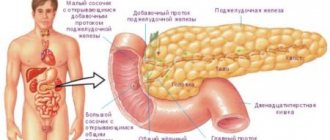
Diagnostics
As practical activity demonstrates, calcifications form in liver tissues over many years. They are easier to see with a CT scan. This diagnostic method makes it possible to obtain more accurate three-dimensional visualization. Examination methods also include:
- X-ray examination allows you to see the liver, large vessels with calcifications. The advantages of the method are speed, affordable cost and low radiation exposure.
- Ultrasound examination is used to exclude other liver pathologies. In this way, it is possible to establish the presence of solid structures in large quantities.
Consequences of calcification
As mentioned earlier, liver calcifications do not cause symptoms or are accompanied by mild symptoms. Because of this, the patient does not know for a long time that he has health problems. However, with pathology, the likelihood of cancer (carcinoma, etc.) increases.
Against the background of calcification, liver dysfunction occurs. But this organ is responsible for pumping and filtering blood. Due to disruption of the gland, other organs also suffer, and as a result, the general condition of a person worsens.
Therefore, it is so important not to miss routine examinations and be attentive to your health.
Calcifications in the liver: causes and symptoms of calcification in the left and right lobes, methods of treatment
These formations are small areas filled with deposits of calcium salts. In order for calcifications to form in the liver, the reasons must be very serious. In particular, this can be triggered by the following influences:
- pathological neoplasms;
- infestations of helminths and protozoa;
- infectious diseases;
- mechanical trauma.
If we turn to the mechanism of formation, most scientists believe that calcification of the left lobe of the liver, as well as the right, is formed as a result of the destruction of liver tissue, as well as against the background of calcium metabolism disorders in the human body. There is another opinion, according to which these deposits are one of the ways to protect the body from further growth of the focus of pathological changes, inflammation or necrosis. However, in both cases, calcification in the liver is not an independent disease, but only a consequence of a previous pathological process.
They are classified by number, size and shape. In particular, the following types are distinguished:
- small;
- large;
- linear;
- single;
- multiple.
A focus of lime deposits can form anywhere in the liver parenchyma, even involving blood vessels and bile ducts.
Such a formation as a single liver calcification most often forms against the background of helminth infections, for example echinococcosis. This is due to the rarity of massive infestation of the organ with large parasites. Although the liver is an ideal nutrient medium for them, the complex breeding cycle of helminths and the high level of hygiene of the population prevent them from entering the human body in large quantities.
Most often, a person does not notice the presence of the parasite for a long time, because the liver compensates for the work of hepatocytes destroyed by it, and the symptoms of general intoxication, as a rule, are attributed to other pathological processes. During this time, a single focus of calcification has already formed at the location of the helminth. It most often does not cause noticeable inconvenience to its wearer.
Typically, such calcification in the liver is detected on an ultrasound scan prescribed for other reasons.
There is no such diagnosis as liver calcifications, and therefore there is no code corresponding to this symptom in ICD 10. A gastroenterologist will advise you on how to treat a single calcification in the liver with medication.
Multiple lesions
If there is more than one calcification, the patient’s situation worsens. What this means for the body is not difficult to understand. After all, more hepatocytes fall out of work than with a single lesion. In addition, they can infringe on blood vessels and bile ducts, disrupting liver function, even leading to the appearance of areas of inflammation and necrosis. The formation of a large number of foci of calcification occurs in response to serious pathologies:
- viral inflammation of the liver (hepatitis);
- abdominal tuberculosis affecting the liver;
- parasitic diseases caused by protozoa (amoebiasis);
- metastatic calcinosis (disorder of hormonal control of calcium metabolism);
- metabolic calcinosis (a disorder of the buffer systems that retain calcium ions within the bloodstream and in the cellular fluid).
The best answer to the question about multiple calcifications, what they are and how to treat them, would be advice to look for the disease that led to their formation.
By the term calcifications, doctors understand calcareous deposits that gradually accumulate and group in the liver tissues, often as a consequence of an inflammatory process.
They gradually take the place of dead cells, increasingly covering the parenchyma.
Their main danger is that they constantly damage adjacent healthy tissues of the organ, thereby provoking a further increase in the source of inflammation.
