Mothers of young children are most often concerned about lumps of undigested food found in stool. Looking into the pot and finding feces with pieces of food, every mother, due to the instinct of caring for her offspring, begins to suspect problems in her child. However, it is quite possible for young children to have undigested food in their feces, since the children’s digestive system is in a state of formation. The digestive ability of a child’s gastrointestinal tract is not yet developed enough to cope with large volumes of solid food. Well, what if undigested food is found in the stool of an adult? Should I be worried about this?
Normal or sign of a problem
It usually doesn’t occur to a healthy person to look for undigested food residues in the stool. The exception is situations when food pieces are visible to the naked eye. If a person experiences discomfort, difficulty defecating, or pain in the abdominal area, then you should consult a doctor and have your stool tested. The presence of undigested food in the feces of an adult can be both within the normal range and beyond it. How do you know which category your situation falls into? It is worth paying attention to your own feelings over the past few days and assessing how much plant food you eat per day.
For example, if the day before you ate a lot of vegetables, fruits, herbs, and coarse grain products, do not be surprised that you can see undigested food in your stool. The fact is that plant foods are rich in indigestible fiber. Consumption of such food in large quantities leads to accelerated movement of the food bolus through the intestinal tract. As a result, the gastrointestinal tract simply does not have time to digest even the food that it is capable of breaking down completely. Hence the remains of food in the stool. If your general health is not affected, there is no need to worry. But if you experience discomfort and the regular presence of visible pieces of undigested food in your stool, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms
Undigested food debris in the stool may be accompanied by the following clinical signs:
- abdominal pain - they can be cramping, aching, sharp, localization will also depend on the underlying factor;
- nausea, which is often accompanied by vomiting (in most cases, this symptom occurs immediately after eating);
- bad breath;
- heartburn, belching;
- flatulence, bloating;
- a feeling of fullness in the stomach even with a minimal amount of food consumed;
- an increase in body temperature, which will indicate an infectious or inflammatory process;
- weakness, malaise, lack of appetite;
- loss of body weight against the background of a general deterioration in health.
It should also be noted that if the patient already has a history of chronic gastroenterological diseases, then their relapse is possible.
Taking into account that such symptoms occur to varying degrees of severity in any gastroenterological disease, it is impossible to carry out treatment on your own, since such measures can have an extremely negative impact on health and lead to irreversible pathological processes.
About fiber
Plant fiber is essentially a mixture of complex polymer compounds, lignin and various polysaccharides, which make up all the membranes of plant cells. Such dietary fiber is not digested by gastrointestinal secretions. Some of them, namely pectins, gums, mucopolysaccharides, dissolve in water and are almost completely fermented in the intestines thanks to the microorganisms living there.
During the fermentation process, energy is released and beneficial microelements are absorbed. Digestible fibers in feces, if found, are in minimal quantities. Cellulose, another fiber polysaccharide, is only partially fermented. The intestinal microflora cannot influence lignin at all. Such insoluble plant fibers are eliminated from the body in the feces as undigested pieces of food.
It is thanks to fiber, its ability to irritate the intestinal walls, that the normal movement of the food bolus through the gastrointestinal tract and the subsequent removal of digestive waste occur.
Most fiber is found in grains, unrefined grains, legumes, nuts, vegetables and fruits. For normal peristalsis, it is necessary to regularly consume a sufficient amount of cereals and whole grain bread. Among vegetables, you should give preference to carrots, beets, cabbage, tomatoes, dill and other greens. Citrus fruits, apples, and apricots are rich in fiber, but bananas contain very little. If the content of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice is reduced, then the digestible fiber elements are not broken down, which is why undigested food appears in the feces in the form of fairly large pieces.
Causes of the phenomenon
The process of digestion of chewed food occurs due to the work of the gastrointestinal tract and under the influence of accelerated peristalsis in two ways: wave-like, or gradually, so the reasons that caused failures in the system may differ.
- In the first case, a failure occurs based on the nature and physiological characteristics of the body, manifested against the background of improper selection of food products or for other reasons, for example, swallowing unchewed pieces of food during meals.
- Pathological changes occur against the background of chronic diseases, where lientorrhea is one of the symptoms.
Physiological
The physiological causes of manifestations of lientorrhea include factors that do not cause absolutely any harm to the body and do not significantly affect the functioning of its organs.
- Functional dyspepsia. This type of manifestation is mostly the result of a negligent attitude towards a healthy lifestyle and a healthy diet. In addition to incomplete digestion of food, belching, pain in the upper part of the stomach and nausea are observed.
