Specialists simply make small holes in the area of the bubble and remove the stones through them. At the same time, recovery after such an operation occurs much faster, and there are practically no scars left on the skin. That is, this type of intervention is used most often.
If you have gallstone disease, the operation can be performed without a scalpel. For example, now in medicine they use specialized technical means that are capable of crushing the formed elements. This method is called shock wave lithotripsy. This procedure is not possible everywhere. After the procedure, small stones are simply dissolved with the help of medications and removed from the body.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
Basic preventive measures should be aimed at reducing cholesterol and bilirubin levels, as well as preventing bile stagnation. These include:
- balanced diet;
- active lifestyle and physical activity;
- timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
If stones have already formed, then to prevent colic attacks you must adhere to a strict diet and drink plenty of fluids. To minimize the risk of stone movement, it is recommended to avoid prolonged bending of the body.
The prognosis depends on the rate of formation of stones, their size and movement.
Most often, gallstones lead to the development of dangerous complications and the need for surgical intervention.
Forecast
With timely treatment, the likelihood of getting rid of gallstone disease without surgery is quite high. If stones have just begun to form or have not yet hardened, conservative treatment methods will have a positive effect.
As the number of stones increases, the disease becomes less treatable, and the likelihood of avoiding surgery decreases. But timely surgical intervention (removal of the bladder) will help avoid digestive problems and prevent liver disease. The risk of organ rupture and peritonitis disappears - a gallbladder filled with stones is a “time bomb” and can make itself known at any moment. Therefore, it is not worth the risk.
Nutritional Features
For more effective treatment, the patient is prescribed diet No. 5. For gallstone disease, it is considered optimal. So, the caloric intake with this diet is about 2800 kcal daily. If the patient is obese, then these indicators can be reduced to 2300 kcal. You need to eat at least 5 times a day in small portions.
You need to drink clean water, and as much as possible (from two liters per day). Try not to drink carbonated water; alcohol is prohibited. Tea, juices and herbal infusions are best. Products for cholelithiasis must be fresh and safe. It is forbidden to eat fatty, fried, smoked, spicy foods, chocolate, canned food, sausages and semi-finished products, fish and meat broths. Also, try to avoid using garlic, pepper, lard, onion, sorrel and excessive amounts of salt while cooking.
Allowed products are: bran bread, vegetables and fruits, low-fat dairy products, lean meat and fish. Moreover, the latter should be baked in the oven or steamed. Eat porridge and boiled eggs (no more than 1 per day). Use olive oil instead of sunflower oil. If you are experiencing a period of exacerbation, then the products should be ground.
You cannot prescribe a diet for yourself. Try to consult with an experienced specialist in this field, as well as your doctor. If you don’t know what you can cook for gallstone disease, the recipes presented in this article will be very useful to you.
So, take 300 g of potatoes, 25 g of carrots, 19 g of butter, 350 g of water, 7 g of parsley and 25 g of onions. All vegetables must be boiled. Gradually add oil and parsley to the “soup”. It is advisable to chop the carrots and potatoes.
Carrot and potato puree is healthy and very tasty during illness. All vegetables must be boiled and crushed (grinded). Next, add a little milk and a little salt to the mixture. Now the puree can be brought to a boil and served.
A very useful vegetable in such a situation is eggplant. It can be stewed in sour cream sauce. To prepare this dish, take 230 g of eggplant, herbs, a little butter and salt. For the sauce you will need 50 g of water, 50 g of sour cream, a little butter and flour. We cook the eggplant last.
The sauce is made like this: fry the flour in a heated frying pan, add oil and water. Boil the mixture for about 20 minutes. Lastly, sour cream is added. Now peel and cut the eggplant, salt it and leave for a few minutes to remove the bitterness. Next, place the pieces in a frying pan and simmer a little over low heat. Lastly, add the sauce to the eggplant and leave the dish to simmer for another 5 minutes. Bon appetit!
Nutrition menu for gallstones: what is possible and what is not
For cholelithiasis, therapeutic diet No. 5 is prescribed.
Patients with gallstone disease are prescribed therapeutic diet No. 5. Its basic principles are as follows:
- Fast food and snacks are prohibited
- Baked goods and confectionery products must be limited to a minimum
- Soda, low alcohol and alcoholic drinks, coffee are prohibited
- It is recommended to eat warm first courses. If they are in meat broth, the meat should be lean and the broth should be second
- Vegetables are also the basis of the diet. You can eat everything except raw cabbage and legumes
- Consumption of fresh fruits and berries is necessary. These are apples, bananas, melon, strawberries, etc.
- The intake of fried and fatty foods, in particular of animal origin, which is a provocateur of increased cholesterol and, as a consequence, the formation of gallstones, is sharply limited.
- Small and frequent consumption of food is recommended, from 4 to 6 times a day. This ensures optimal bile movement
- Regarding nutrient intake, fats need to be reduced. The norm of carbohydrates (complex) on diet No. 5 is up to 350 g, fats and proteins – up to 90 g
- There is no need to reduce your daily caloric intake. For gallstones, a person should consume about 2500 kcal per day. If he is overweight, this point is discussed with the doctor.
- Doctors also recommend introducing fiber and healthy fats into your diet in the form of bran and Omega3 dietary supplements.