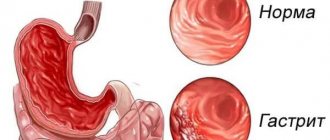
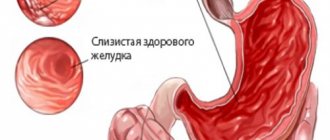
Gastritis is called inflammatory or inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the walls of the stomach, which can be caused by various factors: errors in nutrition, poisoning, alcohol abuse, etc. Some chronic diseases and bacterial infections, in particular Helicobacter pylori, also lead to gastritis.
Gastritis can be recognized by pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, sometimes diarrhea and other dyspeptic disorders.
The acute form of gastritis without proper treatment can quickly turn into chronic, which is dangerous due to its complications. This is why it is so important to consult a doctor at the first signs of illness.
Catarrhal gastritis - what is it?
Catarrhal gastritis (banal, simple) is the most common form of acute gastritis, characterized by inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the gastric mucosa : swelling, hyperemia, erosions, hemorrhages.
Functional disorders of the stomach are manifested first by increased secretion and increased tone of the walls, then by suppression of secretory function and hypotension.
The disease develops against the background of:
- acute intestinal infection (salmonellosis, food poisoning, etc.);
- consumption of spicy or irritating foods (bitter pepper, vinegar, ethyl alcohol, etc.);
- taking certain medications (salicylates, sulfonamides, antibiotics, iodine, etc.);
- allergic reaction to certain foods (eggs, milk, citrus fruits, etc.)
Complications of catarrhal gastritis can include cardiovascular failure, toxic damage to the myocardium (the muscular middle layer of the heart, which makes up the bulk of its mass), kidneys, and liver.
Rare complications
Each case of gastritis must be considered separately, since the variety is simply amazing. For example, what superficial atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is, even a therapist, let alone an ordinary person, cannot always answer. Only gastroenterologists know its symptoms and features thoroughly, because it is a very rare variety.
It differs from all others in that it occurs against a background of low acidity. However, this does not at all alleviate the patient’s condition. Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is characterized by the proliferation of the epithelium and its covering with polyps. Subsequently, the disease is characterized by thinning and degradation of the gastric mucosa. In essence, this is the process of formation of a benign tumor, which under unfavorable conditions will degenerate into a malignant one.
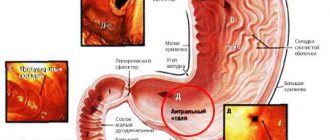
Congestive gastropathy in the antrum is prone to complications. The most common of them include bleeding from pathologically altered vessels of the stomach. Sometimes, this is a late and only symptom of the disease. In more than half of patients diagnosed with gastropathy, fibrogastroscopy reveals ulcers, erosions and perforations.
The most dangerous complication is the development of a tumor process in the gastric mucosa. Since the process of restoration of the mucous membrane is disrupted, and the organ’s protective system works “to wear out,” uncontrolled cell growth may occur against the background of inflammation.
If catarrhal gastropathy is left unattended, the manifestations of the disease will soon intensify, and the inflammation will cover the entire surface of the mucous membrane and penetrate deep into the tissues. This situation threatens atrophy of the mucous membranes, the appearance of erosive foci and ulceration of tissues.
With the development of pangastritis, inflammatory processes will spread to the duodenum and acute duodenitis will occur. If you refuse treatment in this case, the pathology will take over the entire digestive tract. Numerous ulcers will appear and internal bleeding will occur.
Symptoms
The disease develops rapidly. The first symptoms of catarrhal gastritis appear 3-4 hours after exposure to provoking factors.
An attack of acute gastritis is accompanied by sharp cramping pain in the epigastric region, nausea, and vomiting, which does not bring relief . The vomit contains mucus and an admixture of bile .
The patient notes heaviness and burning in the upper abdomen , general weakness, and dizziness. The tongue is covered with a white or grayish coating, the mouth feels dry or, on the contrary, increased salivation.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
Simple gastritis of infectious or allergic origin, occurring with frequent vomiting and diarrhea, may be accompanied by fever, symptoms of dehydration, severe weakness, and sometimes muscle cramps.
Symptoms
The onset of hemorrhagic gastritis is no different from other types. Pain in the epigastrium during palpation or after eating, heaviness, belching and nausea are observed. Then symptoms of gastric bleeding are added with a change in the color of the vomit and feces. The disease in question differs from other types precisely in the symptoms of anemia, because there can often be hidden bleeding.
Hemorrhagic gastropathy, accompanied by acute internal bleeding, manifests itself with special symptoms in the form of:
- thick black vomit;
- tachycardia;
- pale skin;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- black liquid stool.
Chronic gastric bleeding in hemorrhagic gastritis manifests itself with similar symptoms as in the acute form. Symptoms may be supplemented by brittle nails and the development of iron deficiency anemia.
The pathology, which developed against the background of diseases of the stomach and other organs, is characterized by a clinical picture that combines signs of diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis or myocardial infarction.
At first, the disease shows no signs. In frequent cases, the first symptoms are covered by those that are inherent in other ailments in which gastropathy develops. After some time, gastropathy has symptoms, as with gastritis, it is accompanied by pain and heaviness in the stomach, flatulence, nausea and heartburn.
In addition, appetite is disrupted, vomiting appears, after which the patient’s well-being becomes better. In half of the patients, there is a disturbance in the formation of bile, the tone of the large intestine is disturbed, and constipation occurs.
Diagnostics
Typically, diagnosing simple gastritis does not cause difficulties for a practicing physician. Examination of the patient, establishing the fact of dietary errors, taking medications or existing food allergies - this is quite enough to make a preliminary diagnosis.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct laboratory tests: a general blood and urine test, a stool test for occult blood, and a bacteriological analysis of vomit.
On our website: Chronic superficial gastritis - symptoms, treatment, diet
For banal (catarrhal) gastritis, instrumental diagnostics are also indicated.
- Gastroscopy (FGDS, FEGDS, EGDS) is a study of the condition of the gastric mucosa using a special instrument - a gastroscope, the most informative diagnostic option . Be prepared for the fact that if the doctor suspects a neoplasm, you will undergo a biopsy of the epithelium of the stomach or esophagus.
- X-ray with contrast – assessment of the relief of the walls of the stomach.
- Electrogastrography – determination of the state of the motor-evacuation function of the stomach.
- Intragastric pH-metry is a study of the state of the secretory function of the stomach.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed: ultrasound of the abdominal organs, multislice computed tomography (MSCT) of the abdominal organs, antroduodenal manometry.
The effectiveness of folk remedies in the treatment of gastritis
In modern medical practice, folk remedies are actively used. But their use must be preceded by diagnosis. Otherwise, some decoctions and herbal infusions can cause a completely opposite and irreversible reaction in the body.
Thus, when starting treatment, the gastroenterologist first of all inquires about the patient’s diet and nutritional regimen, based on which he excludes the list of harmful foods and prescribes a diet and a corresponding regimen.
Returning to the issue of including folk remedies in the treatment regimen, the type and stage of gastritis, as well as the level of stomach acidity, should be clearly defined. It is also noteworthy that if the disease is identified before the acute stage, diet and herbal infusions are quite capable of neutralizing and curing the disease.
Therapeutic treatment of gastritis can also include, along with medications, traditional treatment recipes. Today, all kinds of herbal infusions, gastric infusions and teas are sold through pharmacy chains.
You can relieve the inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa with vegetable juices. First of all, potato juice is recommended. It should be consumed immediately after receiving it, without waiting for it to acquire a dark shade. After drinking half a glass of this juice, you should definitely eat in the next half hour. You should drink juice before main meals for at least 21 days.
A decoction of flaxseed is used in the same way as potato juice. The action of these two recipes is identical.
Cabbage juice is also recommended, but should be used with caution.
Treatment
If the disease is severe, the patient requires hospitalization in a hospital.
Drug therapy is prescribed taking into account functional stomach disorders and the reasons that led to the development of simple gastritis.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
Diet therapy is considered one of the main methods of treating the acute form of the disease. The patient is prescribed a one-day fast, then a special gentle diet taking into account the acidity of gastric juice; the regimen should be followed for 7-10 days.
The final treatment will depend on the final diagnosis in the patient’s medical record.
There are several forms of the disease, which differ in the localization of inflammation, morphological signs, severity and other factors.
Types of catarrhal gastritis:
- Spicy. With this type of simple gastritis, the integrity of the mucous membrane and its regenerative function are impaired. The disease is characterized by rapid onset of clinical symptoms and acute course.
- Focal . Characterized by the localization of inflammation in certain areas of the stomach. Clinical manifestations of focal catarrhal gastritis are similar to other forms of the disease.
- Diffuse. With this form of catarrhal gastritis, inflammatory changes affect the entire gastric mucosa. Untreated diffuse gastritis quickly becomes chronic with atrophic tissue damage.
- Atrophic. This form of simple gastritis is manifested by atrophy (death) of the glandular tissue of the stomach and its replacement with connective tissue.
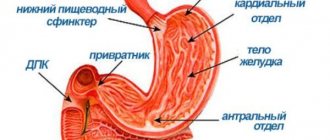
- Antral. With antral catarrhal gastritis, inflammation is localized in the antrum of the stomach, which leads to deformation and narrowing of this part of the organ.
- Distal. Characterized by pathological changes in the distal stomach.
- Bulbit. Inflammatory changes affect the bulbus (duodenal bulb). Catarrhal bulbitis has an acute course and severe symptoms.
- Duodenitis. Catarrhal duodenitis is pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum. It is often combined with other gastrointestinal diseases - gastritis, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis.
Treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor!
On our website: Is it possible to cure alcoholic gastritis?
What do doctors usually prescribe?
Treatment of the disease begins with gastric lavage and subsequent intake of adsorbents . Depending on the severity of the course and functional disorders, the following drugs are additionally prescribed:
- Painkillers (analgesics, antispasmodics) – for severe combat syndrome.
- Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs - if pathogenic flora is detected.
- Gastroprotectors, proton pump inhibitors, H2-histamine receptor blockers and antacids - for increased stomach acidity.
- Infusion therapy - for dehydration.
- If necessary, additional antiemetics (prokinetics) are prescribed.
Attention! Only your attending physician can prescribe medications, but if you do not have the opportunity to get to him or call an ambulance, start with activated charcoal. Then something like phosphalugel or Maalox. Read about contraindications!
Folk remedies
Treatment of catarrhal gastritis with folk remedies is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
What can be used as adjuvant therapy?
- A mixture of honey and aloe juice. Mix the ingredients in a 1:1 ratio. You need to take the product within 20-30 minutes. before meals. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
- Oatmeal broth. Pour 1 cup of oat grains into 1 liter of boiling water and let it brew for 12 hours. The mixture is then simmered over low heat for another 30 minutes. and insist again for 12 hours. Take ½ glass of the cooled product before meals. The course of treatment is 1 month.
- Potato juice . Take ½ glass of freshly squeezed potato juice before each meal. The course of treatment is 10 days. Then you should take a ten-day break and repeat the treatment.
Alternative treatment should not replace drug therapy!
Diet
- In the first 1-2 days from the onset of the disease, you should completely abstain from food. Warm tea or mineral water in small portions is allowed.
- On the second or third day, slimy soups, weak broths, pureed rice or semolina porridge, and jelly are introduced into the patient’s diet.
- The 4th day menu can be supplemented with dried white bread, steamed meat cutlets, boiled chicken or fish, and mashed potatoes.
Next, the patient is prescribed treatment table No. 1, and after 7-8 days from the onset of the disease, you can switch to normal nutrition.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The main reason for the development of the inflammatory process in the stomach is a violation of the diet. Constant overeating, abuse of fatty foods, black coffee, alcoholic beverages, poor chewing of food, hasty eating - all these factors are favorable prerequisites for the development of an inflammatory process in the stomach.
Other predisposing factors to the development of gastritis are:
- Inflammatory diseases of the digestive system (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, duodenitis and others).
- Past food poisoning.
- Eating too hot or cold food.
- Genetic predisposition.
As a rule, the inflammatory process spreads to the entire mucous membrane of the stomach, but if the pathological process covers only a certain area, then doctors diagnose “focal gastritis.” The symptoms of this type of inflammatory process are the same as those of most types of gastritis.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
The prognosis for catarrhal gastritis is favorable : timely treatment and compliance with all medical prescriptions lead to complete recovery.
The disease can become chronic if it is repeatedly exposed to etiological factors (factors that caused the development of the disease).
In case of severe disease, acute heart failure and toxic damage to internal organs may develop.
Kinds
There are several types of gastritis depending on the inflammation process:
- Catarrhal diffuse gastritis. Inflammation spreads throughout the entire organ.
- Catarrhal focal gastritis. Damage occurs partially to the organ. In most cases, the presence of antral gastritis is determined.
Additionally, there is a classification depending on what the symptoms are, the location of the pain, and the course of the disease.
There are three types of catarrhal gastritis:
- Atrophic. This type occurs in most cases due to genetic predisposition. Due to the development of this form of the disease, the cells of the stomach are replaced by connective tissue. In this regard, an inflammatory process occurs, and the immune system tries to protect the body. Catarrhal atrophic gastritis has its own characteristic manifestations - atrophy of the gastric mucosa.
- Spicy. The main causes of this type are overeating, as well as eating large amounts of foods containing preservatives. As a result, there is a disruption in the renewal of stomach cells and blood circulation within the organ. Additionally, nausea, vomiting, unpleasant odor from the mouth and general weakness appear.
- Chronic. This type of gastritis appears at an advanced stage of the disease. The destructive process affects the deeper tissues of the stomach. This process occurs, and the following symptoms appear: impaired secretion of hydrochloric acid and atrophic changes. Additionally, vomiting, nausea, a sharp deterioration in appetite and weight loss, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth occur.
Homeopathy
“Amarin” – oral drops containing substances of plant origin; used for gastrointestinal disorders caused by impaired secretion and gastric motility, spasms, and pain. Recommended for use from 11 years of age, 10-20 drops diluted in a small amount of liquid, drunk three times a day. Contraindicated for stomach and duodenal ulcers, high blood pressure. A possible side effect is allergies;
"Gastricumel" - tablets containing substances of plant and mineral origin, activate the body's defenses and normalize gastric dysfunction. Children under 12 years of age are recommended to grind 1 tablet and dissolve it in two tablespoons of water. Give the resulting solution at the age of 2-6 years, two teaspoons, from 6 to 12 - 3 spoons.
"Gepar compositum" is an injection solution, a complex drug prescribed for disorders of the digestive organs. It is administered once every 1-3 days subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously. There are no data on side effects or contraindications;
"Kalium Floratum" - tablets, applicable for all age categories, differ in dose and frequency, depending on age and the nature of the gastropathy - acute or chronic. For children under one year old, 1 tablet dissolved in water 1-2 times a day is recommended, for adults the same amount, but the frequency of administration can be up to 6 times. If you are hypersensitive to the components of the product, allergic reactions are possible.
All these drugs can be prescribed to pregnant women only with the permission of a doctor, because they have not been subjected to clinical trials in this category of patients.