Normal coprogram indicators
There are two generally accepted methods for assessing stool: macroscopy and microscopy.
Macroscopic examination evaluates the visual characteristics of feces, and microscopic examination evaluates its initial data under a microscope. During a macroscopic assessment of stool, the laboratory technician determines the following parameters:
- Consistency. A normal fecal bolus in older children is soft, and in infants it is unformed.
- Color. In children who are breastfed, the stool is colored gray or yellow. Afterwards, the stool gradually turns brown.
- pH acidity. Depending on the type of food consumed, this indicator can be neutral or sour.
- Smell. A variable parameter that is indicated in case of sharp deviations from the norm.
Microscopic examination of stool includes determination of:
- Muscle fibers (not detected with sufficient digestion).
- Neutral fat (minimum amount allowed).
- Fatty acids (can be detected in small quantities).
- Connective tissue (absent).
- Soap (slight presence is allowed).
- Plant fiber (may contain single cellular elements, digestible, indigestible - allowed in varying quantities).
- Starch (absent or minimal presence).
- Iodophilic flora (should not be contained in a healthy intestine).
- Leukocytes (single cells allowed).
- Mucus (minimal presence).
- Epithelium (single cellular elements).
Connective tissue in stool
Not detected
– During normal digestion, connective tissue is not detected in the stool.
Discovered
– The presence of meat residues indicates insufficient function of the digestive glands, or an excess of meat in the diet. The connective tissue may visually resemble parts of helminths, thick mucus, or a fungal infection. Microscopy gives an idea of the structure of connective tissue fibers. Children who receive meat feeding before the age of one year have a large amount of undigested muscle fibers in their feces.
Causes of undigested food in stool
Normally, a healthy child may periodically have small particles of undigested rough food (peel of vegetables, fruits). Perhaps the products chosen were not of the best quality. We talk about the right thing in the relevant articles. If the act of defecation is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations and pain, then changes in the coprogram are not a deviation from the norm.
A large amount of vegetables and fruits in a child’s diet leads to the appearance of lumps of undigested fiber in his stool. This is fine.
You should be concerned if the products of digestion are visible to the naked eye, mucus is present, peristalsis is accompanied by pain, an abundance of bowel sounds, and pain.
The predominance of plant foods in a child’s diet leads to the appearance of small lumps of undigested fiber due to the accelerated movement of the food bolus through the intestines and the physiological deficiency of the enzyme capable of breaking it down.
This condition does not require drug correction. It is enough to reduce the intake of fiber to normalize fecal parameters.
An equally common cause of the appearance of undigested food particles in a child’s stool is functional dyspepsia. In addition to poor breakdown of foods, the baby may experience periodic regurgitation, decreased appetite, frequent loose stools mixed with mucus, etc. This condition occurs as a result of:
- Gross violations.
- Non-compliance with diet, overfeeding.
- Dentation (baby teething).
- Inconsistency of the diet with the age characteristics of the child (early introduction of complementary foods, mechanically poorly processed food, etc.).
- Taking drugs that reduce the secretory capabilities of the digestive tract (antisecretory, sorbents).
Intestinal and pancreatic juices in children in the first year of life are produced in limited quantities, sufficient only to digest foods in the form of a mushy or finely chopped consistency. As the body matures, its digestive capabilities expand.
Another common cause of food particles in the stool is. At the birth of a baby, his intestines are completely sterile, but already from the first hours of life, the process of colonization of microflora into the body begins. If there is an insufficient number of beneficial bacteria, intestinal digestion is disrupted, feces change their consistency (become more liquid), acquire an unpleasant odor, and undigested food particles appear in it.
Muscle fibers in stool: what a microscopic examination of stool can tell you
The food consumed by a person is first crushed in the mouth, moistened with saliva and passing through the digestive system, converted into feces in the large intestine. Various sections of the gastrointestinal tract are responsible for the gradual digestion and absorption of nutrients.
The composition of feces can indicate not only disturbances in the digestive process, but also indicate which part of the gastrointestinal tract has ceased to function normally. Therefore, in order to diagnose some diseases, the doctor resorts to prescribing a stool analysis - a coprogram.
Prescribing a coprogram and correct collection of tests
Muscle fibers are not normally detected in stool
In order to prescribe a coprogram, the doctor must have certain grounds. It may be indicated in the following situations:
- in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal pathologies
- for suspected helminthiasis
- in order to assess the effectiveness of the therapy
Comprehensive preventive examinations also involve stool analysis. Using a coprogram, you can identify various disorders in the child’s digestive system:
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the intestines
- cystic fibrosis
- presence of parasites
- lactose intolerance
In order for the coprogram to bring reliable results, when collecting feces it is necessary to adhere to certain rules. A couple of days before the analysis, you should stop eating foods that contain meat and that affect the color of stool.
These include various green vegetables, tomatoes, beets, and red fish. They are able to distort the result of a coprogram when searching for hidden blood in the patient’s stool. Sometimes, the doctor independently prescribes a special diet for the patient. The products prescribed by her contain proteins, carbohydrates and fats in a certain amount.
This creates a maximum load on the digestive system, as a result of which stool analysis helps to detect any, even the slightest, deviation in the digestive processes.
Before the analysis, you should avoid taking various enzymes and medications that affect intestinal motility.
Taking antibiotics, drugs containing iron and bismuth, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs should also be postponed.
Read: Leukocytes in feces: what does this indicator indicate?
People who have had a barium x-ray or colonoscopy need to wait a few days for the test. It is not advisable for women to donate feces for coprogram during menstruation. People suffering from hemorrhoids should delay testing until the problem is resolved if the hemorrhoids bleed.
Stools for analysis must be obtained naturally. It is recommended to donate stool obtained as a result of morning bowel movements. Evening samples can be stored in the refrigerator for ten hours. The material for analysis is collected in a special sterile container. It will be enough to collect 15g of material for analysis.
A coprogram is a stool analysis performed to confirm various gastrointestinal diseases. It can also be used for complex preventive examinations.
What can a microscopic examination of stool tell you?
Coprogram: decryption
The absorption of food is a complex mechanism of interaction between various organs of the human digestive system. It begins in the oral cavity and proceeds throughout the digestive tract, right up to the anus. Food processing occurs not only at the mechanical level, but also at the chemical level - as a result of the action of gastric juice and various enzymes on nutrients.
Using a microscopic examination of stool, it is possible to determine which foods eaten by the patient were poorly digested. Based on the information received, the specialist can determine what kind of digestive problems a person has.
Feces in normal form are a homogeneous mixture of various substances, which consists of products obtained as a result of secretion and excretion of the gastrointestinal tract, remnants of undigested or poorly digested food, particles of the upper intestinal tissues and its microflora. When carrying out a coprogram, the homogeneity of feces is determined as detritus. With normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, food is processed well and detritus has a more uniform appearance.
If any disorders develop in the patient’s digestive system, food is not fully digested, so undigested remains of consumed foods begin to appear in the stool. Thus, among the remains of animal products, fats and muscle fibers can be found in feces.
Read: Leukocytes in feces: what does this indicator indicate?
Plant foods are represented in the analysis in the form of fiber and starch.
All these components, present to varying degrees in the analysis material, can tell about specific diseases of the patient’s digestive system.
The quality of a person’s life depends on the efficiency of the body’s digestive system. Food is the main source of various nutrients that the body needs to meet all its needs.
Microscopic examination of stool can tell you how efficiently your digestive system is doing its job. Depending on the presence of various components in the stool, the doctor diagnoses this or that deviation from the norm and determines its cause.
Principles of correction of digestive disorders
Depending on the reasons that led to incomplete digestion of food, the principles for eliminating them can be very diverse. A pediatrician will help determine the origin of the symptoms and correct them. In some situations, parents can correct the situation themselves.
During natural feeding of the baby's mother, if changes appear in the stool, it is worth eliminating fatty, smoked and fried foods. If such measures are ineffective, you should consult a doctor.
If, after the introduction of new foods, the baby's stools become more frequent and undigested food particles appear, then it is advisable to postpone their use and repeat them after 2-3 weeks. Continuing complaints about changes in stool after discontinuation of the innovation are a reason to consult a doctor.
There is never a need to force a child to eat; he himself can determine the amount of feeding required from the cradle. Overfeeding not only leads to further problems, but also significantly undermines the functioning of the immature digestive system. In adulthood, such children develop chronic diseases, some of which significantly reduce the quality of life.
From the birth of the baby and throughout childhood, parents need to constantly monitor the frequency of stool and changes in its visual characteristics. Timely seeking medical help will quickly eliminate the cause of undigested food elements in the feces and maintain healthy digestion in the baby.
A coprogram is the study of feces to determine their properties, chemical and physical composition, the presence of abnormal inclusions to confirm the diagnosis of a particular disease, as well as to track the dynamics of diseases and the effectiveness of therapy.
Fecal contents are formed when chyme (a bolus of food) moves through the digestive tract from entering the oral cavity to the anal canal. Therefore, the results of the coprogram are a valuable diagnostic criterion for determining gastrointestinal diseases.
What should you do if you find leftover lunch in your stool?
The digestive organs are capable of digesting certain amounts of food consumed by a person. If you eat more than normal
, the digestive system will not be able to cope with an excess of food. When a stressful state is observed, the process of processing the contents of the stomach becomes more difficult.
What to do in such cases
:
- try to chew it more thoroughly while eating;
- eat at frequent intervals, but in small portions;
- do not overeat;
- give dishes more aesthetics so that they look more appetizing;
- do not drink liquid while eating or immediately after it;
- You can drink water an hour and a half before meals, but no more than a glass;
- stop taking medications
that the doctor did not prescribe, so as not to worsen your health condition; - do not read during breakfast or lunch and do not watch TV, so as not to provoke the appearance of a stressful state;
- stop eating in a hurry;
- make meals separate - consume proteins only with proteins, carbohydrates - with carbohydrates.
You can try to normalize the functioning of the digestive organs using alternative medicine methods.
When is a coprogram prescribed?
In feces you can find microorganisms of various numbers and types, fecal pigments, particles of undigested food, and epithelial cells from various areas of the intestine.
In accordance with the characteristics of fecal contents, an experienced laboratory technician will easily identify pathological processes that are localized in one or another part of the intestine.
A coprogram is prescribed for:
- Worm infestation.
- Acute, chronic stomach diseases.
- Neoplasms.
- Diseases of the duodenum.
- Various infections.
- Pathologies of the pancreas, liver, gall bladder and ducts.
- Pathological processes in the small intestine.
- To assess the effectiveness of the therapy and the need for treatment correction.
With the help of scatological analysis, it is possible to identify dysbacteriosis (a condition when the ratio of normal and pathogenic microorganisms is disturbed and increased reproduction of the latter occurs).
The coprogram is rarely used as an isolated diagnostic method; more often, its purpose is combined with other studies. However, despite this, the diagnostic value of scatological analysis is very great.
Classification
The diagnosis of steatorrhea does not mean any specific disease; rather, it can be considered as a separate symptom of problems in the digestive tract.
Determination occurs when 5-4 grams of fat is detected in stool for every 100 grams of stool.
For the reliability of the results, preliminary preparation of the patient (diet, abstinence from alcohol), as well as repetition of the study several times, is necessary.
What types of steatorrhea can be distinguished:
- Nutritional or nutritional. The development of this pathology is preceded by improper and irrational nutrition, consumption of large amounts of fats and, as a result, their incomplete absorption.
- Intestinal steatorrhea. Shows problems with fat absorption in the small intestine.
- Pancreatic steatorrhea. Occurs in case of pancreatic insufficiency, production of digestive enzymes in a smaller volume.
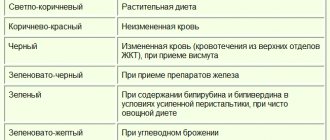
Color
The normal color of stool is brown (various shades) due to the presence of stercobilin in it. The shades of stool depend on diet and medications taken. So, a vegetable diet can give stool a greenish tint, coffee and blueberries - black, dairy products - light yellow, beets - red, and antibiotics - golden.
With some pathologies, the color of stool also changes:
- Red-brown stool - bleeding from the lower intestines.
- Black - bleeding from ulcers of the duodenum or stomach.
- Green - the presence of enteritis, dysbacteriosis.
- - diseases of the biliary tract, liver.
When deciphering the stool coprogram in children (see photo below) who are breastfed (naturally) fed, the yellow, green-yellow, golden-yellow color of the stool is determined. Artificially produced feces are light brown or pale yellow.
Children under six months old may secrete bilirubin in their stool, which gives the stool a greenish color. That is, if, besides green stool, there are no other symptoms, then this condition does not require treatment.
Microscopy
The presence of protein indicates inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, polyps, ulcers and neoplasms. In a normal coprogram there is no protein.
Blood appears in the stool due to bleeding, which can be caused by helminths, tumors, ulcers, and polyps. Changed blood indicates bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, and unchanged blood indicates bleeding in the lower parts.
An increase in the level of stercobilin appears in the feces during hemolytic anemia. A decrease in this indicator is a sign of blockage of the bile ducts.
The appearance of bilirubin indicates dysbiosis and acute inflammatory processes.
The presence of mucus is a sign of intestinal infections (dysentery, salmonellosis, colitis). However, it is worth taking into account the age of the child, since in case of stool coprogram (decoding in children), mucus may be a variant of the norm (children under one year old).
The presence of pathological flora is a sign of dysbiosis.
In the stool coprogram (when deciphered in children), detritus, if its amount is below the age-appropriate norm, may indicate disturbances in the digestive process.
The presence of a large amount is a violation of the secretion or absorption of bile.
Unchanged - pancreatic pathologies.
The presence of starch grains - malabsorption syndrome, chronic pancreatitis.
Soap (of which normally there should be a small amount) - duodenal problems, pancreatitis, gallstones.
In the stool coprogram (decoding in children), leukocytes in large numbers indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Fatty acid. Not normally detected. If they are present in the stool, one should suspect enzyme deficiency, acceleration of intestinal activity and impaired bile outflow.
Plant fiber. If the fibers are insoluble (for example, vegetable peels, etc.), this is normal, but if there are soluble fibers in the stool, this indicates a lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Connective tissue fibers are normally absent. Their appearance is a sign of pancreatitis.
Increased levels of ammonia in stool are a sign of intestinal inflammation.
The presence of pathogenic bacteria - intestinal diseases and dysbiosis.
The pH of feces can be different (slightly acidic, slightly alkaline, neutral). This indicator depends on the person’s nutrition.
Stool analysis: results of coprogram analysis
Not found
– During normal digestion, connective tissue is not found in the stool.
Discovered
– The presence of meat residues indicates insufficient function of the digestive glands, or an excess of meat in the diet.
The connective tissue may visually resemble parts of helminths, thick mucus, or a fungal infection. Microscopy gives an idea of the structure of connective tissue fibers.
Children who receive meat feeding before the age of one year have a large amount of undigested muscle fibers in their feces.
Muscle fibers are unchanged
Not detected
– Normally, with sufficient activity of the digestive glands, there are no muscle fibers in the feces.
Discovered
– Insufficient activity of gastric juice or pancreatic enzymes does not allow the gastrointestinal tract to digest muscle fibers (meat).
