673
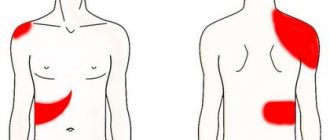
Acute cholecystitis is a disease in which the walls of the gallbladder are damaged. The pathology has a pronounced course: the concentration of cholesterol in the bile increases, the walls of the bladder atrophy, and the outflow of bile is disrupted. In old age, destructive changes in the organ may occur.
Acute cholecystitis requires complex treatment, which includes taking medications: antibiotics, pain relievers, antispasmodics and choleretic agents.
General principles of therapy
Treatment of cholecystitis with medications is carried out depending on the intensity of the inflammatory process and the severity of symptoms. If there are stones in the organ or its ducts, drugs can be used to treat cholecystitis, but only if the stones do not cause discomfort to the patient. Drug treatment of gallbladder inflammation consists of the following principles:
- choleretic drugs, the purpose of which is to improve the outflow of bile and eliminate congestion;
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- antibacterial therapy;
- analgesics;
- antispasmodics for cholecystitis;
- enzymes;
- antifungal tablets;
- sulfonamides.
The treatment regimen is selected individually for each specific case. All dosages and duration of therapy are prescribed only by the treating specialist.
Treatment of acute cholecystitis is often carried out in a hospital setting, since if conservative methods of treatment are ineffective, radical intervention may be necessary to remove stones from the gallbladder or its ducts.
Fish fat
This is an animal fat that is obtained mainly from cod liver. Produced in capsule and liquid form.
- The value of this product comes down to its huge content of omega-3 acids and fat-soluble vitamin D.
- Although it is recommended to limit fats during cholecystitis, taking fish oil is extremely useful.
- But only admission is allowed only in case of stable remission.
- During an exacerbation, taking fish oil is contraindicated.
Cholecystitis is a serious pathology that, if not properly treated, can lead to dangerous complications. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment recommended by a gastroenterologist.
Rolitene - a drug against overactive bladder
The problem of unstable bladder behavior can occur in both females and males. Experts recommend taking Roliten, a drug that helps reduce organ hyperactivity.… Read more
Antibacterial therapy
Many specialists prescribe medications for cholecystitis that contain antibacterial substances. This treatment is especially important if an additional bacterial infection develops during acute cholecystitis. Therapy with such medications is usually carried out in the early stages of the disease.
Only the doctor decides what medications to take to cure cholecystitis. The duration of the course and dosage are prescribed by a specialist.
Typically, the duration of antibiotic therapy does not exceed seven days, since such substances aggressively affect the microflora of the intestinal tract. At the same time, it is recommended to use bifidobacteria and lactobacilli to restore the microflora (lactiale, laktovit, bififirm, bifidumbacterin). In parallel with antibiotics, the doctor prescribes multivitamin complexes. For the treatment of non-calculous cholecystitis of a bacterial nature, broad-spectrum tablets are used.
When is antibiotic use indicated:
Levomycetin is prescribed for the treatment of cholecystitis
- the presence of severe pain in the right side;
- profuse and frequent vomiting;
- stool disorder with frequent visits to the toilet, frequent watery stools.
Before curing a disease with the help of such agents, a sensitivity test should be performed. List of the most effective drugs for cholecystitis:
- Erythromycin. Belongs to the group of macrolides. Release form: tablets and solution for injection into the body with a dropper. It is used to treat twice a day.
- Levomycytin. Release form: tablets and solution. Taken on an empty stomach three times a day.
- Ampiox. Belongs to the penicillin group. A combined drug that reduces the signs of acute and chronic illness.
Choleretic medications
There are two types of choleretic drugs: choleretic drugs, which are designed to ensure that bile is produced at an increased rate, and also means for the outflow of bile. To restore the full functioning of the organ, the bile ducts should be cleared of congestion. For these purposes, preparations of plant and synthetic origin are used. Typically, such treatment is prescribed simultaneously with antibacterial therapy.
The most effective medications from this group are:
For cholecystitis, choleretic drugs are prescribed
- Alohol. A herbal preparation that helps normalize liver function and restores the process of bile formation. This is the prevention of the development of stones in the ducts. Alohol increases the efficiency of the entire gastrointestinal tract; it can be used to cure constipation and flatulence. The protocol for taking it is one tablet twice a day on an empty stomach. Cannot be used for peptic ulcer disease and liver dystrophy.
- Holagol. The main form of release is drops. Among the most effective medicines, Cholagol is on the list of leaders. Drops increase the outflow of bile, gently weaken, relieve spasms. Treatment protocol: 7-8 drops before meals three times a day. Cannot be used if there is an individual intolerance to active substances, kidney dysfunction, or during pregnancy.
- Oxafenamide. Increases the production and excretion of bile, relieves spasms. Take one tablet three times a day. The duration of therapy is at least a month. Contraindications: liver dystrophy.
Drugs for the treatment of cholecystitis should only be prescribed by a doctor. After the examination, he will decide how to treat the disease. Symptoms and treatment of the disease are closely related, since the duration and treatment regimen will depend on the severity of the symptoms.
