- August 28, 2018
- Gastroenterology
- Natalia Kalinichenko
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract occur in every person throughout his life. Most often, gastritis develops, that is, inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Approximately 90% of all people on the planet have had at least one episode of exacerbation of the disease.
There are several types of gastritis:
- hypoacid;
- hyperacid
- anacid gastritis.
Lack of treatment provokes the development of a chronic form and, as a result, peptic ulcer disease or even cancer of the stomach.
Anacidic form
Anacidic gastritis is characterized by zero acidity and is quite rare among patients. Pathology can occur after gastritis with low acidity. There is almost no hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which prevents food from being properly digested. Proteins supplied with food are practically not digested, and their breakdown products poison the entire body of the patient.
As a result of the disease, parietal cells atrophy, an imbalance of microflora occurs, microbes and viruses almost freely enter the body along with food. Against this background, the mucous membrane becomes thinner, the immune system practically does not resist, and all sorts of diseases develop, including the appearance of cancer. Due to decreased motor skills, the patient suffers from constipation.
Symptoms and signs
Low acidity in the stomach promotes the active proliferation of pathogenic microbes in the intestines, so the patient may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, and flatulence.
Anacidic gastritis is a disease that is often accompanied by acute intestinal infections, since the protective function of the stomach is weakened.
A person also experiences disturbances in the absorption of protein and iron, which can lead to the development of anemia, accompanied by numbness of the tongue and fingers, a yellowish tint to the skin, and a burning sensation.
Very often, anacid gastritis has the following symptoms:
- Gray coating on the tongue;
- Deterioration or complete loss of appetite;
- Flatulence and belching, accompanied by an unpleasant odor, a metallic taste on the tongue;
- Weakness, dizziness, heaviness and discomfort in the abdomen after eating;
- Pain in the upper abdomen;
- Failure of the body to accept foods rich in proteins, constipation or diarrhea.
If the disease is not treated at the initial stage of development, the symptoms intensify and the following signs appear:
- Very strong weight loss;
- Increased pain syndrome, which is girdling in nature;
- Dysbacteriosis, anemia;
- Development of cholecystitis or pancreatitis.
Disruption of the digestive process leads to a lack of minerals, vitamins and proteins in the body. As a result, hair and nails become dry and brittle, blood pressure decreases, tachycardia and dizziness appear.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many reasons for the development of anacid gastritis:
- smoking;
- abuse of strong alcoholic drinks;
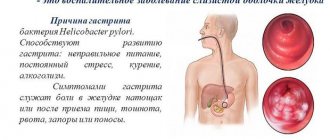
- infectious diseases, including Helicobacter;
- fasting, especially long-term;
- autoimmune disorders;
- constant dietary nutrition, especially the passion for mono-diets;
- poor nutrition.
Often the disease develops against the background of typhoid fever or dysentery, naturally, if these diseases were not cured in time.
People who spend most of their time in an office or work in other sedentary jobs are at risk. Eating the “wrong” foods also leads to the formation of the disease.
Causes
In modern times, the causes of the development of pathology have not been sufficiently studied. Doctors suggest that the lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach may be due to metabolic disorders. The disease can also be provoked by pathology of the repair of the gastric epithelium, which arose at the genetic level under the influence of many factors.
Therefore, the disease can be inherited. Also, hyperacid gastritis, which has not been treated, eventually gives way to anacid gastritis, since most cells die due to excess acid, acidity first returns to normal, and then decreases to abnormal limits.
Among the most common reasons that can provoke the appearance of the disease include:
- Genetic predisposition, heredity;
- Regular consumption of unhealthy foods;
- Constant non-compliance with diet;
- Consumption of coffee, alcohol and nicotine;
- Frequent use of medications;
- Allergies, disorders of the immune, nervous or endocrine systems;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or ENT organs;
- Damage to infections, fungi, pathogenic bacteria;
- Improper treatment of gastritis, which leads to its transformation into a chronic form.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of antacid gastritis, depending on the degree of development of the pathology, can manifest themselves as follows:
- pain and heaviness, especially after eating;
- “loose” stools or, conversely, constipation;
- apathetic and lethargic state;
- due to a decrease in the amount of hydrochloric acid, the absorption of vitamins and nutrients decreases, and the patient begins to rapidly lose weight;
- nausea, including vomiting, which may contain mucus and bile;
- a decrease in pressure may be observed;
- develop anemia;
- bloating and severe gas formation;
- Girdle pain may appear.
An advanced form of the disease can cause the development of cholecystitis, stomach diseases, dysbacteriosis and pancreatitis.
But the most unpleasant and dangerous sign of anacid gastritis is a putrid odor from the mouth. This is due to the fact that food is not completely digested and ferments.
Teeth marks and a gray coating may appear on the tongue. Some patients experience headaches. The appearance of belching is always accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms of anacid gastritis
The clinical picture of this disease consists of gastric and intestinal dyspepsia syndromes. In this case, the following are observed:
- nausea after eating;
- feeling of heaviness, fullness in the upper abdomen;
- rare profuse vomiting of undigested food, bringing relief;
- belching rotten;
- bad breath;
- dull pain in the epigastric region;
- bloating;
- pain along the intestines;
- diarrhea, less often - constipation.
If the disease exists for a long time, then a dystrophic syndrome is observed, which is associated with impaired absorption of vitamins and protein deficiency. The patient develops general weakness, pallor, dryness, flaking of the skin, brittle nails and hair, decreased vision and general immunity.
Chronic anacid gastritis of an autoimmune nature is characterized by an anemic syndrome, but its manifestations are usually nonspecific. With a long course of the disease, symptoms of damage to the nervous system appear in the form of weakness, numbness in the legs, and impaired coordination of movements.
Diagnostics
To prescribe treatment, you will need to undergo a complete diagnosis. A biochemical blood test is required. The stomach contents are examined for the presence of Helicobacter. If there is a suspicion that the development of B12-deficiency anemia has already begun, then bone marrow puncture is performed.
If an X-ray examination is prescribed, it is carried out exclusively with a contrast agent.
During diagnosis, the inner walls of the stomach look pale, the folds on the mucous membrane become flat, until they disappear completely.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Based on clinical manifestations, it is impossible to distinguish between hyper- and hypoacid gastritis. Therefore, the main importance is attached to analyzes and hardware examination. Patients are prescribed:
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy - insertion of a probe with an optical device allows you to examine the esophagus, all parts of the stomach and duodenum, and take mucosal material for biopsy.
- pH-metry is carried out during fibrogastroscopy with a special probe or radiocapsule.
When examining biopsy specimens, not only Helicobacter is revealed, but also the extent of its spread throughout the mucous membrane.
The main method for diagnosing the form of gastritis, the presence of complications and cancerous degeneration
If it is impossible to perform intragastric intubation, the acidity of the gastric juice is judged by the level of uropepsinogen in daily urine, as well as by the concentration of serum gastrin (in case of insufficient acid formation, it is increased, in cases of antral atrophic gastritis, it is sharply reduced). Morphological studies provide a more complete analysis of the capabilities of the fundic glands and the degree of atrophic changes.
Helicobacter pylori infection is confirmed by the detection of special antibodies in the blood of patients. In clinics, an x-ray method is used, which makes it possible to identify polypous growths, deformities of the antrum, tumors, and impaired folding. Ultrasound is a low-information method for detecting stomach diseases, but it helps to identify other pathologies of the digestive organs.
Drug treatment
For this disease, medications are prescribed that relieve pain and promote the production of gastric juice. Drugs that replace hydrochloric acid may even be prescribed. Enzymes are used to improve gastric motility. If megaloblastic or iron deficiency anemia occurs, it is recommended to take iron supplements and vitamin B12.
If the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection is confirmed and a diagnosis of anacid gastritis is made, drugs with an antibacterial effect are prescribed, which will have to be taken for at least 7 days.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of anacid gastritis, you just need not to violate the rules of prevention. Eat properly and on time, do not eat food on the go or dry, do not put it off until later, avoid drinking alcohol and tobacco products.
It is important to monitor your daily routine. Lead an active lifestyle and carefully monitor the cleanliness of your mouth. A simple action will strengthen the immune system and nervous system. If you follow the rules, a person will never worry about the symptoms and treatment of anacid gastritis.
source
Phytotherapy
Oddly enough, it is with this pathology that medicinal herbs help. Tinctures can be made from St. John's wort, plantain and nettle.
To improve your appetite, use fresh cabbage juice. After thoroughly grinding the leaf, the juice is squeezed out and consumed before each meal, approximately 150 ml.
It is also recommended to use sea buckthorn oil, which contains bioantioxidants that reduce the toxic effects of aggressive substances that the stomach cannot digest. It promotes additional protection of the mucous membrane, relieves inflammation and accelerates the healing of wounds and ulcers. The number of bacteria decreases. In this case, you can drink 1 teaspoon, at least 3 times a day. To achieve results, take the oil for at least 4 weeks in a row.
To improve gastric motility, use plantain juice. After taking the juice, patients observe an almost complete disappearance of bloating, and bowel movements improve. The effect can be noticed after a 3-week course of treatment.
The main thing is that the patient must understand that the use of herbal medicines (regardless of whether the patient prepares them himself or purchases ready-made dosage forms) requires patience. Treatment can last for years.
You can make a decoction at home from the leaves of plantain and St. John's wort, which are mixed and poured with a glass of boiling water. Boil the mixture for about 10 minutes, after straining, take 1 tablespoon, 20 minutes before meals.
Treatment of anacid gastritis
The approach to zero acidity therapy should be comprehensive and multidirectional. A combination of several therapeutic techniques is necessary.
Diet therapy
The basic principle of rational nutrition when reducing the functional activity of the digestive tract is frequent split meals. In conditions of reduced acidity, it is difficult for the stomach to process even a small amount of food, so you should never overeat.
It is important that the food is not too fatty, rough, or spicy . Such dishes make digestion difficult and irritate the mucous membrane.
It is necessary to ensure that the products contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals, since their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract is difficult due to illness.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed based on the causes and symptoms of the disease.
- When H. pylori is detected in the stomach, eradication therapy is carried out aimed at its destruction. Its peculiarity in the anacid state is the ban on the use of gastric secretion blockers - Omez, Nexium, Losek. Only antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
- Specific treatment for autoimmune gastritis has not been developed . If the patient has severe B12 deficiency anemia, hormonal therapy with glucocorticoids is recommended.
- For vegetative-vascular dystonia and neuroses, psychotherapy is performed . Anti-anxiety and sedatives are prescribed.
- , Acidin-pepsin and Abomin tablets are prescribed as replacement therapy These preparations contain not only hydrochloric acid, but also enzymes - pepsins.
- Medicines that normalize the motility of the digestive tract - Cisapride, Metoclopramide, Domperidone. Improves the evacuation of food from the stomach, eliminates nausea and vomiting.
- fixative drugs (Imodium, Smecta) only for prolonged diarrhea.
- Taking vitamin-mineral complexes is important for signs of a dystrophic condition. Anemia is treated with Cyanocobalamin injections.
The use of enzyme preparations such as mezim, festal, creon against the background of replacement therapy for anacid gastritis is inappropriate. Mineral waters (Narzan, Essentuki No. 17) with zero production of hydrochloric acid are not effective enough. Medicines that stimulate regeneration (actovegin, solcoseryl) are prescribed only in the presence of atrophic changes in the mucosa.
Folk remedies
Official medicine recognizes the effectiveness of many folk recipes that have a positive effect on the condition of the gastric mucosa during anacid gastritis. In particular, plantain is useful because it increases the secretory activity of the digestive system.
Juices and infusions from the leaves of the plant are used for medicinal purposes. A brewed herbal tea made from St. John's wort, blueberries and plantain is effective . Take preparations based on plantain, 1-2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day before meals.
Yarrow, stinging nettle, chamomile, knotweed, immortelle, and rosehip also have a positive effect on the gastric mucosa. They can be brewed individually or in combinations.
White cabbage juice, which is obtained from its crushed leaves, also stimulates the digestive tract. Drink ½ glass of juice 3 times a day 20-30 minutes before meals. However, in case of severe flatulence, it is better to refuse such treatment.
Treatment of anacid gastritis is a long process, even if you strictly follow all medical prescriptions. The success of therapy largely depends on the cause of the decrease in gastric acidity. Functional secretory disorders are best corrected without structural restructuring of the mucous membrane. This inflammation goes away without consequences. For autoimmune and atrophic anacid gastritis, lifelong replacement therapy is necessary.
Diet food
It is clear that anacid gastritis is such a serious and chronic disease that requires constant control over oneself, one’s diet and treatment.
First of all, you will have to give up refractory animal fats and rough products. Avoid eating fried and fatty foods. It is best to cook in vegetable oil, or in extreme cases, ghee. In no case should you overeat; it is better to switch to fractional meals with a certain regimen so that anacid gastritis does not continue to develop.
The diet in this case does not imply the consumption of sour fruits and vegetables, although there is a strong opinion that it is precisely such foods that increase the acidity of the stomach. There have even been studies conducted on this topic that did not yield positive results. It turned out that sour fruits do not have any positive effect on enzymatic activity.
It is better to include in your diet foods that actually increase the secretion of gastric juice, these could be:
- broths with meat and fish;
- vegetable soups;
- milk and kefir;
- lightly salted herring.
During periods of remission, nutrition should be complete, with sufficient amounts of fats and proteins. You should not give up carbohydrates, salt and nitrogenous substances, foods high in vitamins C and B. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the diet should be gentle.
Nutrition for anacid gastritis does not imply the consumption of alcoholic beverages, kvass and baked goods. If you want to drink coffee or tea, the drinks should not be strong. If there are pies, then they should be not hot, or better prepared in the oven, with an insipid dough.