The presence of unchanged (striated) fibers is a symptom of acute pancreatic insufficiency, for example, with pancreatitis.
Children who receive meat feeding before the age of one year have a large amount of undigested muscle fibers in their feces, since at this age the pancreas is not yet fully formed.
Muscle fibers are changed
Not detected
– Normally, with sufficient activity of the digestive glands, there are no muscle fibers in the feces.
Few detected
– Normally, with sufficient activity of the digestive glands, there are no muscle fibers in the feces. With an excess of meat food in the feces, altered muscle fibers may be present in small quantities and the normal activity of the digestive glands is maintained.
Found many
– Insufficient activity of gastric juice or pancreatic enzymes does not allow the gastrointestinal tract to digest muscle fibers (meat). With partial activity, altered, unstriated muscle fibers, partially digested, are found. This indicates the preservation of the pancreas, but may indicate the presence of inflammation (pancreatitis).
Neutral fat in feces
Not found
– Normally, there is no neutral fat in feces.
Detected
– Impaired fat digestion in the absence of pancreatic enzymes and impaired production or secretion of bile leads to the appearance of neutral fat in the feces.
Fatty acids in feces
Not detected
– Normally there should be no free fatty acids in feces.
Discovered
– Fatty acids are contained in feces when there is insufficient activity of pancreatic enzymes and absence of bile secretion.
Soap
Not detected
– Norm
Soaps, digestible fiber, unchanged muscle fibers, modified fibers, starch, bilirubin, neutral fat, fatty acids
– Soaps in combination with unchanged and modified muscle fibers, fiber and starch are a sign of accelerated passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract, for example, in case of intestinal infection, poisoning, increased peristalsis.
Soaps, fatty acids, neutral fat
– The lack of normal activity of the pancreas, a decrease or absence of bile secretion leads to the appearance of neutral fat, fatty acids, and soaps in the feces.
Indigestible fiber
Not found -
In the absence of plant foods in the diet, there is no fiber in the feces.
Discovered
– Plant fiber can only be partially digested by the human gastrointestinal tract, under the action of enzymes from intestinal microorganisms. Fiber is mainly excreted unchanged in feces.
Indigestible fiber is the coarse fibers of plants and the cell walls of their membranes. This fiber creates volume in feces and is also a sponge that adsorbs toxins and removes them out.
Coarse fiber stimulates peristalsis and improves digestion processes
Digestible fiber
Not found
–With normal digestion, digestible fiber is not detected in the feces.
Found in small quantities
– A variant of the norm, a small content of digestible fiber in the form of individual cells not connected to each other is acceptable.
Found in large quantities, starch, foamy feces, acidic reaction
The appearance of digestible fiber in the feces in large quantities indicates insufficient activity of the pancreas and the accelerated movement of chyme through the digestive tract.
Starch
Not found
– Starch must be digested completely under the action of salivary and pancreatic amylase, enzymes of the intestinal flora.
Found in large quantities, amilorrhea
– Starch found in stool indicates a lack of pancreatic or small intestinal enzymes. With normal enzyme levels and gland activity, starch may remain in the stool due to accelerated movement through the intestines. This happens with disorders of intestinal motor function or intestinal infections.
Starch grains found in small quantities
– Partially undigested starch may be present in the stool due to excessive starch in the diet. In this case, they speak of relative enzyme deficiency. This requires diet correction and balanced nutrition.
Iodophilic flora
Not found
– Normal intestinal flora should consist of more than 90% lacto and bifidum bacteria. Iodophilic flora is not detected in feces.
Discovered
– Iodophilic intestinal flora are bacteria that are stained dark by iodine preparations. These are cocci, rods, yeasts, which are responsible for the processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines. Normally, they make up less than 10% of the intestinal flora.
When the ratio of lactobacilli, bifidumbacteria and iodophilic microorganisms changes, the digestive processes in the intestine are disrupted. This is manifested by bloating or intoxication. Changes in bacterial composition may be related to dietary composition.
