Hepatitis is an inflammatory process of a viral nature or caused by exposure to toxic poisons: alcohol, drugs, medications. In addition, inflammation can develop into an autoimmune disease. The danger lies in the fact that people do not notice the progression of the disease, and the clinical symptoms are so insignificant that the patient, without testing, will not know about the presence of the deadly virus in the body.
The inflammatory process is also dangerous because, by triggering autoimmune mechanisms in liver cells, it destroys healthy organ tissue. Detection of the disease in its final stages often cannot be treated. Inflammatory processes are divided into types: C, B, A, G, E, with their own characteristics and diagnostic methods.
Distinctive features of hepatitis
Previously, in medicine, all types of liver infections were called Botkin's disease. The nature of the disease was considered to be as follows: inflammatory processes were caused by a dangerous type of viral infection. Only in the 20th century did scientists discover that Botkin’s disease was an inflammatory process with an individual nature of occurrence, its own pathogen, method of infection and treatment regimen.
Now in medicine this viral infection is called “hepatitis”, and then a letter is added identifying the order of discovery of viruses.
People often pronounce the name of the disease like this: “Hepatitis C”, “Hepatitis G”. Despite the division into subtypes, the disease shows a similar clinical picture. The microbe that causes inflammatory processes in the liver exhibits common hepatotropic features, leading to damage to tissues and metabolism in the liver. Each virus disrupts the functioning of an organ in its own way.
Different subtypes of the disease manifest themselves in different ways in the human body; some include individual chronization of processes. The most mysterious and interesting type of liver infection is rightfully considered C, which has long remained a mystery to medicine. And even now, this type of liver infection has not been fully studied and keeps unsolved secrets, which makes the disease unpredictable.
Viral hepatitis C
Inflammation of the liver, caused by all kinds of viral infections, does not show gender predisposition. Both women and men get sick equally. The severity of the disease does not differ between both sexes. The only “but”: pregnant women suffer the symptoms of hepatitis more severely than others.
In addition to the poor health of the mother, the virus can negatively affect the fetus and the further condition of the child even after birth. The fetus is especially at risk in the last months of pregnancy and when the disease is severe.
Any type of inflammation of the liver tissue is similar in clinical picture. We will try to carefully consider and study the general characteristics of each for further recognition of the virus in the human body.
It is possible to become infected sexually with any type of viral liver disease, even through saliva, although most often hepatitis B and C are considered a “sexual” disease. Other pathologies in the liver are usually kept silent due to their less destructive impact on health. The most dangerous viruses for humans are viruses of types B and C.
In addition to viral liver diseases, there are types:
- alcoholic;
- autoimmune;
- toxic.
We will consider each of the hepatitis identified in medicine in the article. It is important to identify diseases in the early stages of their course.
Features of treatment of hepatitis C in women
When the first symptoms of the disease occur, you need to consult a doctor, do tests, and confirm the diagnosis. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. The stage, general condition, and possible complications are taken into account. In uncomplicated cases, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. Severe liver manifestations, bilirubin intoxication, and other pathological conditions are indications for hospitalization.
This is interesting: Is it possible to become infected with hepatitis C through a needle prick?
Treatment is aimed at supporting the liver and restoring full functionality. Antiviral therapy is carried out, which involves taking medications with direct and indirect action. The classic method of treatment is the simultaneous use of Ribavirin and Interferon. The average course duration is 12 weeks.
Innovative antiviral drugs are used to treat hepatitis. Their action is aimed at eliminating the ability of the virus to reproduce. The concentration of pathogenic microorganisms drops, and the organ is gradually restored.
Treatment involves following a strict diet. Fatty foods, fried, spicy, salty foods are excluded from the diet. It is prohibited to eat canned meat, fish, sausages, smoked meats, and drink alcohol. The daily diet is based on easily digestible foods with low fat content. A split diet and plenty of drinking are provided.
Routes of transmission of viral hepatitis
Liver viruses are divided into appropriate types depending on the method of transmission of the disease from one carrier to another, as well as the damage caused to tissues when entering the human body. Certain groups of hepatitis can be transmitted through everyday contact (through toys, appliances, food), are expressed quickly and recovery occurs quickly. After such hepatitis, as a rule, there are no terrible consequences.
The second types of liver infections are called “parenteral”. They are recognized as the most dangerous, capable of changing structure, resistance to drugs, quite often becoming incurable and settling in the organ forever, gradually turning a healthy liver into a cirrhotic or cancerous one.
