Want to create a site? Find Free WordPress Themes and plugins.
Many of our patients are interested in the question: how does hepatitis C manifest in women, are there any gender differences in the symptoms of this disease?
The virus of this dangerous disease spreads only through the blood and has the following routes of entry into the body:
- during a transfusion of contaminated blood,
- sexually
- through medical, cosmetological and other similar instruments that were previously used on an infected person,
- during childbirth from an infected mother to her child.
A woman may not even know that she is infected after visiting a beauty salon, where she received a manicure with tweezers that were poorly cleaned after another client. Therefore, it is important to know what hepatitis C looks like in women and what early signs of the disease you should pay attention to.
Those service areas where there is a violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes should be considered potentially dangerous in terms of HCV infection. These include hairdressers, tattoo parlors, dental offices, etc. A lot of infections with this virus are observed among injection drug users. Statistics confirm that HCV is spreading faster than HIV/AIDS.
At the same time, it is important to know that the infection cannot get through the mother’s milk to the child during breastfeeding, nor can it be transmitted by touch or through the air (like ARVI or influenza).
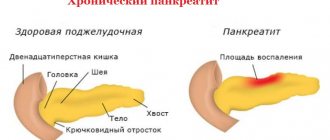
Signs of hepatitis C in women
Once in the body, HCV is carried by the bloodstream to the liver, where it begins its destructive effect on its cells. The acute phase of the disease occurs after an incubation period, which can last up to six months. Symptoms of the active stage of the disease:
- Temperature rises to 38-39 degrees.
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
- The coating on the tongue is white or yellow.
- Headaches and muscle pain.
This picture is more reminiscent of the flu, except that there are no symptoms from the respiratory system. And only if, in addition to the listed signs, there is heaviness on the right under the ribs, should you suspect problems with the liver.
A distinctive feature of hepatitis C in the acute stage is the rare occurrence of jaundice - yellowing of the mucous membranes, eyeballs and skin. And this makes recognizing the disease even more difficult. The active phase of viral hepatitis C usually subsides on its own, very rarely developing into severe forms of liver damage.
The next phase begins - chronic.
Consequences of hepatitis C for women's health
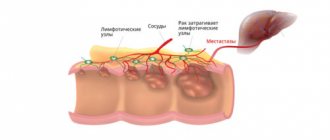
The pathology, in the absence of therapeutic measures, continues to progress. Healthy liver tissue is involved in the inflammatory process, and the functions of the organ are disrupted. Fibrosis develops, in which the cells are replaced by scar tissue. The liver is capable of regenerating, but with fibrosis the process is impossible.
The most dangerous complication is cirrhosis. It develops in the later stages of the disease. The period is individual for each patient. The organ gradually dies and the entire body is affected. A complete cure for cirrhosis is considered possible only by transplanting a healthy donor organ.
Chronic inflammation often provokes pathological changes that cause cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma is a dangerous form of cancer that is difficult to treat. The disease has a high mortality rate.
Common complications include chronic intoxication, liver failure, and coma. Damage to the organ causes pathological enlargement of the spleen, ascites, and blood poisoning. All of these violations pose a threat to the patient’s life.
This is interesting: Hepatitis C: what is it and how is it transmitted?
Chronic hepatitis C in women: treatment, symptoms
HCV is characterized by an unpleasant feature that distinguishes it from hepatitis A and B viruses: 90% of it remains in the human body after the acute phase of the disease and provokes a chronic course. The manifestations of the disease are so similar to a lot of other diseases that a woman does not even think about hepatitis:
- the temperature sometimes rises slightly,
- unstable emotional state,
- headaches and joint pains,
- constant fatigue, drowsiness, poor health,
- causeless weight loss,
- lack of appetite, sleep disturbances,
- weakness, decreased mental performance,
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract,
- feces and urine change color and composition,
- itchy skin, nosebleeds,
- the appearance of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Signs of hepatitis C in women can also manifest themselves in the form of changes in the normal course of menstruation, which become more abundant and last longer.
You should know that with viral hepatitis C, not all symptoms may be present, but even if there are two or three of them, this is a serious reason to suspect something is wrong. Many other diseases give similar symptoms, which confuses both the patient and the doctor, and treatment is not prescribed as needed.
Incubation period
The incubation time - from infection to the first noticeable signs of the disease - proceeds differently for everyone. During this time, the pathogen integrates into liver cells and forces them to reproduce the viral genotype.
This is interesting: Treatment of hepatitis C with generics: effective or not?
The enemy agent multiplies and infects new areas. The body's immune system produces antibodies to fight HCV. The outcome of this struggle depends on several factors:
- Virus genotype. There are 6 types of the virus that appeared as a result of its mutation. In Russia, genotype 1b is common, with a long incubation period and hidden signs of pathology. Genotypes 3, 1a, 2 are less common, but their clinical manifestations are more pronounced. Genotype 3 develops rapidly and is common among drug addicts.
- The immune system. A healthy body and strong immune system can cope with a minor infection during the first 2 weeks without significant signs of illness. Sometimes the struggle takes an acute form - the first signs of the disease become noticeable after 2 months. If the patient seeks help in time, then with proper treatment he gets rid of the problem. With weakened immunity, the incubation period is extended to 6-12 months - without noticeable traces of pathology.
- Lifestyle. Bad habits (especially alcohol, which poisons the liver), physical and nervous overload, and poor nutrition weaken the body's defenses. It gives a weak response to HCV invasion, the incubation period is extended to 3-6 months. The first signs of hepatitis C are manifested by symptoms of concomitant diseases.
The insidiousness of hepatitis C lies in the long incubation period and mild symptoms of the disease.