- As a side effect of medications. Some medicinal substances during the treatment of diseases can create conditions that inhibit the functioning of the digestive system by reducing secretion, which is responsible for the release of gastric juice and a number of enzymes.
- Dysbacteriosis. A downward change in the balance of microflora beneficial to the body can negatively affect the quality of food absorption.
Pathological
The category of pathological factors that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and create a number of disorders includes several chronic diseases.
- Pancreatitis.
- Gastroenteritis.
- Cholecystitis.
- Colitis.
In addition to the presence of food particles in the stool, other symptoms may be observed that directly indicate the development of the disease.
Typical causes for children
For manifestations of lientorrhea, characteristic causes are the presence of high-fiber ingredients in food, against the background of diarrhea and in chronic (hereditary) diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Doctors identify two main reasons that explain the situation causing disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract:
- The immaturity of the organs that are involved in the absorption of food is the retardation of their development or an excess of the amount of food that has to be processed. This often happens in children during infancy, especially at the moment when the baby is partially given foods containing vegetables and fruits with a high fiber content in the form of complementary foods.
- The second moment occurs during the period when the child, while processing food, does not completely chew it, which leads to large fragments entering the stomach - the organ simply does not have time to fully assimilate them.
If there are no other symptoms such as fever, diarrhea, pain or vomiting, parents should not panic. Only if such manifestations are observed constantly, you should seek help from specialists for clarification.
Stool analysis indicators
Consumed food, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, is subjected to chemical and mechanical processing. This is where water and nutrients are absorbed into the blood and lymphatic system, as well as the formation and removal of all undigested food debris from the body in the form of feces. Its density depends on how long it takes for the food bolus to pass through the entire gastrointestinal tract. During normal functioning of the digestive system, feces should not be too loose or too dense. If the consistency of the stool is very different from the norm, and its smell is too strong, this is a reason to take a stool test to determine the digestibility of food.
If a person is healthy, the coprogram should not contain mucus, blood, digestible plant fiber, as well as starch, a large number of muscle fibers and fats. And indigestible fiber in the feces of an adult can be in any volume. This indicator depends on your usual diet.
During the stool examination, all undigested particles are evaluated. It’s bad when digestible plant fiber is found in large quantities. This may indicate a number of problems:
- low stomach acidity;
- accelerating the release of bolus food from the intestines;
- pancreatic insufficiency.
Yellow feces with pieces may be the result of liver disease, gall bladder, pancreatic dysfunction, overeating dairy or coarse plant foods, which increases fermentation in the intestines. If undigested food is a mixture of seeds, seeds, peels and veins of plants, then everything is in order, such food is, in principle, indigestible for the human body.
Diagnostics
To determine why there is undigested food in the stool, the doctor prescribes a set of diagnostic measures.
The initial stage in any case will be a physical examination of the patient, during which the doctor:
- collects data on the current clinical picture - when symptoms began to appear, with what frequency;
- ascertains personal and family history;
- studies the patient's medical history.
The following laboratory and instrumental research methods are also carried out:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- general analysis of stool for occult blood and helminths;
- endoscopic examinations;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- pH-metry;
- PCR;
- ELISA;
- Helicobacteriosis test.
The diagnostic program presented here is approximate: it can be adjusted depending on the clinical parameters of the patient himself, as well as taking into account the data that was collected during the initial examination.
Based on the results of diagnostic measures, the cause of the appearance of such a symptom will be determined, and treatment tactics will be developed.
Causes and treatment
What should you do if you find pieces of undigested food in your feces (lientorrhea)? First of all, you need to understand why this happens. The cause may be a common stomach upset and subsequent diarrhea, after spicy food, for example, or eating unwashed vegetables and fruits. Diarrhea can also occur in a pregnant woman, as well as due to a gastrointestinal infection. In such a situation, the appearance of pieces of fruits, vegetables and other products in the stool is associated with less time for the food bolus to pass through the intestines, which is why the food is not completely digested.
If there are no symptoms of the inflammatory process, such as fever, chills, blood in the stool, treatment boils down to consuming plenty of fluid and prescribing a diet.
Other reasons for finding poorly digested food in the stool can be found out from the coprogram. A detailed study can reveal the presence of protozoa and bacteria, the culprits of the infectious process, as well as other elements indicating gastrointestinal diseases. Low stomach acidity is often associated with gastritis, hence the appropriate treatment in the form of enzymes and other drugs.