The general classification of hepatitis divides them according to the mechanism and type of spread of infection into two sections, with the indicated routes of transmission:
- A disease that has a fecal and oral method of infection (type A and E viruses). It is transmitted by airborne droplets in the household environment.
- Diseases spread mainly through the blood, so-called parenteral hepatitis types B, C, D, G. It is possible to become infected in other ways, but the hemopercutaneous method is considered the leading one.
In addition to careless blood transfusion or non-compliance with the rules of medical hygiene of the instruments necessary for manipulation (an untreated needle for grafting, for example), transmission of inflammatory liver infections of types B, C, D, G by other means is common:
- All types of body modification procedures (body piercing, body tattooing, ear piercing) performed by unskilled workers in unsanitary conditions that do not meet the required standards.
- The use of one needle by many people, a method of transmission of hepatitis, is common among drug addicts.
- The spread of the virus through sexual intercourse is mainly hepatitis type B. C is quite rarely transmitted through sexual contact.
- Infection from mother to child. The presence of HIV or a serious form of hepatitis in the last months before childbirth significantly increases the risk of a child being born with congenital hepatitis.
More than 45% of patients hospitalized with hepatitis become infected in an unknown manner that they cannot remember. By the way, breastfeeding does not transmit liver infections from one person to another. Mothers with hepatitis may not be afraid to feed their baby breast milk.
All of the listed types are interconnected, for example, oral-fecal, household, and water methods follow from one another. Therefore, it is possible to become infected with hepatitis B, C through sexual contact or the parenteral method.
Risk groups among women
The disease is provoked by viral microorganisms. There are 8 known genotypes of viruses, which indicates a high adaptive capacity of the infection. Pathogenic microorganisms survive in unfavorable conditions and have low sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and antiseptics.
The main mechanism of distribution is parenteral. From an infected organism, the virus infects a healthy person. Infection occurs through blood, rarely through other biological fluids. On average, the incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months.
All women have a risk of infection, but certain categories have an increased risk of infection.
Risk groups include:
- Patients who have undergone major surgery (including caesarean section)
- Medical workers, laboratory personnel
- Housing and communal services employees
- Women whose family members are infected with the virus
- Patients who received blood transfusions
- Women who are promiscuous
- Persons in prison
- Injecting drug addicts
The infection can penetrate through skin lesions when performing cosmetic and medical procedures with non-sterile instruments. Infection through unprotected sexual contact and transmission to the child during childbirth is possible.
This is interesting: Test strips for hepatitis C: deciphering the results
Symptoms of a diseased liver
After the virus enters the liver tissue, it manifests itself in a different period of time depending on the form of the disease. Eg:
- Hepatitis type A shows its first signs 2-4 weeks after infection.
- Hepatitis B stays in the body without symptoms for two months, sometimes up to six months.
- Hepatitis C is the most secretive and serious enemy for humans. It can appear 2 weeks after infection or hide in the human body for many years, making it a potential carrier of a serious and dangerous infection for healthy others.
You can find out about problems with the liver by identifying the clinical symptoms of the inflammatory process in the tissues of the organ:
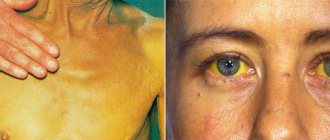
- Change in body temperature. It is with this deviation from the norm and other influenza symptoms that hepatitis type A begins. The pathology is also accompanied by muscle pain, headache, and muscle spasms. When HBV infection is activated in the human body, the body temperature begins to rise, but hepatitis C is not always accompanied by hyperthermia.
- Jaundice in various variations. The symptom appears a couple of days after the onset of the disease. Moreover, jaundice either intensifies the symptoms or weakens them to the initial state. The symptom is observed mainly with inflammation of the liver type A. With C or alcohol-toxic hepatitis, the symptom is not recorded at all. With these diseases, the rich yellow color of the skin becomes not a sign of a speedy recovery, but, on the contrary, calls for alertness.
- Skin rash and itching. Characteristic of cholestatic types of inflammation in the liver. Symptoms are manifested by the accumulation of foreign acids due to damage to the liver tissue and injuries to the ducts.
- Significant decrease in appetite. It is detected in all types of hepatitis at different periods of disease activation.
- Feeling of heaviness under the right hypochondrium. Sometimes the liver and spleen increase in size, but this is typical only for serious forms of hepatitis.
- Gag reflexes and nausea. Manifestations begin in the last stages of the disease or when the disease is severe.
- Malaise, constant fatigue. The patient feels lethargic and lacks physical activity.
- Joint pain.
