The biological clock of each organism is individual. Constipation is a consequence of disruption of the digestive process. Proctological diseases can pose a serious threat to human health.
It is impossible to identify a single, correct frequency of bowel movements. If a person does not have discomfort in the intestinal area, then the norm may be to have bowel movements several times a day or three times a week.
The presence of blood in the stool is one of the signs of a possible disorder or serious disease of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
The color of the blood discharge, the thickness and richness of the stool, may determine the preliminary assumption of a violation of the integrity of a certain part of the gastrointestinal tract. An accurate determination of the cause, complexity and treatment options of the disease can only be determined by contacting a specialist.
Causes of bleeding during constipation
Causes of blood in the stool during constipation:
- Haemorrhoids. Stagnant masses of feces damage hemorrhoidal cones. With constipation, the stool has a fairly thick and even hard consistency, which complicates the process of excreting feces and is accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane.
- Rectal fissures. A sufficiently high density of feces when moving through the lower part of the intestine forms corresponding defects. Strong stretching of the wall shell is accompanied by damage and cracks, which is manifested by bleeding.
- Intestinal polyps are primarily benign formations. The slightest damage to the surface of the polyps leads to bleeding, which is inevitable in the presence of stagnant fecal accumulations.
- Colon cancer. The more the disease progresses, the heavier the bleeding becomes. Constipation becomes chronic.
- Angiodysplasia of the colon is a difficulty in the growth and formation of blood vessels. They become characterized by excessive fragility. Bleeding begins as a result of pressure on very thin vessels from thick and hard accumulations.
The actual pattern arising from the causes of blood discharge as a result of constipation will be mechanical damage to the internal part of the mucosa due to the difficulty of promoting accumulation in the intestines.
Infectious causes
The following may also affect the appearance of blood in stool and infections:
- In dysentery, the disease develops due to infection by bacteria of the genus Shigella. Due to severe irritation of the mucous membrane, the patient has frequent and very loose stools, up to 10-30 bowel movements per day. In addition to pus and various mucus, stool may also contain bloody discharge.
- With protozoal infection, the intestine (its thick section) is affected by protozoan amoebae. The stool is characterized by impurities of pus, mucus, and blood.
- Balantidiasis is an infection caused by the protozoan balantidia. In addition to the disease occurring in a latent, asymptomatic form, frequent liquid bowel movements with blood may be observed.
Acute intestinal diseases are also signaled by the manifestations of blood discharge in the stool. An infection such as salmonellosis (bird eggs, dairy, meat products) enters the human body through food. A detailed article about salmonellosis and its symptoms can be found here.
The source of the disease chooses its habitat in the small intestine, gradually producing toxins. The diarrhea is foamy and filled with blood and mucus. The disease is also accompanied by an increase in temperature to 38 C.
Intestinal infectious diseases are easily transmitted from a sick person to a completely healthy person, therefore, in addition to timely diagnosis and treatment, timely disinfection and isolation of the patient and his things are also important.
Factors that may cause constipation with blood
A healthy lifestyle is a harbinger of protection against many ailments. Poor nutrition, stress and various mental disorders leave a negative imprint on the harmonious interaction of body systems.
The main factors for the development of constipation with blood:
- Lack of active lifestyle.
- Dietary disorder.
- Taking medications that negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract.
- Abnormal intestinal development processes.
- Disturbance of innervation (communications with the central nervous system).
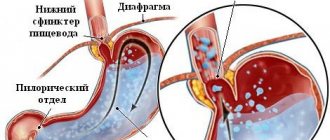
Mechanism of constipation
The retention of stool after 48 hours is already referred to by doctors as constipation. Evacuation may be incomplete or difficult.
The accumulation of feces in the rectum occurs to a definitely required volume. Next, a natural process of pressure occurs on the walls of the rectum, which should end in natural defecation. If this does not happen, the rectum expands. Obviously, for the next urge to defecate, the pressure becomes greater, as does the size of the already dilated rectum.
