Causes of a metallic taste in the mouth in men
The taste of iron appears in the mouth of men for various reasons, many of which have nothing to do with the condition of their body.
- Drinking mineral water that contains iron elements can lead to the appearance of a characteristic taste in the mouth.
- Drinking unboiled tap water also often causes a metallic taste.
This is due to the fact that centralized engineering communications are in unsatisfactory condition and almost all are covered with a layer of rust.
Dishes
Many people cook in dishes made of aluminum or cast iron. In the case when the dish consists of acid-containing products, a chemical reaction occurs in the saucepan or frying pan. As a result, after eating such a dish, people develop a metallic taste in their mouths.
Crowns
If a person has metal crowns inserted, they begin to deteriorate over time, as they are forced to systematically come into contact with aggressive environments. As a result, the interaction of metal ions with the acid contained in food begins to occur in the oral cavity.
Medicines
Some people experience unpleasant taste sensations due to the use of certain types of medications, for example, tablets:
- Lansporazole.
- "Tetracycline".
- "Metronidazole"
- Dietary supplements, etc.
As a rule, after completion of drug therapy, unpleasant symptoms disappear.
Currently, it has become fashionable to switch from regular cigarettes to electronic ones, which, according to most people and manufacturers, are absolutely harmless to the human body and the environment. If this gadget has an appropriate certificate confirming its high quality and compliance with standards approved at the legislative level, then, as a rule, chickens do not have problems.
According to statistics maintained by many medical institutions from around the world, it is the female audience who often turns to specialists with complaints about the appearance of a metallic taste in the oral cavity. If this category of patients has an unpleasant taste from time to time, then this can be associated with the diet, in which some new products may have appeared.
But, in the case when the taste of metal begins to accompany them constantly, then it should be considered as a signal from the body about the development of serious pathologies:
- Hormonal disorders that can occur in the female body due to age-related changes. Also, hormonal imbalance can be a consequence of the development of problems in the endocrine and reproductive systems.
- Most women regularly go on diets because they strive to have slim and toned figures. Due to unbalanced nutrition, they experience taste changes.
- Those girls and women who decided to stop eating sugar in its pure form and switched to its substitutes may feel a metallic taste in their mouth.
- Expectant mothers may also encounter this problem, in any trimester of pregnancy. Experts associate this condition with taking vitamin-mineral complexes, which contain various microelements, including metals.
Modern medicine knows different types of diseases, the development of which causes a metallic taste in the mouth.
Anemia
With the development of this pathology, people exhibit characteristic symptoms that allow one to suspect the disease:
- Metallic taste in the mouth.
- Headaches occur systematically.
- Weakness and fatigue appear.
- The skin becomes painfully pale and may dry out.
- My head starts to feel dizzy.
- Nail plates and hair become brittle.
- Cracks appear in the corners of the mouth.
This disease can be provoked by excessive blood loss, poor nutrition, or lack of iron during the active development of the body.
Poisoning
Severe disturbances in the human body can be caused by the penetration of the following heavy metals and salts:
- arsenic compounds;
- mercury;
- copper;
- lead, etc.
Victims exhibit characteristic symptoms, for example, a metallic taste, general weakness, nausea, and dizziness. Quite quickly, pain appears in the muscle tissues, and vomiting begins.
Hypovitaminosis
If there is a lack of vitamins in the human body, then all systems and organs will suffer from this.
People can suspect hypovitaminosis based on characteristic symptoms:
- decreased mental abilities;
- increased nervousness;
- the appearance of a metallic taste;
- decreased physical capabilities;
- sleep disturbance, etc.
People can normalize their condition by taking special vitamin and mineral complexes and a balanced diet.