To summarize, it turns out that pieces of food in feces do not always indicate any digestive problems. However, it is worth thinking about your diet and additional examination if you feel discomfort in the abdominal area.
The appearance of undigested food residues
in an adult's stool may be the result of an upset stomach, an infection, or constipation.
But most often this is not a pathology - some types of fiber are simply not completely absorbed by the body, and this is the norm for it. In other cases, a healthy person should not experience lumps or pieces of undigested food during bowel movements.
Associated symptoms
Short-term lientorrhea, not associated with diseases of the digestive tract or other problems, usually remains asymptomatic. Slight heaviness in the abdomen and moderate flatulence may occur.
The following signs speak in favor of pathology:
- the appearance of a sharp and unpleasant odor of feces;
- severe bloating;
- pain around the navel and in the sides of the abdomen;
- rumbling in the stomach and flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- increase in body temperature (indicates an active inflammatory process).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Diarrhea from too much water
What could be the causes of this problem?
Several types of plant-based fiber are intended for human consumption – digestible and non-digestible. Each of these species can be found in feces
after the act of defecation.
Digestible fiber
. If it is observed in the stool, this indicates a lack of hydrochloric acid in the body, which is responsible for the breakdown of cells.
A low level of acidity causes pieces of fruits and vegetables to remain in the stool. Usually these are particles of carrots, potato tubers, grapes, and beets.
Accordingly, the process of assimilation of useful microelements does not occur from them. Normally there should be no digestible fiber.
Indigestible fiber
.
This includes grains, vegetable and fruit peels, legumes, and plant stems.
Products made from indigestible fiber are not affected by gastric juice
If there is not enough hydrochloric acid in the stomach, then there will be more particles of unprocessed food than in a healthy person. Then the process of removing feces from the intestines will be accompanied by diarrhea. The only items that do not fit into this category are elements of products that are not intended for food - fruit seeds, fruit cuttings.
Microscopy
The presence of protein indicates inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, polyps, ulcers and neoplasms. In a normal coprogram there is no protein.
Blood appears in the stool due to bleeding, which can be caused by helminths, tumors, ulcers, and polyps. Changed blood indicates bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, and unchanged blood indicates bleeding in the lower parts.
An increase in the level of stercobilin appears in the feces during hemolytic anemia. A decrease in this indicator is a sign of blockage of the bile ducts.
The appearance of bilirubin indicates dysbiosis and acute inflammatory processes.
The presence of mucus is a sign of intestinal infections (dysentery, salmonellosis, colitis). However, it is worth taking into account the age of the child, since in case of stool coprogram (decoding in children), mucus may be a variant of the norm (children under one year old).
The presence of pathological flora is a sign of dysbiosis.
In the stool coprogram (when deciphered in children), detritus, if its amount is below the age-appropriate norm, may indicate disturbances in the digestive process.
The presence of a large amount is a violation of the secretion or absorption of bile.
Unchanged - pancreatic pathologies.
The presence of starch grains - malabsorption syndrome, chronic pancreatitis.
Soap (of which normally there should be a small amount) - duodenal problems, pancreatitis, gallstones.
In the stool coprogram (decoding in children), leukocytes in large numbers indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Fatty acid. Not normally detected. If they are present in the stool, one should suspect enzyme deficiency, acceleration of intestinal activity and impaired bile outflow.
Plant fiber. If the fibers are insoluble (for example, vegetable peels, etc.), this is normal, but if there are soluble fibers in the stool, this indicates a lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Connective tissue fibers are normally absent. Their appearance is a sign of pancreatitis.
Increased levels of ammonia in stool are a sign of intestinal inflammation.
The presence of pathogenic bacteria - intestinal diseases and dysbiosis.
The pH of feces can be different (slightly acidic, slightly alkaline, neutral). This indicator depends on the person’s nutrition.
Food particles in stool due to dysbacteriosis
The development of pathology leads to deformation of the normal intestinal microflora - the number of pathogenic bacteria
, and the number of beneficial microorganisms decreases. At the initial stage of the disease, the balance between them is disturbed more and more, but this is not yet noticeable for the body.
If the immune system is normal, the balance between bacteria will be restored naturally. When dysbiosis develops further, pathogenic bacteria predominate in the intestinal microflora.
Then there is a decrease in appetite, a feeling of unpleasant taste in the mouth, bloating, vomiting, loose stools or constipation.