If this situation is repeated frequently, and the rectum constantly has an unnatural, enlarged size, various disorders will be obvious. In order for the rectum to regain its previous appearance and a person to stop feeling discomfort, a long course of treatment is sometimes necessary.
The following mechanisms for the occurrence of constipation are distinguished:
- Atonic. Due to decreased intestinal function, the process of fecal movement is disrupted. As a result, the large intestine has insufficient tone of the smooth muscles of the walls, which is characteristic of the atonic mechanism.
- Spastic. In the case of excessively high tone in certain areas of the intestine, a spasm occurs, which interferes with the normal process of defecation. Most often, it is this mechanism of constipation that is typical due to nervous strain or poisoning of the body.
Ways of formation of a difficult act of defecation:
- Nutritional. Occurs during the development of the process of general dehydration of the body.
- Mechanical. The process of impaired motility and peristalsis
- Neurogenic or dyskinetic. The characteristic causes of development are stress and nervous disorders, overstrain and conflicts, and neuroses.
What to do if there is bleeding from the anus?
If you find blood from your anus, treatment for such a problem should begin after the cause has been established, since this is just a symptom and not an independent disease.
Accordingly, in order to accurately determine the cause of bloody discharge from the anus, and to reliably make sure that they are not associated with cancer or other dangerous intestinal disease, you should contact a proctologist for examination. He will tell you what to do and what examinations you should undergo to clarify the diagnosis.
Color of blood in rectal bleeding
The color of blood during rectal bleeding, as well as the volume of discharge, differ depending on various factors. The brighter the color of the blood discharge, the closer the source of inflammation is to the anus.
So, the color of blood during rectal bleeding:
- Scarlet blood may indicate an anal fissure or damage to the hemorrhoids.
- Darker, brown blood in the stool indicates inflammatory phenomena, but in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
What does it depend on? Most often, this is due to the fact that the blood changes its consistency, including color, as it moves towards the anus. In infectious diseases, blood is most often present in the stool in the form of streaks.
Bleeding may have an unpleasant odor and a peculiar stickiness. This mass is called melena - black and sticky stool that has been in the rectum for a long time, and, having interacted with bacteria, is already broken down into chemicals (hematin). This phenomenon is typical for bleeding due to ulcers in the stomach or duodenum.
Treatment
Treatment of constipation, accompanied by blood in the stool, depends on the cause of the disorder, that is, the underlying disease that caused it:
- If gastric bleeding is caused by an ulcer, neoplasm or intestinal obstruction, the patient is immediately hospitalized in surgery or oncology.
- If the symptoms of the disorder are due to mild or moderate ulcerative colitis, treatment can be done on an outpatient basis with medications and a special diet.
- For anal fissures or hemorrhoids, the disease is treated by a proctologist, based on the degree of its severity. Thus, mild and moderate forms are corrected with diet and medication, and advanced forms are corrected surgically.
What to do, who to contact?
If the first signs of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract appear, you should consult a specialist. A proctologist is a doctor who deals with diseases of the sigmoid and rectum.
Situations when it is necessary to call emergency medical care:
- The amount of blood increases, and it is not possible to stop the bleeding optimally quickly.
- The presence of intense, profuse vomiting, mixed with blood.
- Presence of hematomas, nosebleeds...
- Weakness of the body.
- Increased body temperature and acute abdominal pain.
Abuse of optimally rapid provision of medical care can result in death for the patient, and is therefore unacceptable.
How to prepare for the examination?
The own research of specialists from the proctology department of the Altermed clinic made it possible to make a visit to a proctologist as easy and comfortable as possible. There is no longer any need to fast the day before and plan the procedure for the morning. In the proctology departments of Altermed, a way has been found to successfully cope with all these difficulties. This is Microlax bowel preparation.
The use of Microlax microenemas makes fasting unnecessary, does not require special equipment or premises, and saves a lot of time. The laxative effect occurs 5-15 minutes after administration of the drug. The quality of bowel cleansing is such that treatment can begin immediately after rectoscopy and anoscopy. If it is necessary to use during pregnancy and lactation, Microlax does not require special precautions.
