The gallbladder is susceptible to many diseases, including inflammation of the organ and cholecystitis. This disease is devoid of any specificity and often accompanies other pathologies in their development. In clinical practice, there is an acute form, which is dealt with by surgeons, as well as a chronic form, which is dealt with by therapists and gastroenterologists.
As experts note, there is a tendency for cholecystitis to increase among the population, while symptoms remain even after removal of the gallbladder. Let's consider the causes of the disease, its characteristics and medications that can eliminate the pathology. Doctors in all cases prescribe antibiotics for inflammation of the gallbladder, differentiated by the direction of their action.
Why does the gallbladder become inflamed?
Foci of inflammatory processes appear in the gallbladder for many reasons. These include the following:
- intensive formation of stones, damaging the mucous membranes with sharp edges. Also, when moving, congestion occurs, which interferes with the normal movement of bile;
- violations of a healthy diet, the presence of high-fat, high-calorie dishes on the menu, frying in vegetable oil, lack of a diet;
- overstrain at work, negative emotional background, hysteria and mental disorders;
- problems in heredity, genetic predisposition;
- congenital and acquired anomalies in the structure of the biliary organ, presented in the form of an inflection or constriction of the bladder, the development of septa. When bile stagnates, inflammation can spread to neighboring systems;
- imbalance of hormonal metabolism by taking hormonal drugs during IVF or contraception;
- the patient has food allergies and other forms of it;
- disorders of immune etiology;
- treatment with medications that have side effects that have a risk of stone formation. This could be Cyclosporine or Octreotide, as well as Clofibrate and similar drugs;
- sudden significant weight loss;
- infection by bacteria or viruses. Parasites may appear. They penetrate into the cavity of the gallbladder from other systems, where they are in dormant mode;
- infection through the lymph flow or blood vessels from the intestinal tract or duodenal cavity.
What is cholecystitis?
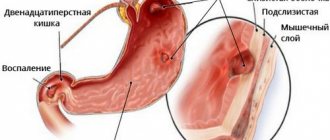
Inflammatory processes in the gall bladder organ are distinguished by the nature of their course. This may be acute cholecystitis, which develops in the shortest possible time due to gallstone disease with obstructions or obstructions. The resulting cholestasis is a place for favorable reproduction of clostridia, staphylococci or streptococci, Klebsiella or Escherichia coli.
A chronic form of inflammation is also possible, which is caused by pathologies of the biliary system and is a separate independent disease. It usually occurs during an exacerbation of gallstone disease and gradually develops independently.
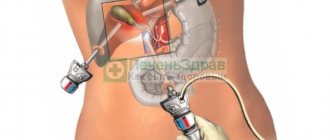
Any form of cholecystitis is accompanied by the formation of stones (calculous form) or without the formation of stones (acalculous form). Any form of cholecystitis requires antibiotics. Doctors supplement therapy with complex procedures regulated for each stage. Cholecystectomy is performed only when the patient’s life is at risk, but if the inflammation has spread to the abdominal cavity, then the symptoms will remain even after removal of the gallbladder.
Read also: Main indications for gallbladder removal
What are the symptoms of cholecystitis?
Sometimes cholecystitis occurs without any symptoms at all, especially in chronic form. In this case, the patient does not experience discomfort, and the pathology is detected during a random examination of other diseases. But usually the symptoms are still quite vivid and worsen after heavy feasts, drinking alcohol, intense exercise or riding in transport, as well as strong anxiety of the person.
All symptoms of gallbladder inflammation are combined into several specific syndromes:
- The pain syndrome is distinguished by the localization of pain of varying severity in the hypochondrium area. Possible irradiation to the neck or shoulder blades, to the shoulder on the right;
- Dyspepsia syndrome is characterized by constant swelling of the peritoneum, bitterness in the mouth, diarrhea alternating with constipation, as well as bursting heaviness in the stomach. The patient cannot tolerate fatty foods;
- intoxication syndrome causes the patient's body temperature to rise to febrile levels, general weakness and problems with appetite, muscle aches and other manifestations;
- Autonomic disorders manifest themselves in the form of excessive sweating, tension before menstruation, and frequent headaches.