Then the intestinal walls become inflamed under the influence of pathogens and cannot absorb nutrients
and digest food completely.
Then its remains are observed in the feces of adults during bowel movements. If the disease is not treated, it will develop into a dangerous infection and reduce immunity.
Should I be concerned if I see undigested food leftovers?
Usually you see these particles in your stool and it is not a cause for concern. Some people may be concerned that they are not getting enough nutrients in their diet. However, the body is not designed to break down all forms of fiber.
If you eat more slowly and chew your food more carefully, you may end up with fewer food particles in your stool. Food that is chewed more thoroughly and in small pieces helps digestive enzymes break down the food.
Another option is to steam food, especially vegetables. By making foods softer, they break down more easily and maximize the absorption of nutrients.
Typically, it takes one to three days for food material to pass through the digestive tract and exit through the stool. If you notice food particles in your stool much earlier, it may indicate that your stool is passing faster than usual.
The stool should pass easily. It should not be hard or dry, although the appearance of the stool may vary from person to person. The general appearance of the stool should be soft and brown in color.
What should be the correct treatment?
Only a specialist in this field can reliably determine the cause and make a diagnosis, so you need to consult a doctor. If undigested pieces of food appear in the stool more than once, this is a reason to undergo a course of treatment.
In a single case, you just need to take a closer look at your diet
and lifestyle.
In the process of healing the body, it needs a diet that excludes from the menu foods containing coarse fiber, alcohol and carbonated water, and fatty meat.
The doctor prescribes antibiotics, antiseptic and antifungal medications.
To restore the intestinal microflora, Mezim-Forte and Creon are used. If you have loose stools with remnants of undigested food as a result of a lack of hydrochloric acid, drink Omeprazole to stop progressive gastritis.
If there is a rapid evacuation of undigested stomach contents, then this is a sign of inflammation
against the background of colitis or gastroenteritis. Then hospitalization and inpatient treatment with the use of antibiotics, Regidron and Analgin are needed.
When the reason for stool with irregular consistency lies in the presence of coarse fiber products in the diet, it is enough to simply stop eating them.
Treatment results
- normalization of the intestines and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- eliminating the reasons why stool with undigested pieces of food was formed;
- prevention or treatment of already occurring complications of lientorrhea;
- restoring the patient’s well-being and improving his quality of life.
To make an appointment with gastroenterologists at the First Family Clinic, you can call the phone number listed on the website or contact us online. Our clinic uses advanced diagnostic methods using expert-class equipment from leading medical equipment manufacturers in the USA and Japan. This ensures high accuracy of examination results and, accordingly, correct treatment and its timely initiation.
Reception is carried out at the multidisciplinary centers of the clinic at the addresses: Kamennoostrovsky Prospekt, 16 (metro Gorkovskaya, metro Petrogradskaya, Petrogradsky district) and Kolomyazhsky Prospekt 36/2 (metro station Pionerskaya, metro station Udelnaya, Primorsky district).
What should you do if you find leftover lunch in your stool?
The digestive organs are capable of digesting certain amounts of food consumed by a person. If you eat more than normal
, the digestive system will not be able to cope with an excess of food. When a stressful state is observed, the process of processing the contents of the stomach becomes more difficult.
What to do in such cases
:
- try to chew it more thoroughly while eating;
- eat at frequent intervals, but in small portions;
- do not overeat;
- give dishes more aesthetics so that they look more appetizing;
- do not drink liquid while eating or immediately after it;
- You can drink water an hour and a half before meals, but no more than a glass;
- stop taking medications
that the doctor did not prescribe, so as not to worsen your health condition; - do not read during breakfast or lunch and do not watch TV, so as not to provoke the appearance of a stressful state;
- stop eating in a hurry;
- make meals separate - consume proteins only with proteins, carbohydrates - with carbohydrates.
You can try to normalize the functioning of the digestive organs using alternative medicine methods.
Treatment
The treatment program is compiled individually. As a rule, to eliminate such disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, conservative therapeutic measures are sufficient: taking medications and following a diet.
At the same time, it should be noted that some pathological processes, for example, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, cannot be completely eliminated. However, provided you follow your doctor's recommendations regarding nutrition and medication, you can achieve a long stage of remission.
What is the best herb to brew?
To eliminate the symptoms of dysbiosis, diarrhea and get rid of problems with the process of digesting food
, it is recommended to take herbal infusions that relieve inflammation and restore sensitive intestinal microflora.
- Eucalyptus infusion. It is effective for indigestion, constipation, metabolic disorders in the body and problems with food processing. To prepare it, three tablespoons of dried leaves are brewed with 2.5 glasses of hot water and left until cool. Drink a third of a glass before meals.
- Mint decoction. Leaves of the plant - 3 tbsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water, cover tightly
and infuse. After cooling, take the drug ½ glass every 4 hours. - Chamomile officinalis. Pour a couple of tablespoons of dry raw materials into a mug of hot water, cover with a lid and a towel. After straining, consume 70 ml during an exacerbation.
- Brew a herbal mixture of sage, chimney and chamomile at the rate of 3 tbsp. per glass of mixture. Drink instead of tea for 2 months.
Take care of your digestive system and it will function properly!
Why undigested food appeared in the feces is a question that worries those whose tests have shown that their feces contain food remains.
For various reasons, undigested foods can appear in the stool of both adults and children.
Folk remedies
When using alternative medicine, it is important to consult a specialist. This is necessary in order to know in which direction the treatment should be carried out.
Popular herbal infusions that restore intestinal microflora:
- mint – 3 tbsp. l. The leaves of the plant are combined with 200 ml of boiling water. After cooling, use 100 ml 3 times a day. Mint decoction reduces nausea, has a choleretic effect, eliminates bloating and discomfort, stimulates the production of the hormone estrogen;
- chamomile – 2 tbsp. l. dried flowers are poured with 200 ml of hot water, sealed tightly and allowed to brew. You need to drink the medicine 70 ml 3-4 times a day. The product is a wonderful antiseptic;
- eucalyptus - 2 tbsp. l. dried leaves of the plant are brewed in 300 ml of boiling water. After cooling, the medicine is filtered. Take 100 ml before meals;
- infusion of chamomile, sage and smoke - 3 tbsp. l. a mixture of herbs in equal proportions is combined with 200 ml of boiling water. Use for 2 months instead of tea.
Sometimes adjusting the diet and using folk recipes is enough to eliminate the pathology.
You can help your body restore digestive function through treatment with folk remedies, but you should still consult a doctor first.
Undigested food particles in feces are not considered a pathology if you feel normal and eat fiber - some types of fiber are not completely absorbed by the body and are excreted unchanged. Lientorrhea becomes a pathological sign when other symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction are associated.
Popular herbal infusions that restore intestinal microflora:
- mint – 3 tbsp. l. The leaves of the plant are combined with 200 ml of boiling water. After cooling, use 100 ml 3 times a day. Mint decoction reduces nausea, has a choleretic effect, eliminates bloating and discomfort, stimulates the production of the hormone estrogen;
- chamomile – 2 tbsp. l. dried flowers are poured with 200 ml of hot water, sealed tightly and allowed to brew. You need to drink the medicine 70 ml 3-4 times a day. The product is a wonderful antiseptic;
- eucalyptus - 2 tbsp. l. dried leaves of the plant are brewed in 300 ml of boiling water. After cooling, the medicine is filtered. Take 100 ml before meals;
- infusion of chamomile, sage and smoke - 3 tbsp. l. a mixture of herbs in equal proportions is combined with 200 ml of boiling water. Use for 2 months instead of tea.
A consultation with a doctor is necessary in order to find out in which direction the treatment should be carried out. In one case it is necessary to normalize intestinal motility, in others it is necessary to stimulate the production of enzymes.
Pathology or normal?
Indigestion of food does not always indicate insufficient functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Inadequate digestion of food (lienterea) may be the result of an infectious disease, constipation, or indigestion.
But most often, the appearance of undigested pieces and fragments of individual products in feces is not a pathology, since not all of their parts are able to be digested in the human gastrointestinal tract.
Why might undigested food appear in the stool of an adult with a completely healthy gastrointestinal tract?
To answer this question, you need to have at least an approximate idea of what happens to different foods in the stomach and intestines.
There are two types of fiber in plant foods: digestible and indigestible. The first should not appear in the feces undigested.
If it is nevertheless found in excrement almost unchanged, this indicates insufficient production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
This is also evidenced by the discovery of almost whole pieces of vegetables and fruits in feces: carrots, beets, potatoes.
Bran, peel, seeds, membranes, and stem fibers contain indigestible fiber.
These are the coarsest parts of plants, covered with a double shell and consisting of cellulose and lignin, which are unable to be digested in the human gastrointestinal tract.
Indigestible fiber in stool does not indicate pathology - this is an absolutely normal phenomenon.