- Dark urine, colorless feces. The urine becomes dark brown, similar to dark beer, and the stool becomes discolored. These are the main signs of any hepatitis.
- Increased laboratory parameters. Bilirubin, AST, and ALT samples increase two to three times, depending on how severe the stage of the disease is. The number of platelets in the blood decreases.
According to severity, the following types are distinguished:
- Mild form of flow. Most often, this type of disease is recorded with hepatitis type C. There is no jaundice, body temperature is within normal limits or slightly increases, there is heaviness in the right hypochondrium, and appetite decreases.
- The average form of the disease. Symptoms are present in a mild form, but there are also severe ones - joint pain occurs, occasionally vomiting, nausea, and no appetite.
- Severe form of hepatitis. All possible symptoms of the inflammatory process are intensified.
- The most severe form of the disease is fulminant. Characteristic of cases when a number of types combine into one severe inflammation of the liver tissue. As a result of the accelerated course of superinfection, liver failure occurs, and then the death of the patient.
Hepatitis, dangerous in domestic conditions
At home, we are faced with common types of liver hepatitis, which reveal an oral, fecal nature of spread from one carrier to another. This is hepatitis A. Hepatitis E is also classified as a household virus.
Let us first consider the distinctive characteristics of these types of inflammatory infectious processes of the body’s “filter”. Inflammations transmitted in everyday life, through saliva, through a kiss, or by airborne droplets, are dangerous.
Hepatitis A
Type A liver inflammation is considered a highly contagious infectious disease. Before the types of hepatitis were identified, it was simply called infectious or Botkin’s disease (when they didn’t even know about hepatitis B).
Hepatitis B at that time was presented in serum form. The virus that causes the disease is microscopic in size, but is highly resistant to antibodies and also contains RNA. Although scientists say that the pathology is easily picked up by carriers of any age, it appears more often in children over one year of age.
Infectious inflammation, which affects the lining of the liver and triggers infectious processes, mainly ends with the complete recovery of the patient with the acquisition of additional stable immunity to the virus. The transition of hepatitis A, caused by an infectious pathogen, to a chronic form is extremely rare in practice.
Hepatitis E
This infectious disease also contains RNA, reproduces well and lives in water. There is a high probability of contracting the disease from a potential carrier of hepatitis E - through fruits, vegetables and other food products that have not been heat-treated. The transmission option is highly probable. Carriers of hepatitis E become young people in the range of 15-30 years. The most extensive outbreaks of the disease occur in Central Asia and the East. In Russia, virological hepatitis E practically does not occur.
The possibility of spreading the disease through household means cannot be ruled out. The chronic form of hepatitis E has not yet been encountered in medicine.
Features of the disease
Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or biological fluids (menstrual and vaginal discharge, saliva, semen), which become infectious long before the first symptoms. A person may not even realize that he is infected and transmit the virus to healthy people.
The virus itself has the ability to survive outside the human body for about a week, and upon penetration into the body, cause an infection.
The incubation period lasts on average 2.5 months, maximum six months from the moment of infection, after which hepatitis most often becomes chronic.
Hepatitis B and resulting hepatitis D
The HBV type virus, or the so-called serum infection, is a pathogen containing DNA, exhibits a complex component and chooses the human liver environment to inhabit. To take root in the tissues of a completely healthy person, the slightest drop of type B infection is enough. Therefore, the disease is easily transmitted not only through medical means, but also through sexual intercourse, as well as to a child whose mother turned out to be a carrier of the virus during pregnancy.
The course of hepatitis B is extremely difficult to predict. A number of variants of the course of the disease are named. Options for the development of events:
- The patient is simply a carrier of infection.
- The virus causes a complication called liver failure, which often takes a person’s life as a result.
- The development of a chronic process leads to cirrhosis of the liver and the initial stage of cancer, and then death. It is almost impossible to cure the chronic type in the final stages. The last stage means the beginning of irreversible processes in the body.
The incubation period for inflammation of variety B can last from a couple of months to six, and the period of acute viral infection entails the following symptoms, such as:
- Headache, elevated low-grade body temperature.
- Weakness, malaise, the person is left without strength.
- Joint pain.
- Vomiting appears, constantly nauseating, which leads to a complete lack of appetite.
- Rash on the body, itchy skin.
- Heavy sensation under the right hypochondrium.
- The size of the liver and spleen increases.
- Yellowness appears on the skin, in other words – jaundice.
- The main indicator of the presence of the virus in the body is discoloration of stool, as well as darkened urine color.