Patients may notice other manifestations, the severity of which varies from mild to unbearable with colic. Biliary colic requires emergency intervention, but even after removal of the gallbladder, problems in the biliary system remain unresolved.
Rationale for the need to take antibiotics
Drug therapy for patients with inflammation of the gallbladder has the main goal of restoring the movement of bile from the biliary organ. To improve the outflow, it is necessary to take courses of choleretic drugs, but usually cholecystitis does not go away after this. If inflammation is present, then the microflora is necessarily changed and pathogenic microorganisms develop. Bacteria can be anything, including fungal infections, but the type can only be determined by special tests in the laboratory.
Antibiotic therapy is the most affordable and effective way to get rid of any form of cholecystitis if it appears due to the proliferation of bacteria. Even if it is possible to cure the symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder and unblock the gaps in the channels for the outflow of bile, bacteria and infections do not go away, causing frequent relapses. In some cases, pus may be released, including after removal of the gallbladder. Antibiotics with targeted or broad spectrum action will help against all these phenomena.
Indications for use
One of the reasons for the occurrence of this pathology is the penetration of harmful microorganisms into the body. If their activity is not stopped, the infection will spread, leading to the formation of an abscess and even the death of the patient. To prevent this from happening, the doctor prescribes antibiotics. Only such drugs can destroy microorganisms and stop the spread of infection.
The doctor prescribes antibiotics for cholecystitis if the following symptoms occur:
- Pain syndrome localized in the right side closer to the ribs, which is constantly intensifying, as well as pain syndrome throughout the abdomen;
- Increase in body temperature to 390C and above;
- Nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Joining the pathology of other infectious diseases.
The drugs are also recommended for use if blood tests reveal signs of infectious processes.
How do drugs work in the treatment of cholecystitis?
Using antibiotics recommended by a doctor can significantly improve your overall health, and if taken correctly, the entire course will eliminate the infection. The average duration of taking these drugs is about 10 days, and it is prohibited to continue taking them on your own. Antimicrobial drugs cause thrush and dysbacteriosis. All antibiotics are classified into several groups, based on the mechanism of action of the active substance on the cell with the infection. Some drugs preserve its integrity by exchanging proteins inside, while others destroy it.
First group
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | The first generation drug, Cefazolin, has a wide spectrum of action against many pathogenic microorganisms. This medicine is contraindicated in infancy, during pregnancy at any stage, and with caution when breastfeeding |
| 2 | with a large dosage of penicillin in bile, the condition of the gallbladder improves, which allows us to consider this remedy as the main one in the treatment of cholecystitis |
| 3 | the use of Cephalexin is required in acute forms of the disease. this antibiotic has a broad spectrum and is not used in children under 12-14 years of age, as well as in cases of chronic liver and kidney diseases |
Read also: Why do you need to take enzymes after gallbladder removal?
Second group
- Levomycetin therapy is used only against salmonella, dysentery or typhoid fever;
- the effectiveness of Erythromycin has been proven in cases of exacerbation of cholecystitis;
- for lesions by Escherichia coli, streptococci or enterococci, Tetracycline is prescribed;
- in severe forms of the disease of enterococcal etiology, a course of Gentamicin is required.
It is important that the antibiotic is prescribed by a doctor, since each of them has its own spectrum of action and a lot of side effects. The specialist also takes into account a number of the patient’s diseases, acute or chronic.
Parasitic lesion due to cholecystitis
It is important to know!
78% of people with gallbladder disease suffer from liver problems! Doctors strongly recommend that patients with gallbladder diseases undergo liver cleansing at least once every six months... Read more...
Inflammation of the gallbladder is usually accompanied by active proliferation of enterococci or Escherichia coli, in which case the following medications are needed:
- Cefazolin;
- Cephalexin;
- Levomycetin;
- Tetracycline;
- Ampicillin;
- Gentamicin.
In addition to the traditional effect on the affected cells, the active substances of the antibiotic may differ in their localization and method of release. According to experts with varied clinical practice, Ampicillin, Penicillin or Tetracycline are most effective in the treatment of cholecystitis. This is due to the place where the active substances accumulate – in the bile.
The effect of antibiotics for cholecystitis
Now in medical practice there are several standard regimens for treating cholecystitis with antibiotics. Depending on the course of the disease, its complexity, periods of exacerbation and other factors, the doctor may use or independently create new treatment regimens.
Standard regimens for the use of antibiotics for cholecystitis:
- Aminoglycosides in combination with ureidopenicillins and Metronidazole. Antibiotics are administered by injection: Gentamicin (up to 160 mg) in the morning and evening Metronidazole 500 mg and Azlocillin 2.0 three doses per day.
- Cephalosporin antibiotic drug from the penicillin group: Ceftazidime 1.0 (3 doses per day) Flucloxacillin 250 mg (4 doses per day).
- Cephalosporin antibiotic and Metronidazole: Cefepime 1.0 in the morning and evening, simultaneously with Metronidazole 500 mg 3 times a day.
- Ticarcillin with Clavulanic acid 3 g 1 time every 5 hours intravenously (up to 6 injections per day).
- Penicillin antibiotics and fluoroquinolone drugs: Ampicillin 500 mg 5-6 times a day Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 3 times a day.
In a critical situation, when the patient's blood urgently needs to be cleared of a certain medication, hemodialysis can be performed. Paradoxical situations often arise when the occurrence of cholecystitis is caused precisely by the use of certain types of antibiotics.
This may be due to increased dosages or too long treatment.
Recommendations from specialists on taking antibiotics
Antibiotic therapy is recommended by a doctor in cases of severe pain due to cholecystitis, a rise in temperature to febrile levels, as well as in cases of increased bladder size and leukocytes in blood tests. Acute forms of the disease require the use of the erythromycin category of antibiotics - Spiramicide, Azithromycin or Roxithromycin. They tend to accumulate in bile secretions, providing an excellent therapeutic effect.
Inna Lavrenko
auto RU
When organ walls are affected by inflammatory processes, Furazolidone, a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is effective for inflammation of any etiology, is often used. Contraindicated for use in diseases of the renal system. All of these products should be taken in combination with Baktisuptil and vitamins C, B and A.
If the symptoms of acute cholecystitis increase intensively, there is no time to take long-term courses of drugs; in this case, you can take broad-spectrum antibiotics. This is Cephalosporin, Ampiox or Gentamicin. If drug therapy does not help, surgery is necessary to treat the bile organ with stones that have filled more than half of it. After removal of the gallbladder, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent inflammation in the operated areas.
Rules for taking antibiotics
The treating specialist prescribes antibiotics at his own discretion, based on the characteristics of the patient’s disease. But there are also a number of regulated factors that must be followed regarding antibiotics:
- cholecystitis in children and in older patients requires different types of medications. They are prescribed after there is no result after a course of antibacterial treatment;
- antimicrobial agents are prescribed when pain increases, which cannot be relieved by conventional means;
- the introduction of antibiotics into the body in acute forms of cholecystitis is carried out through intravenous infusions or intramuscular injections, which can increase their effectiveness;
- The patient is given injections at least three times during the day, with the minimum course being a week, and the maximum being 10 days. Tolerability and test results can adjust the course of the disease and the required dosage.
Read also: Causes of bends in the gallbladder and treatment
At the end of the course of antibiotics, the patient recovers, but this does not happen in all cases. Sometimes systemic infections can only be cured by surgery. To prevent the development of inflammation and its transition to the chronic stage, it is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol and junk food. Lists of permitted and not recommended products are issued by a gastroenterologist.
Clinical studies confirm that the body quickly becomes accustomed to a certain type of antibiotic, which reduces its effectiveness. Therefore, doctors do not allow drugs with antimicrobial effects to be taken for preventive purposes.
What are the side effects?
When taking antibiotics, there are a number of negative consequences caused by the side effects of the drugs:
- the development of dysbiosis in the intestinal tract is caused by the death of bacteria due to taking medications;
- severe forms of intestinal dysbiosis, accompanied by vitamin K deficiency, bleeding from the gums and nose;
- Candidiasis develops in the oral cavity, and the mucous membranes in the vagina are also affected. This occurs when Candida fungi multiply, the pathogenic effects of which cannot be treated with conventional antibiotics;
- rashes and skin dermatitis, swelling in the larynx and itchy symptoms are a sign of an allergy, while the injection sites become inflamed and an abscess may develop.
