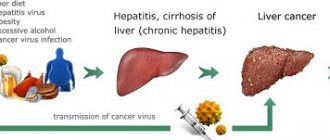
Opisthorchiasis is a parasitic disease, the source of which is the presence in the human body of one of two varieties of worms of the trematode genus - the cat fluke or the squirrel fluke. In the presence of opisthorchiasis, mainly internal organs such as the liver, bile ducts and pancreas are affected. The disease is treated mainly with medications and strict adherence to the diet prescribed by the doctor. Moreover, the diet for opisthorchiasis in adults is different from the diet recommended for children. This circumstance should be taken into account in the presence of the disease in different age categories of family members.
What is strictly prohibited in food for opisthorchiasis?
There are products that can actually harm treatment and aggravate a person’s condition.
And there are not so few of them. From the first days of the diet, exclude these dishes and do not indulge yourself. You can't eat:
- Fresh bread;
- All pulses;
- Flour;
- Porridge made from barley or corn grits;
- All kinds of donuts;
- All pancakes are made with flour;
- Fried foods and sweet pastries.
You will also have to give up white cabbage, any eggplant, regular green onions, spinach and sorrel, any varieties of corn, turnips, radishes and radishes, onions, any asparagus, fresh and pickled garlic, and all canned and pickled vegetables. Nuts and sunflower seeds are prohibited.
It is not recommended to eat meat and fish products: sausages, all kinds of canned meat, as well as kidneys, liver and tongue, sushi; it is forbidden to eat salted and smoked fish, respectively, and canned fish.
Fatty dairy products, fermented baked milk and whey, as well as all salty cheeses are prohibited. Don't eat whole eggs. Mushroom and fish, as well as meat broths, are also unacceptable. Lard and cooking fats are prohibited.
Useful foods for opisthorchiasis
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the patient must adhere to diet table No. 5. This diet helps normalize the functions of the liver and biliary tract and improves bile secretion. Also used for hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, cholecystitis.
During the day, the calorie content of food should be from 2200 kcal to 2500 kcal. The patient's body should receive about 350 grams of carbohydrates and 90 grams of fats and proteins per day.
Groups of useful foods and dishes for opisthorchiasis:
- drinks: homemade compotes, jelly, juices (not sour and tomato juice without salt), rosehip decoction, weakly brewed tea, weak coffee with milk;
- all low-fat dairy and fermented milk products;
- vegetarian, milk soups;
- fish, meat (not fatty varieties);
- porridge (crumbly);
- sweet berries, fruits;
- biscuits and other flour products made from unleavened dough, day-old bread (rye, wheat);
- 1 egg per day (can be eaten boiled or as an omelet);
- in small quantities honey, sugar, jam;
- vegetable oils and butter (maximum consumption limit is 50 grams);
- greens and vegetables, dried fruits.
All dishes must be steamed, boiled or stewed. Food should be served at room temperature. The number of meals is at least 5, but not more than 6.
Traditional medicine for opisthorchiasis
Traditional medicine should be used in combination with drug therapy.
Treatment should begin with birch tar. 20-30 minutes before meals you need to drink a glass of milk, to which 6 drops of tar are added. You need to drink milk once a day for a decade. After this, give the body a break for 20 days. Then repeat the same cycle of procedures 2 more times. In general, the course of treatment lasts 3 months.
Infusions and decoctions of St. John's wort, aspen bark, cumin seeds, plantain leaves, nettle, dandelion, tansy, buckthorn, wormwood, coriander seeds, and pumpkin will help drive out parasites. These herbs will help improve the separation of bile, relieve the inflammatory process, and kill and remove flatworms.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis involves proper processing of fish. When frozen for 7 hours (at a temperature of -40) or 1.5 days (at -28), when salted for 10-30 days (it all depends on the size of the fish, the salt density should be 1.2 g/l, and air temperature +2 degrees Celsius), during heat treatment (cooking, stewing, frying) for at least 20 minutes after boiling, opisthorchids die and the fish is disinfected.
Dangerous and harmful products for opisthorchiasis
It is necessary to exclude from the patient’s diet foods that stimulate the secretion of gastric juice and pancreatic secretion. You cannot eat fried or smoked foods. Products containing large amounts of cholesterol and purine should also be eliminated from consumption.
These products include:
- freshly baked bread and rolls;
- mushrooms, lard, caviar, meat and fish of fatty varieties and soups cooked on their basis;
- spices and herbs: pepper, horseradish, mustard, radish, green onions, sorrel, spinach, radish;
- refractory, cooking fats and trans fats;
- canned food, sausages, marinades, preserves, vinegar, dressings and sauces;
- excessively cold or hot foods and drinks;
- alcoholic drinks, sweet sodas, cocoa, strong coffee;
- sour fruits and berries and fruit drinks and smoothies made from them;
- store-bought sweets, pastry cream, ice cream and other cold sweets and cocktails.
