General information
Aganglionosis of the large intestine (congenital megacolon) is one of the most common developmental anomalies of the digestive organs.
According to observational data, the prevalence of Hirschsprung's disease in the population of newborns ranges from 1:30,000 to 1:2,000. In 90% of patients, the disease debuts before the age of 10. In boys, the anomaly is detected 4.32 times more often than in girls. In 29.0-32.7% of cases, the pathology is associated with other developmental defects, while in 9% of patients, colonic aganglionosis develops as part of Down syndrome. The disorder was first described in the writings of Danish pediatrician Harald Hirschsprung in 1888. The relevance of timely detection of the disease is due to the severity of its complications.
Hirschsprung's disease
Common Causes
Many people believe that every child up to a certain age looks cute with a chubby belly. But still, its size, like that of a frog, should cause fear, not tenderness.
The work of a child’s body is significantly different from that of an adult. If a child has a big belly, the reason for this may be minor. For example, a baby is prone to frequent gas formation in the intestines or bloating.
As the child grows, the internal organs also develop, so abdominal pain is normal. Children often experience colic.
Pathogenesis
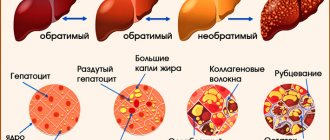
The absence of ganglion cells in the area proximal (upper) relative to the anus leads to denervation of this area. As a result, intestinal motility slows down, and the passage of feces further through the gastrointestinal tract becomes more difficult. All this leads to constipation and disruption of the frequency of bowel movements.
To push feces further through the intestine, the area proximal to the affected area experiences severe stress. Hypertrophy of its muscle layer occurs. Therefore, the upper healthy area of the intestine is always enlarged. For comparison, this can be clearly seen in the photo of a healthy person and one diagnosed with Hirschsprung’s disease. The patient will always have an overly protruded abdomen.
There are no ganglion cells not only in the muscle layer, but also in the mucous membrane. Therefore, not only peristalsis, but also normal absorption of nutrients is slowed down in the affected area of the large intestine. Which leads to disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
The development of Hirschsprung's disease is caused by a violation of embryogenesis, presumably at 7-12 weeks of gestation, when the nerve plexuses of Meissner (in the submucosal layer of the colon) and Auerbach (in the muscular layer of the intestine) are formed. Due to the premature cessation of neuroblast migration or their insufficient differentiation, instead of the typical submucosal and myenteric plexuses with ganglia, the intestinal neurostructures are represented by individual nerve fibers and glial elements.
The sooner the migration of neuroblasts is completed, the more extensive the aganglionic portion of the colon wall is. Acetylcholinesterase accumulates in the mucous layer, which causes intestinal spasm, which is a pathognomonic sign of Hirschsprung's anomaly. Due to tonic spasms and lack of peristalsis, the denervated segment becomes a functional obstacle to the movement of feces. Chronic retention of intestinal contents leads to constant constipation and significant expansion of the overlying intestine.
Big belly in a newborn
Abdominal bloating in newborns is considered a natural phenomenon. And all because of weak muscles and abdominal walls. The size of the liver also has an effect, because in a newborn baby it is larger in size than other internal organs. Intestinal colic occurs due to weak functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which the stomach becomes rounded. Therefore, it is not a terrible situation when a child has a big belly at one year old.
But excessive belly size can also indicate health problems. The most common cause of this phenomenon is considered to be congenital pathologies, such as polycystic renal disease, liver cirrhosis or ascites. These anomalies can be detected in the maternity hospital during the first examination of the baby.
Many babies under the age of 2 look very touching with a protruding tummy. Those around you are touched and admired. This seems natural to parents, because the body requires a supply of energy to grow, but the muscular frame is not sufficiently developed, and it is difficult for it to hold the abdominal walls. In addition, a large belly is noticeable in the child immediately after eating food, as well as liquid, but it decreases as it is digested. And this is understandable. Most often, children under the age of one year are susceptible to this phenomenon.
But if the child is thin, but has an impressive abdomen, then parents should consult a doctor who will help exclude or diagnose the following diseases:
- Umbilical hernia. Experts say that it affects babies up to 3 months of age and, less often, up to a year. In the case of a hernia, the abdomen takes on a pointed shape and increases in size.
- Rickets and other diseases resulting from impaired metabolism. In this case, the child has a large belly, like a toad; it protrudes not forward, but to the sides. The cause of rickets is considered to be a lack of vitamin D in children's bodies.
- Improper activity of pancreatic enzymes. The body reacts sharply negatively to fructose and sweets.
- Reduced renal and adrenal function.
- Hepatitis. Children over three years of age are susceptible to inflammatory liver diseases.
Life prognosis with ascites
For patients who have developed abdominal hydrops as a result of complications of certain diseases, an important question is: how long do they live with ascites?
Only a doctor can answer this question after he has conducted a full examination of the patient. Life prognosis is influenced by many factors. First of all, it is important to understand how effective the chosen therapy is. Also, a conclusion about the life expectancy of a patient with accumulated fluid can be made based on concomitant ailments.
Doctors identify general factors that can affect the life expectancy of a patient with this disease:
- environment;
- correct menu;
- psychosomatics.
Ascites itself may not cause death, but the patient’s life is threatened by complications that can develop from the pathology.
The accumulation of watery substance in the peritoneum increases pressure, which provokes compression of organs in different parts of the body.
The functioning of the entire body is disrupted, and uneven functioning of many systems occurs that are difficult to treat. Water and electrolyte levels also decrease, which worsens the patient’s general condition.
The accumulation of large amounts of fluid can trigger the development of many ailments. Clinicians identify the following exacerbations:
- bacterial peritonitis;
- hydrothorax and respiratory failure;
- intestinal disorders;
- umbilical hernia;
- hepatorenal syndrome.
The above consequences of abdominal dropsy can cause the death of the patient. But final conclusions can be drawn only after the degree of development of the initial pathology has been established.
Ascites is a disease that develops from existing ailments. Most often, doctors notice the formation of excess fluid in the following pathologies:
The development of ascites in a woman’s body provokes stage 3 ovarian cancer. Stage 4 ovarian cancer leads to death in 50% of patients due to abdominal hydrops.
The following criteria help doctors quickly assess how long a person can live with accumulated fluid in the peritoneum:
- liver functionality;
- kidney function;
- heart functionality;
- effectiveness of therapy.
Ascites forms in 75% of patients with liver cirrhosis. How long a patient can live can be determined by the form of the first disease. If a person has been diagnosed with compensated liver cirrhosis with ascites, then proper therapy can provide the patient with a favorable prognosis. The effects of ascites will be minimized, and the main functions of the liver will be preserved.
The fourth stage of development of cirrhosis with ascites is characterized by irreversible processes in organs that disrupt liver function. If you do not undergo an operation to transplant the desired organ, then only 20% of patients can live up to 5 years, the remaining 80% of people die much earlier. At this stage, death can only be prevented by an organ transplant.
There is a high probability of death with ascites if the disease develops from renal failure. If the patient is not given hemodialysis on time, death can occur within a few weeks.
Ascites also causes serious harm to the body if it develops from heart failure.
If a patient is diagnosed with stage 3 or 4 of the disease, then death occurs in 30% of cases during the first two years after diagnosis.
The remaining 60% of people survive the two-year treatment period, but death may occur in the next 5 years. Only 10% of patients can hope for a positive prognosis if the disease is detected in time and treatment is started.
When spontaneous bacterial ascites is diagnosed, every second patient can survive, but there is a high probability of relapse. In 43% of cases, the second stage of the disease develops in the first six months, in 70% - within one year. And 75% of patients experience recurrent ascites within two years. Doctors do not yet know whether the disease can recur in the third year of proper therapy.
For patients with refractory ascites, death occurs during the first year of the disease. The prognosis concerns 50% of patients with this diagnosis.
Clinicians identify special risk groups that are most susceptible to the influence of pathology. An unfavorable prognosis may be for:
- people who are over 60 years old;
- patients with low blood pressure;
- people with reduced serum albumin;
- patients with high levels of norepinephrine in the blood;
- people with diabetes;
- patients with liver tumors.
In order to choose the right treatment method, the doctor needs not only to know the etiology of the disease, but also to identify the stage of ascites. Clinicians distinguish 3 main degrees:
- a small amount of fluid that cannot be immediately diagnosed;
- moderate stage of ascites;
- tense ascites.
With a positive life prognosis at the initial stage of the disease, a person can live another 10 years. But this is only possible if the disease was diagnosed in a timely manner and the course of treatment was prescribed correctly. For adequate therapy, it is also important to follow a strict diet and perform laparocentesis.