Excessive amounts of simple carbohydrates support bacteria, which obtain energy through fermentation. Excess protein provokes the development of putrefactive flora.
Iodophilic flora was found, muscle fibers were changed, the reaction was alkaline, the color was dark brown -
Insufficient activity of the digestive glands leads to the fact that incompletely digested chyme enters the intestines, which creates favorable conditions for the development of iodophilic flora. Excess animal protein in the diet and insufficient digestion provokes the development of putrefactive flora.
Iodophilic flora, digestible fiber, starch, acidic reaction were detected -
The processes of carbohydrate breakdown are disrupted as a result of insufficient activity of the pancreas. Undigested or partially digested fiber and starch, and excess simple carbohydrates create an environment for the proliferation of iodophilic flora.
Mucus in stool
Not found
– Normally, mucus in stool is not detected as a separate structure, but is completely mixed with it.
Discovered
– With increased secretion of mucus, it is found in the stool as streaks and deposits of light yellow or white color. This can happen with an intestinal infection, benign or malignant formation in the intestine.
In children under one year of age, excess mucus in the stool is normal, since the intestines are still adapting to work. An increase in the amount of mucus can occur when the balance of microflora is disturbed, and when complementary foods are introduced for which the child is not yet ready.
Epithelium in feces
Not found
– Norm
Found in small quantities
– Normally, a small number of squamous and columnar epithelial cells may be present in the stool. This occurs as a result of the mechanical effect of feces on the walls of the digestive tract.
Found in large quantities, brown stool with red deposits, red blood cells
– With an increased number of epithelial cells, one can judge the inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract. Squamous epithelium enters the stool from the lower rectum. Usually, red blood cells or blood are present along with the epithelium in this case. This can happen with constipation, hemorrhoids, fissures.
Found in large quantities, mucus, digestible fiber, altered fibers, starch, foamy feces, semi-liquid consistency, liquid consistency, mushy -
With an increased number of epithelial cells, one can judge the inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract. The detection of columnar epithelium indicates inflammation in the upper intestines; the level of inflammation helps determine other changes in the coprogram.
Leukocytes in stool
Not detected/single
– Single leukocytes in the stool may be present in a healthy person.
Single leukocytes, mucus, brown feces with bright red coatings
– Changes are characteristic of inflammation of the rectum, hemorrhoids.
Found in large numbers, columnar epithelium
– The presence of a large number of leukocytes indicates acute or chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Columnar epithelium indicates that most likely the source of inflammation is in the duodenum or upper parts of the small intestine.
Found in large quantities, squamous epithelium, mucus -
A large number of leukocytes and the presence of squamous epithelium indicate inflammation of the rectum, possibly a tumor or the presence of polyps.
Red blood cells in feces
Not detected
– normally absent
Changed red blood cells were found in large quantities, black stool
– The presence of altered red blood cells in the stool is a consequence of gastric bleeding or bleeding from the duodenum. The amount of blood detected indicates the intensity of bleeding. Thick black stool indicates an emergency condition, intense bleeding.
Red blood cells were found in large quantities, the stool was dark brown, red-brown -
When bleeding in the small intestine, the red blood cells/blood in the stool have time to partially change, becoming dark red or brown.
Unchanged red blood cells were found in large numbers
– When bleeding from the large intestine and rectum, red blood cells remain unchanged in the stool.
Source: https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/analizes/analiz-kala.htm
Features of the results obtained
With a stool coprogram (decoding in children under 1 year of age and infants), the basic data of a scatological examination are similar to those of an adult, however, in a child’s coprogram there are some features.
In children under one year of age, the presence of leukocytes in the feces can be observed even in absolutely healthy babies. If the child is gaining weight normally and the parents do not complain, then the presence of leukocytes (as well as mucus) is one of the normal variants.
The majority of children's feces have a neutral or slightly alkaline reaction (pH from 6 to 7.6). However, it is worth remembering that the stool of infants is often sour, which depends on the nature of the diet.
If, when deciphering the fecal coprogram in children, the feces have an alkaline reaction, in this case it is worth suspecting imperfect absorption or the development of putrefactive processes in the intestines.
For children under three months of age who are breastfed, bilirubin present in feces is normal. When deciphering the stool coprogram in older children, only stercobilin should normally be present.
Normally, in completely healthy children, small particles of undigested coarse food products, such as nuts, peels of vegetables and fruits, can be periodically observed in the stool. Feces reflect all the features of a child’s digestion and nutrition. It is worth noting that two types of fiber can be found in the feces of an adult – digestible and indigestible.
Such analyzes not only show how correctly or incorrectly the body functions, but also help to identify what exactly the essence of the violations is. It may well be that the food was of poor quality. A similar condition can occur due to gross violations of the diet by a nursing mother, as well as when the child is overfed and does not comply with his diet.
About fiber
Plant fiber is essentially a mixture of complex polymer compounds, lignin and various polysaccharides, which make up all the membranes of plant cells. Such dietary fiber is not digested by gastrointestinal secretions. Some of them, namely pectins, gums, mucopolysaccharides, dissolve in water and are almost completely fermented in the intestines thanks to the microorganisms living there.
During the fermentation process, energy is released and beneficial microelements are absorbed. Digestible muscle fibers in feces, if found, are in minimal quantities. Cellulose, another fiber polysaccharide, is only partially fermented. The intestinal microflora cannot influence lignin at all. Such insoluble plant fibers are eliminated from the body in the feces as undigested pieces of food.
It is thanks to fiber, its ability to irritate the intestinal walls, that the normal movement of the food bolus through the gastrointestinal tract and the subsequent removal of digestive waste occur.
Most fiber is found in grains, unrefined grains, legumes, nuts, vegetables and fruits. For normal peristalsis, it is necessary to regularly consume a sufficient amount of cereals and whole grain bread. Among vegetables, you should give preference to carrots, beets, cabbage, tomatoes, dill and other greens. Citrus fruits, apples, and apricots are rich in fiber, but bananas contain very little. If the content of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice is reduced, then the digestible fiber elements are not broken down, which is why undigested food appears in the feces in the form of fairly large pieces.
Normal coprogram indicators
It is worth noting that sometimes indigestion of fiber in babies can occur due to disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas. But such problems usually manifest themselves in other more pronounced health problems. So, if such a problem arose due to dietary violations, you need to stop consuming excessive amounts of plant fiber and provide your baby with a well-balanced diet.
Treatment of disorders of the pancreas is carried out only under the supervision of a qualified gastroenterologist. The first is usually observed in digestive products due to a deficiency of hydrochloric acid, which separates the cells of the digested fiber. If there is insufficient production of this substance, pieces of vegetables or fruits appear in the feces; of course, the beneficial substances from them cannot be absorbed by the body.
If such a symptom is detected against the background of absolute health and normal well-being, you just need to change your diet. Reduce the amount of plant foods, make your diet balanced.
If there are problems with food digestion in children or adults, it is better to seek doctor’s help as soon as possible. Brew a couple of tablespoons of the resulting mixture in a thermos with half a liter of boiling water. Infuse the medicine overnight - for seven to eight hours, then strain.
What could be the causes of this problem?
Several types of plant-based fiber are intended for human consumption – digestible and non-digestible. Each of these species can be found in feces
after the act of defecation.
Digestible fiber
. If it is observed in the stool, this indicates a lack of hydrochloric acid in the body, which is responsible for the breakdown of cells.
A low level of acidity causes pieces of fruits and vegetables to remain in the stool. Usually these are particles of carrots, potato tubers, grapes, and beets.
Accordingly, the process of assimilation of useful microelements does not occur from them. Normally there should be no digestible fiber.