Now the virus has been modernized, sometimes severe forms of the disease occur. The interaction of two viral hepatitis types B and D is especially dangerous for human life. Previously, virus D was considered a delta infection. It could not exist without the HBV pathogen.
It is possible to become infected with several hepatitises at the same time. Hepatitis D and B activate co-infection in the body of sick patients. But if type D viral cells enter an organ already infected with hepatitis B, in 100% of cases the development of superinfection begins.
In this case, the patient experiences all sorts of symptoms of virological liver disease in an acute form. As a rule, this type of infection develops into fulminant infection, which entails the death of the carrier in the shortest possible time.
When to see a doctor
Hepatitis C in women, the symptoms of which depend on the form of the disease, is the most dangerous of all types of hepatitis. It can lead to severe liver dysfunction, so you should be more attentive to the condition of your body in order to identify the first symptoms.
The main sign of liver disease is pain in the right side. Even if it is absent, but there are other symptoms (the most common are lack of appetite and weight loss, yellowing urine, constant fatigue), then you should definitely visit a doctor.
He will prescribe the necessary tests and studies and write out referrals to specialized specialists: a virologist, an infectious disease specialist and a hepatologist (the latter doctor treats liver diseases).
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can not only prevent the development of hepatitis, but also diagnose other pathologies of the body.
Hepatitis C is the most common type of viral liver infection
Known type C infection is a small virus with incredible persistence in the human body. The infectious object is an RNA encoding five non-structural and three structural proteins. During the development of the inflammation process, the necessary antibodies are formed to them. Looks like a standard microbe.
Hepatitis type C
The pathogen of this type is highly resistant in almost any habitat, tolerates freezing and dry environments, but in microdoses is not capable of infecting a healthy person. The risk of infection from a sexual partner or to a child from the mother is minimal. However, with additional factors present during sexual intercourse, the possibility of infection cannot be ruled out. The risk of infection increases the presence of another STI, for example, HIV infection. Or if there is damage to the skin.
The effect of a viral infection in the liver environment is difficult to predict. It can hide for a long time, being in minimal quantities, and then such “hiding” leads to the development of a chronic process in the human body. Then the virus develops into a severe form, which leads to other dangerous consequences of infection - cirrhosis of the liver and the initial stage of cancer.
The main danger of a disease called hepatitis C is its ability to hide for a long time without symptoms or other associated factors. Even blood tests do not always detect infection in its early stages.
It happens that a dangerous pathogen immediately begins to damage the liver parenchyma. Then they expect the first manifestations of symptoms within a couple of weeks.
The acute course of the disease begins without signs of jaundice. Accompanying symptoms:
- general weakness in the body;
- joint pain;
- nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite;
- fluctuations in laboratory parameters of bilirubin and other liver enzymes.
The patient feels heaviness, tingling in the liver area, observes discoloration of stool, darkening of the color of urine. But pronounced signs of inflammation are not typical for this type even in the acute phase. Early diagnosis of type C infection is possible only using a special method:
- conducting an enzyme immunoassay that detects antibodies in the patient’s body;
- running a polymerase chain reaction to detect RNA infection.
What is hepatitis G?
Hepatitis G today is considered the most mysterious virus among such inflammations. The causative agent is single-stranded RNA infection. The virus has a number of genotypes. Hepatosis of several varieties is similar in structure to its “brother” - infection of variety C.
One of the species chose Africa for its habitat and is not found anywhere else. The second has spread across the planet. The third and fourth chose mainly the southeast of Asia as victims, the last variety took root in the south of the African continent.
Viral hepatitis is spreading in Russia, and there are people who are sick. According to the main modes of transmission, the G virus is similar to other parenteral inflammatory processes. The type of development of the specified infection in the human body is controversial, according to the opinions of many scientists. Doctors classify this infectious pathogen as the last form of the disease (fulminant), and also think that autoimmune hepatitis develops due to bacteria inherent in type G hepatitis.
In addition to the above-mentioned mysterious characteristics, scientists have identified the compatibility of the strain of this type of hepatitis with other parenteral varieties, for example, B and C. This means that a co-infection occurs that does not lead to complications in the course of the main disease - the “guest” does not even affect the strengthening of immune cells when taking interferon.
Hepatitis type G
In its independent form, the infectious pathogen type G occurs in a moderate form without symptoms of jaundice, but rarely leaves the host’s body without leaving a trace. The virus radically changes the structure and damages the cells of the liver parenchyma, which in the future can lead to other health problems. Another point of view: the virus lurks for a long time in the human liver tissue, and then causes serious consequences - cirrhosis or the initial stage of liver carcinoma.
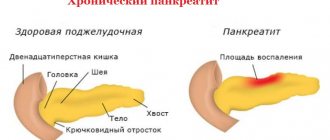
What causes chronic hepatitis?
Chronic hepatitis is a long-term diffuse inflammatory process, localized in the liver tissues and caused by viral infections or the autoimmune nature of the disease.
It is difficult to classify all inflammatory actions in the human body, so it is worth pointing out the main points in clear language for readers.
The liver is recognized as a filter of the human body, but sometimes, as a result of the action of external and internal factors, irreversible processes begin that kill the cells of the parenchyma and internal structure. What happens leads to a change or complete stop in the functioning of the organ. All processes that infect the liver began to be divided into categories:
- autoimmune type, characterized by a huge area of damage to liver tissue cells, which results in a vivid manifestation of all kinds of symptoms;
- cholestatic forms are characterized by the presence of inflammatory processes in the bile ducts, leading to stagnation of bile in the human body;
- chronic type B, C, D;
- alcoholic and toxic forms, caused by the use of alcoholic beverages, drugs and medications;
- chronic types of inflammatory process, the source of occurrence remains unknown.
Chronic form of hepatitis
Externally identified classifying factors of the course of the disease, phases of tolerance, and symptoms do not allow us to establish the general picture of inflammatory infectious diseases of the human filtering organ. There is no information about the negative impact of external factors on damage to liver tissue, such as alcohol, toxic substances and drugs. People know little about serious types of the disease:
- chronic alcoholic hepatitis, leading to cirrhosis of liver tissue;
- nonspecific reactive form of chronic inflammation of various types;
- toxic hepatitis;
- fatty hepatitis;
- drug-induced hepatitis;
- radiation hepatitis;
- ischemic hepatitis;
- chronic hepatitis G, detected later than others.
Based on these data, modern medicine has identified three types of chronic inflammatory process of the liver, determined by morphological characteristics:
- The first is called chronic persistent inflammation. It can be asymptomatic in the body; symptoms begin to appear long after the host has been infected. The active phase develops exclusively after the transition of the inflammatory process in the tissue of the liver lobes.
- The second type is CLH, or chronic lobular hepatitis. Localization of the inflammatory process is directly in the lobules. The difference between this hepatitis and other types is tissue damage by necrosis, which indicates a high phase of liver cell death.
- The third is CAH (chronic active infection), characterized by the transition of infection of the liver tissue into the tissue of the lobes. Severity of symptoms:
- small;
- average (moderate);
- pronounced (severe);
- sharply expressed, or lightning fast.
The difference between the types lies in the course of the disease.
Chronic inflammatory process of the liver
Etiological factors
Inflammatory processes occurring in the liver tissue are included in the etiological types of diseases due to their occurrence due to a number of factors:
- entry into the human body of viral pathogens of bacteriological species (brucella, treponema), parasitic (schistosoma) and viral origin (viral pathogens, herpes);
- consumption of toxic substances, drugs that negatively affect humans;
- ionizing radiation;
- cholestasis syndrome (stagnation of bile and blockage of channels);
- genetic factor - heredity;
- failure of the immune system.
The classification of disease types has been considered by experts many times, but scientists have not come to a single decision. Now, as many as 5 inflammatory processes in the liver have been identified that occur due to the effects of alcohol on the human body.
Considering that not all types of hepatitis have been fully studied, similar forms of diseases are identified. It is not practical to consider each type and subtype of liver tissue lesions. However, it is worth introducing readers to the most understandable and common division of viral liver infections according to etiological characteristics:
- Inflammatory processes caused by a pathogen of viral origin. They arise from microbes of types B, C, D, G. Plus unconfirmed forms today - hepatitis F and TiTi.
- A disease of autoimmune origin. These include types 1, 2, 3.
- An inflammatory process of the liver resulting from long-term use of medications. Often manifests itself in chronic patients who require constant use of medications that can make life easier. Most serious medications negatively affect liver cells, destroying them and impairing their functionality.
- The toxic type occurs as a result of prolonged exposure to psychotropic substances, poisons, drugs, synthetic substances, surrogate alcohol on liver cells.
- The alcoholic form is usually classified as a toxic form of inflammatory liver disease. Some doctors identify infections that occur as a result of drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages.
- The metabolic type occurs under the influence of genetic pathology - Konovalov-Wilson disease. This type of disease is extremely dangerous and leads to the death of the carrier at a young or even infancy.
- The cryptogenic type hides the still undisclosed reasons for the emergence of bacteria in the human liver. The bacterium gradually affects the entire liver parenchyma. Even a thorough innovative examination does not help to identify the cause of infection with this type of virus. The disease is extremely aggressive and quite often leads to concomitant liver problems: cirrhosis and the initial stage of a cancerous tumor of the liver tissue. The liver virus activates this process.
- Secondary type, or nonspecific reactive hepatitis. Occurs mainly as a result of other serious pathologies:
- tuberculosis;
- renal disorders and pathogenesis;
- ulcers and other problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Crohn's disease;
- pancreatitis.
Since many of the listed types of hepatitis pose a real danger and negatively affect the human condition, we will consider a number of pathology options to create an approximate picture. The etiology includes many types of infection.
Chronic hepatitis C
This type of inflammatory liver pathology is extremely common in the post-Soviet space. How long can carriers of this virus live and how do they cope with the side effects of the disease?
People fall into despair when they learn about a diagnosis and study information from unverified sources, books, and pages on the Internet. There is no need to worry or think about your imminent death. People with hepatitis C live a normal life. The only restrictions set at your discretion, depending on the form of the disease, are:
- maintaining proper nutrition, excluding fatty foods from the diet, drinking alcohol and toxic substances;
- increasing immunity, for example, hardening, taking special dietary supplements;
- caution when choosing a sexual partner and maintaining hygiene.
Remember the main thing: the blood of an infected person is infectious in any contact with it. The life expectancy of hepatitis carriers is quite long. There are a lot of cases where even those who like to drink and eat lived quietly for decades without displaying the aggression of the type C virus. Medical literature describes cases of recovery of the sick and the reactivation phase of infection. There were, of course, sad outcomes - the development of cirrhosis or a cancerous tumor, which certainly led to the imminent death of a person.
In many ways, the course of the disease and a good prognosis for future life depend on the patient, his habits and desire for recovery. Doctors have also developed an excellent medicine - interferon.
Genetic hepatitis
The autoimmune, or, in other words, genetic type is common among females. Carriers of viral infection are 8 times more common among women than among men. The pathology is characterized by increased aggressiveness and speed of manifestation in adults. Autoimmune infection quickly progresses to the final stage - cirrhosis, portal hypertension, precancerous condition. This leads to significant mortality of carriers.
Autoimmune liver virus on ultrasound
Scientists believe that the cause is human genetic predisposition. A connection between histocompatibility antigens in the formation of pathology was revealed. People have a potential predisposition to the disease, but a small number are susceptible to the development of an autoimmune virus. Oddly enough, the drug interferon can cause autoimmune pathology in the liver. Viruses also influence the development of the aggressive process:
- hepatitis B, C, A;
- measles;
- herpes of the first and sixth types;
- Epstein-Barr virus.
Statistics provide data: slightly less than half of carriers have previously suffered from other autoimmune diseases. The inflammatory process, as a rule, begins with an acute form. The patient loses appetite, jaundice appears, and the color of urine and feces changes.
For a long time, symptoms of an autoimmune infection are of moderate and increased severity. A complex clinical picture is formed by the following signs:
- complete loss of performance, lack of strength;
- heaviness and tingling in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, complete or partial;
- skin rashes;
- terrible itching;
- occasional jaundice;
- lymphadenopathy;
- increase in the size of the spleen and liver;
- women observe the absence of menstruation, that is, amenorrhea;
- men see an increase in breast size;
- polyarthritis.
The liver rejects alcohol
Inflammation caused by alcohol exposure is considered by doctors as a subtype of toxic infection. The reason for the occurrence is the same - the influence of negative substances on the liver parenchyma. Substances like alcohol irritate and kill liver cells. Viral processes have all the symptoms of standard inflammation. Additionally, the development of the disease can progress sharply in a lightning-fast form or become chronic.
Toxic liver hepatitis
The main signs of the onset of an acute process:
- causeless weight loss, weight loss;
- nausea, gastrointestinal upset, complete loss of appetite;
- enlarged liver, pain when pressing on the right hypochondrium;
- tremor;
- liver failure and coma, leading to the rapid death of the patient.
Sometimes, with the fulminant form of the alcoholic type, low-grade body temperature, bleeding, concomitant infections of the gastrointestinal tract, and inflammatory processes in other organs occur.
Only if a person can stop in time and stop drinking alcohol can one expect a positive outcome and recovery of the liver with minor negative consequences for the functioning of the gland.
Toxic damage
An acute form of a toxic inflammatory process can be caused by just one small dose of poison, which has a hepatotropic property that affects the destruction of liver tissue and damage to the parenchyma.
An acute inflammatory process is accompanied by significant pain when pressing on the area of the liver or spleen. Usually people think that the organ itself hurts, but in fact it is due to the increased volume of the liver. Symptoms that are pronounced:
- serious condition of the patient, loss of strength;
- jaundice that gets worse;
- vomit containing bloody discharge;
- bleeding from the nose, mouth, hemorrhagic lesions of the skin;
- the appearance of mental disorders (excitability or inhibition of reaction).
The chronic form of toxic inflammation develops when small but constant doses of narcotic and other toxic substances enter the body. If the cause of infection in the body is not eradicated in time, after a short time the pathology will develop into cirrhosis or a precancerous tumor. Toxic lesions are treated with interferon.
Treatment methods
Hepatitis C in women, the symptoms of which can be disguised as other diseases, requires carefully selected therapy. It is selected by the doctor, depending on the results of tests and studies. The main goal of treatment is to destroy and remove the virus from the body.
Medications
Drug therapy for hepatitis C depends on the genotype of the virus that has infected the body. The drugs used negatively affect the viral protein necessary for reproduction. Previously, peligated interferons in combination with ribavirin were used for therapy, but this method was considered insufficiently effective and safe.
The following antiviral drugs are currently used:
- “Telaprevir”, “Boceprevir”, “Simeprevir” - against genotype 1.
- “Sofosbuvir” - against genotypes 1-6; Sofosbuvir in combination with Daclatasvir is indicated for the destruction of all genotypes of the virus.
- “Velpatasvir”, “Glecaprevir”, “Pibrentasvir” - against all genotypes of the virus.
There are also combination drugs that are more effective and safe due to the combination of several antiviral drugs at once.
Such drugs include:
| Drug name | Active ingredients | What genotype does it work against? |
| “Dasabuvir” | Consists of 4 antiviral drugs:
| Against genotype 1. |
| “Ledipasvir” | Ledipasvir + sofosbuvir. | Against genotype 1. |
| “Zepatir” | Grazoprevir + elbasvir | Against genotypes 1, 4. |
It is also necessary to prescribe hepatoprotective drugs that protect liver cells from destruction, promote their regeneration and increase the functions of the organ:
- “Phosphogliv” has anti-inflammatory, antiviral and hepatoprotective effects.
- “Essentiale Forte N” - has a regenerating, metabolic, antitoxic effect.
- “Ovesol” is a dietary supplement of plant origin; designed to cleanse the liver, also has a biliary and moderate analgesic effect and regulates the functioning of the organ.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe vitamin and mineral supplements to increase the overall tone of the body.
The average duration of treatment for hepatitis C (not complicated by cirrhosis) is 3 months. The effectiveness of the therapy can be judged by the results of a repeated blood test - liver enzyme levels should decrease.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods are not very effective against the virus, so they cannot completely cure hepatitis C. But with their help, you can stop inflammation in the liver tissues, improve bile excretion, digestion and increase the tone of the body. Before using traditional methods, mandatory consultation with a specialist is required to avoid complications and side effects.
Mumiyo
Such a useful product as mumiyo has many beneficial properties - it has an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect, accelerates tissue regeneration, and helps normalize the functioning of the digestive tract. Shilajit is beneficial for the liver because it helps eliminate bile and toxins and reduces pain.
For hepatitis C, you need to take 0.2-0.3 g of the substance in 10-15 minutes. before meals 3 times a day, washed down with warm water. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks, after which you need to take a break for 7 days and repeat the course.
Milk thistle
Milk thistle contains a unique substance, silymarin, which is a flavonoid.
Its therapeutic effect is as follows:
- Prevents the destruction of cell membranes of hepatocytes (liver cells) and destroys free radicals that cause tumors.
- Accelerates the regeneration of cells and tissues, activates the synthesis of phospholipids.
- Protects liver cells from poisons and toxins, has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Silymarin is a very unstable compound that is destroyed at temperatures above 60 degrees, so preparing infusions and decoctions from milk thistle is impossible.
This is interesting: Preparations for eliminating lice and nits. The most effective treatments
But a powder is prepared from the seed: for this, the required amount of seeds is ground in a coffee grinder or blender and taken 1 tbsp. l. before meals with a glass of water. The course of treatment is at least 14 days. The powder should be stored in a dark glass container in a dry place.
Corn silk
You can prepare a healing infusion from corn silk:
- Place 200 g of dry corn silk in a thermos and add 200 ml of hot water.
- Let the drink brew for 3-4 hours, filter.
- Take 100 ml 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 3 days.
Tea is also prepared from corn silk: 1 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with a glass of water and left for 5-7 minutes. This tea can be drunk up to 5 times a day, the course of treatment is 4-5 days.
Substances contained in corn silk relieve inflammation and spasms, improve bile excretion and cleanse the liver of toxins.
Rose hip
Rosehip contains a large amount of vitamin C, which helps improve immunity, has an antiviral effect and improves body tone.
To prepare rosehip infusion you need:
- Select 15-20 ripe and undamaged fruits, wash them and dry them.
- Place the fruits in a thermos and add 1 liter of hot water.
- Infuse the drink for 8-10 hours, then take 0.5 cups 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Carrot juice with honey and lemon
This drink is a powerful vitamin supplement. Carrots contain carotene, which is necessary to cleanse the liver; Lemon contains a lot of vitamin C, and honey has a powerful anti-inflammatory, biliary and mild analgesic effect.
To prepare the drink, you need to squeeze the juice out of carrots using a juicer, add 0.5 cups of lemon juice and 1 tbsp. l. honey. You can drink the juice as a snack 2-3 times a day for 1 month. It is recommended to prepare the juice each time before use, but if this is not possible, then you can store it in the refrigerator for no more than a day.
Diet
Diet helps slow the progression of the disease. The main goal of the diet is to improve the flow of bile, normalize the functions of the liver and the entire digestive tract. For diseases of the liver, gall bladder and biliary tract, nutrition according to the “Table No. 5” system is most often prescribed.
With this diet the following are prohibited:
- fried, fatty, spicy, canned foods;
- spices and marinades;
- smoked meats;
- store-bought semi-finished products;
- ketchup, mayonnaise and store-bought sauces;
- fast food;
- fatty varieties of meat and fish (preference should be given to chicken and turkey);
- meat broths;
- confectionery and baked goods;
- dairy products with a high percentage of fat, salty cheeses;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- strong tea and coffee;
- sour fruits and berries;
- legumes, spinach, radishes, rarely sorrel;
- onion and garlic.
It is also necessary to give up alcohol and smoking, as they only aggravate the development of hepatitis and negatively affect the liver.
Food must be boiled or steamed; occasionally baked dishes can be allowed. It is recommended to replace meat broths with light vegetable soups. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day, and divide your food intake into 5-6 meals - this way the food will be better absorbed.
Tyubazhi
Tubing is a medical procedure based on heating the gallbladder and liver. The method has a laxative effect and helps remove stagnant bile from the body and eliminate discomfort in the right side - exactly where the liver is located.
Tubages are carried out under the supervision of a doctor and in a hospital setting:
- The patient drinks any choleretic agent (warm mineral water, magnesium sulfate solution, sorbitol, xylitol or herbal decoction).
- The patient is placed on his right side with his knees pressed to his stomach.
- A heating pad is placed under the right side.
- The patient should lie without getting up for 1.5-2 hours, until the first urge to go to the toilet. Bile will be released from the body with feces.
Applying a tubage is also possible at home, but it is not recommended to avoid complications and side effects.
The liver requires proper care
You should not undertake to treat inflammatory processes of the liver on your own, this will negatively affect the outcome and complicate the situation. The only way to identify a dangerous pathology in its early stages, which are still treatable, is with the help of a doctor.
A medical professional will identify a health problem. Folk remedies will help to cope with the residual effects of the disease, but in the acute form, unconventional treatment will harm the general health of the patient. Prevention is the best way to stay healthy. Antiviral therapy carried out in modern clinics helps to avoid infection. In short, everyone has a chance of recovery.
The specialist predicts the early stage of the disease and advises which pills to take for treatment. Symptoms of infection make treatment difficult.
Prevention
Hepatitis C infection can be prevented if you follow the following prevention rules:
- Do not use other people's razors, manicure accessories, toothbrushes; such items should be for personal use, as microscopic amounts of blood may remain on them, which is sufficient for infection.
- Do not visit beauty salons (especially manicure salons), tattoo and piercing salons, or dental clinics that have a dubious reputation; always ensure that needles and syringes are disposable; Do not get piercings and tattoos from artists who work at home, as the instruments there may not be thoroughly sterilized and sanitized.
- Do not use drugs or inject them with a syringe.
- Use a condom when having sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner.
- When undergoing acupuncture, bring your own needles to the session (they can be purchased at the pharmacy).