1941
The color of urine with cirrhosis of the liver often becomes unnaturally dark. This symptom should alert patients. Cirrhosis is often asymptomatic. Only small, insignificant manifestations indicate certain problems in the body.
Darkening of the color of urine cannot be ignored, because the effectiveness of its further treatment depends on the stage at which the disease develops.
Urine in cirrhosis darkens for a number of reasons. Its composition also changes, so laboratory tests and tests must be taken on a regular basis. This way you can control the negative changes in the body associated with the development of a serious illness.
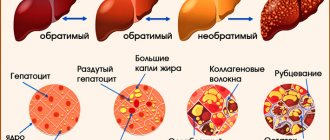
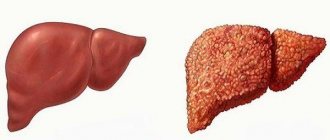
In cirrhosis, liver cells die and are replaced by connective tissue. The changes that have already occurred in the structure of the organ are irreversible. It is no longer possible to completely restore the liver, return it to its original appearance and function, but if you start treatment in a timely manner, you can stop the changes. The liver will perform its functions and will no longer deteriorate, although certain restrictions are imposed on the patient for the rest of his life.
Cirrhosis develops as an independent pathology only in isolated cases. It is often a consequence of other diseases.
The peculiarity of the structure of the liver is that there are no large nerve endings next to it, so this organ rarely hurts. Problems with it are difficult to identify at an early stage. The only confirmation of the presence of certain pathologies is a change in the color of urine and feces. You definitely need to pay attention to these symptoms.
Causes of changes in urine color in cirrhosis
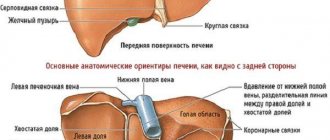
The liver is an important organ of the human body that performs many functions. This gland plays a huge role:
- Acts as a filter, purifying the blood from toxins and poisons;
- Performs a number of metabolic processes related to meeting the body's needs for glucose;
- Temporary storage of excess vitamins A, B12, D, their release if necessary;
- Carrying out hematopoietic processes in the fetus during intrauterine development;
- Regulation of lipid metabolism, that is, the breakdown of fats, the removal of excess cholesterol;
- Production of bile acids, release of bile when necessary;
- Synthesis of a number of hormones.
Another important function of the liver is to temporarily store blood reserves and release it in case of severe blood loss by the body to cover the deficit.
It is in the liver that bile is produced and stored. It is necessary for quality digestion of food. These processes are complex, but perfectly organized by nature.
If serious disturbances occur in the body, the liver ceases to perform a number of functions. As a result, bile and its constituent bilirubin enter the blood and are distributed throughout the body. In this case, the feces become discolored, because bilirubin is also responsible for its color, and there is not enough of it in the intestines.
But the skin turns yellow, as do the sclera of the eyes, and the urine becomes very dark and cloudy. This disorder occurs precisely because of the high level of bilirubin in the body.
The color of urine can change throughout the day; this is a physiological process. In the morning, when you go to the toilet for the first time, your urine is always darker than usual. Then during the day it becomes lighter and lighter, until it becomes a completely white transparent liquid. This effect is achieved provided there is sufficient fluid intake.
If the body is dehydrated, there will be little urine and it will be dark. If the functioning of the kidneys, bladder, or urinary tract is impaired, the urine will be dark and cloudy. In this case, the patient feels a frequent urge to go to the toilet and pain when urinating. This is how you can distinguish kidney problems from liver problems.
If there are liver problems, the urine will be the color of dark beer or medium-strength tea. Sometimes a reddish tint occurs due to blood in the urine. If you shake the liquid, thick foam will appear on its surface, which also visually resembles beer.
If the volume of urine is not reduced, there is no pain when urinating, but the color of the urine is dark, you may suspect problems with the liver. It is impossible to talk about cirrhosis right away: such a symptom often indicates a number of other acute or chronic diseases. But it is mandatory to undergo an examination.
Cirrhosis never develops on its own; it is a consequence of the following pathologies:
- hepatitis B, C;
- alcoholism;
- congestive processes in the liver;
- hereditary factors.
Hepatitis B, C
Alcoholism
Congestive processes in the liver
Characteristic changes in the color of urine are an important symptom, the appearance of which requires a full examination of the body.
Standard blood tests, urine tests, and ultrasound will give a certain idea of the condition of the organ. If the situation is advanced and cirrhosis has already begun, all possible measures must be taken to compensate for this condition. It will not be possible to completely restore health to the gland, but it is still possible to stabilize the situation.
How is liver cirrhosis diagnosed and how is it treated?
For liver diseases, diagnosis begins with a history, examination and palpation. Since many symptoms of cirrhosis may overlap with manifestations of other diseases, additional diagnostics are carried out using laboratory and instrumental methods. Among them, the most informative are:
- A general and biochemical blood test will show increased levels of ESR, leukocytes, bilirubin, AST and ALT. The content of albumin, total protein, urea and cholesterol will be below normal.
- Stool analysis. Discoloration, the presence of undigested food debris, the presence of fats and fiber will indicate cirrhosis.
- Fibrotest will determine the stage of cirrhosis based on indirect indicators in the blood.
- Ultrasound and elastography will show fibrous foci, dilated veins and organ size, signs of ascites.
- CT scan.
- MRI of the abdominal organs.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Liver biopsy.
- Laparoscopy.
Only a combination of laboratory, instrumental examinations and external manifestations can accurately diagnose the disease.
Treatment of the pathology is aimed at compensating liver functions and preventing complications. Medicines prescribed are hepatoprotectors, enteroseptics and diuretics. Drug treatment is supported by a diet with a balanced content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Progression and complications of the disease may require an organ transplant.
Other signs of cirrhosis
Liver diseases are often asymptomatic because this organ lacks nerve endings. The liver just doesn't hurt. Unpleasant sensations arise when the organ increases in size and puts pressure on the hypochondrium and other organs and systems.
If you notice a change in the color of your urine, pay attention to other symptoms:
- digestive problems – feeling of heaviness, flatulence;
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, fatigue of the body;
- all signs of intoxication - severe headache, disorientation in space, confusion.
Changes in urine color in cirrhosis occur in the early stages of the disease. Often this symptom is noticed before a diagnosis is made. The sooner you see a doctor, the greater the chance of saving your liver. Be sure to monitor your health, pay attention to the smallest symptoms, and pay attention to prevention.
Cirrhosis often develops against the background of infections, but liver diseases do not manifest themselves in any way. The same hepatitis C, which is the most common root cause of cirrhosis throughout the world, is called the “gentle killer.” It develops in the body over decades, constantly changes, and destroys the liver.
Only regular examinations and attention to the slightest changes in well-being will help to timely determine the presence of pathology and eliminate its consequences.
Don't be afraid to turn to narrow specialists. Sometimes a detailed consultation with an infectious disease specialist or hepatologist is required for absolutely healthy people so that they learn what cirrhosis is, what consequences it has, and how to avoid this problem.
Complications and further addition of symptoms
At the last, terminal stage of cirrhosis, the liver experiences almost complete degeneration and loses its functions.
Manifestations of the disease take on not just the character of individual external symptoms, but represent quite severe conditions.
Hepatic encephalopathy (brain damage)
The cause of brain dysfunction in cirrhosis is the powerful effect of toxins that the patient’s liver is not able to neutralize.
Signs of brain damage:
- deterioration of memory and speed of thinking
- disturbances of consciousness and intelligence, changes in behavior
- nerve and muscle disorders
Patients may sleep for days and stay awake all night. Irritability and inability to concentrate turns them off from the normal rhythm of life.
Hepatic encephalopathy is sometimes impossible to determine by yourself, and it is detected by a doctor using special tests. At extreme levels of development, it can cause coma (unconsciousness).
Edema
With cirrhosis, excess salt and water accumulate in the body. At first, only the legs and then the entire abdominal area swell.
Swelling, which often appears in the evening, is called spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Their reason is the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the abdominal part.
This complication is life-threatening, although in half of the cases it occurs without symptoms. The general condition may worsen: fever with chills, abdominal pain, problems with appetite and diarrhea may appear.
Water in the abdominal cavity (ascites)
In later stages, numerous scars and tissue compression lead to a significant accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. The load on the kidneys becomes enormous, which is noticeable by urinary retention and dark, brownish urine.
Dilated saphenous veins
This syndrome is called portal hypertension and is extremely dangerous, leading not only to a specific “pattern” on the chest and abdomen, but to serious bleeding and ascites.
Vomiting blood
As a result of bleeding, vomiting occurs, which looks like coffee grounds mixed with blood. Accompanying symptoms are dizziness, fainting or loss of consciousness. Bleeding may occur around the liver, esophagus, or stomach.
Fever
An increase in temperature and a febrile state in the terminal stage can be caused by two reasons:
- necrosis of liver cells and intoxication (self-poisoning);
- concomitant infection of the biliary tract or enteritis.
In the final stage of cirrhosis, signs of dystrophy develop - weight loss, hypovitaminosis. The liver decreases in size.
.
muzhzdorov.ru
Change in urine color during treatment of cirrhosis
The essence of liver cirrhosis is that healthy cells of the glandular organ are replaced by connective tissue. So first fibrosis occurs - minor changes in the structure - and then it turns into cirrhosis.
The reverse process is not possible. Fibrous tissue grows quickly, it is more voluminous than healthy liver cells, so the organ increases in size.
Treatment of cirrhosis is complex, carried out in several directions:
- Eliminating the root cause of the disease.