Any form of cholecystitis with treatment started at an early stage has a favorable prognosis for the patient. It is necessary to seek the help of doctors when the first symptoms appear, and also perform regular examinations as planned. The specialist determines the necessary antibiotic, its dosage and course of treatment, making gallbladder inflammation treatable.
YouTube responded with an error: Access Not Configured. YouTube Data API has not been used in project 726317716695 before or it is disabled. Enable it by visiting //console.developers.google.com/apis/api/youtube.googleapis.com/overview?project=726317716695 then retry. If you enabled this API recently, wait a few minutes for the action to propagate to our systems and retry.
How to help yourself
If the attack takes you by surprise, you will need to relieve the attack of cholelithiasis yourself.
First aid is as follows: you need to lie down on a sofa, bed or chair - a place where you can stretch your legs and feel peace. If the patient is alone at home, it doesn’t hurt to call friends and relatives asking for help. Ask your friends to come, there may be a case of vomiting or an intensification of the attack (painkillers do not always help) so much that you will have to call an ambulance.
Painkillers are often:
- no-shpa;
- drotaverine;
- papaverine;
- antispasmodics of any order.
The attending physicians prevent the problem in advance - offer the patient a painkiller in case of an attack. If you have not received a proposal from your doctor, discuss the names of the medications at your appointment.
Some doctors recommend taking a bath. The water is at a pleasant, warm temperature (from 37 to 39C), and should not burn the human body. There is no need to lie in the bath for a long time: just relax for 10-15 minutes. Then it is recommended to quickly go to bed so that the warmed body does not cool down again and the body temperature does not change. An alternative option that allows you to “warm” the body and improve the functioning of blood vessels is to apply a heating pad to your legs. It is recommended to wrap the patient as much as possible in blankets and warm clothes; in case of cholelithiasis, warmth will serve a good purpose. If the patient's temperature fluctuates, the patient feels chills, wrap the person in a blanket more tightly.
To avoid dehydration, drink plenty of water. Mineral, filtered water is recommended; tap water and carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited.
As a rule, serious attacks last 20–30 minutes; after the specified time has elapsed, you are allowed to leave the bed or bath and continue doing business. If the attack does not end, then the matter is serious and a doctor’s consultation is urgently needed. You'll have to call the hospital and call an ambulance.
Remember: the sooner a stone (or several) is detected in the gall bladder and the patient complains to the doctor, the higher the likelihood of avoiding surgery.
Complications of cholelithiasis and concurrent diseases
If you do not see a doctor in time for gallstones, you may encounter a number of quite serious complications that greatly affect the condition of your body. At first, the stones are small, painkillers cope with the task of dulling the pain, but gradually the formations become more massive, and passage through the biliary tract becomes more difficult. When stones get stuck, blocking the bile ducts, unpleasant phenomena occur:
- biliary cirrhosis of the liver;
- jaundice;
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- cholangitis.
Cholecystitis is accompanied by recognizable symptoms:
- the pain is localized on both sides of the body, acquiring a girdling character;
- yellowed skin;
- change in body temperature;
- pain radiates to the back, creating a sensation of pulsation;
- problems with processing food - vomiting, nausea.
When the stones enlarge and the ducts are blocked, the scary thing is that the pain does not stop and is very intense. In order not to delay treatment until surgery, it is better to worry about preventing consequences in advance.
The following diseases will serve as a prerequisite for the appearance of gallstones:
The common reason for the transition of diseases into each other is the deterioration of the body’s condition. As a rule, clinics remember this relationship and take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of gallstones.
Due to complications and parallel diseases that are not treated in time, a person suffers many times: the first time when he tries to cope with a diagnosed disease, the second time when an additional disease appears, and the patient has to fight on several fronts at the same time. The metabolism and life of a person depend on complications of gallstone disease; symptoms indicating the occurrence of complications require an urgent need to call an ambulance. The attending physician will be able to decide whether it is worth hospitalizing the patient or whether it will be possible to get by with a set of basic measures.
During hospitalization, further treatment course is prescribed individually depending on the cause of the attack in addition to the neglected gallbladder.