Diagnostic techniques for detecting HCV
In order not to waste time, if HCV is suspected, it is important to conduct a high-quality and comprehensive diagnosis. This is a blood test that will reveal the level of ESR and leukocytes, the level of liver enzymes (AST and ALT), and bilirubin. It is necessary to conduct a test for antibodies to HCV and a PCR test that detects the RNA of the virus. It is the latter study that will help accurately determine the presence of the hepatitis C virus in the body. The hepatologist may also order liver tissue biopsy, ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging to detect hepatitis C in women.
When do the first signs appear?
The appearance of the first signs of hepatitis C depends on the genotype of the virus and the state of the immune system. In 20% of cases, the body copes with HCV infection during the incubation period and the person does not feel the disease.
At the next preventive examination, he may be informed that antibodies to HCV have been found in the blood, and the body has experience in fighting this pathogen. In other cases, the incubation period lasts from 20 to 140 days. Then the first symptoms of hepatitis appear:
- chronic fatigue not associated with physical and nervous stress;
- prostration;
- difficulty in mental activity, loss of attention.
Typically, patients attribute these signs to flu, stress, etc. In fact, their body has entered the chronic stage of hepatitis C, when the immune system restrains the rapid development of the virus, but cannot get rid of it.
In foci of infection, the liver tissue (parenchyma) becomes scarred - fibrosis develops, and then cirrhosis. There are no nerve endings in this organ, and its degeneration is not accompanied by pain.
The first sign of changes is the slow poisoning of the body, as the liver gradually loses its function of cleansing the blood of poisons. This development of the disease lasts for 15-20 years, it is typical for 80% of cases.
In 5-10% of infected people, symptoms of acute HS appear in the first two months after infection: pain in the right hypochondrium, indigestion, jaundice. Seeing a doctor and timely diagnosis provide a chance for successful treatment.
Who is at risk for HCV infection?
There are several factors that should alert a woman and force her to get tested for HCV if she has symptoms. These risk factors include:
- The fact of blood transfusion in the period before 1995 - before the mandatory testing of donor blood for HCV.
- Work related to blood: medicine, consumer services, etc.
- Having multiple sexual partners.
- Unprotected sex.
- Clients of beauty salons and tattoo parlors - if the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes was damaged during procedures.
- Living with an HCV patient.
What to expect for a patient with chronic HCV
If a patient does not know the signs of hepatitis C in women, does not suspect that she is infected with a dangerous infection and does not receive treatment, the virus does its job in her body with impunity. Each case is individual: you can live a long life and die for a completely different reason, without feeling the consequences of hepatitis C, or you can die from HCV in 4-5 years. Women's bodies usually show a slower progression of the disease than men's.
But in any case, the virus has a destructive effect on the liver and other organs and systems. The immune system suffers, the liver gradually changes its structure and ceases to perform the functions of purifying the blood and producing bile. The degeneration of liver cells into connective tissue - fibrosis - ultimately leads to cirrhosis. Also, HCV is fraught with an even more terrible consequence - the development of liver cancer.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods include:
- Ultrasound of the liver.
- CT or MRI.
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Liver tests.
- Coprogram.
- Clinical urine analysis.
- Blood test for the presence of virus and antibodies.
- Electrocardiogram.
After the test results, a liver tissue biopsy is prescribed.
Diagnostic symptoms:
Thickening and enlargement of the liver, and in advanced cases, the spleen.- Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Protein in urine.
- Increased amount of bilirubin in the blood and aminotransferase enzymes.
- An increase in transaminase values helps determine the stage of the disease. If the indicator is increased by 3 times, a mild course is diagnosed, 3-10 times - moderate severity, more than 10 times - severe.
Hepatitis C in women: treatment with generics is a guarantee of recovery
If a woman is diagnosed with hepatitis C, she should not despair. Modern medicine already has the latest generation of drugs that guarantee at least 95% of complete cure. These are direct-acting antivirals, which include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir, as well as other protease inhibitors. Revolutionary drugs act inside the virus, preventing it from multiplying and leading to death, helping to restore liver cells and destroying the virus in the blood. The advantages of the newest drugs in comparison with the traditional interferon-ribavirin treatment method are enormous:
- high degree of complete cure,
- excellent tolerability by patients,
- very few side effects,
- much shorter course of treatment,
- affordable price.
To defeat hepatitis C in women, contact our company for certified generics made in India. We will deliver the drugs by courier and provide the necessary documents confirming their original origin.
Did you find apk for android? You can find new Free Android Games and apps.
How does the disease manifest itself in acute and chronic forms?
The exact duration of the incubation period of the disease is unknown. It has also not been definitively established how quickly the virus develops after infection. The incubation period of hepatitis C in women averages 1.5–3 months. After this period, blood tests reveal a stable level of antibodies, demonstrating the immune system's response to infection. The first manifestations are possible after 2–3 months, or do not occur at all.
The course of infection is divided into two stages: acute and chronic. The first lasts about 6–8 months, the second - until the pathology is identified and therapy begins (or for life). In approximately 40–55% of patients, the pathology does not manifest itself. In other cases, the symptoms of HCV are nonspecific.
How does hepatitis C manifest in women?
- progressive weakness , which appears with adherence to rest and sleep, as well as with usual physical activity;
- sleep disorders (at night it is difficult for a person to fall asleep, despite fatigue, and during the daytime he is overcome by drowsiness, which is accompanied by apathy and inhibition of concentration);
- psycho-emotional instability (it is assumed that irritability, nervousness, and depression are caused by fatigue and deteriorating health).
As a rule, these symptoms of the disease develop first. A little later, minor digestive disorders appear. To the list of how hepatitis C manifests itself in the early stages, you can also add worsening appetite, unpleasant taste in the mouth, and flatulence.