Indigestible fiber
.
This includes grains, vegetable and fruit peels, legumes, and plant stems.
Products made from indigestible fiber are not affected by gastric juice
If there is not enough hydrochloric acid in the stomach, then there will be more particles of unprocessed food than in a healthy person. Then the process of removing feces from the intestines will be accompanied by diarrhea. The only items that do not fit into this category are elements of products that are not intended for food - fruit seeds, fruit cuttings.
Principles of correction of digestive disorders
Grind all the ingredients and mix them well together. The preparation and administration of this medicine is carried out in the same way as in the previous version. Grind ten to fifteen fruits finer and pour half a liter of vodka. Place this medicine under the lid in a cupboard and leave at room temperature for two weeks.
I ask everyone to be TACTIC and SYMPATHY for those who need it, SUPPORT each other. Thank you. 2 times with a difference of 2 months, between these tests there was treatment, but the results are still crappy.. The appearance of a large number of starch grains in the stool (amilorrhea) indicates, first of all, a sharp acceleration of intestinal motility and the accelerated movement of food chyme (diarrhea) .
Causes of steatorrhea in children and adults
The causes of fatty stool in an adult are quite numerous. First of all, they can lie in:
- impaired intestinal motility;
- pancreatitis;
- bile deficiency;
- impaired absorption of fats in the body, which in scientific language is called malabsorption;
- deterioration of the patency of the lymphatic ducts;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Solinger-Ellison syndrome;
- Whipple's disease;
- enteritis.
There are situations when the reasons for the appearance of neutral fat in the stool of an adult are not a pathology. First of all, this concerns, as already noted, the abuse of fatty foods, the use of rectal suppositories and the intake of vegetable oils to combat constipation. These reasons are not dangerous, but it is necessary to warn the doctor in advance that such factors may affect the body. Since these situations can have a direct impact on the results of the coprogram, its implementation will be postponed to another date.
The factors described above are not unique. The reasons why the stool became fatty may be the most unexpected. For example, steatorrhea is often observed in patients with:
- renal pathologies;
- fermentative or putrefactive dyspepsia;
- hepatitis;
- liver cyst;
- liver oncology;
- cirrhosis;
- hemochromatosis;
- amyloidosis;
- cholecystitis;
- giardiasis;
- cholelithiasis;
- cholangitis;
- psoriatic or eczematous lesions of the digestive system.
By the way, for many of these reasons, there is an admixture of fatty acids in the child’s coprogram. However, in children this deviation is characterized somewhat differently.
Features of childhood steatorrhea
Fatty acids in a child’s stool are most often the result of pathologies of the pancreas with impaired production of the necessary enzyme – lipase. There may also be a reason such as a genetic failure. In this case, the gene that is responsible for the production of pancreatic enzymes undergoes a mutation.
Another reason for the appearance of neutral fat in a child’s stool is metabolic disorders. In particular, amyloidosis, which is a serious disease that, unfortunately, cannot be completely cured. It can affect different organs, but the kidneys and liver are most often affected.
Fatty acids in a baby's stool should not always be a cause for panic. In infants, the enzyme system is extremely poorly developed during the first weeks of life, since it is just beginning to adapt to new living conditions. The required amount of enzymes is produced after the baby reaches 3 months of age. It is during this period that neutral fat in the baby’s feces should completely disappear. But if this does not happen, then we are talking about a disease.
Salts of fatty acids in the feces of infants have another reason for their appearance. It is also associated with the physiological characteristics of the baby’s body. In such children, the liver and biliary system still cannot cope with their functions. The reason is the same as that characteristic of the enzyme-producing function.
Good to know! In premature and weakened babies, a stool lipid profile may show an accumulation of fats and soaps. In such children, complete restoration of metabolic processes occurs somewhere around 4-5 months of life. Until then, steatorrhea will be present, so the baby should be under close medical supervision.