Liver calcification develops for several reasons:
- disturbances in the process of metabolism in the body;
- presence of parasites;
- the presence of infectious diseases (malaria, hepatitis, tuberculosis);
- inflammatory pathological processes;
- oncology.
In this video, experts will talk about the signs of liver damage.
Mineral-calcium deposits can be multiple or single and vary in size and shape. In addition, there are metabolic deposits that accumulate in the liver tissue, since they do not have the opportunity to linger in the blood, and metastatic deposits - those that arise as a result of the inflammatory process.
In medical practice, the following classification of calcifications is accepted:
- by deposit size: small (up to 1 mm in diameter) and large (more than 1 mm);
- by type and number of formations: linear, multiple or single.
Pathological processes can develop throughout the entire cavity of the organ, but most often the right lobe of the liver suffers. In addition, mineral deposits can also occur in adjacent organs, such as the spleen. The severity of calcification is determined by the stage of the pathological process that caused the deposits to appear.
Clinical picture
The liver parenchyma does not contain nerve endings, so the development of calcification occurs almost unnoticed by the sick person. More or less noticeable pain begins to occur much later, at that stage of the pathology, when formations gradually begin to affect the blood vessels or lead to enlargement of the liver, deforming the outer shell of the organ.
The first signs of the disease can be noticed in the acute stage:
- weak nagging pain in the right hypochondrium;
- deterioration or complete loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- lethargy, lethargy, weakness;
- bowel disorders (constipation or, conversely, diarrhea);
- nausea, vomiting, frequent belching, heartburn;
- bitter taste in the mouth.
If treatment is not carried out and the pathology has spread to most of the parenchyma, the consequences may become irreversible. At this stage, the characteristic symptoms are hepatic coma and varicose veins, mainly in the abdominal area.
If you focus on the characteristic symptoms, it is almost impossible to detect calcification at the onset of the disease. The presence of deposits does not yet affect the patient’s condition in any way, so he is in no hurry to see a doctor. At this stage, the disease can only be detected by chance, during routine or preventive examinations.
Diagnosis of calcification consists of the following measures:
- blood test (general and biochemistry);
- Analysis of urine;
- determining the level of endocrine hormones in the patient’s blood;
- instrumental diagnostic methods (MRI, ultrasound).
The disease can be diagnosed by indirect signs and symptoms indicating the presence of pathology.
For example, if a patient has a parasitic infection or is diagnosed with tuberculosis, this is a direct indication for ultrasound examinations to detect liver calcification.
This procedure allows you to find and estimate the number of capsules with pathogenic limestone formations. At the same time, it is necessary to do a biochemical blood test - this way you can determine the level of calcium.
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor can assess not only the presence, size and quantity of calcifications, but also determine the nature of the original problem that caused the development of the disease. In addition, during the examination, additional lesions of the liver parenchyma caused by calcifications become noticeable.
In most cases, the presence of salt deposits in the liver cavity is not a direct indication for emergency treatment. The patient is prescribed a number of supportive treatment measures - taking hepatoprotectors and a balanced diet.
Emergency treatment is not required only in situations where the area of liver damage does not increase.
Even with a minimal degree of manifestation of the disease, it is extremely important to seek help from a specialized doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-prescribe certain medications.
If calcification is caused by a viral infection, a course of antiviral therapy should be administered to stop the spread of the pathological process. If the underlying disease is hepatitis or tuberculosis, the patient needs especially careful and attentive treatment.
Along with the treatment of the disease that caused calcification, the patient is prescribed additional medications:
- a course of droppers of the drug "Reosorbilact";
- Ringer's solution;
- glucose;
- "Ursosan" or its analogues, which help remove salts from the body.
In the treatment of diseases affecting the liver, Hofitol is often used. This drug has a pronounced choleretic effect and improves organ function.
For therapy to be as successful as possible, it is necessary to minimize the intake of drugs and products that have a negative effect on the liver (for example, alcohol).
Considering the characteristics of the disease, taking medications with calcium during treatment is strictly contraindicated: “Nycomed”, “Kalcemin”, etc.
Phytotherapy
This method of treatment will not relieve the patient of calcifications, but will improve his general condition and alleviate the course of the disease. It is useful to eat slightly dried pumpkin seeds with green skin; you can also eat pumpkin pulp.
