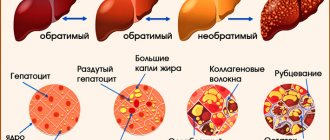
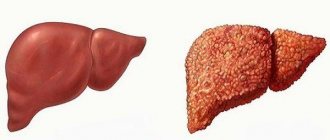
What is liver cirrhosis
The pathological condition of the largest organ (gland) of the abdominal cavity, which is a consequence of circulatory disorders in the hepatic vessels and is characterized by persistent damage, is called cirrhosis. In this disease, healthy liver tissue is replaced by fibrous connective tissue. Without treatment, liver failure and portal hypertension ultimately develop, followed by death. Death overtakes the patient, as a rule, after 2-4 years of illness. Sometimes the consequence of cirrhosis is organ cancer.
Vitamins for full functioning
Before studying the question of what vitamins to take for liver cirrhosis , you need to know what microelements this organ needs. For its normal functioning, it is necessary to receive the following vitamins in the required quantities:
- Thiamine. This is a vitamin that is necessary for the synthesis of fats and proteins. A deficiency of this vitamin can lead to hepatic cellular failure.
- Riboflavin. This vitamin helps to significantly improve the condition of capillaries. Moreover, if you receive riboflavin in the right amount, its beneficial properties help normalize liver function.
- Niacin. It helps to stop destructive processes in cirrhosis. This vitamin enhances the protective function of the liver.
- Choline. It helps neutralize toxins in the body and liver in particular.
- Vitamin B12. It is also called cyanocobalamin. It is very important for the normal functioning of the liver and hematopoietic system.
- Ascorbic acid. This element has a very important role in the process of carbohydrate metabolism. Also, ascorbic acid helps normalize blood clotting and significantly improves the immune system.
- Folic acid. It has a beneficial effect on the immune system, supports the formation of leukocytes, and helps normalize hemoglobin levels.
- Lipoic acid. It helps increase glycogen reserves in the liver. This acid also helps reduce blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
At the same time, vitamins for liver restoration should be taken in combination, and not separately. Only in this case will the organ receive everything it needs for rapid recovery and full functioning.
Symptoms
The main symptom of cirrhosis is pain in the right hypochondrium. However, the onset of the disease may be accompanied by other symptoms, or may be completely asymptomatic (20% of cases). Often it is possible to detect pathology only after the death of a person. For example, at the compensation stage there are no signs of cirrhosis, except for an increase in the size of the liver. It has been noted that in men the disease is more difficult to detect at an early stage. The first signs of cirrhosis:
- dryness and bitterness in the mouth, especially in the morning;
- periodic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, lack of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, nausea;
- periodic abdominal pain, worsening after drinking alcohol, pickled or fatty foods;
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes.
What vitamins does the liver need?
The essential vitamins necessary for the normal functioning of the liver include:
- Thiamine (B1);
- Riboflavin (B2)
- Niacin (B3);
- Choline (B4);
- Pyridoxine (B6);
- Cyanocobalamin (B12);
- Ascorbic acid (C);
- Tocopherol (E).
Let's look at each of them in more detail.
- Thiamine. Necessary for the synthesis of fats and proteins, as well as for the implementation of carbohydrate metabolism. Thiamine deficiency leads to hepatic cellular failure.
- Riboflavin. Improves the condition of capillaries and skin, normalizes the functioning of the liver, stomach and intestines. A lack of riboflavin reduces bile production and impairs its outflow. Contained in spinach, beets, yeast, milk, peaches, tomatoes, pears.
- Niacin. Takes an active part in the energy system, enhances the protective function of the liver and stops the death of its cells. Helps stop destructive processes in cirrhosis. Contained in seeds, buckwheat, beans, nuts, bananas, citrus fruits, green tea, and grains.
How to treat liver cirrhosis
Treatment for liver cirrhosis after diagnosis is prescribed by a gastroenterologist (a generalist) or a hepatologist (a highly specialized doctor). There is a generally accepted standard for complex therapy, which includes medication, physiotherapy, a strict diet, dosed physical activity, and, if necessary, surgery. To stop the development of pathology, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, stop tissue degeneration, and reduce the load on the portal vein. Recently, stem cell therapy has been used to treat liver cirrhosis.
Drugs for liver cirrhosis and hepatitis
The tactics of conservative treatment of chronic hepatitis or cirrhotic degeneration of the liver in a man or woman depends on the stage and type of the disease. Inactive cirrhosis does not require any medications other than vitamin and mineral complexes. The patient is advised to follow a healthy lifestyle so that the disease stops. The progression of cirrhosis is treated with hepatoprotectors based on milk thistle extract. To stop internal bleeding, intramuscular injections of Vikasol are used.