At the second stage of the disease, the chances of a positive prognosis become less. The patient’s body is filled with a large amount of fluid, which significantly aggravates the healing process.
At the last stage of the development of the disease, only supportive therapy is carried out to maximize the patient’s life. With this development of the disease, death can occur a year after diagnosis. The patient’s life can be extended by selecting the correct treatment regimen that affects the source of ascites development.
Source: //OkGastro.ru/bryushnaya-polost/294-prognozy-zhizni-pri-astsite
Classification
Systematization of Hirschsprung's disease is carried out taking into account anatomical and clinical criteria. Depending on the location of the aganglionic area, the most common form of the disease is distinguished: rectosigmodial, detected in 70% of patients, rectal (up to 25% of cases of anomaly), subtotal (3%), segmental (1.5%), total (0.5%). According to the location of the dilated intestine, megarectum, megasigma, left-sided, subtotal and total megacolon, megaileum are distinguished. When diagnosing intestinal Hirschsprung aganglionosis, the following clinical features are taken into account:
- Children's version of the disease. It is detected in almost 90% of patients. It is characterized by rapid development, an almost complete absence of independent defecation, and increasing signs of intestinal obstruction. Surgery is usually performed in two stages.
- Prolonged variant of aganglionosis. Debuts in children. Due to the small length of the denervated segment, it develops slowly. To correct constipation, enemas are used for a long time. It is possible to perform both two-stage and one-stage operations.
- Latent variant of the anomaly. Constipation appears in adolescence, and chronic colonic obstruction quickly develops. To relieve constipation, daily enemas are necessary. The passage of feces is usually restored in two stages.
With a compensated course, independent stool persists for many years; as the disease develops, 3-7 days of constipation occur, the resolution of which requires laxatives or an enema. In patients with a subcompensated condition, constipation lasts more than 7 days without the use of laxatives and enemas. Decompensation of the disease is indicated by the absence of independent defecation and the urge to defecate, compaction of intestinal contents and the formation of fecal stones, and the ineffectiveness of conservative methods of bowel movement.
Complications and consequences
Possible complications and consequences of the undergone manipulation are in the plane of the likelihood of infections entering the body.
Hirschsprung's disease in children, in the absence of proper treatment for a long time, results in a concomitant disorder in the form of dysbiosis. Protein metabolism is not happening correctly.
After surgery, the risk of infection in the intestines increases. Enterocolitis occurs.
In the period after surgery for Hirschsprung's disease, the body recovers completely within six months. Patients may experience spontaneous passage of stool. Sometimes constipation occurs. This condition indicates a slow recovery of the body. Individual characteristics emerge.
Children are under the foster care of a doctor for at least 6 months after surgical procedures. Parents maintain strict control over the baby's condition. With strict adherence to the regimen, the child begins to develop a bowel movement reflex. It is necessary to strengthen the immune system.
The body's adaptation to changes occurs gradually. The patient should not violate the prescribed regimen. If your health worsens, you should immediately consult a doctor. You cannot try to stop the condition on your own. Causes a sharp increase in complications and pathological conditions. Delay is especially dangerous for children.
In the case of Hirschsprung's aganglionosis, patients have impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients, which, in combination with a decrease in appetite, leads to severe malnutrition up to cachexia. Iron deficiency anemia is often detected. Children experience delays in growth and physical development. Long-term stagnation of feces in the intestine provokes dysbiosis and inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane, which can manifest as paradoxical diarrhea.
The most dangerous complications of Hirschsprung's disease are intestinal obstruction, bedsore of the wall with fecal stones and intestinal perforation. Toxic megacolon may occur, which is characterized by dilation of the proximal intestine and excessive growth of pathogenic bacterial flora. This condition often leads to peritonitis and sepsis due to the penetration of intestinal bacteria through the pathologically altered intestinal wall. In this case, sharp diffuse abdominal pain, repeated vomiting, and febrile fever occur.
How long do people live with abdominal ascites, what affects it, and can a person die from the disease?
Ascites is a particularly serious disease in which, due to pathological changes in the walls of blood vessels, fluid enters the abdominal cavity. As a result, organs in the affected location cease to function normally, which can have serious consequences, including death.
Is it possible to die from ascites?
The disease itself is not as scary for vital signs as its complications. Its essence is that the pathological accumulation of fluid creates pressure on the internal organs, leading to dysfunction of their work.
The difficulty of ascites (or dropsy) is that it is extremely difficult to cure. Additionally, the patient’s health condition is aggravated by a violation of the water-salt balance, which results in difficulty in the distribution and removal of water from the body.
As a result, a number of complications can arise. Moreover, many of them significantly increase the likelihood of death.
The most common types of complications are:
- umbilical hernia;
- spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (pathology accompanying ascites caused by cirrhosis of the liver);
- severe functional acute renal failure;
- hydrotrax of the pleural cavity;
- impaired gas exchange from the lungs (respiratory failure);
- intestinal obstruction.
Patients without concomitant diseases can die with ascites if they are at risk. These include people over retirement age, patients with diabetes or cancer, patients with hypotension, increased levels of norepinephrine in the blood and decreased concentrations of serum albumin.
According to medical statistics, abdominal ascites in women most often causes stage 3 and 4 ovarian cancer. The probability of death in such cases is 50%. Moreover, the cause in most cases is ascites, and not the original pathology.
Among the male audience, dropsy is provoked by cirrhosis of the liver. In 75% of cases, it is this that forms ascites. Only a doctor can determine the likelihood of the most unfavorable outcome, based on the form of the primary disease.
In medical practice, there have been cases where the cause of dropsy was renal or heart failure. The mortality rate is extremely high - 90%. The survival period ranges from several weeks (in case of renal failure and lack of timely treatment) to 5 years.
If refractory or spontaneous bacterial ascites is diagnosed, the likelihood of cure is higher. About half of patients recover, but 43% are likely to relapse.
What does life expectancy depend on?
If a doctor makes such a diagnosis, it is important to understand that people with ascites live for different periods of time (even about 10 years). Only a specialist can say exactly how much a person has left, and only approximately, since this parameter is influenced by many factors.
The life expectancy of a patient with ascites is determined by:
- well-chosen therapy;
- the degree of preservation of the functioning of the liver, kidneys and heart;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- psychological state and mood of the patient.
Another important point that determines how long a person can live with dropsy of the abdomen is the timeliness of seeing a doctor. The more advanced the disease, the less curable it is. The stage at which abdominal ascites is located determines life expectancy.
1st degree
A small amount of fluid has accumulated in the abdominal cavity. Visually diagnosing the disease is problematic. In this case, with a well-chosen treatment regimen, the patient may have another 10 years left. Therapy must be supplemented with diet and periodic diagnostics using laparocentesis.
2nd degree
The amount of fluid in the abdomen becomes so large that it is not difficult to visually determine the diagnosis. It compresses the organs so much that interruptions in their functioning begin.
The chances of recovery for a patient with second degree ascites are an order of magnitude less. They depend on the preservation of the functions of vital organs and how quickly it is possible to remove fluid, as well as restore water and electrolyte balance.
3rd degree
The most advanced option, in which it is impossible to cure the patient. Death occurs within 1 year. Medical care consists only of relieving pain and maintaining vital signs for a long time.
Abdominal ascites is a very serious disease that can result in death. Life expectancy in this case is an abstract parameter, largely predetermined by the behavior of the patient himself.
Source: //onkologia.ru/onkogastroenterologiya/vyzhivaemost-pri-astsite-bryushnoy-polosti/
Clinical manifestations of the disease in children
As mentioned above, the disease in children manifests itself depending on the affected area and the length of the area without innervation. The larger the affected area, the more serious the clinical symptoms of the disease become.
Hirschsprung's disease occurs in newborns quite unnoticed while they are breastfed, and the first clinical symptoms begin to appear when transferred to artificial feeding or with the introduction of complementary foods. In addition, in newborns on the first day of life, in the presence of the disease, there is a delay in meconium, which should be expelled within 24 hours after birth.
Depending on the location where the innervation of the intestinal region is disrupted, Hirschsprung's disease in children is divided into several anatomical forms.
- Rectal, in which a small part of the rectum is affected. Symptoms of this form of the disease are characterized by minor constipation due to poor diet and are rarely found in young children. True, this form of Hirschsprung's disease occurs in only 25% of cases and responds well to therapeutic treatment.
- Rectosigmoidal. It occurs much more often and accounts for approximately 70% of cases. Constipation when the rectosigmoid area is affected is more persistent, since in addition to the rectum, part of the sigmoid colon also remains without innervation. Feces do not pass through this area well and can accumulate there in large quantities, causing discomfort to the child and causing chronic pain. This form lends itself well to cleansing enemas only in the initial stages, then they become insufficient. Constipation appears already during the first weeks of life, especially on artificial feeding, and with the introduction of complementary foods, the clinical symptoms only worsen and the child stops going to the toilet independently. In addition to chronic constipation, the appearance of bloating is characteristic of the abdomen, which increases significantly in size and in the photo looks like a frog's belly, which is actually what it is called.
- Segmental, is quite rare and accounts for about 1.5% of all cases. The innervation of the area disappears in small intervals, and healthy parts of the intestine remain between them. The clinical picture will depend on the extent of areas not controlled by the nervous system. Symptoms can vary, from intermittent constipation to the complete inability to go to the toilet on your own, along with bloating and a “frog belly.”
- A type of disease that affects either the left or right side of the large intestine is called subtotal. It is also quite rare and accounts for 3%. This is one of the most severe forms of Hirschsprung's disease, in which treatment with enemas and laxatives is possible only at first, and surgical treatment can no longer be avoided, no matter what ideal diet the child follows. All symptoms characteristic of Hirschsprung's disease, and these are severe constipation, bloating, “frog belly”, lack of body weight, delayed physical and mental development, vitamin deficiency, anemia and fecal stones, will be especially pronounced in this form of the disease.
- Total, with damage to the entire large and occasionally small intestine. Fortunately, this common pathology is extremely rare and accounts for only 0.5% of all cases of Hirschsprung's disease. Severe constipation and bloating are characteristic from the first day of life, and the photo of the baby's abdominal cavity shows signs of intestinal obstruction.
In addition to the 5 forms, several more stages of Hirschsprung's disease in children are distinguished.
- The stage at which the child is able to go to the toilet at least occasionally, or cleansing enemas have a good effect is called compensated. With it, the child’s general well-being also does not suffer, he does not lag behind in development, there is no anemia or signs of hypovitaminosis.
- When clinical symptoms increase, cleansing enemas become less effective, and the general condition of the child begins to deteriorate against the background of prolonged constipation, they speak of the disease transitioning into subcompensation.
- The stage of decompensation develops at the slightest violation of the diet and is manifested by severe constipation, which is difficult to respond to drug therapy, and cleansing enemas do not completely empty the intestines. Sick children develop intestinal obstruction. Of course, the stage of decompensation is more typical for adults, and in childhood its development is possible only with total and subtotal anatomical forms of the disease.
- There is also an acute form of Hirschsprung's disease, which develops only when the diet is violated, and the rest of the time it practically does not manifest itself in any way and does not require constant treatment.
At 3–4 years old, the child’s body changes: muscles and bones become stronger, the stomach tightens, and therefore becomes smaller.
If the child himself is fat, then perhaps we are talking about obesity, and in this case it is necessary to establish the causes of this scourge. Endocrine problems may be the reason why your baby has a big belly. 3 years is a turning point for a child’s body.
There are many reasons why fatness appears in the abdomen, and each of them is very serious.
Ascites in heart failure
The presence of ascites in heart failure is not uncommon, but it does not occur in all patients.
The appearance of ascites in heart failure is facilitated by several factors, in particular:
- Heart defects , especially acquired ones, for example, severe mitral stenosis or tricuspid valve stenosis. But the appearance of ascites can also be influenced by congenital defects, in particular, severe cardiac septal defects, as well as patent ductus arteriosus;
- A group of diseases called chronic cor pulmonale . Such diseases arise for various reasons, and this group includes various ailments of the lungs and bronchi, in which high pressure occurs in the pulmonary circulation;
- Thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches;
- Constrictive pericarditis;
- Cardiosclerosis , the development of which occurred as a result of acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and congenital atherosclerosis.
The doctor is usually able to recognize the presence of ascites against the background of heart failure only when the volume of pathological fluid is 1 liter or more. Until this point, there are usually no obvious signs.
With an increase in the volume of pathological fluid, the patient may note the following signs:
- An increase in the size of the abdomen, with the navel protruding outward;
- The skin on the surface of the abdominal wall becomes very tense, begins to shine, and stretch marks and stretch marks may appear on it;
- When breathing, the stomach remains at rest, its movements are not observed;
- Dilated veins appear on the abdomen, which are clearly visible through the surface of the skin;
- In a supine position (on your back), your stomach is flattened.
Very often, in the presence of right ventricular failure, the patient develops swelling before ascites, which should be paid attention to.
It is important to remember that the appearance of ascites in heart failure indicates the neglect of the underlying disease. In this case, there may be some blueness of the skin (cyanosis), as well as the presence of shortness of breath, which increases significantly in a supine position, pulmonary hypertension, as well as congestive phenomena.
If ascites appears against the background of an advanced disease, provided timely treatment and measures are taken, the prognosis is very favorable, and with proper treatment and compliance with the doctor’s instructions, patients with ascites against the background of heart failure live for decades.
Prognosis and prevention
The outcome of Hirschsprung's disease depends on the time of its detection and the degree of damage to the intestinal nerve ganglia. The prognosis is relatively favorable in case of early diagnosis and surgical correction. Without treatment, infant mortality in the first months of life reaches 80%. Due to the congenital nature of the pathology, specific prevention measures have not been developed. When the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid the development of severe complications.
Aganglionosis of the large intestine is a congenital disease, and therefore there are simply no methods of specific prevention. The most effective preventive measures can be considered early detection of the disease and prescribing the correct treatment. After all, only in this case will the prognosis be favorable and many serious complications will be avoided, and the quality of life of patients after surgery will significantly improve.
Methods of nonspecific prevention include:
- regular exercise (swimming and jogging are especially useful in this case);
- a balanced diet (more fresh vegetables and fruits, herbs, whole grain bread and excluding fried and canned foods, hot herbs and spices from the diet);
- you should eat in small portions;
- You need to drink at least 2-3 liters of clean water per day.
Following simple preventive measures will make life much easier for patients. The main thing is to identify the disease in a timely manner and carry out the correct treatment! Beginning of the form End of the form
Clinical picture and prognosis
The patient notices that his stomach is growing and becoming disproportionate to his body. The accumulation of ascitic fluid occurs within 2-3 months. The initial stages of the process are manifested by bloating and difficulty breathing. If a person has been diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver, at this stage (as well as during the entire treatment) it is worth strictly following a therapeutic diet. This will somewhat slow down the development of severe consequences that threaten human life. Ascites as such does not lead to death, but its course and the effect of treatment can be used to judge the form of the underlying disease.
In medical practice, the following statistics are recorded:
- if the pathology is not controlled by medications and other manipulations, 50% live no more than 12 months;
- a complex, decompensated form of ascites allows us to talk about a five-year survival rate of 20% of patients;
- Abdominal dropsy of compensated form allows you to live with the disease for more than 10 years.
With the development of ascites and the accumulation of a large amount of fluid, the following symptoms appear: respiratory disorders, digestive system failures, problems with urination, and kidney problems.
At this stage, the swollen abdomen is visible to the naked eye. The syndrome is accompanied by: hernias, organ deformation, varicose veins. Therefore, ascites can be determined by simple examination of the abdomen. Veins radiate around the navel, reminiscent of the tentacles of an octopus.
It is important to understand that with sufficient treatment and following the recommendations on diet and regimen, there is a chance to make you feel better and even extend life for several more years.
Attention! For the treatment and prevention of cirrhosis, our readers successfully use the method Read more →
Enlarged internal organs
Due to the increased size of the internal organs, a large belly is noticeable in the child. You don't have to worry about this problem for 1.5 years. But if the child is more than 3-4 years old, then there is a reason for concern. There is a protrusion not of the entire abdominal region, but only of a certain part.
The cause may be inflammation or infection. In such a condition, you need to show the child to a doctor to identify the problem. Gradual enlargement of the abdomen can lead to rupture of the spleen.
With hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), a large belly is considered normal for a child. The following dimensions are considered acceptable: protrusion to the sides of the ribs by 2–3 cm.
This condition is observed in children aged 6 to 7 years. But if the child is much older, then the problem may lie in a certain disease.
An enlarged abdomen is possible with coprostasis (constipation). This is a disruption of the intestinal tract. Coprostasis is diagnosed when the intestines rarely empty their bowels, less than once every two days. This disorder occurs due to a disorder of motor activity and secretion of the colon.
Abdominal hydrocele and kyphosis
At the age of 6, a child’s body is susceptible to problems such as curvature of posture. Incorrect position of the back at the table, weak bone frame are the causes of childhood kyphosis. The disease also occurs due to weakness of the spinal muscles, which prevent the vertebrae from bending forward. As a result, the following problems appear:
- 2-4 folds on the stomach;
- protrusion of the abdomen (in an upright position).
Also, the volume of the abdominal cavity depends on the type of kyphosis. It can be genotypic, that is, hereditary. This is quite difficult to deal with.
Ascites (abdominal dropsy) is characterized by the accumulation of fluid. It cannot be called an independent disease, but rather a symptom, which is a signal indicating disturbances in the functioning of the body. The main causes of ascites include:
- kidney diseases, for example nephrotic syndrome;
- nutritional dystrophy;
- tumors in the abdominal cavity.
Ascites is divided into two types: acquired and congenital. If the belly gradually becomes larger, and a protruding navel is clearly noticeable in the horizontal position of the child, then a doctor’s consultation is definitely needed.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of ascites in liver cirrhosis is carried out using the following methods: using traditional medicine recipes, traditional medications or surgery. Whatever treatment path is chosen, it is necessary to closely monitor the progress of the disease. If progression or complications occur, it is necessary to review the prescribed therapy and make adjustments.
Whatever treatment method is chosen for the patient, there are a number of recommendations that all people with this diagnosis must follow. Complete rest and bed rest are prescribed only to patients with the last stage of ascites; in all other cases, doctors advise limiting physical activity. The diet for liver cirrhosis with ascites primarily consists of limiting the consumption of salt and foods containing it in large quantities. But you should not reduce the amount of fluid consumed, as this can negatively affect blood pressure.
Nutrition for liver cirrhosis with ascites consists of following the so-called table number five. This is the most gentle diet prescribed for liver diseases. So, patients should completely avoid fried foods and foods rich in cholesterol and purine. All products should be easily absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract.
Products should be prepared by boiling, baking or stewing. Coarse foods such as meat should be ground to a puree. It is also worth adhering to the temperature of food consumption; it should not be below twenty and above sixty degrees. You should eat little by little and every three hours.
The minimum life expectancy with ascites is also predicted when abdominal dropsy becomes a consequence of renal failure
Traditional treatment
Treatment of ascites using traditional medicine recipes has been practiced by healers for a long time. Such healing consisted of the use of natural ingredients and herbs, which were taken both internally and locally. This type of therapy is considered quite safe, but it is important to know that the effectiveness of this method has not yet been scientifically proven. Therefore, by agreeing to such procedures, you do so at your own peril and risk.
Dried red bean pods have a good diuretic effect. In order to make a decoction, you need to pour one hundred grams of the product with a liter of hot water and keep it in a water bath for at least fifteen minutes. After the broth has cooled, it must be filtered and taken three times a day, one glass.
One of the most common and used remedies is dried apricots. It can not only get rid of excess fluid formed in the abdominal cavity, but also replenish missing useful elements in the body and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Dried apricots should be poured with boiling water and left for an hour. The recommended daily dose should not exceed five hundred milliliters.
You can remove fluid from the abdominal cavity using parsley decoction. To prepare this recipe, add a bunch of parsley to a liter of water and simmer over low heat for about thirty minutes. After cooling, the broth should be strained and consumed in small portions throughout the day.
To better remove infiltration from the abdominal cavity, diaphoretic teas and decoctions are used; they should be consumed hot. An excellent option would be to brew linden or coltsfoot flowers. These plants accelerate sweating, due to which the amount of free fluid in the abdomen decreases.
Treatment with medications
For abdominal ascites, patients must be prescribed diuretics. The most effective drugs have been proven to be Furosemide and Veroshpiron.
- Furosemide is a fast-acting diuretic. This drug is approved for use by people with kidney disease. Furosemide has a dilating effect on blood vessels, and therefore reduces blood pressure. When taken orally, the diuretic effect is achieved within thirty minutes and lasts for four hours. The drug should be taken in the morning, one tablet. The maximum dosage should not exceed 160 milligrams per day.
- Veroshpiron is a diuretic drug with a potassium-sparing effect of prolonged action. The diuretic effect is achieved a few days after the start of administration. The daily dose is 100-200 milligrams and is selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
In cases where ascites is caused by cirrhosis of the liver, doctors prescribe treatment aimed at supporting the organ. Typically, the patient is prescribed medications such as: synthetic and natural hepatoprotectors, choleretic drugs, phospholipids, amino acids, antiviral and immunomodulatory agents, etc.
With ascites, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity and has no outflow.