Among the variety of types and forms of gastritis, there is a rare type of chronic form of the disease called lymphocytic gastritis. This little-studied pathology is usually diagnosed in older people, most often women; children rarely suffer from the disease.
A serious problem is detected during laboratory examination of the gastric mucosa. The disease itself is not so scary, but the complications it provokes result in severe stomach discomfort and can result in death.
Characteristics of lymphocytic gastritis
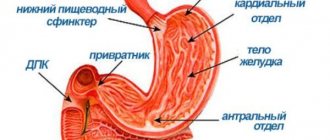
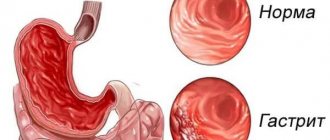
The pathology is an inflammatory process that affects the gastric mucosa. The main sign of a nonspecific form of the disease is considered to be pronounced lymphocytic infiltration of the epithelium (penetration of foreign particles) together with the appearance of plasma cells in the lining of the stomach.
According to doctors, the most likely causes of the appearance of characteristic signs of lymphocytic gastritis can be two main factors:
- Intolerance to gluten (celiac disease) and certain medications. Gluten is a protein found in grains, but for people with celiac disease, the protein becomes foreign. This causes gluten in the stomach to be blocked by immune killer cells, which leads to injury to the healthy cellular structures of the inner lining.
- It has been established that the gastrointestinal tract is infected with a pathogenic microorganism called Helicobacter pylori. The presence of bacteria in the surface layers of the gastric mucosa results in the fixation of characteristic changes in the structure of the epithelium, typical for the form of the disease associated with the bacterium.
Attention! Experts believe that indirect reasons for the development of lymphocytic gastritis are poor diet with a predominance of fatty and salty foods, as well as smoked, pickled, spicy and fried foods. People who abuse alcohol and smoke are at increased risk.
What symptoms indicate pathology?
A nonspecific form of dangerous pathology may not manifest itself in any way, and the sick person will not even know about the stomach problem.
Symptoms of the initial stage of lymphocytic gastritis can be manifested by the following sensations:
- Pain in the stomach area,
- The appearance of belching or heartburn,
- Nausea accompanied by vomiting,
- Bloating, flatulence,
- Constipation or diarrhea.
With a prolonged course of the disease, the pain syndrome manifests itself as cutting or cramping pain. A person loses appetite and weight, signs of iron deficiency anemia develop, and there is a risk of gastric bleeding.
If the symptoms of lymphocytic gastritis develop with increased secretion of gastric juice, the patient’s tongue becomes covered with a white coating.
In the case of gastritis that develops with low acidity, the tongue remains dry, but the patient complains of rumbling in the stomach with its distension. A likely sign is severe vomiting with blood fragments and a sour smell. With a reduced level of acid secretion, no weight loss or appetite occurs.
Symptoms of stomach lymphoma
There are no specific signs; in its clinical manifestations, gastric lymphoma may resemble gastric cancer, less commonly, gastric ulcer or chronic gastritis. The most common symptom is pain in the epigastric region, often worsening after eating. Many patients with gastric lymphoma report a feeling of premature satiety. Some patients develop aversions to certain types of food. Characteristic weight loss is caused by a feeling of fullness in the stomach and decreased appetite. A critical decrease in body weight up to cachexia is possible.
With gastric lymphoma, nausea and vomiting are often observed, especially when eating excessive amounts of food, which further contributes to reducing portions, refusing to eat and subsequent weight loss. As the cancer process spreads, gastric stenosis may develop. In some cases, patients with gastric lymphoma experience bleeding of varying severity (including small ones, with an admixture of blood in the vomit). There is a danger of developing severe complications - perforation of the stomach wall when it grows with a tumor and profuse bleeding when gastric lymphoma is located near a large vessel. Along with the listed symptoms, there is an increase in body temperature and profuse sweating, especially at night.
What happens with lymphocytic gastritis
A rare form of chronic gastric disease is characterized by a non-standard development pattern. Inflammation in the lymphoid type of pathology is not the result of a destructive process in the lining of the stomach due to irritation, but a response to the opposition of lymphocytes.
Local immunity in the stomach is responsible for lymphoid tissue, consisting of special cells, among which there are lymphocytes of varying degrees of maturity, as well as clusters of follicles.
After the penetration of leukocytes (infiltration) and a further increase in their number in the cells of the gastric epithelium, autoimmune reactions develop, which gives the right to speak of lymphoid gastritis as a separate stage of lymphocytic.
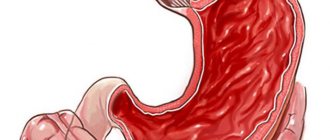
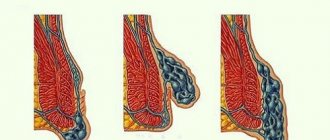
By protecting a segment of the damaged area of the stomach, lymphocytes attack inflammation, saving the body. Under the influence of provoking factors, lymphocytic follicles grow, this leads to uneven thickening of the gastric folds.
Due to impaired production of gastric juice, foci of atrophy are formed, which results in the development of benign lymphoma.
What are the reasons for the violation?
Normally, there are 3–5 leukocytes per 100 gastric epithelial cells. When this indicator increases 10 times, chronic lymphoid gastritis develops.
The mechanism of development of lymphocytic inflammation is not fully understood. According to one hypothesis, gastritis develops against the background of gluten intolerance. In this case, gluten is perceived by the body as a foreign substance. To neutralize and block it, lymphocytes are actively released in the stomach, which, together with this substance, infect the epithelium of the organ. The causes of the disease can be pathologies such as:
- infection of the body by Helicobacter pylori;
- chronic infectious diseases of the throat and mouth;
- hormonal disorder.
Who is at risk?
Smokers are at greater risk of contracting this disease.
The lymphocytic form of gastritis affects women 3 times more often than men. Mostly, the pathology is detected in people aged 60–80 years. In rare cases, it occurs in infants. The risk of developing the disease increases if a person drinks alcoholic beverages, smokes, or abuses fatty and fried foods. The patient can independently provoke inflammation if he takes any medications without a doctor’s prescription, which disrupts the body’s protective functions and contributes to damage to the mucous membrane.
How is the primary diagnosis of pathology carried out?
When the first signs of discomfort and suspicion of gastritis appear, you should contact a specialist. A gastroenterologist deals with problems of the gastrointestinal tract.
The doctor will prescribe a series of studies and tests confirming gastritis in general or its lymphocytic variety:
- A general blood test helps identify the threat of an inflammatory process,
- Thanks to a detailed blood test, the fact of metabolic processes failures is detected,
- Stool analysis checks for the hidden presence of blood in it,
- Histological results indicate the degree of damage to cellular structures,
- By examining gastric juice, the acidity of the medium is determined.
Important! The main method for diagnosing signs of lymphocytic gastritis is fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The results of the study are the most informative; this is the main diagnostic method that allows us to establish the presence or absence of non-standard pathology.
Features of the deep diagnostic process
Lymphocytic gastritis is accompanied by an acute and chronic erosive process. According to the clinical picture, the pathology resembles the early stage of the Helicobacter pylori variety of the disease with a normal or increased level of secretory function.
To confirm gastritis of the lymphocytic type, it is necessary to differentiate it in relation to other special types of gastric pathology and exclude the following diseases.
Signs of autoimmune gastritis
Symptoms of the disease that develops after damage to the gastric mucosa include pallor of the mucosa, detection of polyps against the background of an anemic state.
The main feature of this form of gastritis is concomitant thyroiditis and diabetes mellitus. The cause of the mucosal disorder could be Helicobacter pylori or the consumption of rough food or stomach deformation.
Primary damage becomes a trigger for the start of an immune response, and the mucous membrane continues to be injured, but with antibodies to its own cells. These structures are responsible for the synthesis of hydrochloric acid and enzymes necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. The lesion mainly affects the tissues of the stomach and its fundus.
The disease not only threatens the development of anemia, but also provokes rapidly developing atrophy of the mucosa, tripling the risk of cancer against the background of symptoms characteristic of chronic gastritis.
Diagnosis of erosinophilic gastritis
The pathology, similar in its characteristic symptoms to lymphocytic gastritis, is classified as an allergic type. In this case, the main feature of the disease is the pronounced severity of skin rashes, accompanied by itching.
Diagnosis of allergic gastritis is based on a blood test - the level of eosinophils is greatly increased. If an eosinophilic type of pathology is suspected without an increase in the blood count, a biopsy is necessary if a number of diffuse changes are detected along with swelling of the mucous membrane and erosions.
Important! In people with a predisposition to allergies, signs of allergic gastritis can be triggered by food allergens, medications, even parasites in the body.
Other precipitating diseases
Doctors consider tuberculosis to be the main cause of lymphocytic gastritis. The presence of the disease is indicated by the appearance of blood in the vomit.
In tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and Crohn's disease, the stomach suffers from pathological changes, which causes the development of granulomatous gastritis, one of the signs of which is bloody vomiting. The appearance of blood indicates the formation of cracks due to an erosive process in the mucous and submucosal layer.
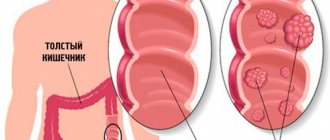
Classification of gastric lymphomas
Taking into account the origin and characteristics of the clinical course, the following types of gastric lymphomas are distinguished:
- MALT lymphoma (the abbreviation comes from the Latin mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue). Included in the group of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. This gastric lymphoma develops from lymphoid tissue associated with the gastric mucosa. Usually occurs against the background of chronic gastritis. It is not accompanied by primary damage to peripheral lymph nodes and bone marrow. The degree of malignancy varies. May metastasize to lymph nodes.
- B-cell lymphoma. Formed from poorly differentiated B cells. Presumably occurs as a result of the progression of MALT lymphomas; indirect confirmation of this hypothesis is the frequent combination of the two listed types of gastric lymphomas. It has a high degree of malignancy.
- Pseudolymphoma. It is characterized by lymphoid infiltration of the mucous membrane and submucosal layer of the stomach. It proceeds benignly, in some cases malignancy is observed.
Taking into account the growth characteristics, the following types of gastric lymphomas are distinguished:
- With exophytic growth. Neoplasms grow into the lumen of the stomach and are polyps, plaques or protruding nodes.
- With infiltrative growth. Neoplasia forms nodes in the thickness of the gastric mucosa. Depending on the characteristics of the nodes in this group, tuberous-infiltrative, flat-infiltrative, giant-fold and infiltrative-ulcerative forms of gastric lymphoma are distinguished.
- Ulcerative. Stomach lymphomas are ulcers of varying depths. They have the most aggressive course.
- Mixed. When examining a tumor, signs of several (usually two) of the types of tumor listed above are detected.
Taking into account the depth of the lesion, determined by endoscopic ultrasound, the following stages of gastric lymphomas are distinguished:
- 1a – with damage to the superficial layer of the mucous membrane.
- 1b – with damage to the deep layers of the mucous membrane.
- 2 – with damage to the submucosal layer.
- 3 – with damage to the muscular and serous layer.
Along with the above classification, the standard four-stage classification of oncological diseases is used to determine the prevalence of gastric lymphoma.
Treatment methods for lymphocytic gastritis
You should immediately consult a doctor if you experience discomfort in the stomach or manifestations characteristic of chronic pathology. After appropriate diagnosis and evaluation of laboratory test results, the specialist selects an individual treatment regimen for lymphocytic gastritis.
What a gastroenterologist will advise first:
- Review the food range, paying attention to the regime,
- Control body weight, avoiding obesity or wasting,
- Give up bad habits, self-medication with over-the-counter drugs,
- Follow the doctor’s recommendations, completing the treatment of lymphocytic gastritis to the end,
- Undergo regular medical examinations, not forgetting a visit to a gastroenterologist.
Principles of drug therapy
During fibrogastroscopy, the patient swallows a flexible hose of an optical probe, the end of which is equipped with a video camera. The doctor observes the results of a detailed review of the stomach cavity and its walls on the monitor screen.
The main advantage of the technique is the ability to obtain material for analysis. Based on the results of the examination and the clinical manifestations of the disease, the doctor prescribes drugs for the treatment of lymphocytic gastritis.
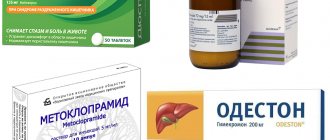
- Correction of gastric juice secretion, as well as blocking histamine receptors, is carried out by prescribing Famotidine, Ranitidine.
- To protect the gastric mucosa, drugs that reduce acid dependence are needed, which is achieved with the help of Omeprazole, Pariet.
- Neutralization of the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid is carried out by drugs such as Maalox, Phosphalugel, Rennie, Almagel.
- Taking Bioagastron, Dalargin, Metacil allows you to protect the gastric mucosa from the formation of cracks and the erosive process.
- Enzymatic preparations that promote food digestion - Panzinorm, Mezim, Creon, Festal - will help regulate the functioning of the digestive tract.
- To combat bacterial flora, it is necessary to take anti-Helicobacter antibiotics - Azithromycin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin.
- Prescribing Domperidone, Motilium, Lactiol, Itomed will help restore motility and proper functioning of the stomach.
- The gastric lining is protected from external irritations by the drug De-nol, which has a wall-enveloping effect.
Important! Positive results from drug treatment of lymphocytic gastritis can only be expected if you consult a specialist in a timely manner. Otherwise, irreversible complications cannot be avoided; untreated ulcers of the mucous membrane lead to the formation of a cancerous tumor.
Doctors recommend combining drug therapy with phytotherapeutic methods:
- Taking herbal decoctions of chamomile, calendula, calamus root, licorice, which alleviate unpleasant symptoms,
- For gastritis with low acidity, you can brew celandine, plantain, wormwood,
- Drinking potato and cabbage juice (freshly prepared) will help restore stomach acidity.
- To eliminate stomach pain and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, an infusion of flax seeds is prepared.
Drug therapy for lymphocytic gastritis must be supported by adherence to a strict diet that helps reduce active inflammation of the gastric tissues and accelerate the healing of erosions on the mucous membrane.