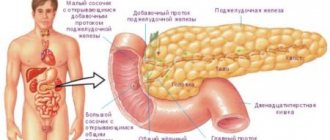
Gastrointestinal pathologies
| In which organs do pathologies develop? | Description |
| In the gallbladder | With the development of cholangitis, dyskinesia, cholecystitis, patients develop a bitter or metallic taste in the mouth, pain occurs in the right hypochondrium, and defecation processes are disrupted |
| In the liver | If a person is affected by this organ, this means that in addition to the taste of metal, nausea will appear, weight will begin to rapidly decrease, pain, belching, etc. will occur. |
| In the intestines | With the development of intestinal pathologies, people experience unpleasant symptoms, which include a specific coating on the surface of the tongue, as well as an unpleasant taste in the mouth |
| In the stomach | A patient may suspect a peptic ulcer by the appearance of heartburn, vomiting, foul-smelling belching, or severe pain, which usually appears at night. If a person has low acidity, then in addition to a metallic taste, he will feel pain after every meal, he will experience heartburn, and bowel movements will be disrupted. |
ENT organs
| In which organs do pathologies develop? | Description |
| On the tongue | An unpleasant symptom is characteristic of glossitis, which develops due to mechanical or thermal impact on the organ |
| On the gums | If a person's gums bleed, he will feel a metallic taste in his mouth. Patients with periodontal disease, gingivitis, and stomatitis face this problem. |
| In the respiratory tract | Some patients experience unpleasant taste sensations after coughing. This symptom is typical for severe respiratory illnesses, such as bronchitis. |
| Infectious lesions of the ENT organs caused by fungi | In humans, inflammation can develop in the paranasal sinuses, ears, and throat. This pathological condition is accompanied by characteristic symptoms: pain localized in the nose, the appearance of a whitish coating on the surface of the tongue and tonsils, drying out of the mucous membranes, changes in taste sensations |
Diabetes
With the development of diabetes mellitus, in addition to a metallic taste in the mouth, a person experiences the following manifestations of the disease:
- skin itching;
- increased appetite;
- blurred vision;
- drying of the mucous membranes in the mouth;
- constant feeling of thirst, etc.
People should contact a health care provider for advice before taking any action to treat unpleasant taste sensations. Specialists will carry out a set of diagnostic measures, thanks to which they will be able to determine the exact cause of the discomfort.
People can temporarily eliminate unpleasant symptoms in the following ways:
- You need to pour table salt (1 tsp) into a glass half filled with water. After all the salt crystals have dissolved, you need to rinse your mouth several times in a row.
- If a person eats sweets, he can temporarily eliminate the taste of iron.
- You can chew half a lemon slice or drink acidified water.
- Spices should be added to tea. Thanks to ginger, cardamom and cinnamon, you can change the taste sensations.
- To eliminate unpleasant taste sensations, experts recommend eating as many fruits as possible, for example, tangerines, grapefruits, and oranges.
- Patients should regularly take hygiene measures. After each meal, you should brush your teeth, as well as the surface of the tongue on which pathogenic microflora is present. To brush your teeth, you need to use not only toothpaste, but also dental floss, with which you can remove food debris from hard-to-reach places.
The taste of iron in the mouth, as if you had just licked a battery, is a rather unpleasant feeling that can appear sometimes or bother you constantly. In addition, many diseases of the digestive system can manifest themselves as such symptoms, so such a signal from the body cannot be ignored.
In this topic, we want to tell you why an iron taste appears in your mouth, what you need to do in this case, and which specialists you should contact. But first, let’s look at what taste is, how it is formed, and which organ is responsible for taste perception.
The tongue not only takes part in the formation of sounds, but is also responsible for the perception of taste. How does this happen?
There are more than two thousand taste buds on the tongue, which contain taste buds. The papillae of the tongue are distinguished by their shape, as well as by purpose. There are filiform, mushroom-shaped, leaf-shaped and grooved taste buds.
Various substances that enter the oral cavity, and, accordingly, the tongue, penetrating deep into the taste bud, irritate the nerve endings located there. The signal received by the receptor is sent to the brain, where, after processing, it provides information about the taste of the substance.
It should also be noted that different parts of the tongue are responsible for the perception of a certain taste: the tip is responsible for the perception of sweet taste, the middle part - sour, the edges of the tongue - salty and sour, and the root - bitter.
The taste depends on the following factors:
- concentration of the main substance in food;
- the area of the tongue on which food has fallen;
- food temperature.
An iron taste in the mouth is not always a consequence of any disease, since this is how the body can react to external irritants. It all depends on how often such a sensation occurs, what symptoms accompany it and in what situation it occurs.
Causes of partial loss of taste
Conventionally, the tongue can be divided into four parts, each of which is responsible for the perception of a certain taste.
Photo 1: The tip of the tongue is responsible for the sensation of sweet taste, the middle - for salty, the back of the tongue perceives bitter, and the edges of the tongue are responsible for sour sensations. Impaired perception is associated with various pathological processes in different parts of the tongue. Source: flickr (“R☼Wεnα”).