The diet must be followed for at least 50 days.
Features of proper nutrition
The menu should include vegetables and fruits, bran and cereals.
It's good to add fermented milk products. Diet in the treatment of opisthorchiasis is also required to prevent re-infection. To do this, within fifty days it is necessary to create conditions in the body so that they are as unfavorable as possible for the life and reproduction of trematodes.
Proper nutrition will also help restore and strengthen the immune system. By the way, when you have to follow a diet for a long enough time, and in our case it’s about two months, it becomes a habit and becomes a way of life.
It is recommended to eat 6 times a day, avoiding eating too hot or too cold foods. The emphasis should be on baked and boiled dishes. Overeating should not be allowed, as this will complicate the work of already affected organs. The caloric content of daily consumed foods should be in the range from 2200 to 2500 kcal.
As for the ratio of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, the diagram will look something like this:
- fats - up to 90 g;
- carbohydrates - up to 350 g;
- proteins - up to 90 g.
It should be remembered that all products must be at a comfortable temperature. Eating hot or cold foods is not allowed. Preference should be given to boiled and baked dishes. Avoid overeating, but you need to switch to quality meals six times a day. The total number of kilocalories consumed daily should not exceed 2.5 thousand.
When following a diet for opisthorchiasis, a person needs to consume 90 grams of protein, 350 grams of carbohydrates and 90 grams of fat daily. At the same time, foods that are saturated with cholesterol, refractory fats and other heavy foods are prohibited. It is necessary to cleanse the body of excess cholesterol by consuming large amounts of fresh vegetables and fruits.
Recommended foods for opisthorchiasis
This point is of utmost importance, so it is strongly recommended to read it. The diet table for opisthorchiasis in adults includes the following products:
The diet table for opisthorchiasis in adults includes the following products:
- Low-fat varieties of fish and meat: rabbit, poultry, milk sausages (no more than 2 per week), flounder, pollock, carp and others;
- It is allowed to consume 1 egg per day in the form of an omelet or boiled;
- Fermented milk products, as well as milk;
- Berries, fruits (non-acidic apples, bananas, pomegranates), dried fruits, herbs and vegetables not included in the list of prohibited foods;
- Cereals, except semolina;
- Sugar and honey are allowed. Sugar consumption should not exceed 10 grams/day (it is advisable to divide the recommended dose into 2 parts), honey - no more than 20 grams/day;
- Rye bread and other flour products based on unleavened dough, as well as crackers, day-old bread;
- Compotes of dried fruits and berries, as well as fresh ones not included in the list of prohibited ones, jelly, juices, weak coffee with added milk, rosehip decoction, weak tea;
The diet menu for opisthorchiasis may consist of the following dishes:
- Breakfast: omelette cooked in a double boiler and vegetables/porridge with milk, with the addition of the permitted amount of vegetable oils;
- Lunch: a glass of kefir, small quantities of fruit or berries;
- Lunch: vegetarian dishes (vegetable soup, for example) and seaweed salad;
- Afternoon snack: pumpkin seeds, compote made from dried fruits or berries;
- Dinner: buckwheat porridge, boiled in water and 1 milk sausage;
Diet menu with 6 meals a day (provided for severe disease):
- First breakfast: pumpkin seeds or a decoction of them;
- Basic breakfast: pumpkin porridge and a glass of weak tea with a little sugar added;
- Lunch: baked fruit (apple, for example);
- Lunch: vegetarian soup (vegetable soup or borscht), vegetable salad;
- Afternoon snack: fruit-based cocktail/compote of dried fruits or berries;
- Dinner: stewed cabbage and vegetable cutlets/fish cutlets;
The dietary menu for gallbladder damage by a parasite is different:
- Breakfast: berries with oatmeal with milk, washed down with light tea with the allowed amount of sugar;
- Lunch: fruit salad;
- Lunch: vegetable salad and puree soup, fruit and berry compote;
- Afternoon snack: kefir;
- Dinner: vegetable puree, fresh natural juice from vegetables or fruits;
There is also a nutrition menu that allows you to prevent the development of opisthorchiasis in humans. A preventative diet consists of eating the following foods:
- Breakfast: porridge from permitted cereals with milk, jelly or compote of dried fruits and berries;
- Lunch: nuts;
- Lunch: medium fat soup, vegetable puree;
- Afternoon snack: berries;
- Dinner: vegetable puree (potatoes), greens, vegetable or fruit salad, weak tea with a little sugar added;
Note that this diet will not bring a preventive effect if you do not follow the simple rules for preparing fresh fish from the carp family.
What foods and dishes should not be eaten with opisthorchiasis?
What should you not eat when you are sick? During the period of rehabilitation and cure of the disease, you should avoid drinks containing alcohol.
| Dish | Prohibited Products |
| Beverages | Strong coffee, cocoa, chocolate, alcohol. |
| Flour products | Fresh bread, buns; products with a rich cream filling. |
| Milk products | Kefir. |
| Soups | Mushrooms containing meat and fish. |
| Eggs | Fried, hard-boiled. |
| Meat and fish products | Lard, butter, margarine, fish and fatty poultry. |
| Other products | Green onions, radishes, spinach, sorrel, pickles, marinades, vinegar, sour berries and fruits, sausage, sauces, smoked and canned products, hot spices: horseradish, mustard, pepper; chilled desserts: ice cream. |
The diet for opisthorchiasis should consist of the following products.
- day-old bread;
- crackers, bread, biscuits;
- bran;
- porridge from semolina, buckwheat, oatmeal, millet and rice cereals;
- cereal-based dishes (casseroles, puddings);
- flax-seed;
- boiled pasta.
- potato;
- beet;
- Chinese cabbage;
- green pea;
- cucumbers;
- green beans;
- zucchini;
- broccoli;
- celery;
- bell pepper;
- carrot;
- pumpkin;
- sea kale.
Fruits and berries (in small quantities):
- apples (not sour);
- watermelons;
- bananas;
- grenades;
- dried fruits (no restrictions).
- most types of meat;
- lean fish;
- marine mollusks and crustaceans.
- sour cream (limited);
- cheese (limited);
- kefir and yogurt with fat content up to 2%;
- skim cheese.
- soups (vegetable, fruit, dairy, pea, pearl barley);
- borscht (without broth).
Eggs (no more than 2 whites daily):
- egg white omelettes;
- hard boiled eggs;
- quail eggs.
- butter (no more than 30 g daily);
- refined vegetable oil (up to 15 g).
- weak tea;
- mashed compotes;
- jelly (not sour);
- fruit drink (not sour);
- infusions of chamomile and rosehip.
Seasonings and sauces:
- parsley;
- dill;
- vanillin;
- cinnamon;
- salt (up to 10 g daily);
- milk, sour cream and vegetable (non-spicy) sauces;
- soy sauce (limited);
- fruit sauces;
- sugar (a little);
- lollipops;
- mousses;
- jelly;
- jelly;
- marmalade;
- cookies (limited);
- marshmallows (limited);
- candies without chocolate;
- nougat without nuts;
- Turkish delight without nuts;
- kozinaki (limited).
A diet for opisthorchiasis involves the complete exclusion of the following food.
Cereals and leguminous products:
- fresh bread;
- baked goods from butter and puff pastry;
- fried pies;
- pancakes;
- donuts;
- any grain legumes;
- porridge from corn and barley groats.
- White cabbage;
- eggplant;
- green onions;
- spinach;
- sorrel;
- corn;
- turnip;
- radish;
- radish;
- asparagus;
- onion;
- garlic;
- canned vegetables.
Fruits, berries and nuts:
- any raw fruits and berries, except those allowed in the list above;
- any nuts, as well as sunflower seeds.
- language;
- liver;
- kidneys;
- canned meat;
- sausage and frankfurters;
- canned fish;
- fatty fish;
- smoked and salted fish;
- sushi;
- shrimps.
- fatty dairy products;
- salted cheeses;
- serum;
- Ryazhenka
- okroshka;
- broths based on mushrooms, fish, meat, spinach, sorrel, and legumes.
- juices;
- soda;
- green tea;
- hibiscus;
- chicory;
- coffee;
- cocoa;
- hot chocolate;
- any alcohol (absolutely prohibited).
Seasonings and sauces:
- chocolate;
- cream products;
- condensed milk;
- sherbet;
- halva.
Meal options for the day
The diet for opisthorchiasis does not require a very varied menu, but it should be strictly followed for a long time to maintain the affected organs. The list of foods included in the diet will gradually change depending on the stage of recovery. The most strict option for severe forms, the most loyal diet after treatment of opisthorchiasis.
Nutrition for severe disease
During the period of initiation of treatment for opisthorchiasis, the doctor prescribes strict adherence to table No. 5. Thanks to it, the hepatobiliary system works in a gentle manner and recovers faster. The daily calorie content of the menu does not exceed 2400 kilocalories, while protein should be approximately up to 80 g per day, half of which is vegetable.
Everything is boiled, in rare cases it is stewed. Products with a high amount of coarse fiber are completely excluded. Table No. 5 is one of the longest diets, which must be followed for at least 6 weeks.
Maintenance diet
After stopping the course of taking medications (for example, Biltricid or Ecorsol) aimed at removing helminths and restoring the affected organ, a maintenance diet is prescribed. The main feature of nutrition during this period is the high energy value of foods. It must fully meet the physiological needs of a person for faster regeneration of damaged tissues.
As you recover, dietary foods such as dates, plums, and blueberries are included in your diet. They can have a positive effect on gastric motility and help the body cleanse itself of toxins.
Preventive diet
Even if the body has recovered after drug therapy, you cannot stop the diet. The diet should be just as balanced and complete, but without the foods listed in the table in the “prohibited” category. Foods high in fiber are added to the diet.
Post-medication diet
Is it possible to stop dieting after taking medications? No! The optimal quantity and ratio of food components containing fiber, corresponding to the physiological needs of the body, is necessary after drug treatment. Helps restore damaged internal organs: from the liver to the pancreas.
As the body recovers, you should eat plums, blueberries, dates, and apples. Fruits improve gastric motility, cleanse the intestines of toxins, and balance the bile flow.
In order not to neglect such an important component of anti-opisthorchiasis therapy as the correct diet, you should understand what exactly happens to the body during opisthorchiasis and why special diets are not required for most other parasitic diseases.
Opisthorchiasis, unlike intestinal helminthiases, is characterized by severe damage to organs that serve as the localization site for Siberian flukes (the causative agents of this disease). These include organs of the hepatobiliary system such as the intrahepatic bile ducts and gallbladder, but in about a third of cases, adult parasites can also choose the pancreatic ducts.
As a result of prolonged mechanical and toxic effects of flukes on these organs, the following complications can develop:
- chronic hepatitis (liver inflammation);
- chronic cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts);
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- liver cirrhosis (irreversible replacement of normal parenchymal tissue with fibrous tissue);
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer);
- hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
Thus, opisthorchiasis is often accompanied by dangerous diseases, the prescription of a special diet for which no longer surprises anyone. These pathologies are especially often found in residents of opisthorchiasis foci, who are characterized by a chronic form of this helminthiasis. It occurs without pronounced symptoms, but becomes acute 10–20 years after infection, as a result of which the organs affected by the flukes manage to become irreversibly diseased.
When treating opisthorchiasis, as well as the time after treatment indicated by the doctor, one should adhere to the therapeutic diet “Table No. 5”, developed by the Soviet therapist, gastroenterologist and nutritionist M.I. Pevzner. Its purpose is to help restore organs of the hepatobiliary systems.
The daily menu should be based on the following principles:
- preparing dishes by boiling, baking, or, less often, stewing while completely avoiding frying;
- avoidance of excessively cold and hot foods;
- avoidance of foods high in oxalic acid, purines, extractives, and coarse fiber;
- avoidance of foods that cause flatulence or increase the secretion of digestive juices;
- limited salt intake (up to 10 g);
- dividing the daily menu into 4–5 meals in equal portions;
- consumption of up to 80 g of protein (50% vegetable), up to 90 g of fat (30% vegetable), up to 400 g of carbohydrates;
- daily calorie content of the menu - 2400–2800 kcal;
- drinking at least 2 liters of fluid per day.
“Table No. 5” is a long-term diet, and, depending on the degree of organ damage, the doctor may prescribe its adherence for a period of 5 weeks to 2 years after deworming. At the same time, adult patients or parents of children being treated for opisthorchiasis are not recommended to eat river fish or give it to children throughout the entire rehabilitation period. Otherwise, there is a high risk of a new infection with opisthorchiasis, as a result of which everything will have to start all over again.
Forbidden foods in the treatment of opisthorchiasis
Food and drinks that can negatively affect organ function are excluded. If you have opisthorchiasis, you should not eat spicy, smoked or semi-smoked foods. Salt intake should be reduced to 10 grams per day. Eliminate all seasonings, sauces and mayonnaise from your diet.
Prohibited drinks include:
- All alcohol. Some home-grown self-healers believe that if you drink vodka, the helminth will go away on its own; this misconception can kill your liver forever. Absolutely all alcoholic drinks are prohibited, including weak cocktails and beer.
- Kvass, homemade and store-bought.
- Red hibiscus tea.
- Any carbonated drinks harm not only the liver, they cause the progression of stomach ulcers.
- Drinks containing caffeine include not only cocoa and coffee, but also strong green tea and chicory.
- Store-bought milkshakes.
- Hot chocolate.
- Juices from citrus fruits, grapes.
Prohibited foods include foods rich in poorly digestible fiber and containing acid that increases the secretion of gastric juice:
- Vegetables and herbs - radishes, sorrel, green onions, rhubarb, horseradish, corn, eggplant, white cabbage.
- Bakery and flour products – baked goods based on white flour, butter and puff pastry, freshly baked bread.
- Sweets - ice cream, cakes, cheesecakes, pancakes, chocolate, syrups and other products with a high sugar content.
- Fruits – lemon, grapes, citrus fruits, persimmon.
- Meat - pork, horse meat, sausages, kidneys, liver, tongue.
- Fish - any river, red sea, fatty varieties; crab sticks, caviar.
- Cereals – beans, beans, lentils.
- Fat-containing foods – margarine, sunflower oil, lard, meat broth.
- Dairy products with a fat content of more than 1.5-2% - sour cream, cream, cheese, milk, kefir, whey.
- Soups – solyanka, rassolnik, okroshka, borscht.
- Canned and pickled foods, mushrooms (including broth based on them).
- Nuts.
Sample menu for various types of opisthorchiasis
Although the menu for patients with opisthorchiasis has certain restrictions, the list of products is still wide enough to prepare delicious and healthy dishes every day. Listed below are those products that may be included in the menu of a patient with the disease during the period of treatment and recovery. Such products include:
- rabbit meat;
- poultry meat is not fatty and skinless;
- veal tenderloin without fat (stewed, boiled and baked);
- soups made with vegetable broth;
- boiled rice, buckwheat or oatmeal;
- pasta;
- low fat dairy products;
- a small amount of kefir drink, sour cream and yogurt;
- Low fat cheese is allowed;
- water, weak tea, dried fruit compotes, fresh juices, various jelly;
- chicken egg, boiled in a bag (no more than 1 piece per week);
- fruits and vegetables are not sour;
- a small amount of dry fruits and berries;
- minimum amount of butter and vegetable oil.
If the patient does not know what can be eaten with opisthorchiasis, and what foods should be excluded from the menu, we advise you to read the list presented below more carefully. It will describe those foods that are best excluded from your diet. These products include:
- alcoholic drinks;
- strong coffee and tea drink;
- natural grape juice;
- any types of carbonated drinks;
- broths that are cooked with fatty meat or bones;
- fresh bread and bakery products;
- fatty meats;
- chicken eggs that have been fried or hard-boiled;
- any types of smoked products and sausages;
- various types of hot spices and seasonings;
- sour types of fruits and berries;
- some types of vegetables, these include radishes, sorrel, green onions and garlic;
- pickled vegetables;
- all types of sweets (cakes, sweet and fatty pastries);
- purchased juices in packs;
- all types of mushrooms.
It is worth noting that with opisthorchiasis of the liver, the weekly menu may differ from another type of disease, and the menu may also differ in adults and children, since the most gentle diet is selected for children. In each individual case, the diet can be weakened or tightened, depending on the course of the disease and its symptoms.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis without following a special diet is impossible. Depending on the course of the disease and the organ on which the disease had a special impact (period of exacerbation of the disease, opisthorchiasis of the liver or pancreas), special nutritional principles are applied. For example, among folk remedies that help in the treatment of this disease, a decoction of pumpkin seeds is often used.
Example of a daily menu
The diet for opisthorchiasis, especially in the first few days after deworming, may seem overly complicated, as a result of which patients usually use ready-made menus. Below are examples of daily menus that can be used for both adults and children.
- Breakfast: oatmeal with milk, low-fat cottage cheese with sugar, weak tea with honey.
- Second breakfast: baked apple.
- Lunch: rice, boiled chicken, compote.
- Afternoon snack: rosehip decoction.
- Dinner: mashed potatoes, boiled fish, tea.
- Second dinner: low-fat kefir.
- Breakfast: vinaigrette with low-fat sour cream, a small slice of soaked herring, some day-old bread, tea with milk.
- Second breakfast: buckwheat porridge, boiled beef, vegetable juice.
- Lunch: vegetable soup with low-fat sour cream, mashed potatoes, vegetables, a small piece of boiled fish, compote.
- Dinner: low-fat cottage cheese casserole, weak tea.
- Second dinner: cookies, jelly.
Among all known parasitic liver diseases, opisthorchiasis is considered one of the most common in the modern world. According to statistics, on our planet the number of infected people is about 21 million people, with the lion's share of patients falling in the countries of the post-Soviet space.
Opisthorchiasis is a parasitic disease caused by helminths that infect the human liver and pancreas.
In modern medicine, several treatment regimens for the disease are known, but Biltricide for opisthorchiasis is recognized as one of the most effective medications that can completely destroy helminths in the human body.
Additional benefits of the diet
Of course, if you start eating healthy to speed up the healing process, you can expect some additional effects of the diet. It allows you to lose excess weight and this is quite obvious: sweets and fatty foods are kept to a minimum, there are no smoked or salty foods on the menu, and everything starchy is practically excluded. That is, the main factors of weight gain are removed on their own, and the figure returns to normal.
So some weight loss during treatment is not necessarily associated with exhaustion of the body fighting the disease, but with a new type of nutrition. And in this case, it only helps to recover faster, and sets the person up to continue to eat right in order to maintain optimal weight and good health.
Removing parasites using folk remedies
The diet should be varied and not limit the patient to any fixed set of foods. Recipes are easy to find in specialized literature.
First courses are prepared avoiding fatty and rich bases:
- nettle borscht;
- soup from any cereal;
- beetroot
Finely chop boiled beets and raw potatoes, which are then cooked in 1.5 cups of water. Cooled potatoes with broth are mixed with beets, and the rest of the products are added.
Second courses, despite the restrictions, are very varied:
- Steam omelette.
- Pilaf with poultry meat.
- Navy pasta.
- Cutlets with crumbly cereal porridge.
- Cottage cheese casseroles.
- Pasta with seafood.
For 150 g of spaghetti take 200 g of peeled shrimp, 2 tbsp. l. tomato paste, garlic clove, and vegetable oil. Cook the shrimp in a frying pan over low heat for a few minutes. At the end, add tomato paste and garlic passed through a press, and cook everything together for another 5 minutes. Spread seafood dressing over cooked spaghetti.
Cottage cheese must be present in the diet:
- millet pudding with cottage cheese;
- cottage cheese casserole with jam;
- lazy dumplings;
- cheesecakes with fresh fruit.
Vegetable dishes are the most varied and necessary for rehabilitation treatment, since the products used are varied and easily accessible:
- Puree of green peas, cauliflower.
- Baked broccoli.
- Pumpkin with dried fruits.
- Milk millet porridge.
Pour 1.5 cups of milk into a ceramic pot and add 0.5 tbsp. millet. Add the rest of the ingredients there: 150 g diced pumpkin, 2 tbsp. l. sugar, a piece of butter and bake the products in the oven for 50 minutes at 180 degrees. Serve the dish hot.
The diet for ascariasis in adults and other types of lesions should include a decoction with a cleansing effect. Honey water against parasites and onion infusion have good properties. The first drink provides cleansing of worms and other pathogenic elements. It's quite simple to prepare. Pour warm water into a glass, add 1 tsp. honey Cinnamon is also added.
You can prepare an infusion of St. John's wort. Preparation is carried out according to the following scheme:
- 10 g of St. John's wort is poured into a glass of hot water;
- the mixture settles for about 30 minutes;
- the drink is filtered and divided into 6 servings;
- drinks throughout the day.
A drink made from seeds has a good effect, which can kill different types of parasites. The preparation looks like this:
- It is recommended to grind a glass of seeds with peel in a coffee grinder;
- pour the raw materials into a saucepan and add 200 ml of cold water;
- place on the stove, simmer over low heat for an hour.
You need to take the medicine on an empty stomach, one glass in the morning. Reviews note that this drink helps eliminate many parasites.
Before starting treatment, you should first undergo a medical examination. It is advisable to develop a menu together with your doctor. The main thing is that the diet for worms should not include prohibited foods that worsen the condition. You may not like porridges or herbal infusions, but it is their use that helps you recover from an infection.
Brief concept of disease
Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease caused by helminths. The cause is parasites belonging to the class of thematodes (liver flukes). They enter the body along with fish that has not undergone proper heat treatment. Carriers are often pets or an infected person.
The larva develops into an adult and infects the organ in which it lives. Most often, their location is the bile duct or bladder, liver, or pancreas.
The disease manifests itself in a person with unpleasant sensations in the limbs, a rash over the body, pain in the hypochondrium, nausea, and fever. With chronic opisthorchiasis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis or other gastrointestinal pathologies develop. Not only the digestive system, but also the nervous system suffers from the activity of helminths. The patient becomes irritable, complains of constant poor sleep, excessive fatigue, and dizziness. Negative manifestations such as tremor of the tongue, fingers or eyelids are observed.
Treatment regimen for opisthorchiasis in adults
Opisthorchiasis are flat helminths about 1 cm long. Infection with them is called opisthorchiasis. Parasites penetrate the body of humans and animals, affecting their pancreas, gallbladder with ducts, and liver. Invasion usually occurs when eating raw or insufficiently fried/cooked fish.
Treatment
Opisthorchiasis does not go away on its own; it needs to be treated. Ignoring the disease can result in serious damage to the liver and digestive organs. It can affect both adults and children, as well as animals that eat fish.
Complex treatment involves taking a number of medications, aimed not only at destroying helminths, but also at supporting the infected body. In addition to deworming drugs, the doctor prescribes choleretic, enzymatic and intestinal motility agents. It is often necessary to take antihistamines. The treatment regimen and dose depend on the patient’s condition and the degree of helminth damage to his body.
Nutrition after drug therapy
Medications help poison opisthorchids. The range of pharmacy products includes a huge variety of treatments for a specific type of worm. The attending physician should prescribe the medicine and method of etching parasites based on examinations of the patient. Natural products based on Populin aspen bark are widely used.
Restorative treatment is carried out only after toxic effects on the body from drugs. Measures are taken to normalize all side effects. Digestive disorders are regulated by laxatives, means to help the functioning of internal organs. Some cases will require the appointment of hepatoprotectors and antispasmodics.
After a post-treatment period of about 3 months, re-diagnosis is carried out in order to identify new opisthorchids. For research, a three-fold stool analysis is required. Biltricide should not be used until six months after treatment. Methods of etching parasites alternate; the method of electromagnetic devices is widely used.
By influencing opisthorchids with a field of a certain frequency, the parasite is killed. There are no harmful effects on the patient; he does not feel anything during the procedure. But there are contraindications for killing worms with devices. Among them, there is a risk of damaging healthy cells of the body.
You can slowly introduce plums, blueberries, bananas, apples with skin, and dates into your diet. These components improve the functioning of the stomach, cleanse the body of harmful substances, and discharge bile.
Diet after treatment of opisthorchiasis
Consequently, the diet after treatment of opisthorchiasis with Biltricide is not disrupted, but is modified over time by the gradual inclusion of certain foods in the diet. In addition to the additional preventive effect on the body, which prevents the re-development of the disease, the dietary diet allows you to speed up the process of recovery of the body after taking toxic drugs. Besides that, it's just useful.
Introducing the consumption of foods rich in fiber helps restore bile ducts damaged by parasites. Also, the diet after treatment of opisthorchiasis is gradually supplemented with fresh fruits and berries (fresh apples, blueberries, apricots, pears, plums, peaches, dried dates and much more).
Nutrition during exacerbation of the disease
During an exacerbation, parasites move along the dilated bile ducts, causing pain and inflammation. In acute cases of the disease, you should adhere to a gentle menu and temporarily exclude fish from the diet. It is necessary to give up sweets in the form of honey, dried fruits, etc.
It is advisable to give preference to soups, vegetable purees and cereals. For a snack, pumpkin seeds, low-fat kefir or seaweed are suitable. Sugar can be replaced with a small amount of fruits and berries.
In acute cases of the disease, you should adhere to a gentle menu and temporarily exclude fish from the diet.
If the disease has worsened and many clinical symptoms of opisthorchiasis appear, then you need to pay close attention to the diet. You cannot completely refuse food for fear of an even greater aggravation. Let's look at a sample menu for one day.
- Breakfast: omelet made from one steamed chicken egg white. Can be supplemented with raw vegetables.
- Additional breakfast: a glass of 1% kefir, 50 g of berries.
- Lunch: vegetable puree soup and some seaweed.
- Afternoon snack: half a glass of dried and peeled pumpkin seeds.
- Dinner: wheat porridge with one milk or chicken sausage.
Special attention in the treatment of opisthorchiasis is paid to therapeutic nutrition. Doctors advise following the “Table No. 5” diet during drug therapy, as well as after recovery.
Its purpose is to prevent re-infection.
To ensure the effectiveness of this diet, experts recommend following the following rules:
- adhere to a strict daily eating schedule;
- cook only by steaming, boiling or baking;
- portions should be small and equal in volume;
- coarse fiber needs to be crushed;
- you need to take 5-6 meals a day;
- Cold dishes are contraindicated; food should be at room temperature.
There are restrictions not only in cooking methods, but also in the choice of products. Fatty foods, smoked foods, alcohol, sweets, flour, sour fruits, and berries are excluded from the diet.
This is the approximate diet menu “Table No. 5” for one day:
- Breakfast: steamed chicken cutlets, fresh carrot salad with apple, coffee diluted with milk.
- Snack: cottage cheese casserole.
- Lunch: soup with rice, cooked in vegetable broth, cabbage rolls, raisin compote.
- Afternoon snack: a handful of dried fruits.
- Dinner: boiled fish, boiled beet salad.
- If you feel hungry, you can drink a glass of kefir at night.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=qhTWJXFttJA
The therapeutic diet calls for a balanced diet so that the body can receive all the necessary nutrients during the course of therapy. It involves revising your usual diet and giving up certain foods. “Table No. 5” is considered a long-term diet, designed to last from several weeks to 2 years.
Recipes
- St. John's wort tincture. Preparation: pour 10 g of herb with a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Divide the resulting infusion into 6 equal parts and take orally for 1 day.
- Fruit salad. Preparation: chop pineapple, kiwi, banana and strawberries into pieces, mix, pour in low-fat yogurt.
- Vegetable soup. Preparation: chop potatoes, onions, bell peppers, carrots, cabbage. Place in a cooking container in which water is boiling, add bay leaf, salt according to taste preferences. In 10 min. Until the soup is completely ready, add any herbs.
By following a diet to cure helminthiasis, allergies, and eating non-prohibited foods, you can prevent acute inflammation of the disease and avoid serious consequences.
Rules for forming a diet for opisthorchiasis
The diet of a patient with opisthorchiasis should be based on foods that do not provoke pancreatic and gastric secretions, as well as stimulate intestinal motility
It is important to switch to fractional 5 or 6 meals a day with a high fluid content. You will have to completely eliminate fried and smoked foods and switch to steamed cooking.
It is not forbidden to stew, boil and bake vegetables, side dishes and lean meat. Products that provoke fermentation in the intestines and flatulence will also have to be postponed until better times.
The total amount of food consumed per day should be approximately 2 kg, with its energy value up to 2.5 thousand kcal. You should not eat food too cold or hot; their temperature should be comfortable for consumption.
It is important that the diet is balanced and the foods are light. The duration of the therapeutic diet is most often up to two months.
During this time, the patient often gets used to a rational and healthy diet, feels all its benefits and no longer returns to heavy, unhealthy food.
Key features of the diet for opisthorchiasis
Due to dietary nutrition, an extremely unfavorable environment is created in the localization of the parasite, which contributes to the destabilization of the life activity of O.felineus, and compliance with the dietary diet contributes to greater effectiveness of medicines.
It is important to understand that the calorie content of food consumed is also regulated. During the period of illness, the daily calorie intake varies between 2200 and 2500 kcal. Accordingly, the daily intake of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins can be expressed in the following scheme (grams): 90:50:350, where 90 grams are proteins, 50 grams are vegetable fats and 350 grams are carbohydrates.
Key principles of dietary nutrition for this helminthic infestation:
- High nutritional value and calorie content of food and dishes;
- The number of meals per day is also regulated. The number of meals should be at least 5 times, but no more than 6 times. Portions should not be excessive; the optimal amount of food consumed should leave you feeling slightly hungry after each meal;
- It is recommended to cook food using steam. Heat treatment by baking is also provided;
- The temperature level of food consumed should correspond to room temperature;
- Water consumption during the treatment period is recommended to be kept within 1-2 liters per day;
Conclusion
Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease that causes disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Following the diet and recommendations of the treating specialist will help the patient overcome the disease and return his body to a healthy state.
Path of infection with opisthorchiasis
The parasite enters the liver, bile ducts, gallbladder and pancreas when eating fish from the carp family (bream, roach, crucian carp, ide, carp, tench).
Forms and symptoms of opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis can be acute or chronic. The acute course of the disease lasts from a month to two. Opisthorchiasis is considered chronic, which lasts from 15 to 25 years and even throughout life.
The acute form of opisthorchiasis manifests itself in the form of urticaria, fever, pain in the joints and muscles, colic in the pit of the stomach and under the rib on the right side, enlarged liver and gall bladder, nausea and gag reflexes, and can make itself felt with heartburn, flatulence, bloating, decreased appetite . During examinations, doctors discover a stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer or erosive gastroudenitis. Cases of lung damage and allergic reactions that carry symptoms of asmoid bronchitis have been recorded.
Opisthorchiasis of a chronic nature manifests itself in the form of pancreatitis, cholecystitis, hepatitis or gastroduodenitis. This occurs due to an imbalance in the human immune system and the onset of irreversible processes that cannot be stopped even after successful removal of the parasite. Also, severe allergic reactions in the form of urticaria, arthralgia, Quincke's edema and simple food allergies can indicate chronic opisthorchiasis.
In addition to affecting the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system, opisthorchiasis negatively affects the nervous system. Patients complain of increased irritability, constant fatigue and lethargy, frequent headaches and dizziness. With a complex course of the disease, excessive sweating, trembling of the fingers of the upper extremities, eyelids and tongue are observed. Sometimes, due to clearly identified neurogenic disorders, patients are misdiagnosed. Doctors can diagnose neurosis or dystonia.
Complications of opisthorchiasis:
- biliary peritonitis;
- cirrhosis, liver abscess;
- pancreatitis of destructive acute nature;
- pancreatic and liver cancer.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis
The source of opisthorchiasis infection is freshwater fish infected with helminths, as well as animals that have eaten such fish (for example, cats). Human infection occurs very quickly. Once in the human body, helminths attach to the intestinal walls, after which they penetrate the stomach, liver and pancreas. They can live in the liver for up to 20 years, gradually destroying the human body.
Like many other parasitic diseases, opisthorchiasis usually begins acutely. The incubation period of this disease lasts 21 days. In the initial stages of opisthorchiasis, a sick person may experience the following symptoms:
- weakness and malaise;
- headache;
- excessive sweating;
- low-grade fever.
Then the person develops characteristic rashes on the body, similar to hives, deterioration of intestinal functions (constipation or diarrhea), indigestion, severe abdominal pain, and a sharp increase in body temperature.
- When can you eat after taking enterosgel?
- How to quickly recover from a hangover
- Why do you sweat a lot after drinking?
- Restoring potency after quitting alcohol