- Reduced activity of structural changes in tissue thickness.
- Replenishment of bile acid deficiency in the intestines.
- Taking hepatoprotectors - drugs that stimulate the regeneration of hepatocytes, due to which the healthy part of the organ takes over all its functions.
Already at the initial stage of therapy, the color of urine should change for the better, that is, become standard. Many patients who have undergone organ transplantation panic during the recovery period when the urine again becomes dark and the feces become colorless.
You should definitely inform your doctor about this, but during the recovery period, when the body learns to live with a new organ, such deviations can often occur. Over time, the warning symptoms disappear.
Signs of the disease depending on the stage of its development
The symptomatic picture in children and adults with the development of liver cirrhosis is the same. Its intensity and nature directly depend on the stage of development of the disease.
Stage 1
This stage of liver cirrhosis is asymptomatic. It can only be detected through laboratory blood tests. At this stage, billiard, alcoholic and primary cirrhosis is manifested only by hepatocyte failure. This can be corrected by taking special medications. Doctors call this stage of the disease development compensatory. But unfortunately, it is detected very rarely.
Stage 2
This stage of development of cirrhosis is called subcompensated and is characterized by a significant decrease in liver functionality. The patient experiences changes in his condition. He begins to worry about weakness, nausea, itchy skin, etc. A laboratory blood test reveals a significant decrease in albumin, the prothrombin index is at 40.
Stage 3
At this stage (decompensated) of the development of liver cirrhosis, a critical number of functioning hepatocytes is noted. As a result, renal failure begins to actively progress and an increase in symptoms is observed, which are supplemented by obstructive jaundice and pain. Most often, it is at this stage of cirrhosis that complications begin to develop. Among them is ascites. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity and an increase in the volume of the abdomen. It is also possible to develop hepatic coma, peritonitis and sepsis. Laboratory tests show a critical decrease in albumin levels and prothrombin index.
Stage 4
This stage of liver cirrhosis is called total. With its development, the functionality of the organ is completely disrupted. A person begins to suffer from constant pain, which is not completely eliminated even when taking strong painkillers. The patient's condition becomes critical and requires constant medical supervision.
It is believed that liver cirrhosis is a disease of alcoholics. But this is far from true. Its development can be diagnosed in both an adult and a small child. Yes, with alcoholism, cirrhosis develops much more often, since constant exposure to ethyl alcohol on the body causes the death of liver cells. But besides alcohol, biliary, toxic, viral, portal or any other type of cirrhosis can also be provoked by:
- viral infections (hepatitis A, B, C, chickenpox, whooping cough, chickenpox, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncology;
- chemical and drug poisoning;
- thrombophlebitis;
- heart failure;
- diabetes;
- impaired fat metabolism, etc.
The causes of liver cirrhosis are varied. And to install them, you will need to undergo a thorough diagnosis. As for the treatment of this disease, it is carried out mainly through the use of special medications and diet therapy.
It is difficult to say how long a person can live after being diagnosed with liver cirrhosis, since everything depends on the severity and degree of development of the disease, whether the patient has complications and his age. But as statistics show, the average life expectancy after diagnosis is approximately 5 years, but this is only if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed.
Liver destruction does not manifest itself in the initial stages. A bright pink or red color of the tongue in liver cirrhosis is a characteristic symptom that can signal pathology before irreversible changes occur in the organ. The development and manifestation of other symptoms depends on the underlying factor that caused the cirrhosis.
Urine formation
Blood absorbs useful substances and transports them throughout the body into tissues and structures. This is necessary so that they are nourished and function properly, as well as for the process of formation of new cells.
Those substances that turn out to be superfluous (water, salt, bile) become the main components of urine and safely leave the body.
It is on how correctly the internal mechanisms work that indicators such as the color of urine, its smell, as well as the consistency and volume released depend.
Change in urine color is the first sign of liver problems. The presence of a disease can be eloquently indicated by an unusual color, loss of transparency, a sharp and rather unpleasant odor and foam that suddenly appears.
Sources used:
- https://bolitpechen.ru/diagnostics/po-simptomam/mocha-pri-zabolevaniyah-pecheni
- https://microbiologu.ru/obshee/cvet-mochi-pri-zabolevaniyax-pecheni/
- https://golovaneboli.ru/zheludok/kak-izmenyaetsya-tsvet-mochi-pri-tsirroze-pecheni.html
- https://jeludok.com/pechen/tsvet-mochi-pri-tsirroze-pecheni-foto.html
- https://progepatity.ru/tsirroz/tsvet-mochi-pri-tsirroze-pecheni
- https://kurenie.me/alkogol/tsirroz/mocha-pri-tsirroze-pecheni.html
- https://zdravpechen.ru/diagnostika/tsvet-mochi-pri-tsirroze-pecheni.html
- https://medpechen.ru/cvet-mochi-pri-gepatite.html