A disease of viral etiology of varying activity requires the administration of corticosteroid hormones and antiviral drugs. Decompensated cirrhosis is treated with increased doses of hepatoprotectors (injections) and lipotropic drugs. Therapy also includes taking vitamins. For biliary cirrhosis, steroid hormones, synthetic bile acids, and proteolysis inhibitors are prescribed. This stage is incurable, and the above-mentioned drugs only slow down the course of the disease and alleviate symptoms. What medications can you not do without:
- Duphalac. A mild laxative, which, in addition to its main effect, has a positive effect on the growth of beneficial intestinal microflora. Available in syrup or sachet form. Prescribed for cirrhosis: 15-30 ml/day. The doctor prescribes the duration of therapy individually. In case of an overdose, abdominal pain and diarrhea may develop.
- Molsidomin. A beta blocker prescribed to lower portal vein pressure. The drug reduces venous flow to the heart and reduces the tone of peripheral vessels. Take 1-2 g orally 2-4 times/day after meals. The course of treatment lasts from several months to several years. Long-term use may result in headaches and decreased blood pressure.
Hepatoprotectors
Drugs that have a protective effect on the liver are called hepatoprotectors. There are many drugs that belong to this family. For cirrhosis, drugs of plant and animal origin, essential phospholipids, and synthetic bile acids are prescribed. Among the popular ones:
- Essentiale Forte. Restores the cellular structure of hepatocytes, activates an enzyme that destroys fibrosis, and normalizes the carbohydrate-lipid balance in the organ. Children over 12 years of age and adults are prescribed 2 capsules 3 times a day with meals. The duration of the course is at least 3 months. Contraindication: individual intolerance to the components.
- Karsil. Herbal hepatoprotector with milk thistle fruit extract. Removes toxins, protects liver cells from destruction. Adults and children over 12 years of age take 2-4 tablets 3 times a day for 3 months. In case of endometriosis and pregnancy, it should be used with caution.
Antibiotics for liver cirrhosis
In uncomplicated cirrhosis, antibacterial drugs are not required. They are prescribed for bacterial complications, suspected ARVI. Effective antibiotics:
- Suprax. 3rd generation antibiotic based on cefixime. The mechanism of action is due to the destruction of the integrity of the pathogen cells. Prescribed 1 capsule 1 time/day for a week. Side effects include: nausea, vomiting, dysbacteriosis, thrombocytopenia, nephritis, dizziness, itching, urticaria, skin hyperemia.
- Normix. Broad-spectrum antibiotic. Causes the death of bacteria that cause intestinal infections. Take 200 mg every 6 hours for 1 to 3 days. The duration of the course should not exceed 7 days, so as not to provoke the development of side effects: increased blood pressure, lymphocytosis, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock.
Diuretics
Even at the stage of hepatitis, congestion occurs in the liver, which causes increased production of lymph. Fluid constantly accumulates, causing swelling of internal organs and limbs. To prevent ascites from developing, you need to take diuretics. Among them:
- Veroshpiron. Potassium-sparing diuretic that prevents water and sodium retention. The daily dose is from 50 to 100 mg once. You need to take pills once every 2 weeks. Contraindications include: Addison's disease, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, severe renal failure, anuria.
- Diacarb. It is an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase, which has diuretic activity. For edema, take 250 mg once in the morning. To achieve maximum effect, take 1 tablet every other day. The duration of treatment is prescribed individually. Contraindications for use are uremia, acute renal failure, diabetes mellitus.
Use of glucocorticoids
In case of liver cancer, the use of glucocorticoids is contraindicated, since they negatively affect the state of the digestive system, contribute to the development of complications, and reduce the patient’s life expectancy. Often these drugs are prescribed together with hormonal drugs for autoimmune cirrhosis that has not reached the stage of decompensation. For treatment the following are used:
- Metipred. Synthetic glucocorticosteroid. Has immunosuppressive, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory effects. The initial dose for intravenous administration is 10-500 mg/day, depending on the symptoms. The average duration of treatment is 3-5 days. Contraindications include: systemic mycosis, breastfeeding period.
- Urbazon. A glucocorticosteroid that has antitoxic, antishock, desensitizing, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory effects. Prescribed intramuscularly or intravenously at 4-60 mg/day for 1-4 weeks. The drug is not used for endocrine pathologies, severe liver and/or kidney diseases, ulcers, and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Prednisolone
The most popular glucocorticoid for cirrhosis. Suppresses the functions of tissue macrophages and leukocytes. Limits the migration of the latter to the area of inflammation. Prescribe 20-30 mg/day. The duration of the course is calculated individually, but not more than 14 days. The drug is not prescribed for bacterial, viral or fungal skin diseases, for skin disorders and in children under 2 years of age.
Diet
With this disease, the diet dictates its own rules. Daily calorie intake should not exceed 3000. Food is consumed up to 5-6 times in small portions. For liver pathologies, salt consumption of no more than 2 tsp is permissible. per day. Solid foods are crushed, fried foods are not allowed. To remove toxins, it is necessary to spend fasting days on dairy products or vegetable soups once a week.
You should not eat rye and fresh bread, puff pastry, rich pastry, fatty broths, meat/fish/dairy products with high fat content. Alcohol, coffee, cocoa, and spices are also prohibited. Authorized products:
- wheat bread made from premium flour;
- vegetable, cereal, milk soups;
- low fat meat dishes;
- lean fish;
- eggs;
- vegetables fruits;
- vegetable oil, butter;
- herbal tea, vegetable and fruit juices, jellies, compotes, jelly.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
In the complex treatment of cirrhosis, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor, depending on the problems that need to be solved. Physiotherapy cannot be carried out in case of severe complications and acute course of the disease. The arsenal of varieties of methods is wide, but the following are most often used:
- Diathermy. In the area of projection of the diseased organ, heating is carried out with high-frequency currents. The duration of the session is from 10 to 40 minutes, the course is up to 40 procedures daily or every other day.
- Inductothermy. Treatment is carried out using a high frequency electromagnetic field. The oscillatory effect leads to positive changes in the diseased organ. The duration of the procedure is 10-20 minutes. Course – 10-15 sessions conducted daily.
- Electrophoresis. Local exposure to drugs is carried out in concentration through the skin by means of current exposure. Session duration is 15-20 minutes. The course of treatment ranges from 10 to 20 procedures performed daily.
Dosed physical activity
If the patient does not have a history of ascites, doctors recommend dosed physical activity for liver pathology. Treated physical training improves metabolism in liver cells, normalizes blood circulation, helps strengthen the immune system, and strengthens the musculoskeletal system. Exercises for therapeutic gymnastics are selected individually. The specialist takes into account the severity of the disease, the patient’s age, and the general condition of the body. A few examples of exercise therapy:
- when lying on your back, when you inhale, the stomach protrudes, and when you exhale, it lowers;
- the same position, arms along the body, first the left leg is bent, the heel does not come off the floor, then the right;
- standing on all fours, while inhaling, lift one leg, while exhaling, pull the knee to the chest, then repeat the same with the other leg.
Surgery
If necessary, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment - a liver transplant. This is an expensive operation, which is complicated by finding a donor. Transplantation is prescribed when conservative therapy does not produce positive results, and the liver is constantly being destroyed. The disadvantage of surgical treatment is the subsequent lifelong use of immunosuppressive drugs. Contraindications to surgery are inflammation of the brain, malignant tumors of the bile ducts and other oncology, obesity, infections, severe heart pathologies.
Diet for cirrhosis
In case of liver cirrhosis, the patient is prescribed diet No. 5, which provides chemical sparing of the liver and normalization of the biliary system. The main task of the diet is to prevent dangerous complications.
Diet features:
- limiting the amount of fat with a normal content of carbohydrates and proteins;
- preference is given to boiled, baked, and less often stewed food; vegetables and flour are not sautéed;
- exclusion from the diet of foods rich in essential oils, nitrogenous extractives, cholesterol, purines, oxalic acid, fat oxidation products formed during frying;
- a ban on spicy, fatty, fried foods, as well as smoked foods, canned food, and pickles;
- high content of foods rich in fiber, lipotropic substances, pectins;
- drinking enough liquid;
- exclude cold dishes;
- stringy meat, vegetables and fruits rich in fiber are pureed.
| Carbohydrates | 400–450 g (of which sugar – 70–80 g) |
| Fats | 80–90 g (of which vegetable – 30%) |
| Squirrels | 90–100 g (of which animals - 60%) |
| Energy value | 2800–2900 kcal |
| Sodium chloride (salt) | Up to 10 g |
| Liquid | 1.5–2.0 l |
In the body of patients with cirrhosis, the potassium content is reduced. This process is activated by ascites and the use of diuretics and prednisolone in therapy. Therefore, the products should have enough potassium, which is rich in potatoes, as well as dried fruits - dried apricots, figs, raisins. If corticosteroid hormones are used in therapy, then the body requires enough calcium to prevent osteoporosis.
With edematous-ascitic syndrome, reduce the intake of liquid and salt, and with geochromatosis, reduce the amount of iron-containing foods (liver, meat, egg yolk, lentils, etc.). Wilson-Konovalov disease is an indication for excluding copper-rich foods from the menu - buckwheat and oatmeal, peas, squid, beans, etc.
How to treat with folk remedies
Treatment of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver will be effective if additional folk recipes are used at home along with medications. It should be remembered that the use of any therapeutic methods must be agreed with a doctor in order to avoid complications of the disease. Folk remedies for the treatment of liver cirrhosis, which are used at home:
- Milk thistle. One teaspoon of crushed seeds is mixed with 1 tsp. leaves of the plant. The resulting mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 20 minutes. The medicinal herb is filtered and drunk at one time. Take to cleanse the liver 3 times a day: on an empty stomach, before lunch and before bed for a month.
- Elecampane. Place 1.5 tbsp in a small container. l. chopped elecampane root, add 500 ml of water, simmer for half an hour, then leave for 20 minutes. Next, the broth is filtered and taken half an hour before meals 2-3 times a day, drinking 200 ml at a time. Duration of treatment – 10 days.
Prevention
Compliance with preventive measures will not allow the development of severe liver pathology. To avoid cirrhosis you should:
- completely stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner;
- limit the consumption of spicy, fatty, smoked, fried foods;
- do not take medications without consulting a doctor;
- enrich the diet with foods high in vitamins and microelements;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene.