What is the disease?
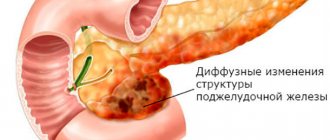
This is an inflammatory process that affects the pancreas. Swelling of the tissues of the pancreas and ducts to the duodenum occurs. Due to swelling, the enzymes produced by the gland cannot enter the esophagus through the ducts.
But lipase, amylase, lactase, chymotrypsin and trypsin, the main task of which is considered to help in the digestion of food, cannot perform their main functions, as they accumulate in the body of the pancreas. But the digestive process of enzymes cannot be stopped, so they begin to slowly digest the tissues that produced them, while poisoning the entire body with toxins.
What methods will help assess the condition of the pancreas?
The pancreas is a fairly large gland, but you cannot palpate it, since the stomach is located in front of it, and the lower ribs are behind it. It hurts so much that the pain cannot be withstood, and ordinary antispasmodics and painkillers do not relieve it. It is better not to bring the organ to such a state. How can you check your pancreas without going to the doctor?
To understand how well it works, pay attention to the following symptoms:
- diarrhea alternating with constipation;
- periodic bouts of vomiting;
- general weakness;
- aversion to fatty foods and complete lack of appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- intense girdle pain at the level of the lower ribs or pain on the left side of the body;
- foul-smelling, light-colored stool;
- increased thirst and hunger.
All of these symptoms may indicate chronic pancreatitis. In acute inflammation, a person feels a sharp pain, which intensifies when lying on his back. There is nausea and repeated vomiting, which does not alleviate the condition, the stomach is swollen, the temperature may rise, and the blood pressure drops. The pain subsides somewhat if you take a sitting position, bending forward, and fold your hands on your stomach. These are extremely dangerous signs - the patient requires urgent medical care.
If you still “sin” on other organs, then it is advisable to check the pancreas at home. How to do it? Observe how you feel and take a mini-test to assess her health. Answer these questions:
- Are you losing weight even though you eat the same as before?
- Has your appetite suddenly decreased?
- Are you often bothered by gas?
- Are you starting to get tired quickly?
- Do you sometimes experience pain in the abdomen and in the left/right hypochondrium?
- Does pain occur in your left side when pressing?
- Do you feel heaviness and pain after eating fatty and spicy foods?
- Do you experience difficulties with bowel movements (constipation and loose stools)?
For each positive answer, add one point. If there are from 2 to 4 of them, then your pancreas is not completely healthy. You should urgently go on a diet and take medicinal decoctions. If you score 4-8 points, then be sure to undergo an examination to check how the pancreas works: you have serious problems.
Symptoms of the disease
In order to understand in time that problems are starting in the pancreas, you need to be attentive to all signals from the body. At different stages of the development of the disease, characteristic symptoms arise that cause discomfort and health problems:
- Pain. As soon as inflammatory processes begin and blockage of the ducts, a person feels an unpleasant sharp pain under the ribs. Depending on the location of the disease, it may hurt on one side, the side, or immediately along the entire circumference of the ribs. The pain is constant and does not subside even at rest.
- Vomit. The stomach stops digesting the food eaten; without enzyme tablets, vomiting immediately appears. Vomiting occurs with every meal.
- Heat . Inflammatory processes in the body and intoxication provoke a protective reaction of the body and an increase in body temperature to 38–38.5 degrees.
- Jaundice. When the pancreas swells, its body can put pressure on the bile ducts, resulting in obstructive jaundice. A person develops all the signs of jaundice: yellowed eyes, palms and skin.
- Diarrhea or constipation. Problems of the digestive tract immediately make themselves felt; lack of enzymes and intoxication cause difficulties with bowel movements.
Drug therapy at home
Drug treatment can be taken at home only on the recommendation of a doctor after examination. For pancreatitis, complex therapy is used, including several groups of drugs:
- Enzyme agents are prescribed for decreased pancreatic function due to the inflammatory process in the organ tissue and the death of its cells. They eliminate nausea and abdominal discomfort, normalize stools, and reduce flatulence. Pancreatin, Festal, Mezim forte are often used. Creon received the best feedback from experts: it is made using a new, innovative technology; one capsule contains many microspheres that dissolve in the lumen of the duodenum, and not in the stomach, thereby significantly improving the digestive process. The drug is prescribed to both adults and children can take it without any particular risk of side effects.
- Antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine) - a tablet of any of them relieves the pain symptom.
- Painkillers are used parenterally in the form of injections or droppers in a hospital setting in cases of acute pancreatitis or severe exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process. They are not prescribed for use at home, and are not recommended for the patient: if the pain intensifies, they can hide the true picture of the disease or the onset of a complication. NSAIDs (Aspirin, Nise and others) should not be used. They irritate the gastric mucosa and can cause bleeding.
- Antibiotics are necessary to prevent infectious complications. Only a doctor prescribes them: the most effective drug is selected taking into account the patient’s condition, the presence of concomitant diseases, existing contraindications and side effects of the antibiotic. The dosage and duration of administration are calculated.
- PPIs - proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantaprazole) - relieve pain. They block the production of hydrochloric acid, thereby reducing the high secretion of pancreatic juice by the gland. Sometimes H2-blockers of histamine receptors (Ranitidine, Famotidine) are used for the same purpose. Additionally, in some cases, antacids are prescribed. They have an enveloping effect and also soothe pain.
Diabetes mellitus is a pathology associated with damage to the endocrine function of the pancreas. Depending on the condition and laboratory data (glycemia level), glucose-lowering drugs are prescribed. They are taken at home strictly by the hour, in the dosage prescribed by the endocrinologist. In severe cases, the patient is prescribed insulin replacement therapy for a long time (sometimes for life). The patient also monitors sugar independently at home using a glucometer.
Any medicine has side effects and application features. Treatment is always prescribed individually. Therefore, the use of drug therapy should be carried out according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. Replacing any drug with another on your own, without consulting a specialist, can lead to negative effects.
Methods for diagnosing pancreatitis
Everyone knows that it is much more effective to treat diseases in the early stages, before the course becomes chronic. But for this it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination at least once a year, thanks to which deviations from the norm, the development of pathologies and deteriorations can be identified in a timely manner.
How to check the pancreas? First of all, you need to contact a general practitioner. It is he who must carefully examine the patient, palpate the abdomen, determine where the disease is localized, and give directions for tests. Even with palpation, the doctor can determine the etiology of abdominal pain.
If there is a suspicion that the cause of pain syndromes is pancreatitis, then the patient is sent for examination to a gastroenterologist, who prescribes all tests that confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
General blood analysis
They donate blood from a finger prick, after which laboratory workers check the number of leukocytes and ESR in the blood. A general analysis allows you to determine whether inflammatory processes are present in the body. Lack of insulin also indicates the development of swelling of the gland.
Blood chemistry
Venous blood is taken for biochemical analysis. It is tested for increased enzymes. This method is especially effective in the acute stage of pancreatitis.
Urine tests
If amylase enzyme is detected in urine, the presence of pancreatic disease is confirmed almost 100%. These tests make it possible to determine pancreatic problems at a chemical level. But, since many ailments have similar indicators and symptoms, the tests must be confirmed by other examination methods.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is an integral part of diagnosis. Using an ultrasound examination, the size of the glandular tissue and its ducts, its location in relation to other organs, the presence of fluid masses in the abdominal cavity or their absence are determined. Ultrasound makes it possible to visually assess the condition of internal organs and exclude suppuration and peritonitis.
Very often, stones in the ducts of glandular tissue lead to pancreatitis. An x-ray makes it possible to visually determine the presence of stones, so-called calcenates.
CT scan
Computed tomography makes it possible to visually determine changes in the size of glandular tissue, narrowing or widening of the ducts. This method is considered expensive, but provides a lot of information, thanks to which a more accurate diagnosis can be made and the correct treatment can be prescribed.
Endoscopy
Using a small probe with a camera, doctors can view the entire situation from the inside in real time. The endoscope is inserted into the duodenum, and the Vater's nipple, through which secretions enter the digestive tract, is carefully examined. Contrast is also injected during endoscopy to make better X-rays and CT scans. But the contrast itself is considered an irritant and can provoke a relapse of pancreatitis.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is considered more of a surgical intervention than a diagnostic method, but it provides important facts about the current state of the disease. Laparoscopy is used more often in acute forms of pathology. This is a minimally invasive method that helps eliminate dead areas of gland tissue. The resulting tests may also indicate the presence of neoplasms and cysts, which is important to recognize in the early development of tumors.
It is better to examine the organs of the intestinal tract using several methods at once. Only after receiving all the results can the doctor make a reliable diagnosis. The importance of a complete examination also lies in the fact that pancreatitis can cause the development of other terrible diseases, such as diabetes mellitus and cholelithiasis. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude all possible side effects of the disease.
Treatment of pancreatitis is prescribed only by the attending physician. Self-treatment can lead to exacerbation of the disease and the appearance of serious complications, which sometimes cannot be restored or completely cured. Therefore, it is very important to adhere to all doctor’s instructions and advice.
You need to completely give up junk food, eat less fried, smoked, salty and fatty foods. If possible, completely avoid alcohol and coffee or reduce the dosage to a minimum. Nervous strain and heavy physical activity are contraindicated for patients.
Diet for this disease plays an important role in the treatment of pancreatitis; only with the help of proper nutrition and medication can long-term remission be achieved. If the symptoms of the disease return, you need to immediately begin treatment and not give a chance to complications.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract usually cause people a lot of problems, but despite this, many delay treatment, trying to cope with the disease on their own. This approach is not only not beneficial, but can provoke dangerous complications and concomitant diseases. So how to check the pancreas? What tests should I take to avoid mistakes? In case of any disturbances in the body, the first thing a person should do is consult a doctor for qualified help. It is the doctor who will prescribe the necessary tests to determine the disease and plan treatment.
How to identify pancreatic disease
Depending on the cause of occurrence, all gland diseases are divided into the following categories:
- inflammation (acute and chronic pancreatitis);
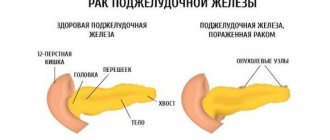
- oncology (benign and malignant tumors);
- stones (calcifications);
- cysts;
- pseudocysts;
- functional disorders (endocrine insufficiency, diabetes mellitus);
- parasitic infestations;
- infectious processes (syphilis, tuberculosis);
- pathologies of the vascular system;
- pancreatic necrosis.
Only a doctor can describe the pathology properly and in full. At the first sign you need to contact him. Initially, all data on complaints and manifestations of pathology is collected. Then general clinical examinations are prescribed.
Explore:
- General blood analysis. An inflammatory picture and anemic syndrome will be observed in it.
- A general urine test will show signs of toxic kidney damage.
- A biochemical blood test is assessed for the activity of nutritional indicators and enzymes: glucose, cholesterol, total protein, ALT, AST, amylase, alkaline phosphatase, CRP. If necessary, the list is supplemented.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. Through the anterior wall of the abdomen, an ultrasound sensor is used to evaluate the condition of the gland, its density, size, and echogenicity. Based on ultrasound, a conclusion can be made about pancreatic diseases.
- Endoscopic ultrasound of the pancreas. Informative for assessing the head of the organ. An endoscope is a thin rubber tube with a camera at the end. An endoscope is inserted through the patient's mouth into the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Through its wall, the condition of the gland can be assessed using ultrasound signals.
- X-ray of the abdominal organs. Shows new growths.
- They may resort to computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. The condition of the organ is assessed in several projections.
- For diagnostic purposes, surgery is performed using punctures in the skin on the abdomen - laparoscopy. Gland pathology is assessed with cameras.
It is difficult to give a definite answer as to whether the pancreas can be treated. It all depends on the pathology, severity, condition of the patient, and duration of the course.
An attack of acute pancreatitis in the early stages can be completely cured at the first signs. In this case, it is necessary to follow a strict diet and all doctor’s recommendations.
Chronic pancreatitis is difficult to cure completely. Doctors call this not a cure, but a stage of remission. When all recommendations are followed, the pathology does not manifest itself clinically.
If the advice is not followed, the exacerbation clinic appears again. So here the course of the disease depends only on the patient himself.
Pancreatic necrosis is not reversible. It can only be treated surgically. Drug therapy is prescribed to maintain the organ.
Cysts are removed surgically. After they are eliminated, all symptoms disappear. The patient is considered healthy.
Diabetes mellitus cannot be cured. But if you follow a diet and replacement therapy, then such patients live a long, full life without significant restrictions.
General rules for preparing for analysis
Before you take pancreatic tests, you need to know how to do it correctly. Doctors usually instruct patients because errors in collecting biological material can lead to significant deviations in the results obtained.
General recommendations come down to several points:
- Studies are carried out on an empty stomach, in the first half of the day. A few days before the tests, you should avoid junk food (fried, spicy, fatty, salty, canned food, coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks). It is also not recommended to consume legumes that can cause increased gas formation;
- Before taking blood, you must refrain from smoking for at least two hours;
- For problems such as constipation, care should be taken to ensure that toxins retained in the intestines do not affect the test result;
- All containers must be sterile and hands must be thoroughly washed with soap;
- When collecting urine, women must perform genital hygiene, after which it is better to use a tampon to guarantee the purity of the collected material;
- To study a general urine test, you need to take an average portion.
These simple recommendations will help you get tested correctly and avoid possible false results. However, it is worth remembering that sometimes laboratories make mistakes, so if you have the slightest doubt, you should undergo the examination again.
Laboratory diagnostics
In diseases associated with inflammation of the pancreas, the main task is to determine its condition. Acute episodes are accompanied by increased release of enzymes, which, depending on the type, can be found in the blood, urine and feces. A study of the liver will also be informative, since its function is closely related to the pancreas. The main tests, on the basis of which the doctor can confidently talk about the disease, are usually the following:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test, including testing for the enzymes diastase and amylase;
- coprogram (very informative for pancreatitis);
- Ultrasound, which can be used to detect fluid in the abdominal cavity, determine the condition of tissues and see possible neoplasms, including cancer;
- MRI and endoscopy. These modern diagnostic methods can provide excellent information about inflammation in the organ being examined.
Blood tests
Every person suffering from pancreatitis wonders what tests need to be taken to diagnose this disease. Usually the doctor prescribes several at once.
- General blood analysis . The first thing that will indicate problems with the pancreas is a high number of leukocytes against the background of an increase in the number of segmented and band neutrophils, as well as an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). It must be remembered that an inflamed liver can also give similar results, so the examination must be approached comprehensively;
- Blood chemistry . The most obvious sign of major problems with the pancreas will be an increase in total and direct bilirubin, which will indicate the presence of an icteric form of pancreatitis. Alarming signals are the growth of sialic acids, seromucoid and gamma globulins;
- Alpha amylase blood test. If its indicator increases (the norm is 16–30 g/l per hour), the doctor has the right to suspect chronic or even acute pancreatitis, stones in the gland and blockage of its duct. If the data obtained is below normal, which indicates insufficient production of this enzyme, we can assume pancreatic necrosis, serious pathologies associated with organ destruction;
- Pancreatic enzyme tests: trypsin and lipase;
- Blood sugar test. In case of serious problems with the pancreas, the results will exceed 6 mmol/l, but this data alone will not indicate a developing disease.
Analysis of urine
When the pancreas is diseased, the level of amylase in the urine, as well as in the blood, increases. This type of diagnosis is not expensive at all, so doctors are happy to prescribe it. In addition to a general urine test, the following studies are used:
- Lasus's test. The results of this test show the amount of amylase and its activity in the urine. In this analysis it will be called “diastasis”;
- Proserine test. Its essence boils down to the fact that after a single administration of proserin, the patient’s urine amylase concentration is checked every half hour. If it doubles and does not return to normal within two hours, the doctor can diagnose pancreatitis. In the case when the body does not respond to the administration of proserin, doctors talk about sclerosis of pancreatic tissue and pancreatic necrosis.
Hormone analysis
The pancreas is an organ that produces hormones, so by their content in the body one can judge its health.
- Insulin is a hormone involved in the breakdown of glucose, the synthesis of protein and fatty acids. A decrease in its content in the blood indicates a disorder.
- C-peptide is a hormone produced together with insulin.
- Glucagon, which performs the opposite function of insulin.
- In various situations, blood is examined for the content of hormones such as gastrin and amylin.
Coprogram
Stool analysis is of great importance in the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including pancreatitis. A clear sign of deviation from the norm will be the presence of undigested muscle fibers, fats and fiber.
List of analyzes
A laboratory test to check the pancreas can be prescribed by a physician or gastroenterologist. During acute inflammation, pancreatic enzymes are activated. Some of them are clearly detected in urine, others in blood, and others in feces.
A comprehensive study of the patient's condition is as follows.
- First of all, you will have to take a classic set of samples: a general blood test, urine test, and the biochemical composition of the blood.
- To identify chronic problems, scatological tests are widely used for various diseases of the pancreas. The coprogram determines the concentration of hydrolysis products and corresponding enzymes in the feces.
- In order to scan the functioning of the glandular apparatus, a secretin-pancreozymin test is performed. It is carried out using a probe with sequential administration of secretin and cholecysto-pancreozymin.
- An iodolipol test is often performed. The patient drinks the drug, and after 2.5 hours the level of iodide in the urine is measured. This diagnosis of pancreatic diseases records the activity of the lipase enzyme synthesized by this organ.
- Glycoamylasemic test - the initial level of amylase in the blood is determined after taking 50 g of glucose. This enzyme test should record an increase in concentration from the original value by about a quarter.
- If it is necessary to determine the extent of pancreatic deformations, doctors will additionally examine the patient’s liver, since the functionality of these organs is largely intertwined.
How else is the pancreas checked? The interpretation of the obtained data is usually supplemented by methods of examining the pancreas using various instruments.
To understand exactly what the problem is, your doctor may order additional tests. Laboratory diagnosis includes testing of blood, urine or stool.
- Glucose. Normally, the level should not exceed 5.5 mmol/l.
- Trypsin. The indicator should not exceed 60 µg/l.
- Alpha amylase. Exceeding 100 units/l indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
A biochemical blood test allows you to find out the level of bilirubin, creatinine, urea, cholesterol, and C-reactive protein.
A urine test allows you to find out the level of amylase and some amino acids, the content of which changes when the gland is not working properly.
A coprogram is required to determine whether the patient’s stool contains an increased amount of fat, fiber, and muscle fibers. This happens due to the fact that in the presence of a disease, the iron is not able to produce a sufficient amount of enzymes, so some of the food is not digested. This is especially true for fatty and protein foods.
One of the most important indicators of pancreatic disease is the level of elastase in feces. On average, the content of this enzyme is 300 mcg/g; exceeding 500 mcg/g indicates disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas.
In order for the examination results to be as reliable as possible, preliminary preparation for the procedures is necessary. As a rule, the doctor warns the patient about it, explaining in detail what and how to do.
A few days before a pancreatic examination, it is usually recommended to follow a diet that excludes any milk or carbonated drinks (especially sweet ones), raw vegetables and fruits. During the 12 hours that precede the procedure, you must completely stop eating.
On the day of the procedure, you should not smoke or drink alcoholic beverages. Medicines should also be excluded, but this point should be discussed with your doctor. Flatulence and increased gas formation can interfere with the procedure, in which case the patient is given activated charcoal to drink.
MRI of the pancreas
The pancreas often exhibits symptoms of the disease only when serious disorders have already occurred. If the patient managed to detect changes in his condition in time, then this is already half the success. Modern medicine allows us to examine the affected organ quite well. To check the pancreas using magnetic resonance imaging, the following organ parameters are important:
- size;
- form;
- tissue density;
- the presence of formations of any nature;
- features of intrapancreatic ducts. The spleen-pancreas canal is examined separately, since the health of the body directly depends on its patency;
- vascularization.
An examination of the pancreas involves using a contrast agent to check every area and see even the smallest changes in the image.
In what cases is it necessary to resort to MRI:
- detection of any changes in the epigastric region during ultrasound diagnostics;
- tumor;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- intraductal hypertension;
- cysts;
- incessant pain in the abdominal area.
So, if you have complaints about the pancreas, you should not delay your visit to the doctor. Timely tests and research will help you maintain your health.
Poor nutrition, widespread addiction to alcohol and smoking, and uncontrolled use of medications do not lead to instant death. They cause acute or chronic inflammatory and sometimes tumor processes in the pancreas and cause diabetes mellitus. Only those who, without waiting for any dangerous symptoms to appear, know how to check the pancreas will take action in a timely manner and avoid severe complications of pancreatitis. Let's lift the veil of secrecy.
How to check the pancreas and how to detect pancreatitis at home?
Problems associated with pancreatic diseases are always serious. Acute and chronic pancreatitis are now far from uncommon, both among the older generation and among the younger population. The reason for this is due to high alcohol consumption among the population, unhealthy diet, and starvation among young people for the purpose of losing weight.
A separate niche is occupied by endocrine diseases of the gland, such as diabetes and cancer. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that acute conditions, with inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases of the pancreas, have a risk of complications and a high mortality rate, even when all necessary medical care is provided to the patient.
Therefore, timely diagnosis of such diseases can not only maintain your good health, but even save your life.
Principles of pancreatic examination
Diagnosis of the pancreas must be comprehensive: it is necessary to obtain information not only about the structure of the organ, but also about its function. Let's explain why.
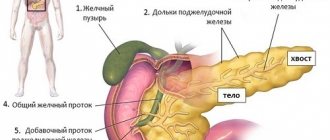
The pancreas is a large gland with a unique structure and functions. It is she who plays a key role in digestion, producing enzymes necessary for the breakdown of proteins and fats into substances that, entering the blood, will nourish the cells. This gland produces insulin, which helps the main energy substrate - glucose - provide energy to cells and tissues. Other hormones are also synthesized in it.
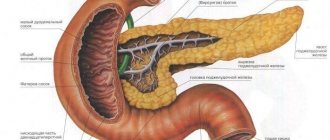
The gland is located in the retroperitoneal space, in front of it are the stomach, transverse colon and duodenum, and on both sides are the kidneys. Inside the organ there are ducts that collect pancreatic juice rich in enzymes from the glandular cells. They flow into one large duct, which opens in the duodenum.
If a certain amount of gland tissue is damaged, the remaining tissue replaces its function, and no symptoms of the disease may appear. At the same time, a situation may arise when a very small area dies or becomes inflamed; this is not noticeable in the structure of the entire gland, but is accompanied by a pronounced change in the function of the organ. That is why the examination of the pancreas must be comprehensive, covering both the structure of the organ and its function.
Causes of pancreatic diseases
At risk are all people who do not think about their daily diet, eat too much fatty foods, fried foods and overly spicy additives.
To break down such food, the pancreas has to produce a huge amount of enzymes, which results in an increased load for it. Alcohol abuse, on the contrary, leads to suppression of pancreatic function and insufficient production of enzymes. Also, the normal functioning of the gland is disrupted by stress.
But the most dangerous thing for a person is the development of cholelithiasis, in which a blockage of the duct with a stone can potentially occur and self-digestion of the gland can begin. In advanced forms of the disease, the gland digests both itself and the organs surrounding it, as a result of which the patient dies a painful death.
Pregnant women are also at risk of various pancreatic diseases. The development of pancreatitis may be preceded by trauma, inflammation of the duodenum, cirrhosis of the liver and metabolic disorders. All of the above leads to one important conclusion - if the doctor suspects pancreatitis, then it is necessary to immediately be examined and undergo a full course of treatment.
www.kakprosto.ru
Laboratory diagnostics
Tests examining the pancreas determine the state of organ function. In acute lesions of the pancreas, there is an increase in the activity of the enzymes it produces. Some of them are more informatively determined in the blood, others in the urine, and some in the feces. To determine the severity of the lesion, indicators of the functions of the organ associated with the pancreas - the liver - are also assessed.
Diagnosis of the pancreas includes the following tests:
- General blood test: during acute or exacerbation of a chronic process, an increase in the level of leukocytes, band and segmented neutrophils, and ESR is noted.
- Biochemical blood test: increased levels of total and direct bilirubin - in the icteric form of pancreatitis (while ALT is slightly increased), increased levels of gamma globulins, seromucoid, sialic acids.
- Pancreas-specific blood tests:
- blood alpha-amylase (its norm is 16-30 g/l per hour);
- determination of trypsin (its activity will exceed 60 μg/l);
- blood lipase (will be increased more than 190 U/l);
- blood glucose - will be increased (more than 6 mmol/l) if the endocrine (islet) part of the pancreas is involved in the inflammatory or destructive process.
Warning! Enzyme activity standards may vary slightly according to different laboratories.
- Determination of trypsin, lipase, amylase in the contents of the duodenal cavity on an empty stomach, and then several times after introducing 30 ml of a diluted solution of hydrochloric acid into the intestine. Normally, the levels of these enzymes in the first two portions of intestinal contents decrease, then gradually increase to the original value; in chronic pancreatitis, there is a significant decrease in all portions.
- Urine tests: amylase, amino acid content (Lasus test). When the pancreas is damaged, an increased content of these substances is observed.
- Coprogram. If there is a deficiency of glandular enzymes, fats, starch, undigested fiber and muscle fibers will be detected in the feces.
Previously, the main test used to diagnose pancreatic diseases was pancreatic amylase, an enzyme produced by the organ. In acute and exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the gland, there is an increase in the activity of this enzyme in the blood - above 30 g/l per hour and in the urine (where it is defined as “urine diastasis”) - above 64 U/l per hour. With the death of areas of the pancreas - pancreatic necrosis, sclerosing pancreatitis - there is a decrease in amylase activity both in the blood (below 16 g/l per hour) and in the urine (below 10 U/l).
To date, the main laboratory diagnostic criterion for pancreatic damage is the enzyme elastase, determined in stool. In case of insufficiency of gland function, the activity of pancreatic elastase is less than 200 mcg/g, in case of severe damage to the organ - less than 100 mcg/g.
Warning! All blood tests are taken on an empty stomach, but some pancreatic tests require some preparation. This point must be clarified, if not with a doctor, then with the staff of the laboratory where you plan to undergo diagnostics.
Laboratory stress tests
In some cases, it may be necessary to perform certain tests not only on an empty stomach, but also after introducing certain substances into the body - a stress test.
There are the following load tests:
- Glycoamylasemic test. The initial concentration of blood amylase is determined, after which the person must drink 50 g of glucose; After 3 hours, a repeat amylase test is performed. In pathology, after 3 hours there is an increase in this enzyme by more than 25% of the initial level.
- Proserine test. The initial concentration of urine diastase is determined, after which the drug “Proserin” is administered. Then, every half hour for 2 hours, the level of diastase is measured: normally it increases no more than 2 times, but then returns to normal. For different types of pancreatic pathology, different indicators are determined.
- Iodolipol test. Upon awakening, the patient urinates, then takes the drug “Iodolipol” orally. Then, after an hour, one and a half, two and 2.5 hours, the level of iodide in the urine is determined. This diagnosis of pancreatic diseases is based on the activity of the lipase enzyme produced by this organ. Normally, iodide begins to be detected in the urine within an hour, and the degree of its excretion increases and is maximum - in a portion of urine collected after 2.5 hours.
- Secretin-pancreozymin test. It is based on a change in the chemical composition of the contents of the duodenum after the introduction of a hormone-like substance secretin into it (it causes an increased secretion of pancreatic juice rich in bicarbonates and enzymes into the intestine).
- The glucose tolerance test is important for diagnosing damage to the endocrine apparatus of the pancreas. In this case, the blood glucose level is determined on an empty stomach, one hour and two hours after ingesting a glucose solution. This test is prescribed only by an endocrinologist, and he also interprets it, since there is a danger of complications associated with an increase in the blood level of this simple carbohydrate.
Study of duodenal contents
Duodenal contents are the masses that fill the duodenum. They consist of fragments of food that have already been treated with hydrochloric acid from gastric juice. In addition, it is into the intestinal lumen that the excretory duct of the pancreas and gallbladder opens.
Therefore, the duodenal contents are supplemented with bile and pancreatic juice, which has the entire complex of digestive enzymes. The study of its composition and concentration of individual components plays a huge diagnostic role for some time, as it helps to examine not only the pancreas, but also the liver and gall bladder, as well as clarify the condition of the duodenum.
It should be noted that the production of pancreatic juice, although considered cyclical and associated with meals, in reality it occurs constantly. Secretion in the organ in the time intervals between meals is called basic, or spontaneous; during these periods, a minimum amount of juice is released.
After eating, the iron is activated and much more juice is produced, up to 5 ml every minute. In just one day, up to 2 liters of digestive secretion are poured into the lumen of the duodenum.
Duodenal contents are obtained using a probe
If a doctor suspects a patient has chronic pancreatitis, then from the entire list of tests that need to be taken, the study of duodenal contents comes to the fore. But the stimulant that instantly acts on the pancreas is not a portion of food, but special chemicals. They can be injected directly into the stomach or into a vein. Thus, hydrochloric acid or 10% cabbage juice is used for oral administration, and pure secretin and pancreozymin are used parenterally (into a venous vessel).
In addition, these stimulants of pancreatic juice secretion have different effects. Some of them cause increased formation of the liquid component of the secretion and mineral salts, while the concentration of digestive enzymes decreases. Others, on the contrary, do not change the amount of juice, but increase the level of hormones and enzymes in it. Therefore, what chemical stimulants should be used to check the condition of the organ is decided by the doctor on an individual basis, taking into account both the presumptive diagnosis and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Duodenal contents are collected by probing. Usually two probes are used simultaneously: one takes masses from the stomach, and the other from the duodenum. The patient comes for examination on an empty stomach, and first, “spontaneous” contents are collected for 30 minutes.
Then a stimulant is injected into the stomach or intravenously, and after 5 minutes they begin to “pump out” the masses, which already contain a large amount of pancreatic juice. For a qualitative examination of the pancreas, it is necessary to take 6-8 portions of duodenal contents.
MRI of the pancreas
The obtained material is examined according to the following criteria:
- serving volume in milliliters;
- color shade;
- transparency;
- presence of impurities;
- amount of bicarbonates;
- bilirubin concentration;
- activity of digestive enzymes - amylase, lipase, trypsin.
A healthy or pathological pancreas has different parameters of duodenal contents. Thus, with active destruction of an organ, the total amount of juice and the concentration of enzymes change, and impurities appear. In chronic pancreatitis, the organ, even artificially stimulated, cannot provide a sufficient level of enzymes in the duodenal contents. Each indicator in this study is of great importance.
Study of organ structure
The examination of the pancreas is based on the properties of the tissue: it is not visible during a normal x-ray examination, but the ducts of the pancreas can be examined x-ray by injecting contrast into them. The gland is easily accessible for ultrasound examination, and Doppler ultrasound determines the blood flow in its vessels. Computed tomography visualizes its structure layer by layer, but its magnetic resonance analogue is optimal for determining the smallest structures of an organ. Let's look at everything in order.
X-ray methods
- Plain radiography allows one to visualize only calcification of the gland tissue and large stones in its ducts.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is the introduction of an X-ray contrast agent into the ducts of the gland from the duodenum using an optical apparatus, which is used to perform fibrogastroscopy.
- Selective angiography is an X-ray examination of the vessels of the gland after the injection of a contrast agent into them.
- Computed tomography helps in diagnosing tumor and inflammatory processes in the gland.
Each of the examination methods requires the patient to carry out preparatory procedures.
Ultrasonography
This method is not as accurate as a tomographic examination, but due to its simplicity and safety, it is basic for the primary diagnosis of gland pathologies. Ultrasound allows you to visualize acute and chronic inflammation, tumors, abscesses, cysts; Doppler ultrasound is invaluable for the initial assessment of organ blood flow. This method requires preliminary preparation. We talked about how to carry it out so that the result of the study is reliable in the article: Preparation for ultrasound for pancreatic pathology.
Magnetic resonance imaging
NMR imaging is the most informative method for studying the gland, which very accurately visualizes organ tissue layer by layer. When combining MRI with the introduction of contrast into the ducts (cholangipancreatography) or vessels (angiography), maximum reliability of the study of the pancreas is achieved.
Indications for MRI of the pancreas are as follows: