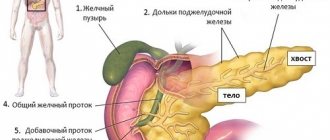
Main symptoms:
- Pain in the left hypochondrium
- Undigested food in stool
- Girdle pain
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Vomit
- Heaviness in the stomach
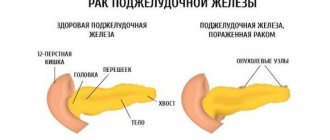
Fibrosis (sclerosis) of the pancreas is a complex process, which is characterized by the replacement of complete and functional cells of this organ with connective tissue. The gland itself consists of two types of tissues, which are different in type - parenchyma and stroma. The stroma is a kind of frame of this organ, and the parenchyma is formed; they produce hormones and pancreatic juice. If the gland is exposed to unfavorable factors for a long time, this will lead to irreversible death of its cells.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
The affected cells are gradually replaced by connective tissue. If the glandular tissue of an organ is replaced by scar tissue, fibrosis develops. If the cells are replaced by adipose tissue, then this pathological process in medicine is called lipomatosis.
A condition often develops when the affected areas of the pancreatic parenchyma are simultaneously replaced by both scar and adipose tissue. In this situation, lipofibrosis develops. Its occurrence is more typical for patients suffering from diabetes. This is due to the fact that the development of lipofibrosis leads to metabolic disorders.
Fibrosis is a dangerous condition, as its progression leads to disruption of the functioning of the organ. The fact is that connective tissue does not have the ability to produce either hormones or enzymes. In addition, both fibrosis and lipomatosis are processes that cannot be reversed. If they occur, then there is no way to restore the affected glandular tissue. In some cases, connective tissue can grow rapidly, leading to the formation of a tumor.
Etiology
The formation of fibrotic changes in the pancreas is caused by the influence of the following predisposing factors:
- inflammation of this organ, which can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Most often, it is chronic pancreatitis that leads to the development of such a disease;
- disruption of the functioning of the bile ducts;
- the course of infectious diseases;
- alcohol or tobacco abuse;
- poor nutrition, i.e., a predominance in the diet of fatty, salty and spicy foods, smoked foods and sweets, as well as carbonated drinks;
- uncontrolled and long-term use of medications;
- severe poisoning of the body with chemicals and toxins;
- cystic fibrosis or a genetic predisposition to the development of such a disease. It is this hereditary pathology that causes the development of fibrosis in children;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- hyperthyroidism syndrome;
- a person has systemic scleroderma or mumps;
- disruption of the normal blood supply to the pancreas;
- internal or open injuries of this organ;
- diabetes;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- food poisoning;
- autoimmune processes.
The main risk group consists of representatives of both sexes over sixty years of age.
Cystic fibrosis is a possible cause of pancreatic fibrosis
Classification
In gastroenterology, it is customary to distinguish two forms of pancreatic fibrosis:
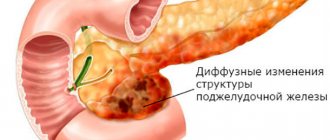
- diffuse - in this case, the tissues of this organ are uniformly replaced by connective tissue;
- focal - differs in that this type is characterized by partial replacement of the pancreas with fibrous tissue; during diagnosis, areas of changes are visible.
The progression of fibrosis is that healthy cells of this organ are replaced by connective tissue, and scarring often occurs. In cases where normal pancreatic cells are replaced by adipose tissue, this process is called lipomatosis.
Quite often, a condition develops during which healthy cells are replaced by both scar and fatty tissue - in medicine, such a condition is called pancreatic lipofibrosis.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of such a disease have a large number of signs, which largely depend on what etiological factor served as its source.
In cases of exacerbation of pancreatitis, the symptoms will be as follows:
- the appearance of pain in the area under the left ribs. The nature of the pain can vary from sharp and acute to constant and aching;
- nausea, which is accompanied by vomiting. Vomiting often occurs after eating fatty foods;
- bowel dysfunction - stool has a liquid consistency. In addition, particles of undigested food are clearly visible in them. Some patients complain of constipation;
- discomfort and heaviness in the stomach;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- increased gas formation;
- increase in abdominal size;
- exhaustion.
If pancreatic fibrosis occurs in a severe form, then the clinical picture will include:
- pronounced pain syndrome, which will manifest itself in cutting pains. Such a manifestation will occur regardless of what a person eats;
- girdle pain that occurs on an empty stomach, as well as thirty minutes or four hours after a meal;
- constant heaviness in the stomach;
- severe belching with an unpleasant sour smell of recently eaten food;
- nausea with frequent vomiting;
- aversion to food;
- increase in body temperature;
- bloating and flatulence;
- significant reduction in body weight;
- frequent urge to defecate - liquid stool with admixtures of undigested food particles.
In cases of focal forms of fibrotic changes in the pancreas, the intensity of symptoms directly depends on the size of the pathological focus. If the neoplasm, consisting of connective tissue, has large volumes, then it will certainly compress the organs adjacent to the pancreas, in particular the liver. This will cause the patient to feel constant vomiting, and the skin and mucous membranes will acquire a yellowish tint.
In addition, this disease leads to a lack of fat-soluble vitamins in the body, including A, K, D and E. Their deficiency can be expressed in:
- increased bleeding;
- development of osteoporosis;
- impaired vision adaptation to darkness.
Most patients have symptoms of diabetes mellitus:
- dry mouth;
- strong thirst;
- itchy skin;
- weakness;
- increased urge to urinate;
- sleep disturbance.
Symptoms of diabetes
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis of the pancreas)
To exclude the disease in newborns and children under 1 year of age, screening is carried out (routine examination of all children). One of the earliest symptoms of cystic fibrosis in children is excessively salty sweat due to increased levels of sodium and chlorine in the secretions. A person's skin becomes salty.
Further, thick mucus can form in the upper respiratory tract, especially in the bronchi. This leads to a constant, lingering cough (one of the signs of cystic fibrosis), which may be accompanied by purulent discharge, loss of sleep, vomiting, and severe shortness of breath. A serious symptom is persistent or frequently recurring lung diseases. Also, patients with cystic fibrosis may experience polyposis and sinusitis. Polyposis is a disease in which benign formations called polyps appear in the nose. With the further development of cystic fibrosis, the skin will become blue, the chest will become barrel-shaped, and the intercostal spaces will retract.
When thick mucus begins to clog the pancreatic ducts, the absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract is reduced. This leads to the following symptoms:
- frequent stools with a greasy consistency;
- constipation, bloating, pain in the abdominal area;
- rectal prolapse - partial prolapse of the rectum;
- slow weight gain and height with normal, nutritious nutrition.
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disease, meaning if parents have the defective gene but are not affected, the child may develop the disease in 25% of cases. This mutation occurs on chromosome 7 and encodes a protein on which the transport of chlorine and sodium throughout the cells of the body depends. This protein is called cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator, abbreviated CFTR. When CFTR production is impaired, chloride production is reduced, resulting in increased sodium absorption through mucosal tissues. It is because of this that the mucus becomes thick and viscous and thereby clogs the ducts of the external glands.
Small bronchi in the upper respiratory tract become clogged, which can lead to infection and, as a result, pneumonia. Very often, patients with cystic fibrosis develop chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD. This disease leads to irreparable changes in the human respiratory system. In patients with cystic fibrosis, COPD often worsens, which leads to a worsening of the situation as a whole.
As a result of blockage of the ducts in the pancreas, the entry of digestive enzymes into the stomach and intestines is reduced and greatly reduced, which leads to incomplete processing of food in the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, such enzymes help process fats and other nutrients and absorb all the beneficial microelements. Due to this disorder, patients often experience changes in stool. It becomes oily, abundant and frequent. There is a delay in growth and weight, a general depressed state, and a decrease in muscle mass.
Changes in the intestines lead to greater absorption of water. Cystic fibrosis in children, especially newborns, causes frequent constipation, bloating, pain and vomiting. Such symptoms are also observed in older age.
Patients with cystic fibrosis are very often infertile or have great problems conceiving. In men, the prostate gland can become blocked, which leads to infertility.
Complications
Complications that cystic fibrosis can lead to:
- polyposis in the nasal sinuses and frequent infectious diseases of the lungs;
- bronchiectasis - incurable saccular expansions in the walls of the bronchi, which arise due to purulent-inflammatory destruction in the bronchial tissue;
- pneumothorax - accumulation of air in the chest (requires immediate treatment);
- respiratory failure is a condition of the body's respiratory system when not enough air enters the lungs, which leads to a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood;
- Diabetes is an incurable disease when insufficient levels of insulin in the body lead to an increase in blood sugar levels. This occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas, which produces insulin;
- inflammation of the gallbladder (jaundice) - occurs due to blockage of the bile ducts. Gallstones can also form in the gallbladder. In severe forms, cystic fibrosis in adults causes liver cirrhosis (destruction of healthy liver tissue and its replacement with scar tissue);
- prolapse of part of the rectum - often occurs in children. This comes from the severe overexertion that a person experiences with constipation;
- Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by thinning of bone tissue. When the absorption of nutrients in the intestines is impaired, this leads to a deficiency of essential vitamins and microelements in the body, including vitamin D, which is involved in the formation of bone tissue.
Diagnostics
It is not possible to make a correct diagnosis based only on clinical manifestations. For this reason, diagnosis is complex.
First of all, the gastroenterologist needs to:
- conduct a detailed survey of the patient to obtain a complete picture of the course of such a disease;
- get acquainted with the life history and medical history of not only the patient, but also his immediate relatives. This is explained by the fact that some of the etiological factors are hereditary in nature;
- perform a thorough physical examination, which must include palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, examination of the condition of the skin and sclera.
Among the laboratory examinations it is worth highlighting:
- clinical and biochemical blood test - will indicate signs of the inflammatory process and the level of pancreatic enzymes. If their activity is low, there is a possibility of total damage to this organ;
- general urine test - to determine ketone bodies and diastase levels;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- Lucas test - in cases of suspected cystic fibrosis.
The basis of diagnostic measures is the following instrumental examinations of the patient:
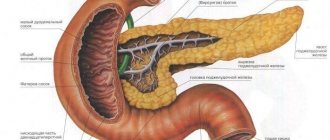
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - to analyze the echogenicity, volume and shape of the affected organ. Echogenicity will be increased and the size of the pancreas will be reduced;
- ERCP - to identify changes in the ductal apparatus that are caused by scarring;
- CT scan of the pancreas - the procedure is performed to obtain a more detailed picture of this organ;
- Biopsies are the main method for diagnosing pancreatic fibrosis. It involves taking a small part of this organ, which makes it possible to obtain complete information regarding the morphological changes of the pancreas.
ERCP procedure
Treatment
Elimination of pancreatic fibrosis is based on several methods:
- taking medications;
- maintaining a gentle diet;
- surgical intervention.
Drug treatment includes the use of:
- antispasmodics;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- enzymes - in case of absolute pancreatic insufficiency, such drugs must be taken constantly and in large dosages;
- sugar-lowering substances;
- detoxification therapy;
- insulin therapy.
Good results can be achieved with the help of diet therapy, which requires compliance with several rules:
- frequent and small meals;
- avoiding overeating;
- thorough grinding and chewing of food;
- eating food at the same time every day;
- plenty of drinking regime;
- complete rejection of fatty, spicy foods, salty, sweet, smoked foods, marinades, strong coffee, carbonated drinks, as well as those ingredients that increase the secretion of gastric juice;
- eating only warm food, it should in no case be excessively cold or very hot;
- preparing dishes without adding fat, namely by boiling, steaming, stewing and baking.
Surgical intervention is used in the following situations:
- housing and communal services;
- the formation of large tumors that compress neighboring organs;
- severe course of the disease;
- rapid weight loss;
- ineffectiveness of conservative methods.
In all cases, except the first, complete or partial resection of the pancreas is indicated.
Diet
During therapy, it is recommended to follow a special diet. Fried, fatty and irritating foods should be excluded from the diet. It provokes increased production of pancreatic enzymes, which increases the load on this organ. The menu should be designed so that there are at least 5 meals a day.
All dishes need to be steamed, fruits should be baked in the oven, and vegetables should be boiled. The main diet consists of cereals, lean meats, cereals and vegetables. Sweet dishes are allowed no more than once a day, and they should be consumed in minimal quantities. As drinks, you should choose fruit drinks, black and green tea, decoctions of berries and vegetables, and compotes.
Prevention and prognosis
There are no special preventive measures for this disease; people need to adhere to general recommendations:
- completely give up bad habits;
- in the early stages, treat those diseases that can cause the development of pancreatic fibrosis;
- enrich the diet with vitamins and nutrients, and completely avoid junk food;
- avoid stressful situations;
- take medications only as prescribed by the clinician and strictly adhere to the daily dosage;
- be regularly examined by a gastroenterologist.
The prognosis of the disease is determined by several factors - the degree of spread of the pathological process and the patient’s compliance with all therapeutic recommendations of the attending physician.
Since there are no methods for completely getting rid of fibrosis, a favorable prognosis will consist of lifelong intake of enzyme substances and abstinence from alcohol.
How long a patient has to live is determined by the individual course of the disease. Often the life expectancy is ten years.
ethnoscience
Medicinal methods, like traditional medicine, are not able to stop the degeneration of parenchyma. However, with the help of traditional medicine, it is possible to reduce the load on the pancreas and improve its performance.
So, for fibrosis, it is recommended to take infusions and decoctions from the following plants:
- elecampane and oats;
- centaury and purple sedum;
- rosehip and fennel;
- dill;
- peppermint;
- violet;
- coriander;
- cottonweed;
- St. John's wort.
Prevention of the disease
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to reduce the negative influence of factors that can provoke the death of pancreatic cells. A very important point is the complete abandonment of bad habits and moderate intake of fatty foods.
All of the above factors negatively affect almost all digestive organs, and even more so the pancreas.
Disease prognosis
There are no drugs that can restore the turnover processes of organ tissue. In mild forms of the disease, manifestations of the chronic form of pancreatic inflammation should be avoided. A strict diet and giving up bad habits will help with this. During periods of exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to take medications prescribed by a doctor.
Timely diagnosis, treatment and strict adherence to all recommendations of the gastroenterologist will prevent the development of unpleasant complications.
- Diet for pancreatic dysfunction
- Treatment of the pancreas for diabetes mellitus
- What can you eat after pancreatic surgery?
- Does ultrasound show pancreatic cancer?