1190
According to statistics, liver cirrhosis is diagnosed in women three times less often than in men. Typically, the diagnosis is made to patients aged 35-40 to 60 years. The disease does not immediately manifest itself as pain in the hypochondrium, a jaundiced tint of the skin and mucous membranes.
At the initial stage, symptoms of liver cirrhosis in women may be hidden and resemble other pathologies. This makes early diagnosis difficult and entails irreversible changes in the structure of the organ.
About the liver that suffers
This section is devoted to a brief analysis of the structure and function of the liver to make it clear why certain symptoms of liver cirrhosis appear.
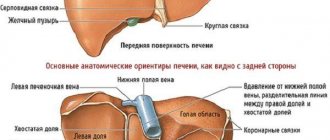
So, the liver is the largest and heaviest organ, located below the right lung, under the diaphragm, covered by the right part of the costal arch. It performs many functions. This:
- cleansing the blood of toxic or unhealthy substances formed by the body itself, directly entering the blood or absorbed into it from the intestines or urinary tract;
- protein synthesis:
- some of which retain the liquid part of the blood in the vessels, preventing it from entering the tissues and causing swelling;
- others are the basis of antibodies, gamma globulins;
- still others provide blood clotting;
- the fourth are the basis of enzymes that provide the main reactions in the body;
- the formation of bile - a stimulator of intestinal motility, a substance that emulsifies fats (breaks them into small droplets) so that they are better broken down by pancreatic enzymes;
- storage of the “energy substrate” – glucose – in the form of glycogen.
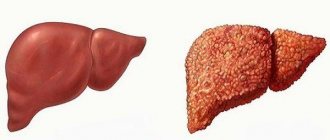
The internal structure of the liver is honeycomb-like lobules with a blood vessel (vein) inside, separated by connective tissue. With cirrhosis, fibrous (coarser connective) tissue appears in place of this lobule, and the “separators” (all or partially) remain in place. These new “lobules” are called “nodes”, which can be large (several lobules, the node is more than 3 mm) or small (connective tissue separates each node, like the previous lobule).
Because dysfunctional tissue appears in place of normal cells, all liver functions are affected. Gradually developed fibrous areas compress the vessels located in the lobules. This leads to increased pressure in the system that drains blood from the liver - portal hypertension. To unload this system, blood begins to bypass the liver (vein connections are provided for this by nature): the veins of the esophagus, stomach and rectum expand. When pressure in the vessels is maintained, these veins lose their tone, becoming varicose, and bleeding periodically develops from them.
Statistics
The highest incidence of cirrhosis is observed in developed countries: 14-30 cases per 100,000 population; Moreover, in the last decade the frequency of occurrence has increased by 12%. This is most often associated with eating habits: the more fried and gourmet foods and alcohol are contained in the diet, the higher the chance of getting sick.
Cirrhosis is one of the six leading causes of death, again, in developed countries: 300 thousand people die from this disease every year. Most often, people aged 35-60 years old suffer from it; men, due to their greater susceptibility to alcoholism, suffer 3 times more often.
Why do people get cirrhosis?
The causes of liver cirrhosis are varied. Let's name them in descending order:
- Frequent alcohol consumption is the cause of 35.5-50% of liver cirrhosis. Alcoholic cirrhosis does not develop immediately, but after 10-20% of years from the beginning of frequent (in some cases, daily) alcoholization, when 80-160 ml of 96% alcohol is regularly consumed. Recent studies say that in the development of cirrhosis, it is not so much the toxicity of ethanol itself that matters, but rather poor nutrition due to the fact that part of the energy requirement is covered by alcohol, but at the same time beneficial amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids and carbohydrates are not supplied.
About 12% of cases of this disease are asymptomatic. This feature is characteristic of cirrhosis in men.
- Chronic (less often acute) inflammation of the liver, that is, hepatitis, often ends in cirrhosis. Hepatitis caused by viruses is most capable of this. The “leader” in this regard is viral hepatitis C - a disease that has practically no special manifestations. Fortunately, it is well treated at the moment.
Cirrhosis can be caused by viral hepatitis B, B+D, which are quite difficult to treat. Hepatitis A, on the contrary, almost never becomes chronic and does not cause cirrhosis.
- Cryptogenic cirrhosis. This is a disease with an unknown cause, when the results of laboratory and instrumental studies do not find a single cause of the disease. This liver cirrhosis is more common in women, about 20-30% of the total incidence.
- Drug-induced hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis. This is an inflammation of the liver that can occur in response to various medications. Particularly toxic to the liver are drugs for tuberculosis, parkinsonism, cancer, drugs of gold, mercury, lead, and some antiseptics (based on dimethyl sulfoxide) with long-term use.
- Previous toxic inflammation of the liver. Thus, the liver is damaged by methyl alcohol, ethylene glycol contained in alcohol substitutes, as well as some poisonous mushrooms. If a person did not die from acute damage to the liver tissue, and after an acute period did not allow the organ to recover (took alcohol, toxic drugs, suffered from viral hepatitis), such a disease can develop into cirrhosis.
- Autoimmune hepatitis. The degeneration of liver tissue into fibrous tissue can be caused by its damage by antibodies - proteins of one’s own immunity, which can consider liver cells to be foreign agents.
- Fatty non-alcoholic hepatitis. This inflammation of the liver, leading to cirrhosis, develops against the background of metabolic disorders, for example, diabetes, galactosemia or obesity.
- Primary cirrhosis or primary biliary cirrhosis. This is an autoimmune inflammation that begins with an attack of one's own antibodies on the bile ducts located inside the liver. Prolonged stagnation of bile in these pathways leads to degeneration of the liver tissue.
- A disease such as primary sclerosing cholangitis, when, usually against the background of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, antibodies arise to the intrahepatic bile ducts, which cease to function, becoming like a glass rod.
- Secondary biliary cirrhosis. This is a condition that develops as a result of a violation of the passage of bile along the biliary (usually intrahepatic) tract. Here, unlike the primary “brother,” there is no autoimmune mechanism. The causes of secondary biliary cirrhosis are:
- stones in the bile ducts;
- compression of the bile ducts by tumors;
- compression of ducts by enlarged lymph nodes in lymphocytic leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis;
- Secondary biliary cirrhosis can occur even in newborns. This is caused by congenital underdevelopment or complete absence of extrahepatic ducts;
- purulent inflammation of the intrahepatic bile ducts;
- narrowing of the bile ducts after surgery on the organs of the hepato-biliary zone;
- extrahepatic bile duct cysts.
- Damage to the liver by worms, for example, echinococci or alveococci.
- Hemochromatosis. This is a disease in which iron is deposited in tissues, including the liver.
- Wilson-Konovalov disease. In this case, due to genetic disorders of enzyme systems, copper is deposited in the brain and liver.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome. This is a blockage of blood flow through the hepatic veins.
- Heart failure, as a result of which the hepatic vessels are always overcrowded, which has a negative effect on the liver.
- Deficiency of the enzyme ɑ1-antitrypsin, resulting from a genetic defect. This leads to the development of bronchitis and cirrhosis.
Brief description of the pathology
Primary cirrhosis of the liver in women develops against the background of progressive autoimmune processes in the body. In the early stages of development, there is no clear clinical picture. The presence of pathology is confirmed by changes in the composition of the blood. As the disease spreads, it covers healthy cells of the organ, provoking their replacement with connective and scar tissue, as can be seen in the photo. This process is accompanied by a loss of liver function.
The pathology is typical for women in the age group of 40-60 years. However, modern medicine more often records cases of early development. Often the first signs of liver cirrhosis in women are observed during pregnancy. This is due to the load placed on the body and its complete restructuring.
Stages of the disease
Histological examination of organ tissue will help determine the stage of the disease. For this purpose, a puncture is performed, during which a small section of the liver is taken. According to ongoing research, the following stages of pathology are distinguished:
- Stage 1 (portal stage). When studying the structure of the liver, necrotic areas, inflamed foci and infiltrates are recorded. There are no stagnant processes, the parenchyma is not involved in the pathological process;
- Stage 2 (periportal stage). The inflammatory process extends deep into the organ, and the bile ducts are affected. Stagnant processes are observed in the organ, signs of progression appear, including swelling of the cytoplasm;
- Stage 3 (septal stage). This stage is characterized by the development of fibrous changes. A thorough examination of the liver reveals connective tissue cords, and the copper level is elevated;
- Stage 4 (cirrhosis). The organ is completely replaced by connective and scar tissue, the functional purpose is reduced to zero. In the absence of supportive therapy, the person dies.
Comprehensive diagnostic measures will help determine the beginnings of cirrhosis in women. Timely examination and diagnosis make it possible to prescribe the optimal treatment regimen. Correct and competent treatment increases the chances of a favorable outcome.
Pregnancy with a severe diagnosis
It is quite possible to conceive a child in the presence of a pathological process. However, before a future pregnancy, it is advisable to consult with your doctor and visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. The pathology does not affect the ability to get pregnant. Difficulties arise during the period of active fetal development.
Before conception, the specialist recommends undergoing a full range of studies aimed at determining the condition of the mother’s body. This measure will allow us to predict possible complications during pregnancy and begin to implement an algorithm of measures to suppress them.
If the disease is detected randomly in pregnant women, this information must be provided to an obstetrician-gynecologist. The specialist must maintain full control over the woman’s condition, select the optimal medications and adjust the treatment regimen. All actions are aimed at ensuring that a woman can give birth to a healthy child without complications . For this purpose it is necessary:
- take a blood test in a timely manner;
- stop taking medications that have a negative effect on the liver;
- adhere to dietary nutrition to reduce the load on the digestive system;
- strengthen the body with vitamin and mineral complexes.
The development of pregnancy with liver cirrhosis is possible, the main thing is not to self-medicate
The development of pregnancy with cirrhosis of the liver is possible, the main thing is not to self-medicate. Consultation with a doctor will help you choose the optimal treatment regimen and increase the likelihood of a favorable outcome. The most positive prognosis is observed in the early stages of the disease. There is a risk of complications during pregnancy with twins.
Attention: the course of pregnancy in the presence of abnormalities in the liver is a purely individual process. Its favorability is influenced by many factors. To avoid serious complications, experts recommend promptly notifying your doctor about the problem. Especially if a woman wants to give birth on her own (without a planned cesarean section) or there are twins in her womb.
How does cirrhosis manifest?
Signs of liver cirrhosis do not appear in all patients; 12-20% of them have an asymptomatic course of the disease until the stage when icteric discoloration of the skin and ascites occur - an enlargement of the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid in it.
The first signs of pathology are:
- Feeling of fullness in the abdomen. At the same time, products that reduce gas formation improve well-being.
- Decreased performance.
- After drinking alcohol, breaking a diet, or lifting heavy weights, pain appears in the right hypochondrium. It is caused by increased blood supply and stretching of the liver capsule. This pain goes away on its own; drugs like No-shpa, Drotaverine, Spazmalgon do not help.
- A person quickly gets full: after small portions of food there is a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
- Body temperature periodically rises to low levels.
- When brushing your teeth, your gums bleed.
- Periodically, for no apparent reason and with normal pressure, nosebleeds are observed. This is due to increased pressure in the portal veins and decreased blood clotting
The disease then develops in one of three ways:
| Flow options | Option where symptoms of increased pressure in the vein system supplying the liver predominate | An option in which the growing nodes primarily compress the bile ducts | Mixed option |
| Symptoms of liver cirrhosis | Initially, you are worried about flatulence, nausea, and vomiting. A person gets tired quickly, his mood is changeable, he is prone to whims. Frequent nosebleeds appear. The period of ascites in cirrhosis. Initially, pain appears in one place of the abdomen, then in another. Afterwards, severe weakness occurs and periodic vomiting occurs. Pain in the right hypochondrium, periodically in the left hypochondrium (enlarged spleen). The abdomen enlarges and cannot be pulled in. Dilated veins are visible on its front wall. After 6-24 months, a cachectic period (exhaustion) develops. Weight drops sharply, the skin becomes pale and flabby. Periods of weakness, during which low blood pressure is detected, periodically - vomiting brown contents or black loose stools (gastrointestinal bleeding). Death occurs from hepatic coma or the addition of infectious diseases. The entry of bacteria into ascitic fluid - ascites-peritonitis - if it does not end in death, it greatly shortens life | The first significant symptoms are:
Symptoms appear slowly, gradually. Later other signs are added:
Death occurs from bleeding | Signs of increased pressure in the portal vein appear and quickly progress: pain in the right hypochondrium, bleeding gums, bleeding from the hemorrhoidal veins and nose. Against this background, jaundice, itching, yellow spots on the eyelids (xanthelasmas), and thinning of the skin develop. The above symptoms go along with stool disorders, abdominal pain, nausea, belching, mood changes, and vomiting. Sensitivity - temperature, pain, tactile - is impaired in the arms and legs. In the final stage, hepatic encephalopathy develops. This is a euphoric mood followed by depression, personality changes, sleep disturbances, slurred speech, disorientation. The kidneys also suffer, which is manifested by swelling of the face, lack of appetite, decreased amount of urine, and pale skin. |
| As a result of what diseases | Budd-Chiari syndrome, after hepatitis, as a result of heart failure, with hemochromatosis | Biliary cirrhosis – primary and secondary, sclerosing cholangitis | Alcoholic cirrhosis, may be posthepatitis cirrhosis |
There are the following stages of liver cirrhosis:
- Compensatory. There are no symptoms yet, although some of the cells have already died, but the remaining cells are working in an enhanced mode.