Sweet taste is lost
Loss of sweet taste can occur due to an inflammatory process at the tip of the tongue, a burn injury, or injury to this area. Disturbances in the papillae of the tongue, pathologies of nerve impulses to the brain are also factors in reducing the sensation of sweetness.
If you don't feel the salty taste
A weakening of the sensation of salty taste or its complete loss indicates injury to the middle part of the tongue. Bacterial and fungal infections (candidiasis) affect the tissues where the taste buds are located.
Loss of salty taste perception is often caused by heavy smoking, which causes the taste buds to atrophy. Malignant neoplasms in the brain provoke ageusia or hypogeusia of salty taste, since the brain cannot recognize the incoming impulse.
Loss of sweet and salty taste
There are also several reasons that provoke the loss of sweet and salty taste at the same time:
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants;
- hypovitaminosis (especially vitamin B12);
- lack of zinc in the body.
Partial loss of taste (sweet or salty) is often noted in patients suffering from epileptic seizures. Also common factors of hypogeusia are:
- changes in the deep parts of the temporal lobe of the brain, which is accompanied by mental disorders and schizophrenia;
- neuritis of the fifth or seventh pair of cranial nerves;
- damage to the brain stem.
What does iron taste in mouth mean?
Taste is formed on the tongue, which has many receptors. They are called papillae. Their surface contains substances that, when interacting with molecules of other substances, change their composition, creating nerve impulses. They are transmitted to the brain.
Non-specific taste shades recognized by him can be an alarming symptom, and also indicate the presence of pathologies. A metallic taste in the mouth means that processes occur in human organs in which ions of iron, copper, arsenic or mercury accumulate in the oral cavity.
The reasons for this phenomenon may be:
- various diseases;
- the effect of medications;
- physiological changes in the functioning of the body.
Why does the tongue feel sweet?
Lots of carbohydrates in the diet, excessive sweet tooth. A persistent sweet-milky taste is a symptom of a carbohydrate metabolism disorder. Excessive consumption of high-calorie foods containing glucose. Fans of salty, spicy foods experience taste discomfort. The constant presence of this symptom of taste disturbance can be caused by various diseases and poor diet.
Through saliva, a person continuously feels a sweetish taste in the oral cavity. This constant unpleasant feeling is unusual. It confuses and irritates. Changes in metabolic processes are the cause of this condition. The taste buds located in the oral cavity react sensitively to any disturbance in the body.
Nervous system infections:
- Pathologies cause a significant disturbance of taste and greatly change the electrical activity of the central and peripheral nervous system. An imbalance in the complex structure can cause taste disturbances.
- A sweet or unusual metallic taste occurs because the taste buds that transmit taste information from the epiglottis and throat to the brain are damaged.
Endocrinological disease – diabetes mellitus:
- A symptom of a hidden disorder due to impaired carbohydrate metabolism, increased levels of glucose in the blood in an uncontrolled form is a constant sweet taste in the mouth.
- Some sugar imbalance is observed, if the process of insulin production is disrupted, serious complications arise. This causes a pathological taste of sweets in the mouth. The process of sugar penetration into lymphatic and blood vessels and saliva is consistently disrupted.
- Diabetic patients often report taste discomfort in the mouth because peripheral nerves are damaged due to neuropathy.
Neurological disorders:
- Touch, taste, and smell are sensory functions that are controlled by the body’s nervous system through nerve fibers. The brain continuously receives electrical signals associated with taste signals, since many nerve fibers go to the structures of the organ.
- A constant sweet taste in the mouth often appears due to disruption of the functioning of the brain and changes in the functioning of the nerves.
Dangerous pseudomonas respiratory tract infections:
- When the pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa enters the human body, it causes the development of various unrelated pathologies. With a serious sinus infection, chest pain, ear and nasal diseases develop.
- There is a loss of taste. This perversion of perceived taste is a side effect of sinus pathology.
Pancreatitis, indigestion;
- The pancreas is responsible for many processes in the body. If this secretory organ gives an SOS signal, a burning sensation, itching in the pit of the stomach, and heartburn occur inside the sternum in the morning. Disgusting taste sensations last for quite a long time and disrupt the complete digestion process.
- Impaired liver function, damage to the pancreas, indigestion, reflux of bile into the stomach, digestive problems in patients with acid reflux after long holidays lead to the continuous presence of a sweet taste, since the acid present in the stomach rises to the esophagus. Pain often occurs in the patient's chest area. An unpleasant set of teeth appears.
Lesions of the nervous system of an infectious nature:
- A viral infection that enters the human body causes the development of dangerous meningitis and encephalitis. Severe damage to the nervous system occurs.
- The activity of nerve cells is disrupted, the ability to sense taste is impaired.
Chemical poisoning:
- Acute dysfunction and the appearance of a sickly-sweet taste occurs due to the penetration of phosgene, pesticides, and lead into the body. A sign of chronic intoxication is a sweet and sour taste in the mouth, irritability, fatigue, and insomnia.
- If poisoning is suspected, medical intervention is required. The taste problem will resolve itself if the cause of the poisoning is eliminated.
A sweet taste on the tongue is a sign of dental problems:
- Stomatitis, periodontal disease, and caries very often accompany the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms in the body. Pseudomonas aeruginosa actively colonizes the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
- This gives a powdered sugar sensation in the mouth.
Excess metal in the body
A steely taste in the mouth may indicate the accumulation of large amounts of metals in the body:
- gland;
- copper;
- aluminum;
- mercury;
- arsenic.
| Tongue piercing | Constant contact of iron products with taste buds causes deposition of metal ions on the mucous membrane. |
| Cheap jewelry | Products made of various metals, when in constant contact with the skin, enter into chemical reactions with it, releasing iron, aluminum or copper ions. These particles enter the body and accumulate in it, causing an unpleasant taste in the mouth. |
| Insufficient oral hygiene | Plaque or tartar, caries, food particles - all this provokes the constant presence of a steely taste due to the accumulation of decay and rotting products. |
| Dental devices: braces, dentures, dental crowns | With these devices, eating foods that are high in acid causes a chemical reaction that causes metal particles to accumulate in the mouth. |
| Mineral water with a high content of iron or copper ions | Drinking large amounts of ionized water causes excess metals in the human blood. |
| Cooking in non-enamel cookware | The combination of metal utensils and foods with a high acid or alkali content can cause some reactions with the release of metal particles that enter the human body with food. |
| Accumulation of heavy metals | Poisoning can occur during repairs, while working in factories and warehouses. Such metals are not excreted from the body; they accumulate and cause severe intoxication. In addition to the steely taste, vomiting, dizziness, nausea and migraines may often occur. |
A nonspecific taste often indicates hypovitaminosis and anemia. Insufficient iron, or anemia, is a common cause of a steely taste in the mouth.
There are also other symptoms:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- pallor;
- tachycardia or arrhythmia;
- drowsiness;
- dry skin;
- decreased sense of smell or vision
- migraine.
The development of anemia can lead to:
- various bleedings;
- pathologies of the stomach or intestines;
- poor nutrition;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- previous operations;
- bacterial, viral and colds.
Improper and insufficient nutrition provokes the development of hypovitaminosis. A person suffering from a lack of vitamin B1-B12, vitamins A and E, and folic acid feels a steely or bitter taste on the tongue.
At the same time, he exhibits:
- apathy;
- weakness;
- iron taste in mouth;
- weakened immunity;
- memory impairment;
- slowness of thought processes;
- visual and hearing impairment.
A metallic taste in the mouth is a sign of damage to internal organs and system malfunctions. But an unpleasant taste of metal does not always signal a health problem; its appearance can be triggered by dietary errors or failure to comply with hygiene rules.
A metallic taste in the mouth indicates a malfunction of the body.
Some medications, poisoning with hazardous substances, vitamin deficiency, pathological processes in the oral cavity, respiratory and digestive systems, and some other factors that are not hazardous to health can provoke the appearance of an iron taste.
What causes a copper taste in the mouth?
- drinking mineral water with a high content of iron ions;
- after installation of dentures, piercing – the appearance of a strange taste is caused by sour foods;
- after eating, the appearance of an unpleasant aftertaste can be caused by cooking acid-containing foods in dishes made of aluminum or cast iron;
- with the accumulation of plaque on the tongue, the formation of tartar - such problems arise from improper oral care;
- taking antibiotics, glucocorticoids, drugs to reduce the level of hydrochloric acid or sugar, statins, anti-allergy drugs;
- smoking, alcohol abuse - these factors often provoke the appearance of a wet iron taste in men.
A coating on the tongue can cause an unpleasant taste.
In case of poisoning with salts and vapors of heavy metals, in addition to a sharp metallic taste, myalgia, dizziness, dry mouth occurs, confusion often develops, severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and weakness occur.
Even constant contact of the skin with metal jewelry can provoke the appearance of a steely taste.
Women suffer from a bitter metallic taste more often than men - this is due to certain hormonal characteristics.
Causes of unpleasant aftertaste:
- during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause, the appearance of an unpleasant taste may be a sign of anemia, vitamin deficiency;
- changes in taste perception due to hormonal changes are one of the first signs of pregnancy; such symptoms are considered normal if they appear no later than 3–4 months;
- a strong metallic taste also appears during menstruation, which is also associated with changes in hormonal levels, or heavy menstruation;
- taking oral contraceptives, dietary supplements for weight loss.
During menstruation, women often experience a metallic taste in their mouth.
Dental problems, inflammation of the tongue, and gums are the most common cause of a rusty iron taste.
The taste of metal in the mouth - what does it mean:
- Periodontitis is an inflammatory process accompanied by bleeding gums, loosening of teeth, plaque appears within a few hours after brushing, and saliva becomes more viscous.
- Glossitis - when the tongue becomes numb, a burning sensation occurs, blisters and ulcers appear in the mouth, salivation increases, the person complains of the feeling of a foreign object in the mouth.
- Stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs with certain systemic diseases, infection with pathogens. The pathology has many forms and may be accompanied by swelling, bleeding, redness of tissues, pain, enlarged lymph nodes, fever, and severe salivation. Ulcers, aphthae, and blisters appear in the oral cavity; an unpleasant odor is felt even after brushing the teeth.
Metallic taste in mouth caused by bleeding gums
A metallic aftertaste often indicates the development of severe pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract; each disease is accompanied by a number of additional signs, which helps to quickly establish an accurate diagnosis.
Gastrointestinal pathologies and metallic taste:
- Iron deficiency anemia is a consequence of severe blood loss, insufficient consumption of foods containing iron, and gastrointestinal pathologies. All these diseases are accompanied by weakness, chronic fatigue, the skin becomes pale, peels, nails break and peel.
- Deficiency of folic acid, vitamin B12 - develops when the process of absorption of useful elements in the intestine is disrupted, with long-term use of barbiturates, drugs for the treatment of convulsive conditions. The skin becomes pale with a yellow tint, the person experiences weakness, frequent attacks of dizziness and tachycardia, and a decrease in blood counts is observed.
- Hepatitis, cysts, malignant neoplasms in the liver - diseases are accompanied by drowsiness, pain in the right hypochondrium, gums bleed, feces become lighter and urine darker, blood clotting worsens, bitterness appears on the tip of the tongue. One of the main signs is a decrease in the volume of the upper and lower extremities, while the abdomen increases due to the accumulation of fluid in it.
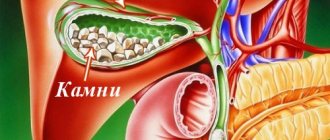
- Cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia - there is a dull pain in the right side, which radiates to the back, problems are accompanied by bouts of vomiting, stool disorders, and a slight increase in temperature.
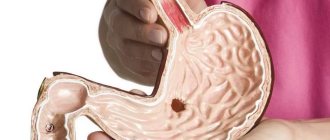
- Ulcer, gastritis with low acidity - these gastrointestinal diseases are accompanied by the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, nausea, constipation, discomfort in the center of the abdomen after eating, flatulence, rotten belching, heartburn.
Changes in taste often accompany infectious diseases of the larynx, ears, and throat; most often, the cause of the taste of steel is pathogenic fungi.
Causes:
- Otitis, diseases of the throat, sinuses - the infection first affects one of the organs and gradually spreads to other tissues. The disease can be recognized by a white coating on the tonsils, in the oral cavity, a dry cough, sore throat, pain and congestion in the nose and ears.
- Lobar pneumonia - the temperature rises to 38.5 degrees or more, pain appears in the sternum, brown sputum is released when coughing, the disease is accompanied by signs of severe intoxication, increased heart rate and breathing. When the form is advanced, the nasolabial triangle and nail plates become purple.
- Tuberculosis - weakness, sudden weight loss, increased sweating during sleep, low-grade fever, when coughing, sputum mixed with blood comes out.
- Lung abscess is a consequence of bacterial pneumonia; there is a strong increase in temperature, headache, decreased appetite, weakness, and the sputum contains patches of pus and blood.
- Bronchiectasis can be congenital or develop after bronchitis, tuberculosis, or lung abscess. Frequent coughing attacks are accompanied by the release of sputum, which has an unpleasant odor and contains patches of pus; unpleasant symptoms are more pronounced in the morning.
Otitis media can cause an unpleasant taste
In a child, frequent bronchitis, which is accompanied by thick and viscous sputum, may indicate cystic fibrosis - a congenital pathology caused by a defect in a certain enzyme. Additional symptoms are thickening of the fingertips, nail plates become convex, and deformation of the chest is observed.
Since the causes of a metallic taste are quite different, it is necessary to visit a therapist if unpleasant symptoms appear.
Diagnostics
During the initial examination, the doctor determines the nature of the accompanying symptoms, the intensity and location of the pain syndrome, changes in the condition of the skin and nails, and records signs of an inflammatory and infectious process.
Medicines
List of factors that cause strange taste sensations
A strange taste is a nonspecific symptom detected in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity, liver failure, cerebrovascular accident, and localization of infectious agents in the upper respiratory tract.
Additional reasons that contribute to the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth include:
- Taking medications, mainly antibiotics. The side effect of most antimicrobial drugs is a disruption of the natural microflora of the body, the development of dysbacteriosis and candidiasis of the mucous membranes. The negative effects of medications are accompanied by the appearance of a strange aftertaste. Discomfort can also be caused by the presence of individual intolerance to the components of the tablets, the death of pathogens, and exacerbation of chronic ailments.
- Dehydration. An unpleasant taste that periodically appears in the mouth may be a consequence of a lack of fluid in the tissues of the organs. Water deficiency occurs when you abuse carbonated drinks, alcohol, tea, and coffee.
- Metal poisoning: mercury, arsenic.
- Incorrect oral care. Poor hygiene is one of the reasons that causes an unpleasant taste in the mouth in the morning and increases discomfort after eating.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Oncology. Malignant tumors localized in various organs can cause the appearance of an unusual taste and bad odor. Among such neoplasms are cancer of the lungs, liver, and soft tissues of the mouth.
- Dietary features: constant overeating, unbalanced menu, eating at night.
Bad taste that appears in the mouth may be accompanied by a number of additional symptoms: fetid odor, the formation of deposits on the tongue, dry mucous membranes, belching, discomfort in the stomach, flatulence.
The reactions of receptor zones to the development of anomalies in the body are differentiated into several types. The most common ones include the appearance of sour, sweet, metallic, salty or bitter tastes. Sometimes patients in medical clinics complain of the appearance of a taste of mold, pus or soda, localized in the throat, tongue and lips.
If the strange taste that appears in the mouth is transient, then you can eliminate the symptom yourself. The development of special physiological conditions accompanied by the appearance of the discomfort in question (menopause, heavy menstruation) requires the supervision of a specialist. If an abnormal taste occurs that is permanent, you should immediately consult a doctor.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3zTZz-M5SRc
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
The taste of iron in the mouth also indicates the development of pathologies of the digestive tract. Pathologies of this system have pronounced symptoms, which allow an accurate diagnosis.
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Gastritis |
|
| Ulcer |
|
| Low or high stomach acidity |
|
| Cholangitis, gallbladder dysfunction, cholecystitis. |
|
| Changes in intestinal microflora and neoplasms in it |
|
| Poisoning |
|
Liver diseases
A metallic taste in the mouth also means that a person may have liver problems.
Liver disease is one of the causes of iron taste in the mouth.
In addition to non-specific taste, other symptoms may appear:
- vomit;
- nausea;
- weight loss;
- drowsiness;
- aching pain under the right rib;
- change in color of stool to lighter;
- darkening of urine;
- bleeding gums;
- low blood clotting.
The combination of several signs indicates the presence of diseases:
- hepatitis;
- liver cysts;
- tumors.
Liver cancer is characterized by a decrease in the size of the limbs due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, which sharply increases in volume.
Oral diseases
An unpleasant taste in the mouth may be a consequence of diseases of the oral cavity and its mucous membranes. Most often, these problems are associated with poor cleaning and care of teeth and gums. A metallic taste in the mouth means that dental abnormalities are actively developing.
Stomatitis
It can begin after suffering an infectious disease, taking strong antibiotics, or the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. This pathology is characterized by redness of large areas of the oral mucosa.
Among the signs of the disease are:
- bleeding and sore gums;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- profuse drooling;
- ulcers and blisters of the mucosal surface;
- unpleasant strong odor from the mouth.
Glossitis
Symptoms of the pathology are:
- tongue soreness;
- his numbness;
- sensation of a foreign object in the oral cavity;
- profuse drooling;
- iron taste in mouth;
- burning tongue;
- blisters and blisters on the mucous membranes.
All 3 pathologies are associated with gum inflammation. At the same time, they bleed and hurt. It is also possible for teeth to become loose and the viscosity of saliva to increase.
Causes of loss of taste
The diagnosis of “hypogeusia” is made to the patient if he experiences a change in taste sensations. Changes in taste can be of different nature:
- Injuries to the taste buds on the tongue. Occurs with burns of the mucous membrane and mechanical damage. Experts equate this ailment to transport losses.
- Damage to receptor cells. This phenomenon already applies to sensory disorders.
- Diseases of a neurological nature in which there is atrophy of the afferent nerve or dysfunction of the taste analyzer.
The reasons for the loss of taste in food can be completely different. This phenomenon can be provoked by serious diseases and a lack of certain substances in the body:
- Facial nerve paralysis. With this pathology, there is a violation of the sensitivity of the very tip of the tongue.
- Traumatic brain injury. In this case, a person cannot identify complex taste compositions. At the same time, it distinguishes sweet, salty, bitter and sour tastes well.
- Colds. In this case, it may happen that senses such as smell are lost, which is associated with severe swelling of the nasopharynx.
- Cancers of the tongue. Most often, the tumor develops closer to the base of the tongue, on the side. This leads to the death of taste buds. The disease is accompanied by pain and bad breath.
- Geographical language. This original name characterizes inflammation of the papillae of the tongue. With this disease, spots of different sizes and shapes appear on the surface of the tongue.
- Oral candidiasis. It is manifested by the appearance of a cheesy layer on the tongue and oral mucosa. When the plaque is removed, bleeding ulcers appear. The disease occurs with a disturbance in the sense of taste.
- Sjögren's disease. This is a genetic disease in which the functioning of the glands is disrupted. Due to a lack of saliva, the oral mucosa dries out and becomes susceptible to infections. With this syndrome, patients cannot taste food.
- Hepatitis. In the acute course of the disease, dyspeptic symptoms are observed, which are accompanied by a change in taste perception.
- Side effects from radiation therapy. After treating oncology with this method, patients experience a lack of taste.
- Deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals. It has been revealed that problems with taste can be caused by a deficiency of zinc and vitamin B.
- Side effects from medications. Some antibiotics, antidepressants, antihistamines and vasoconstrictor nasal drops can lead to this unpleasant phenomenon.
- Long-term smoking. We are talking not only about cigarettes, but also about a pipe. Tobacco smoke is a toxic compound and leads to atrophy of the taste buds on the tongue.
The reason that the taste has changed can be any injury to the pharynx, nose and head in general. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis.
If a small child complains that he has lost taste, do not rush to conclusions. Kids sometimes get cunning when they don’t want to eat this or that dish.
Hormonal disorders
A steely taste in the mouth can appear due to some hormonal imbalance. This often occurs during pregnancy or breastfeeding and indicates the onset of anemia. It is also possible for a nonspecific taste to appear during menstruation and menopause, since during this period significant blood loss or an increase in blood volume in the body is possible.
In addition to a metallic taste, hormonal imbalances are characterized by:
- deterioration in vision clarity;
- pale skin;
- jumps in body temperature;
- increased sweating.
Any changes in a woman’s hormonal balance should be strictly monitored by a gynecologist, since similar symptoms can be caused by tumors in the woman’s reproductive system.
Taking birth control medications
With additional use of hormonal medications, the perception of taste by the papillae of the tongue may be impaired. This is due to hormonal changes in the body and stress experienced by the brain. The taste of iron that appears when taking hormonal drugs is an individual reaction of the body. To confirm their dependence, it is necessary to stop taking medications for a while.
Medicines such as antibiotics:
- Doxycycline;
- Metronidazole;
- Doxilan;
- Tetracycline;
- Innolir;
May have side effects such as iron taste.
A similar effect on taste perception is exerted by:
- biological additives;
- mineral complexes;
- drugs to restore blood pressure;
- antiallergic drugs;
- holistic;
- drugs for the treatment and control of diabetes mellitus.
Poor nutrition
A metallic taste in the mouth also means that a person can eat incorrectly, causing a lack or excess of iron and vitamins, as well as eating foods containing heavy metals.
An unbalanced diet leads to the development of stomach diseases, and fried, smoked and peppered foods provoke poisoning of the entire body, which causes an unpleasant sour taste. Using tap water also causes a steely taste as the walls of the pipes are susceptible to corrosion by the humid environment.
Prevention measures
If you are convinced that the symptom is temporary and does not pose a threat of a serious illness, then you can use some alleviating methods. They will help prevent recurrence of unpleasant sensations:
- Don't forget about simple oral hygiene rules. When brushing your teeth, pay attention to your tongue, because a huge number of microbes accumulate on its surface.
- Drink more fluids. It will dilute gastric juice and replenish a dehydrated body; fruit juices are especially effective.
- Eat more fruits and vegetables. Citrus fruits and other sour fruits promote the secretion of saliva, which “washes away” unpleasant sensations (we recommend reading: why does sour saliva form in the mouth and what to do?).
- Watch your diet, try not to overeat. Meals should be regular, balanced and varied.
Bad habits
Various bad habits have a great influence on the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth or on the lips.
These include:
- Smoking: with cigarette smoke, about a thousand harmful substances enter the body, which not only poison it, but also accumulate in it.
- Alcohol: By affecting the brain's ability to transmit nerve impulses, it can distort taste perception. Also, after consuming it, the liver is overloaded, which contributes to the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Drinking coffee on an empty stomach: caffeine greatly irritates the gastric mucosa and increases its acidity. This causes digestive problems and a steely taste in the mouth.
Metallic taste in the mouth - all about the problem: causes and methods of diagnosis
To determine the cause of a metallic taste in the mouth and make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo examination by several doctors:
- therapist;
- gynecologist - for women;
- dentist;
- gastroenterologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- oncologist.
Then, if necessary, additional tests are prescribed:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- feces for enterobiasis;
- blood biochemistry;
- histology of mucosal material;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- cytological analysis;
- gastroscopy;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Depending on the results obtained, the doctor will select an individual treatment regimen and the necessary medications.
Diagnostics and consultation with a doctor
If you experience this symptom, it is important not to delay and consult a doctor for consultation and examination. To begin with, you can make an appointment with a therapist, he will determine whether there is a problem and prescribe treatment or refer you to another specialist.
A gastroenterologist will help you get rid of the taste of soda if it is associated with gastrointestinal diseases. He will order an ultrasound of internal organs, examination of the stomach, gastric juice, conduct other necessary examinations and be able to name the cause of concern.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods also help to cope with the metallic taste in the mouth:
- Rinsing the mouth with apple cider vinegar diluted in a ratio of 1:10.
- Brushing your teeth and rinsing with baking soda diluted 1:20 with water.
- Irrigation of the oral cavity with saline solution: 1 tsp. diluted in 200 ml of warm boiled water.
- Green tea, which is strongly brewed or chewed in dry form.
- Eating spices: cinnamon; coriander; ginger.
The appearance of any foreign taste in the mouth, including iron, requires special attention, and if additional alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a therapist and gastroenterologist to determine the exact cause of its occurrence. An iron taste can mean both safe physiological processes in the body and signal the development of serious diseases.
Treatment of a pathological symptom
be based on eliminating causes
A sour taste is often identified as a consequence of poor nutrition, when it is recommended to take only dietary foods.
There is a need to minimize the consumption of acidic vegetables and fruits, as well as meat. This is due to the fact that such products have a negative effect, multiplying bacteria that form an unpleasant acidic taste in the mouth.
The list of food items should include:
- Porridge made from buckwheat, wheat and barley.
- Sweet ripe fruits and affordable vegetables - tender apricots, juicy pears, melons, sweet apples and carrots.
- Dairy products.
- Green tea.
Only a doctor can prescribe a therapeutic diet, taking into account all the features of the course of the disease (acidity in the mouth) and the individual properties of the patient’s body.
If the cause of the unpleasant taste in the mouth is identified by the dentist, then, as a rule, it is necessary to sanitation the teeth in the presence of caries, and in case of gum disease, you can rinse the mouth with a decoction of oak bark or chamomile.
In order to completely get rid of the disturbing taste after eating sweets, it is worth remembering that this symptom cannot exist on its own, but has a reason.
In the case when the only correct factor is established by passing the necessary tests and undergoing hardware diagnostics, only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3zTZz-M5SRc