Reasons for the development of cholecystitis
The main factors in the formation of the disease are:
- infection with parasites (roundworms, lamblia);
- diseases of the digestive organs (gastritis, hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- previously suffered inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- food poisoning;
- stagnation of bile caused by an inactive lifestyle, excess weight, cholelithiasis, congenital anomaly;
- poor nutrition;
- inflammation in the small intestine or liver (duodenitis or hepatitis);
- stones;
- injury to the abdomen in the gallbladder area;
- burns.
In addition, the cause of cholecystitis is considered to be a hereditary predisposition.
Sulfonamides
For cholecystitis of the gallbladder, treatment is also carried out with the help of sulfonamides. These are drugs that have an antimicrobial effect. Used if the patient cannot tolerate antibiotics. These drugs help get rid of an attack of acute or chronic disease, especially if it is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the intestinal tract.
This group of medicines includes:
- Sulfapyridazine. Has an antimicrobial effect. This is a good drug for eliminating inflammation. Quickly absorbed into the intestines. The duration of therapy is 7 days, take one tablet per day.
- Sulfalene. Has a long-lasting bacteriostatic effect. Do not use if you have an allergic reaction to the active substances of the product during pregnancy.
The taken remedy works better when combined with antibiotics.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are an important component of drug treatment for cholecystitis. However, such drugs are prescribed only after a detailed diagnostic study. It is very important to determine what exactly caused the inflammation in the gallbladder.
Most often, cephalosporin antibiotics are prescribed for the treatment of cholecystitis . Such medications are extremely effective and have a wide spectrum of action.
Penicillin antibiotics can accumulate in bile, which helps quickly relieve the pain of bacterial cholecystitis. In acute inflammation, doctors recommend taking antibiotics of the erythromycin group.
On average, the duration of such therapy should not exceed 10-14 days, since due to the use of antibiotics, a person may experience complications in the form of side effects.
Treatment with antifungal drugs
Due to long-term treatment with antibiotics, the human body's immune capabilities are significantly reduced. This leads to the fact that fungal division is activated. Often people who have just finished taking antibiotics experience candidiasis of the mucous organs. To prevent this, it is advisable to carry out parallel therapy with antifungal drugs.
The most popular drugs in this group are Nystatin and Metronidazole. Such products have a gentle effect; they increase the activity of beneficial bacteria in the body. The use of these drugs reduces the risk of thrush by almost 98%.
Before such therapy, it is best to consult a doctor.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodic drugs help get rid of attacks of spastic pain. Release form: tablets, drops, suppositories. Eliminate the pain that often accompanies gallstone disease by affecting smooth muscles. Many reviews mention the effectiveness of the following medications:
For cholecystitis, antispasmodics are prescribed
- Drotaverine or no-spa. It acts quickly and completely relieves pain. Not used in childhood if there are severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver, with glaucoma, hypertension, or prostate hyperplasia.
- Platifilin. It is quickly absorbed and begins to act. It is important to consult a doctor before use.
The listed drugs are not allowed to be used in the presence of colitis, tuberculosis, Crohn's disease, or a predisposition to the development of an allergic reaction to active substances.
Drugs for the treatment of cholecystitis
In the initial stages of cholecystitis, which is a disease that does not cause significant discomfort, drug treatment is possible. It is very important that all tablets and injections are prescribed exclusively by a qualified doctor based on diagnostic data. Only a specialist will assess the individual characteristics of the body and select the optimal dose.
Currently, the following groups of drugs are used to treat cholecystitis::
| Group | Drugs | Action |
| Choleretic drugs | Allohol, Cholenzym, Liobil | Normalizes the production and outflow of bile. |
| Antispasmodics | Biospa, Vero-Drotaverin, Droverin, Odeston | Relieves pain caused by the movement of stones in the gallbladder. |
| Antibiotics | Azithromycin, Roxithromycin, Spiramycin, Ampicillin | They fight infections that have leaked into the gallbladder and have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. |
| Sulfonamide drugs | Sulfadimethoxine, Sulfalene, Sulfadimezin | They are used for inflammation of the intestines or colon that occurs during antibiotic therapy. |
| Antifungal drugs | Metronidazole, Nystatin, Fluconazole, Furazolidone | Prescribed due to antibiotic therapy, which causes accelerated division of Candida fungi. |
| Hepatoprotectors | Essentiale forte, Karsil, Liv-52 | Restore liver function, accelerate liver tissue regeneration |
Antifungal
If the doctor prescribes antibacterial agents, patients are additionally advised to use antifungal agents for preventive purposes. This treatment is especially important for patients with weakened immune systems and the elderly.
The most popular drug in this group is nystatin. It is well absorbed, there are very few contraindications for use.
Many patients are interested in whether the disease can be cured forever. Experts say that the chronic form is not completely cured, but only goes into remission. An acute attack can be eliminated completely with proper, timely therapy. To prevent problems with the biliary tract, you should eat right and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Diagnostic measures
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a laboratory blood test and the following diagnostic measures:
- Ultrasound . Allows you to identify changes in gallstone size, deformation of the organ, and the presence of stones.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy . Allows you to detect reflux of bile into the stomach from the duodenum.
- Laparoscopy . Allows you to determine the size and location of the gallbladder. Using a laparoscope, you can assess the condition of nearby organs.
- Retrograde pancreatic cholangiography . Helps detect pathology of the gallbladder ducts, as well as the pancreas.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe duodenal intubation to conduct a microscopic examination of the bile. This analysis allows you to determine the presence or absence of inflammation, as well as the presence of parasitic infestation.