- Subcompensatory. At this stage, the first signs of the disease appear: weakness, a feeling of bloating, pain in the right hypochondrium, loss of appetite. “Mesh” appears on the skin; hair falls out.
- The last stage of liver cirrhosis is decompensation. Ascites, jaundice, bleeding, atrophy of the muscles of the limbs and upper shoulder girdle, and hypothermia appear here.
Patients with cirrhosis at this stage have a characteristic appearance:
- pale yellow loose skin;
- with combs;
- yellow eyes;
- red and purple “spiders” of blood vessels are visible on the skin of the face and body;
- thin and thin arms and legs;
- bruises on arms and legs;
- large belly with a protruding navel;
- on the stomach - a network of dilated veins;
- red palms with reddened and thickened terminal phalanges, dull nails;
- swelling in the legs;
- enlarged breasts, small testicles in men.
Pregnancy and liver cirrhosis
To bear a child, you need good hormonal levels in the female body; without good standard indicators, it is not possible to bear a full-fledged child. Unfortunately, many women who are at risk for liver cirrhosis, having become pregnant at an early, asymptomatic stage, refuse to terminate the pregnancy and decide to continue, despite the complexity of the disease and its possible complications.
In such cases, the treating gynecologist, obstetrician-gynecologist warns the expectant mother about all possible negative consequences for the development of the fetus, various possible pathologies, not only for the unborn child, but also for the mother herself. A normal course of pregnancy, unfortunately, is not always possible, since the disease is complex requires the use of toxic medications to maintain and save the mother’s body, but against this background, the health of the unborn baby is at risk, various congenital pathologies and complications from the woman’s health in the future are possible.
Complications of cirrhosis
Complications of cirrhosis are:
- Ascites: an enlarged abdomen, which practically does not disappear when lying down, looks tense, and when pressing on the abdomen, the volume shifts to the side.
- Portal hypertension. We described its symptoms above.
- Acute liver failure develops with rapid progression of cirrhosis. In this case, the disturbance of consciousness quickly progresses, the skin becomes yellow, nausea and vomiting appear, bleeding develops - internal, gastrointestinal, uterine, hemorrhoidal.
- Chronic liver failure. Personality changes gradually develop, sleep suffers, jaundice increases, and ascites develops.
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. This is a complication of ascites when intra-abdominal fluid becomes infected with bacteria contained in the intestines due to permeability of the intestinal wall. The disease is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the condition, an increase in temperature to high levels, difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Hepatorenal syndrome. This is the name for kidney damage that occurs against the background of portal hypertension. Symptoms: decreased amount of urine, increased weakness, nausea.
- Liver cancer. Its symptoms differ little from those of cirrhosis itself.
Symptoms in advanced stages of the disease
The advanced disease is characterized by a large belly that bulges out unhealthily, popularly called dropsy.
Such large sizes do not arise from obesity, so dieting will not help reduce it. Fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, so it expands and can reach terrifying sizes. Secondary symptoms do not disappear and become progressive. All this suggests that the liver is completely damaged, and if you do not immediately take care of your health, death is possible. In addition to severe swelling of the abdomen, the limbs also begin to swell. This brings discomfort during sleep. Vomiting with blood cells, frequent loss of consciousness, muscle cramps, and increased dizziness may occur. If hepatic encephalopathy occurs, it can lead to damage to the brain, where its basic functions are severely impaired. Coma and death follow.
In order not to bring the disease to the final stage, it is worth undergoing medical examinations on time, doing blood tests and monitoring your well-being. Early detection of the disease makes it possible to cure it without consequences or relapses.
How is the diagnosis made?
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis consists of several stages. The diagnosis itself is made using instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound as a screening method. It “allows” only to make a preliminary diagnosis, but is indispensable for diagnosing portal hypertension and ascites;
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging. These are more accurate methods than the first;
- Biopsy. This method allows you to determine the type of cirrhosis - small or large nodular, as well as the cause of the disease;
After diagnosis, if the cause is not found based on the results of histological examination, the search for it continues. To do this, blood is examined for:
- Hepatitis B virus DNA and hepatitis C virus RNA by PCR method;
- antimitochondrial antibodies;
- cerruloplasmin and copper levels;
- alpha-fetoprotein – to exclude blood cancer;
- level of T-lymphocytes, immunoglobulins G and A.
The next stage is to determine how much the body has suffered from liver damage. To do this:
- Liver scintigraphy. This is a radionuclide test that allows you to see which liver cells are still working.
- Biochemical blood test for tests such as proteinogram, lipidogram, ALT, AST, bilirubin - total and one of the fractions, alkaline phosphatase, cholesterol, coagulogram, potassium and sodium levels.
- The degree of kidney damage is urea, creatinine.
Presence or absence of complications:
- Ultrasound is suitable for excluding ascites;
- varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach are excluded by FEGDS;
- varicose veins of the rectum require examination by sigmoidoscopy;
- Hidden, invisible bleeding from the digestive tract is excluded by analyzing stool for occult blood.
What type of liver does it have with cirrhosis? It can be felt through the anterior wall of the abdomen. The doctor feels that it is dense and lumpy. But this is only in the stage of decompensation.
Ultrasound shows foci of fibrosis (“nodules”) inside this organ: less than 3 mm are small nodes, more than 3 mm are large. Thus, with alcoholic cirrhosis, small nodes first develop, and a biopsy reveals fatty hepatosis and specific changes in the liver cells. In the later stages, the nodes become large and mixed, fatty hepatosis gradually disappears. In primary biliary cirrhosis, the liver is enlarged, and unchanged biliary tract is detected. Secondary biliary cirrhosis is the cause of liver enlargement and the presence of obstructions in the bile ducts.
Treatment of the disease
How to treat cirrhosis of the liver. To do this you need:
- eliminate the cause of the disease;
- stop the progression of liver tissue degeneration into fibrous nodes;
- compensate for any violations that have occurred;
- reduce the load on the veins of the portal system;
- cure complications and prevent the development of further problems.
Eliminating the causes of illness
This treatment depends on the causes of liver cirrhosis:
- In case of alcoholic cirrhosis, eliminate the intake of alcohol into the body.
- For viral hepatitis, special antiviral agents are prescribed: pegylated interferons, ribonuclease, and so on.
- Autoimmune hepatitis is treated with drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Cirrhosis resulting from fatty hepatitis is treated with a low-lipid diet.
- Biliary cirrhosis is treated by eliminating the narrowing of the bile ducts.
Creating conditions for liver restoration
Immediately after diagnosis, while the person is being examined for the cause of the disease, he is prescribed a diet for cirrhosis:
| General rules | Can | It is forbidden |
| Protein: 1-1.5 g/kg body weight. They are canceled at the terminal stage, when consciousness is impaired; Fats – 80-90 g/day (1:1 animal and protein origin); Carbohydrates – 400-500 g/day. Number of meals: 5-6 per day, in small portions |
|
For ascites, exclude juice |
Lifestyle with cirrhosis is also adjusted:
- Do not lift heavy objects, as this can cause gastrointestinal bleeding;
- rest more;
- measure abdominal volume and weight daily: an increase in both indicates fluid retention;
- Be sure to consider the ratio of fluid intake (not just water) and urine excreted. There should be a little less of the latter;
- with the development of ascites, it is necessary to reduce the volume of fluid taken to 1-1.5 l;
- control changes in your handwriting: for example, write a short phrase every day, putting the date in your notebook.
Drug therapy
In case of cirrhosis, each drug is prescribed with reason, because the liver is damaged, and an extra load of drugs is not beneficial for it. But you can’t do without these medications:
- Duphalac, Normaze or Prelaxan. These lactulose preparations bind amino acids that are toxic to the brain and cause encephalopathy.
- Hepatoprotectors are drugs that improve the functioning of liver cells: Heptral, Ornitox, Ursohol.
- Diuretics - to remove excess fluid from tissue. For cirrhosis, the drug Veroshpiron works well in small doses.
- In some cases, with ascites, it makes sense to take antibiotics that cleanse the intestines: Kanamycin, Ampicillin. This is the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
- To reduce pressure in the portal vein, Molsidomine and beta blockers: Propranolol, Atenolol are effective. In this case, blood pressure control is necessary.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative treatment for liver cirrhosis offers the following recipes:
- Mix 10 g, 20 g of wheatgrass rhizomes, 20 g of rose hips. 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of water into the mixture and cook for 10 minutes. Then cool the broth, take 1 tbsp. twice a day.
- Take 3 tbsp. washed oats, birch buds, 2 tbsp. crushed lingonberry leaves, pour 4 liters, leave for 1 day in a cool place. Separately make a rosehip decoction. After a day, mix both decoctions and add 2 tbsp. corn silk and knotweed. Boil the entire infusion for 15 minutes, strain, and store in the refrigerator.
- You need 3 heads of garlic, 4 lemons, 200 g of olive oil, a kilogram of honey. Cut the peel off the lemons, remove the seeds, grind the lemons and garlic in a meat grinder, combine with butter and honey. Mix the mixture, put it in the refrigerator for a day and then store it there. Take a teaspoon 30 minutes before meals three times a day. You need to eat everything, then repeat this manipulation three times a year.
Disease prognosis
Cirrhosis of the liver is incurable unless a liver transplant is performed. With the help of the above drugs you can only maintain a more or less decent quality of life.
How long people live with cirrhosis of the liver depends on the cause of the disease, the stage at which it was discovered and the complications that had developed at the time of treatment:
- with the development of ascites they live 3-5 years;
- if gastrointestinal bleeding develops for the first time, from 1/3 to half of people will survive it;
- if hepatic coma develops, this means almost 100% mortality.
There is also a scale that allows you to predict life expectancy. It takes into account test results and the degree of encephalopathy:
| Parameter | Points | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Ascites | No | The abdomen is soft, goes away under the influence of diuretics | The abdomen is tense, its volume does not decrease well when taking diuretics |
| Changes in personality, memory, sleepiness | No | Mild degree | Strongly expressed |
| Total bilirubin | Less than 34 µmol/l | 31-51 µmol/l | More than 51 µmol/l |
| Albumen | 3.5 g/l or more | 2.8-3.5 g/l | Less than 2.8 g/l |
| Prothrombin index | More than 60% | 40-60% | Less than 40% |
| Sum of points | 5-6 | 7-9 | 10-15 |
| How long do they live? | 15-20 years | It is necessary to transplant the liver, but postoperative mortality is 30% | 1-3 years. If a transplant is performed at this stage, the probability of dying after the operation is 82 out of 100 |
Author:
Krivega Maria Salavatovna resuscitator
Prevention
Cirrhosis can be avoided by any woman if you use a few simple rules. Among them are:
- Timely treatment of hepatitis and vaccination against the virus.
- Refusal to self-administer therapy using medications and other drugs.
- Maintaining proper nutrition.
- Constant use of vitamins and minerals.
- Quitting bad habits, especially alcohol.
- Annual diagnosis of the liver and the whole body.
- Maintaining hygiene.
Cirrhosis of the liver in women or men is a serious disease that is fatal even with treatment.
According to statistics, people with stage 3 cirrhosis cannot live more than a year, and at the last stage, the life period is measured in months.