The Proctology Clinic provides diagnostics using the most modern equipment. The best doctors in St. Petersburg - both men and women - and a delicate approach are at your service.
Popular questions
- ❓ What diseases can be a sign of bleeding from the anus?
Discharge of blood from the anus without pain or with pain can be a sign of a large number of diseases. From the safest, but very detrimental to the quality of life, lesions of the anal canal or anal fissures, and those that pose an immediate threat to life, cancer of the rectum and sigmoid colon. At the appointment, the Doctor asks the patient in detail about the type of blood, its quantity, features of discharge and many other aspects of rectal bleeding, on the basis of which an examination and treatment plan is built. - ❓ How to stop bleeding from the anus?
It is impossible to stop bleeding on your own without knowing the source. In case of massive bleeding accompanied by loss of consciousness (fainting or pre-fainting), severe weakness, low blood pressure, you should contact the emergency medical service (03,103,112). If blood is released periodically, after or during stool in small or medium quantities, you should visit a coloproctologist.
- ❓ Which doctor should you contact?
Treatment and examination of blood discharge from the anus is carried out by a coloproctologist, or in his absence by a surgeon. Diagnostic studies are performed by a coloproctologist, a surgeon and an endoscopist.
What diseases can be predicted by bloody stool?
A qualified specialist can unambiguously diagnose the disease, based on an analysis of the studies performed. It can be assumed, in addition to infectious diseases, diseases of the rectum and anus, neoplasms, as well as other diseases of the digestive system.
For example, possible diseases such as:
- Ulcerative colitis. Chronic form, inflammatory process of the colon lining.
- Crohn's disease. Severe chronic form of gastrointestinal disease.
- Cirrhosis of the liver and ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
Preventing constipation
Prevention of constipation is necessary to exclude the possibility of exacerbation of the disease, possible complications and acquisition of a chronic form.
Basic rules for preventing constipation:
- In case of emergency, use laxative enemas or laxatives to get rid of accumulations in the rectum. Do not use these methods on a regular basis.
- Follow your diet and, if necessary, consult a nutritionist.
- An active lifestyle promotes the harmonious interaction of systems throughout the body.
- Timely preventive examinations by a doctor in order to detect the disease early.
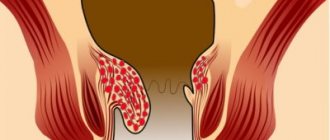
Haemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids affect two thirds of people over 45 years of age. The cause of the disease is varicose veins of the straight anorectal region. These veins can expand outside the anus and inside the rectum. Most often these two options are combined.
Manifestations of hemorrhoids:
- itching in the anus
- discharge of scarlet blood during bowel movements
- visible prolapse of nodes when straining or at rest
- severe pain due to infection and node thrombosis
Bleeding from hemorrhoids can be of varying intensity: from a few drops during bowel movements to copious discharge of blood, worsening the general condition and causing chronic anemia.
In any case, the diagnosis can only be made by a proctologist who will conduct a digital examination, rectoscopy, or use other methods.
Treatment of hemorrhoids:
- The first step should always be normalization of stool. Constipation and excessive bowel movements should be avoided. To do this, use fractional meals, including prunes, kefir, beets and other vegetables with fiber in the diet (see diet for hemorrhoids). If there is no effect, you can use mild plant-based laxatives (Mukofalk, Senade, prebiotics with the active ingredient Lactulose, see all laxatives for constipation)
- In the initial stages of the disease, it is possible to relieve symptoms with medications. To stop bleeding, rectal suppositories are used (Natalsid, Proctosan, see suppositories for hemorrhoids). To relieve pain, use painkillers (ointments for hemorrhoids)
- In case of disease progression, sclerotherapy and surgical treatment methods are used. The effect of the operations is good, but the risk of relapse remains (see external hemorrhoids: treatment, internal hemorrhoids).