In addition, the stomach and other digestive organs can only handle a certain amount of food at a time.
When overeating, the body simply does not have enough enzymes and enzymes, and some of the products will leave the intestines undigested.
The digestion process can be disrupted due to poor nutritional culture, when a person immediately after a heavy lunch begins to engage in physical labor, eats during illness or under stress. Meals should take place in a calm environment.
After eating, you need to rest a little - in this case, the body will be able to direct the necessary resources to digestion, and the intestines will leave a fully digested breakfast, lunch or dinner.
If undigested food appears in the stool regularly, this may be a signal of poor functioning of the pancreas, stomach or small intestine. It is in these organs that the breakdown of foods into individual proteins, fats and carbohydrates occurs.
Indigestion in children
If abnormalities of this kind are detected in a child, this may alert parents. In fact, it all depends on age. During the first year of life, food may not be completely digested due to the fact that the gastrointestinal tract is not fully formed. This is precisely the reason for the incomplete digestion of food even by very young children who eat exclusively milk and formula. With the introduction of a new product into the diet, the likelihood of undigested food appearing in the child’s stool increases.
Reasons for the appearance of undigested food in the stool of an adult
Lienterea in an adult most often appears due to chronic inflammatory diseases of the stomach (gastritis) or pancreas (pancreatitis).
These pathologies require qualified and urgent treatment, since chronic inflammatory processes worsen over time and lead to tissue death. The case may end with an ulcer, diabetes, or oncology.
Therefore, the appearance of undigested food in feces must be taken seriously. To find out what kind of pathology this symptom signals, you will have to conduct additional studies, including a general blood test.
After collecting an anamnesis and receiving the results of primary tests, the gastroenterologist will most likely issue a referral for one of the instrumental studies: FGDS, ultrasound or computed tomography.
It makes it easier to make a diagnosis by knowing which food is not digested: carbohydrate or protein. To break down proteins and carbohydrates into simple substances, the stomach and pancreas secrete different enzymes.
In addition, the digestion of proteins, carbohydrates and fats occurs in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
This allows us to draw a conclusion from the composition of undigested food about which organ is working poorly.
If the examination reveals a disease of the stomach, small intestine, pancreas or liver, the doctor will begin immediate treatment.
Treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract consists of taking antibacterial medications, enzyme and anti-inflammatory therapy.
When treating any gastrointestinal disease, it is necessary to follow a diet of varying degrees of severity.
General principles of dietary nutrition for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- thorough processing of products (coarse and indigestible parts are removed: films, tendons, seeds, peel, stalks);
- food is prepared in certain ways - stewed, boiled, baked, steamed;
- fatty, spicy, sweet, salty and sour foods are excluded from the diet;
- complete ban on alcohol and smoking;
- introduce fermented milk products enriched with lacto- and bifidobacteria into the menu;
- food is taken in small portions five to six times a day.
The listed measures help eliminate the causes of undigested food in the stool of an adult.
Principles of therapy
If lientorrhea associated with pathology of the digestive tract is detected, treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist. Therapy is based on diet and medication.
General recommendations during exacerbation:
- frequent split meals - small portions 5-6 times a day;
- reducing the total calorie content of food to 2200 kcal/day;
- rational distribution of meals throughout the day (minimum in the evening);
- consumption of mechanically processed food (priority is given to pureed cereals, purees, boiled meat and fish);
- refusal of fried, spicy and salty foods;
- limiting the amount of salt to 5 g per day;
- reducing the proportion of extractives in food.
We recommend reading:
Bacteriological culture (tank culture) of feces: essence, preparation and analysis
After the exacerbation subsides, the diet is expanded to include foods rich in protein. The total calorie content of food increases to 2600-2800 kcal/day.
Medicines
Conservative treatment is based on the prescription of enzyme preparations that facilitate the digestion of food and normalize the functioning of the digestive tract. The selection of specific medications is carried out by a doctor, taking into account the severity of the pathological process. The dosage and duration of administration are determined individually.
Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- antibiotics for detected Helicobacter pylori infection;
- adsorbents to remove toxins from the intestines;
- probiotics to restore the microflora of the digestive tract;
- symptomatic drugs to relieve pain, heartburn, flatulence, etc.
We suggest you read: What can an adult eat if they have diarrhea: can they eat if they have diarrhea, the basics of nutrition if they have an upset stomach.
In case of severe damage to the digestive tract, surgical treatment is indicated.
Indigestion of food in a child
Why do particles of undigested food appear in children's stool? The reasons for this phenomenon depend on the age of the baby.
In a child under one year old, food may not be completely digested due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract.
For this reason, even very young children who eat only milk and formula may suffer from incomplete digestion of food.
When a new complementary food is introduced into a child's menu, the likelihood of undigested food appearing in the stool increases.
In addition, a child’s gastrointestinal tract is much shorter than that of an adult, and food spends less time in it, which is why some of its fragments do not have time to be digested.
Undigested food can be visible in the child’s stool with the naked eye as whole pieces of vegetables, fruits, cookies, etc., eaten the day before.
In other cases, undigested fragments can only be detected by laboratory testing.
This is how lactase deficiency is detected - a pathology in which undigested carbohydrates and lactose are found in children's stool.
The appearance of undigested pieces of food in a child’s stool should alert you only if this phenomenon is accompanied by symptoms of dyspepsia:
- loose stools;
- bloating;
- intestinal colic;
- impurities in feces (mucus, etc.).
These symptoms indicate an imbalance in the composition of the intestinal microflora. Dysbacteriosis cannot be ignored - it must be cured. Otherwise, disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems of the body will progress.
In addition to dysbiosis, the causes of dyspepsia can be intestinal infection and improper diet. To prevent these phenomena, new dishes are introduced into the child’s diet gradually.
All products must be absolutely fresh. Eggs need to be boiled for a long time, milk needs to be boiled. It is better to chop meat and fish and give it in the form of puree - this will reduce the content of muscle fibers in the child’s feces.
Vegetables and fruits are washed and rinsed with boiling water. Herbal products should not show any damage: darkened or softened areas, specks, etc.
If, despite following all the rules of feeding and hygiene, particles of undigested food still appear in the child’s stool, then you must tell your pediatrician about this.
Only a doctor can assess the degree of danger. Based on the accompanying symptoms, the doctor will give either recommendations for correcting the child’s diet or a referral for laboratory testing of stool.
Now you know how a digestible product differs from an indigestible one and what you need to do if fragments of food eaten the day before appear in the stool of a child or adult.
Plant fiber is one of the most important nutritional elements found in fruits, legumes and cereals. Belonging to the group of disaccharides (or complex carbohydrates), it has the form of fibers that form the cell wall of plants. You can understand what this substance looks like by breaking a celery stalk at the thickest part. The fibrous threads stretching between its two ends are dietary fiber.
Many nutritionists advise including foods rich in this useful substance in your diet, as their consumption promotes weight loss, improves intestinal motility, accelerates digestion, and helps absorb toxic substances, mucus and fats. The daily fiber intake for a healthy person is 25–30 grams.
To date, two types of dietary fiber have been identified.
- Digestible plant fiber - pectin, resin, hemicellulose. The cells have a round shape, a thin shell and are interconnected by a pectin layer. The process of breakdown of intercellular connections begins in the stomach and continues in the duodenum. When there is a lack of hydrochloric acid, dietary fiber is present in the feces in the form of cell groups, resulting in a lack of nutrients in the body.
- Plant fiber is indigestible - this includes the skins of fruits and vegetables, cellulose and lingin. These products have a thick double-circuit shell; its cells cannot be digested and are excreted from the intestines almost unchanged, having previously absorbed cholesterol, toxins and bile acids.
What foods contain plant fiber?
Which plants have the most plant fiber? Products containing high levels of these biological components include the following:
- whole grains – contain many soluble fibers rich in beta-glucans. These adhesive substances have immunomodulatory properties and help reduce blood cholesterol levels;
- bran - waste from flour milling, consisting of 40 percent coarse fibers;
- legumes – lentils, peanuts, beans, beans;
- fruits – the pectin layer is present in all fruits;
- vegetable crops - here preference should be given to spinach, cabbage, celery;
- flax seeds – one tablespoon of these seeds contains approximately 7 grams of fiber;
- Buckwheat is almost twice as high as other grains in terms of insoluble fiber content. Five glasses of porridge completely fill the required daily requirement.
Indications and contraindications for taking plant fiber
Science has long known the numerous beneficial properties of dietary fiber, which are indications for its use. These include:
- lowering blood cholesterol levels;
- prevention of stone formation in the gallbladder;
- slowing down the absorption of carbohydrates - useful for people suffering from type 2 diabetes;
- normalization of intestinal microflora, stimulation of peristalsis and prevention of constipation;
- absorption and removal of harmful substances from the body: heavy metals, toxins, radionuclides;
- regulation of biliary function of the liver.
In addition to the undeniable benefits of fiber, there are a number of contraindications for its intake, in particular the acute stage of gastritis, peptic ulcer, colitis and enteritis of infectious etiology. As the inflammation subsides, you can resume taking cereals, legumes and fruits, after consulting with a gastroenterologist.
Also, an excess of this substance interferes with the absorption of calcium and iron, and can also provoke increased gas formation (flatulence).
What to do if plant fiber is not digested?
The digestive system cannot break down insoluble fiber due to the lack of special enzymes. Therefore, the presence of grain epidermis, plant particles and fruit peels in the stool is normal. On the contrary, the presence of digestible plant fiber in feces indicates low acidity of gastric juice, accelerated elimination of food bolus from the intestines and diseases of the pancreas.
In this case, a consultation with a doctor is necessary, during which the doctor will collect the patient’s medical history and decide on a list of diagnostic measures. Based on the latter, it will be possible to draw a final conclusion about the root cause of the pathology and draw up a program for its treatment.
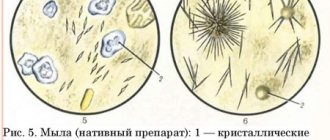
They are salts of fatty acids that are formed with a tendency to constipation and delayed excretion and evacuation of feces and are normally present in small quantities.
Soaps are presented in the form of lumps that cannot be detected by visual inspection, and are determined only by microscopic examination.
Dysbacteriosis
The above symptoms indicate an imbalance in the intestinal microflora. It is impossible to ignore dysbiosis (it will go away on its own), it must be treated, otherwise the disorders will worsen more and more, and be complicated by the addition of other diseases. In addition to an imbalance of microflora, the cause of dyspepsia can be an intestinal infection or an incorrectly selected diet.
Meat and fish products must be pureed, this reduces the content of muscle fibers in the child’s excrement. Vegetables and fruits should be washed and rinsed with boiling water. Products of plant origin should not have any damage: darkening or soft areas. If, despite carefully observing all these rules, food particles are still found in the child’s stool, then the pediatrician must be informed about this. He will assess the degree of danger and, based on the accompanying symptoms, determine further actions.
How to treat the disease so that undigested food remains no longer appear in the stool.
- Migraine symptoms and causes in women
- Vegetative vascular dystonia causes
- Causes of heaviness in legs in men
- Tremor inside the body. What causes internal tremors in the body and how to get rid of it. The whole body shakes: reasons
Why do soaps appear in feces?
The reasons for the appearance of fatty acids and soap in human feces may be such pathologies as impaired patency of the common bile duct, deficiency of pancreatic enzymes, as well as fermentative dyspepsia in the intestines.
Impaired flow of bile into the intestinal lumen is most often associated with blockage of the common bile duct or papilla of Vater, through which pancreatic enzymes enter the cavity of the duodenum. This situation occurs with cholelithiasis, when the cause of obstruction of the duct is a gallstone, as well as with cancer, when the duct is compressed from the outside, for example, cancer of the head of the pancreas or Vater's nipple.
Insufficient supply of pancreatic digestive enzymes causes inhibition of the breakdown of fats received from food. The most common cause of decreased secretory activity of the pancreas is acute and chronic inflammatory lesions of the organ, such as pancreatitis.
Fermentative dyspepsia is an intestinal pathology in which normal digestion in the intestinal lumen is disrupted. Most often it occurs when you overuse fatty foods, when your own digestive enzymes are not enough to ensure the complete breakdown and absorption of all incoming fats.
The appearance of soap in feces is characterized by a tendency to constipation, since it takes time for the formation of this component from fatty acids and neutral fat.
Constipation in bedridden elderly people
04.03.2020
All about caring for bedridden patients at home
04.03.2020
Radical mastectomy as a major operation to remove the breast
04.03.2020
Diagnostic scheme
To determine the cause of lientorrhea, an examination is prescribed:
- Coprogram. Normally, feces should be well-formed, without a strong odor or pathological impurities. The appearance of protein, connective tissue, pus, blood, fatty acids and starch indicates the development of pathology.
- General clinical blood and urine tests. Allows to identify the inflammatory process and concomitant pathology.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. It is used for an initial assessment of the situation and making a preliminary diagnosis.
- Endoscopic studies. Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are used for visual assessment of the intestinal mucosa, detection of tumors, polyps and other conditions.
Based on the results of the diagnostics, the optimal treatment tactics will be selected.