Treatment
To achieve a positive effect in therapy for anacid gastritis, an integrated approach is required, which consists of properly selected drug treatment and nutritional correction. A prerequisite for the patient’s recovery and reducing the risk of relapse is strict adherence to the prescribed recommendations. Since atrophic changes in the mucous membrane occur with anacid gastritis, symptomatic treatment is indicated. Its basis is left by gentle nutrition.
Diet
The most significant place in the treatment of the disease is occupied by diet. Since one of the causes of anacid gastritis is its serious errors, a correctly chosen diet will help to significantly reduce the severity of symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition.
When compiling a diet, it is necessary to take into account some nuances. Thus, the patient must:
- eat fractionally - in small portions, and often - from 4 to 6 times;
- eliminate fatty, smoked foods, fried, spicy foods, and alcohol;
- consume ready-made meals exclusively warm;
- enrich the diet with foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice;
- eat slowly, trying to chew food thoroughly so that it is absorbed faster and better, as well as to minimize injury to the organ mucosa.
- Follow the diet, maintaining equal pauses between meals.
Drug therapy
As a rule, with anacid gastritis, the excretory function of the stomach is seriously damaged, but at an early stage it can still be restored. Therefore, medications are selected taking into account the stage of the disease, severity and individual characteristics of the body. The traditional treatment regimen includes the following medications.
- Preparations to improve the digestion of food and eliminate the lack of gastric juice - “Acidin-Pepsinum”, an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid.
- Preparations to increase acidity levels - “Plantaglucid”, “Plantain juice”.
- Products with an enveloping effect to protect the internal membranes of the organ from irritation - “Maalox”, “Phosphalugel”, “Gastronorm”.
- Enzymes to compensate for their deficiency - in order to improve the digestion of food and its breakdown - “Pancreatin”, “Festal”, “Mezim Forte”, “Enzibene”.
- Vitamin B12 to eliminate signs of anemia - “Medivitan”, “Aktiferin”, Cyanocobalamin.
- Antispasmodics to suppress pain - “Drotaverine”, “No-Shpa”.
- Prokinetic drugs to improve motor skills - Motinorm, Primer, Domperidone, Motilium.
If the impact of Helicobacter has been proven, eradication therapy may be prescribed. It involves the use of a number of medications:
- "Pentoprazole" - a proton pump inhibitor;
- "Amoxicillin" - an antibiotic from the group of synthetic drugs;
- "Clarithromycin" is a drug from the macrolide group.
Bismuth preparations or antacid medications may also be added to the treatment protocol.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine, which offers effective recipes for the preparation of various remedies, often becomes an auxiliary method of therapy. After consultation with a specialist, the following may be used:
- fresh cabbage or plantain juice;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- herbal mixtures using popular medicinal herbs - mint, chamomile, St. John's wort, immortelle, yarrow, calendula.
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms of chronic gastritis with reduced/zero acidity are not specific enough and can mimic many gastrointestinal pathologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a number of examinations:
- Collection of complaints and medical history.
- Clinical examination, palpation of the abdomen.
- Laboratory tests: general clinical and blood tests;
- bacteriological examination of stomach contents;
- urease breath test (to detect H. pylori);
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
Causes and mechanism of development
Hypoacid and anacid gastritis is inflammation of the walls of the stomach, accompanied by reduced/zero function of the parietal cells of the organ. It is characterized by a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice and is necessary for normal digestion of food. This condition develops much less frequently than hyperacidity gastritis, and its exact cause has not yet been determined. However, scientists identify a number of provoking factors that can affect the development of the disease:
- regular consumption of very spicy or hot foods;
- frequent consumption of coffee, strong tea, energy drinks (especially on an empty stomach);
- long breaks between meals;
- lack of first courses in the diet, dry food;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse.
Sometimes chronic hypoacid gastritis develops against the background of acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa, after shigellosis (dysentery) or typhoid fever. Another probable cause of the pathology is Helicobacter pylori infection.
Modern theories associate the development of anacid gastritis with irreversible damage to the parietal cells of the stomach by one’s own immunity. Against the background of an autoimmune attack, atrophy of glandular cells occurs, and the release of hydrochloric acid gradually stops. This disease is often also called atrophic gastritis. In the pathogenesis of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, the development of the following syndromes is distinguished:
- disruption of food processing processes: proteins, fats and carbohydrates are not digested properly in the stomach;
- slowing down intestinal motility;
- decreased bactericidal activity of gastric juice: pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply in the gastrointestinal tract;
- immune suppression.