Garlic will help improve liver function. Take 2 peeled slices, cut them into slices and fill with warm water (200 ml). The infusion is left overnight, filtered in the morning and drunk on an empty stomach. The procedure should be repeated twice a day for 14 days.
Milk thistle has also proven itself well. It should be consumed daily before meals, after grinding it to a powder state.
In newborns, calcification is extremely rare and indicates the presence of concomitant heart diseases. Individual isolated deposits of calcium salts, even if there are quite a lot of them, rarely pose a danger to the life and development of the child. Such babies need constant monitoring by doctors in order to notice negative dynamics in time.
The presence of calcifications in the liver may not bother the patient at all. Many people live with this diagnosis their entire lives without even knowing it is there.
Diagnostic measures
It is almost impossible to detect calcification, especially in the initial stages, if symptomatic manifestations are taken as the basis for diagnosis. Since calcifications do not cause any inconvenience during this period, the patient does not consult a doctor. Mostly, the disease is detected by chance, during a preventive medical examination.
Diagnostic studies include the following activities:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- urine tests: general, UIA, according to Nechiporenko;
- tests for the level of endocrine hormones;
- instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, MRI, radiography).
This disease is diagnosed more often in the later stages or by chance, in the presence of indirect suspicions of the presence of pathology. Thus, parasitic infestations and tuberculosis are direct indications for ultrasound examination of the liver.
It is prescribed for the purpose of searching for lime capsules that isolate pathogenic formations. A biochemical blood test with a mandatory calcium level test also helps determine pathology in the early stages.
During instrumental studies, the amount, type and size of salt deposits are identified. Diagnostics also shows the underlying process that caused tissue calcification and associated damage to the parenchyma, which is possible if there are hard deposits in it.
Features of calcification in the fetus and newborn
After the 20th week of intrauterine development, ultrasound diagnostics in the fetus can reveal subcapsular hyperechoic inclusions in the liver up to 0.3 mm. These are calcifications formed as a result of an inflammatory process that occurred in the abdominal cavity of the fetus. Such deposits are diagnosed both in the prenatal period and immediately after childbirth.
Deposits form not only in the liver (especially in the right lobe), but also in the spleen of a newborn baby. Isolated deposits, even in large quantities, do not pose a threat to the development of the child.
Only those microcalcifications that form during meconium peritonitis are dangerous. They affect metabolic metabolism and the formation of immunity. Such a child may be born prematurely or with significant underweight.
Treatment of calcifications in the fetal liver is not required. If indicated, it begins after the birth of the child.
Traditional treatment
If there are protracted diseases of the organ, it is recommended to carry out a course of treatment until complete recovery. When the test results are negative and the liver is functioning normally, no therapy will be needed. If in prison there are chronic diseases of the liver and gall bladder, you should be regularly observed in the clinic and get tested. Should be considered:
- When curing calcifications, it should be taken into account that they are considered only the result of another disease. Therapy is based on eliminating the main causative agent of the disease. For example, when a disease occurs after hepatitis, you should take antiviral substances and medications to improve liver function and immunity. After such a complex, the destruction of salts begins.
- When the kidneys are affected together with the liver, it is rational to implement a method other than renal blood purification. Surgical intervention aimed at eliminating areas of salt deposits is not rational, since this process will only lead to injury to the organ, which can cause more significant consequences. Sometimes calcifications are simply considered to be old formations from treated diseases. If there are no symptoms, no therapy is carried out.
To prevent the accumulation of calcium salts in the liver, preventive measures must be taken. A diet containing cereals is recommended. It is recommended to drink as much liquid as possible daily to remove harmful elements.
How to avoid the problem: prevention methods
The main way to prevent the formation of calcium salt deposits is to prevent the development of diseases that provoke calcification.
If a patient has calcium deposits in the liver, he needs to change his diet and lifestyle to avoid complications. The following recommendations should be followed:
- Avoid alcohol.
- Reduce your intake of animal fat.
- Eat as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible.
- Steam or boil food.
- Replace confectionery products with honey, nuts and dried fruits.
Since calcinosis often occurs against the background of helminthic infestation, preventive measures should be instilled in every child. You should wash your hands often, especially after handling animals. Do not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits. Avoid contact with people with hepatitis, use the services of medical clinics and beauty salons with a good reputation, give up promiscuity, strengthen your immune system and avoid stress.
Calcinosis is a pathological condition due to which calcium salts are deposited in the human liver. Formations can be systemic, metastatic and metabolic, rarely form, and are difficult to treat with medication.
Calcifications in the liver are often diagnosed accidentally during a routine examination of the patient. Salt formations are deposited gradually, without causing significant discomfort. As it increases, symptoms appear and the functionality of the gland is impaired.
The reasons for the development and provoking factors of calcifications in the liver, what it is, how diagnostics are carried out - in detail in the article.
How does it appear on ultrasound?
Although ultrasound is less suitable for detecting foci of calcification than MRI or X-ray, calcification in the liver can still be detected on ultrasound in a man or woman. On screen, it appears as a rock-like hyperechoic structure with an acoustic shadow behind it, as it is similar in consistency to bone. Ultrasound is often prescribed not for the purpose of diagnosing calcification, but to exclude other diseases.
Calcification in the liver on ultrasound
How to identify a violation
Calcium salts can accumulate in the gland for a long time after an inflammatory process, parasitic invasion or mechanical trauma, while the clinical picture is completely absent or mild, so calcifications are often detected during a routine examination.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see a three-dimensional image of the stone. X-ray examination also makes it possible to detect deposits. In the photograph, the calculus appears as a high-density formation. Ultrasound examination can detect compactions in the liver.
Calcifications appear as multiple or single dense formations, behind which there is an acoustic shadow. Computed tomography determines the exact position and size of the deposit. As an addition to instrumental research, a biochemical blood test can be used. It makes it possible to monitor the level of calcium in the blood.
Traditional treatment
Calcifications in the liver can cause serious complications. To avoid them, use herbal treatment, which consists of the following options:
- Honey based recipes. Mix 1 kilogram of product with 1 kilogram of currants. Use daily, half an hour before meals, in a teaspoonful dosage.
- For the purpose of prevention, on an empty stomach in the morning you need to consume 30 g of honey with the addition of royal jelly, and in the afternoon, a tablespoon of honey plus a teaspoon of pollen.
- You can mix a tablespoon of honey with apple juice and consume it in the morning/evening.
- Squeezed cabbage juice. In order to prevent most diseases of the liver, stomach, and intestinal tract, it is necessary to drink vegetable juice at a dosage of 120 ml per day.
- Lingonberry leaves. Pour 10 g of leaves into 200 g of boiled liquid, put on low heat and boil for a few more minutes. Then you need to strain the resulting tincture from the leaves and use it up to 3 times a day.
Eat more natural fruits, beef and fermented milk drinks. Avoid smoking, alcohol and coffee. Sports exercises also have a beneficial effect on the body's condition.
Any liver failure can provoke disruption of the functioning of the general organ system. You can find out a few more alternative treatment options for this disease by watching this video.
Is it worth treating liver calcifications?
To minimize the harmful effects of calcifications on the liver, you should understand what it is: prescribing treatment after a correct diagnosis is not difficult. These formations are always secondary and can only be overcome by overcoming the underlying disease.
The fight against calcifications includes drip administration of solutions of glucose, Ringer, rheosorbilact. If there are foci of lime deposits on the kidneys, hemodialysis is prescribed.
Surgical removal of calcifications in most cases is not practiced due to the fact that the harm caused to surrounding healthy tissues outweighs the benefits of such surgical intervention.
After treatment, you will have to adhere to certain dietary restrictions for the rest of your life:
- When cooking, minimize the use of fats;
- reduce consumption of table salt, fried, spicy and fatty foods;
- take protein in the form of fish dishes and fermented milk products;
- eat more seasonal homemade fruits, herbs, and vegetables;
- drinking - up to 2 liters per day, provided the kidneys are healthy;
- only natural sweets - dried fruits, honey;
- giving up alcohol and tobacco.
Answering the question about what calcification of the left or right lobe of the liver is for the human body, an experienced doctor will call such a pathology a marker of the presence of serious problems in the body. Whether they are a thing of the past or still threaten human health will be revealed by a more thorough examination.
It is necessary to adhere to a healthy diet
Folk remedies
The advice of healers comes down to three main points:
- eat more pumpkin seeds and pulp to expel worms from the body;
- drink plenty of clean water to remove toxins and excess salts;
- eat well-cooked fish and meat in order to destroy parasites in them.
Since treatment with folk remedies is always a complex undertaking, it is recommended to use turmeric and milk thistle to maintain the overall performance of the liver.
You cannot treat calcifications on your own. Their detection is a reason for a comprehensive diagnosis. It is very important to find the root cause that triggered their appearance.
Chronic diseases of the liver and gall bladder in combination with mineral accumulations cannot be ignored. In this case, the doctor will recommend taking another course of maintenance therapy to stabilize the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to undergo biochemical blood tests periodically. Do not forget that calcifications can form in tumors, so you need to make sure that there is no malignant process.
Calcifications are not treated if:
- the liver is working normally;
- and the results of other diagnostic tests are negative.
The patient should undergo an ultrasound scan every 3 months to monitor the size of the liver itself and mineral accumulations. The growth of calcifications and their entry into the hepatic ducts is dangerous. Any deterioration in health, digestive disorders, pain or discomfort in the right hypochondrium is a reason for an urgent visit to the doctor. Delayed medical treatment can cause serious liver damage.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of calcifications in the liver, first of all, you need to pay attention to your diet. It is recommended to minimize the consumption of fatty, fried, spicy foods, baked goods, sweets, and salt. Coffee and alcohol-containing drinks are prohibited. You need to eat more:
- fruit;
- vegetables;
- greenery;
- dietary meat;
- seafood.
Eating honey, raisins, nuts, and dates will be beneficial. Dishes must be steamed, boiled or baked.
Particular attention should be paid to the drinking regime - the daily water intake should be at least two liters. Compliance with this condition will help remove toxic substances and waste from the body that cause liver diseases.
Alternative medicine methods also have a positive effect on the functioning of the liver; they improve its functional ability and also eliminate pain. For example, pumpkin seeds help prevent infection by parasites, resulting in a reduced risk of calcifications. Infusions of medicinal herbs (milk thistle) in combination with honey improve the function and condition of the liver. Such measures can be used as adjuvant therapy.
What is the danger?
If the pathological process that caused the appearance of foci of calcification in the liver still occurs in the body, then delay in seeking medical help will lead to an increase in the amount of calcifications and a further worsening of the condition. Therefore, you need to be examined immediately, treat the underlying disease and, after recovery, undergo a quarterly liver ultrasound.
Calcifications themselves do not pose a danger, except when they are located near the blood and bile ducts.
Factors in the development of calcinosis
Liver calcifications can appear as a result of various pathologies. Salt deposits in the tissues of the gland parenchyma occur against the background of long-term and severe inflammatory processes. Inflammation is caused by any disease.
- Metabolic disorders (including calcium metabolism disorders).
- Invasive diseases (diseases that are caused by helminths and arthropods).
- Inflammatory liver damage, which is provoked by various pathogens.
- Viral hepatitis with acute or chronic course and its long-term therapy.
- Complication of tuberculosis.
- Replacement of hepatocytes with calcium.
Even minor inflammatory reactions increase the likelihood of salt deposits forming. Quite often, calcinosis occurs against the background of parasitic diseases (malaria, amoebiasis, echinococcosis, etc.). The patient may not be aware of the presence of parasites in the body for a long time. They often settle in the liver tissue, since this organ provides an excellent environment for their reproduction.
The tuberculosis bacteria penetrates the liver tissue through the blood and lymphatic vessels. Sometimes the bile ducts are damaged. With tuberculosis, the liver is covered with multiple microcalcifications, and the tissues of the organ gradually decompose.
After hepatitis, calcium salts are most often deposited in the liver. Sometimes formations appear in gland tumors. Most often, pathology indicates metabolic disorders and calcium metabolism disorders.
The body reacts to a pathological process with calcification. Thus, it seems to seal the problem area so that it does not spread further. Due to the accumulation of calcium salts, hepatocytes or cells of another organ are damaged, their scarring begins, and a salt plaque forms in necrotic areas. It is this formation that prevents the spread of the inflammatory process beyond the organ.