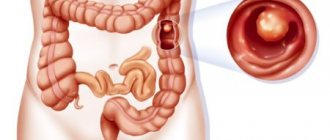
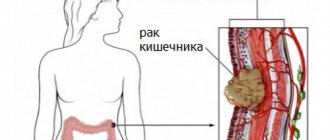
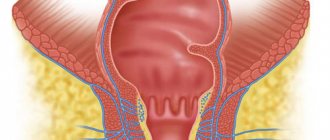
What are intestinal polyps?
These are single or multiple benign formations consisting of mucous structures. They protrude above the surface of the epithelial layer. Polyps have the following structure:
- base;
- vascular pedicle;
- body of education.
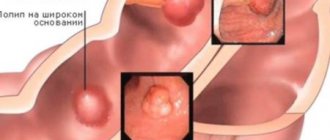
However, sometimes there are polyps in the intestines (symptoms and treatment may vary) that do not have a vascular pedicle. In this case, the body of the neoplasm is attached directly to the base. This polyp may be reddish, pink or gray. The size of the formation also varies (from a few mm to a couple of cm). However, not only intestinal polyposis occurs. The formations can cover the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and even the nasal cavity.
Types of intestinal polyps
Several types of such formations have been described in medical practice. Polyps in the intestines can be:
- Glandular
are formations that grow on the inner surface of the intestine. Such polyps are dense in consistency. Their size can reach 2-3 cm. In addition, there are these types of formations: tubular, villous, tubular-villous and glandular-villous. - Juvenile
- polyps that form in the intestines during the intrauterine development of a child. More often they are diagnosed in early childhood or adolescence. Sometimes such polyps can resolve on their own. - Hyperplastic
- nodular formations that appear due to pathological proliferation of the mucosa. The size of such polyps is no more than 0.5 cm. More often they are multiple in nature. - Lymphoid
- formations that form where there are clusters of lymphoid follicles. This type of polyp is small in size. Their presence in the body is often accompanied by bleeding. - Inflammatory
- polyps that occur in Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. More often, such formations are small lumps surrounded by ulcers.
Polyps in the intestines - causes
To this day, experts are studying the factors that provoke the development of this pathology.
Hyperplastic colon polyp and other types of growths are formed for the following reasons:
- Frequent and prolonged constipation.
Due to the slow progression of food bolus, carcinogenic compounds are in contact with the mucous membranes longer, which negatively affects their condition. - Poor nutrition
is the presence in the diet of high-calorie foods, rich in animal fats and containing a small amount of coarse dietary fiber. Such food slows down intestinal motility and provokes the release of excess bile acids. - Genetic predisposition
to the development of this pathology. - Long-term gastrointestinal disorders
(enteritis, dysentery, ulcerative colitis).
Colon polyposis most often occurs in the following categories of people:
- alcohol abusers;
- having nicotine and drug addiction;
- leading low physical activity;
- working for a long time in hazardous work;
- in contact with toxic substances;
- having poor immunity.
Why are polyps in the intestines dangerous?
Any formation cannot be left without due attention, since in the future it may acquire a malignant form. The rate of transformation of a benign tumor into cancer depends on the type of growth. For example, for glandular ones it is 7-10 years.
Polyps in the intestine provoke the following complications:
- anemia;
- intestinal obstruction;
- purulent processes in the area of neoplasms;
- inflammation of the intestinal walls;
- the appearance of cracks in the anus;
- exacerbation of hemorrhoids.
Varieties
Anatomy of the cecum
There are several classifications of cecal cancer, the main of which are divisions of the disease depending on the histological structure of the tumor and the stage of development of the disease. Thus, the tumor, according to its structure, is divided into:
- adenocarcinoma - formation occurred from the colon mucosa;
- signet ring cell carcinoma – this type of disease has the appearance of vesicles;
- glandular-squamous - based on the name, consists of flat and jelly-like epithelium;
- squamous;
- undifferentiated – characterized by aggressive development, serious condition of the patient, difficulties in treatment and unfavorable prognosis;
- unclassified - consisting of tissues and cells that do not belong to known histological forms.
Division of cecal cancer by stages of progression:
- zero degree or precancerous condition - there is a small tumor that affects the upper layer of the intestinal mucosa. Regional lymph nodes are not damaged, there is no metastasis;
- the first stage – the spread of the oncological process into the deep layers of the organ is observed;
- second stage - germination occurs on the outer wall of the intestine. Lymph nodes are not involved in the pathogenic process, and no metastasis is observed. The prognosis depends on the degree of damage to the outer wall, but in most cases it is quite favorable;
- third stage – the lymph nodes are damaged and the tumor grows into nearby organs. Survival rate is five years;
- fourth stage - not only the surrounding internal organs and regional lymph nodes are damaged, but distant organs are also covered with metastases. The prognosis is extremely unfavorable - death occurs within five years.
The earlier the disease is detected and treated, the more optimistic the outcome will be.
Polyps in the intestines - symptoms
Initially, the pathology occurs without any visible signs. However, as the formations grow, their presence becomes obvious.
Signs of polyps in the intestines:
- traces of blood in the toilet after defecation;
- flatulence;
- itching near the anus;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- pale skin;
- Painful sensations may occur during bowel movements.
Signs of intestinal polyposis - first symptoms
According to statistics, in 70% of cases, pathology is discovered by chance: during an examination of the body, prescribed to confirm the presence of completely different diseases. The patient has no idea that he has a polyp in the intestine - no alarming symptoms appear. This is the insidiousness of this violation. When alarming signals begin to appear, the pathology is already in an advanced form of development.
Rectal polyp
In women, this section of the digestive tract is close to the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems, so the pathology may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- false urge to urinate;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
In addition, colon polyp provokes other pathological disorders. You can judge them by the following criteria:
- bloating;
- bowel dysfunction;
- pulsations in the abdomen;
- feeling of heaviness;
- feeling of a foreign body in the intestines;
- false urge to defecate.
Among the specific symptoms of a growing polyp, you can focus on the following:
- discharge of mucus or ichor from the anus;
- the presence of blood impurities in the stool;
- constipation, which makes it necessary to take medications with a laxative effect.
In men, polyps in the rectum have almost the same symptoms as in women. Growths that increase in size provoke the development of problems in the functioning of the genitourinary system. Often there is a discharge of prostatic secretion from the anus, erectile dysfunction and even the occurrence of infertility. When growths are localized in the anal sphincter area, patients sometimes complain of their loss.
Polyp of the sigmoid colon
This pathology is not uncommon. The first symptoms begin to appear when the polyps reach 2.5-3 cm in size. The following symptoms appear more often:
Polyps in the intestines - treatment
Diagnostic procedures are a mandatory stage preceding therapy. Depending on what polyps are found in the intestines, symptoms and treatment may vary. For this reason, therapy is not prescribed without proper examination.
Diagnostics involves the following manipulations:
How to treat polyps in the intestines depends on the size of the tumors and the area of their localization. Each case is considered individually. Regardless of what polyps are found in the intestines (what are the symptoms and treatment), the doctor will definitely give the patient recommendations regarding nutrition. The patient's diet should consist of foods rich in plant fiber, vitamins and antioxidants.
The following products are especially useful:
- sprouted wheat;
- non-acidic fruits;
- white cabbage and seaweed;
- dishes made from pumpkin;
- dairy products;
- lean boiled or steamed meat;
- porridge;
- vegetable stew.
At the same time, experts strongly recommend excluding the following foods from your diet:
- pickles;
- conservation;
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- fried food;
- products containing dyes, flavors and other harmful components.
It is important to adhere to these rules:
- You should eat fractionally (5-6 times a day and in small portions).
- You cannot combine protein and starch-containing foods.
- All meals taken must be warm. Hot and cold food have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane.
Treatment of polyps in the intestines without surgery
Therapy at the initial stage of development of the disease involves wait-and-see tactics with monitoring the growth dynamics of growths. In itself, drug treatment in the fight against polyps is considered ineffective. It is often used to eliminate negative symptoms, as well as in preparation for surgery and at the recovery stage after surgery.
For example, for bleeding polyps, the following ointments are prescribed:
- Hepatrombin;
- Heparin liniment;
- Heparoid Zentiva.
In addition, the following enzyme-containing medications can be prescribed:
If a patient has anemia, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
Antispasmodics can also be used during therapy. The following drugs are most often prescribed:
Antibacterial therapy may also be prescribed. The following medications are most often prescribed:
If polyps are found in the intestines, treatment with folk remedies can be carried out. However, it is important to remember that such “drugs” must be used strictly under the supervision of a doctor, because each of them has its own contraindications and features of use. In addition, folk remedies are only an auxiliary method of influencing tumors. The effectiveness of treatment increases if they are used along with medications.
- dry raw materials - 6 tablespoons;
- vodka – 500 ml.
- Hemlock is poured into a glass container and the raw material is filled with vodka.
- Seal the dishes and place them in the kitchen cabinet.
- Infuse the drug for 12 days, shaking it regularly.
- The finished composition is filtered.
- Store it in the refrigerator.
- Take the medicine 1 dessert spoon three times a day. If the infusion is taken regularly, the tumors decrease in size.
Honey-camphor mass for rectal polyposis
- camphor oil – 1 tablespoon;
- natural liquid honey – 1 tablespoon;
- iodine - a couple of drops.
- The components are mixed.
- Soak a gauze swab with the medicinal mass.
- It is injected into the lumen of the rectum in the evening and left until the morning.
- The course depends on the intensity of the disease. More often, 5 procedures are done, then after a week's break, therapy is continued.
Surgery to remove polyps in the intestines
This method of combating tumors is considered the most effective. Removal of polyps in the intestines can be done in the following ways:
- Electrocoagulation
is a procedure in which an operating instrument is inserted through the anus. This device has a special loop that allows current to pass through. It heats up to the desired temperature, captures the polyp and cuts it off. - Transanal resection
- this procedure is recommended for patients with a precancerous tumor. During such a surgical intervention, a special device is inserted through the anus, with the help of which polyps and the areas of the intestine affected by them are excised. - A colotomy
is a procedure in which an incision is made in the abdomen. Through this hole, the affected part of the intestine is removed, after which the polyps are removed. - Transanal excision
- such a surgical intervention is performed only when the growths are located at a depth of no more than 10 cm from the anus. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor expands the anal canal, and then uses a scalpel to remove the polyps and apply sutures to the mucous membrane. - Endo-microsurgical transanal excision
is a procedure performed using a proctoscope. Here's how to remove polyps in the intestines: an endoscopic loop is inserted through the anus and the growths are cut off with it.
Polyp in the cecum - what is it?
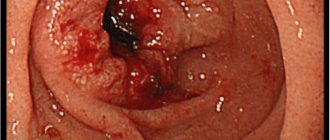
The polyp of the dome of the cecum is predominantly a benign neoplasm. The structure of the polypous lesion depends on its type. Polypous lesions grow inside the organ cavity and have a stalk or a wide base. Despite the initially benign course, the cells of the body of the growth can change and become malignant.
Considering the anatomy of the organ, its initial segment has a hemispherical shape, the total length barely exceeds 10 cm, and the width is 6-9 cm. It is in the dome, the widest part of the cecum, that polyps are formed.
The organ cavity serves as an “incubator” where beneficial bacteria are grown and nutrients are absorbed from the incoming food. When the function is impaired, the entire lower part of the digestive system suffers.
Classification
According to morphological structure and pathogenesis, several main types of polyposis units are distinguished:
- Hyperplastic . The neoplasms have a small cone shape with a diameter of no more than 4-5 mm. They grow both on a stalk and on a broad base. In rare cases, they develop into cancer and spread to other parts of the intestinal tract.
- Adenomatous or glandular . At the heart of the polyp are glandular cells capable of constant dynamics of growth, development, and chaotic division. Adenomatous polyps have a wide stroma, the body resembles a cauliflower inflorescence. The diameter of the neoplasm is from 3-5 mm to several cm. Almost 65% of all adenomatous polyps degenerate into cancerous tumors over a long period of time, so treatment of adenomatous polyp is surgical.
- Villous . Tumors have a wide stroma or a long stalk. The body of the neoplasm is covered with multiple microscopic flagella-villi. Over several years, villous polyps spread to the sigmoid and rectum. In 85% of all cases, the villous polyp of the sigmoid colon becomes malignant. The main danger is the possibility of malignancy of only the villi and a long asymptomatic course.
- Villous-glandular . The structure of the polyps has a rough villous structure and non-epithelial filling - glandular cells. Instability and rapid growth significantly increase the risk of cell malignancy.
- Juvenile . They occur in childhood and tend to quickly spread throughout the mucous membranes of the entire intestinal tract. The surface of the polypous lesion resembles a grapevine. Cases of cell malignancy are rare. Detailed information about the treatment of rectal polyp in a child is here.
Regardless of the morphological structure, even initially benign neoplasms can become malignant.
What to do?
Detection of polyps of the dome part of the organ occurs by chance during preventive diagnostics or examination for other complaints. Patients consult a doctor only when characteristic symptoms appear, when the neoplasms reach impressive sizes, line the entire organ from the inside, and become malignant. Therefore, it is recommended that if you experience a persistent feeling of discomfort in the intestines, you take the COLON VIEW test at home.
With early or late detection of polyps in the cecum, differential diagnosis and surgical intervention are important. Ignoring the symptom complex or choosing a wait-and-see approach without regular diagnostic examinations leads to colorectal cancer in 65% of all cases.
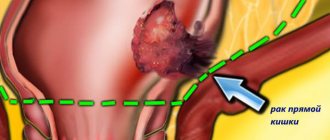
Malignant tumors of the cecum are:
- Adenocarcinoma consists of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane.
- Undifferentiated cancer is an aggressive type of cancer.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma – the cells take on the appearance of vesicles.
- Squamous cell carcinoma – consists of squamous epithelial cells.
- Unclassified cancer - if the tumor cannot be classified into any of the forms, it is classified as this type.
- Glandular squamous cell carcinoma is formed from glandular and squamous epithelial cells.
Symptoms of a polyp of the cecum
Considering the anatomical location of the organ (on the right along the iliac line of the peritoneum), patients describe the first symptoms precisely in the projection of the location of the cecum. Early signs begin when the diameter of the neoplasm is about 1.5-2 cm.
Typical manifestations of pathology are:
- heaviness in the liver structures, pain, nagging sensations after fatty foods;
- compaction of the peritoneum upon palpation;
- decrease in hemoglobin (with bleeding, traumatization of growths, insufficient blood nutrition);
- blood impurities in the stool (obvious or detected as a result of laboratory tests);
- flatulence, bloating;
- spasms regardless of food intake;
- bowel dysfunction (alternating diarrhea with constipation).
As polypous units progress or spread over the surface of the inner lining of the intestine, the tissue becomes coarser and becomes scarred.
What's happened
Cecal cancer is a low-quality tumor that begins its development from mucosal cells. Most often, the location of the tumor is observed at the junction of the small and large intestines.
Pathology is diagnosed in 10-20% of cases of all colon cancers. More often, the pathology occurs in people after 45-50 years of age, and is observed with equal frequency in men and women.
The first symptoms are quite difficult to independently determine, since they can differ depending on the location, size of the cancer node, and concomitant pathologies. Often the symptoms resemble those of hemorrhoids.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
Feces for stomach cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
The disease is characterized by moderate growth and slow spread of metastases, and the formation of secondary tumors is observed mainly in advanced stages of the pathology; distant organs and tissues are not affected.
Cecal cancer belongs to the moderately aggressive diseases; the prognosis directly depends on the timely diagnosis and implementation of therapeutic measures. With a very favorable prognosis, we can talk about complete elimination of the disease and restoration of all body functions.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are aimed at assessing the structure of polyps, dynamics, differentiation with other tumor-like neoplasms and cancer.
The set of diagnostic measures includes the following stages:
- Laboratory tests (analysis of stool, urine, blood);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs to exclude combined or other pathologies;
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic research method; intestinal colonoscopy with removal of polyps is possible;
- Irrigoscopy is a radiopaque method for identifying the outlines of a polyp and its anatomy. What is better, irrigoscopy or colonoscopy, can be found out in a separate article.;
- Sigmoidoscopy with a thorough examination of the intestinal sections at a distance of 10-12 m from the anus.
During endoscopic examination methods, a biopsy of the polyp is possible. Histological examination allows us to assess the morphology of the polyp, make a prognosis for removal and the postoperative period.
If the diagnosis is unclear, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed. In case of a complicated clinical history, consultations with specialized specialists are required: proctologists, surgeons, oncologists, cardiologists, gastroenterologists.
Rehabilitation
Cecal cancer and its treatment involve damage to the intestine, and therefore patients require a long recovery. It is important during this period to adhere to a diet with plenty of healthy and easily digestible food. Vegetables and fruits that are rich in essential vitamins are recommended. A moderate motor regimen will be useful, which will enhance peristalsis and normalize the digestion process.
Conservative treatment
There are no adequate conservative treatment methods. If small single polyps are detected, a wait-and-see approach may be prescribed with regular examinations at least 2 times a year. The disadvantages of this tactic are the likelihood of malignancy of the cells, as well as the patient’s lack of discipline - after the first two examinations, many patients simply stop undergoing diagnostic procedures.
Drug therapy is symptomatic and is also used after surgery.
The main drugs are:
- Cytostatics to prevent malignancy and growth (Cisplatin Methotrexate Cyclophosphamide);
- Antiseptic douching with solutions of aqueous Chlorhexidine, Furacilin;
- Antibiotic therapy.
Systemic drugs and local agents can be used as drugs: suppositories, microenemas, enemas with antiseptic solutions.
Alternative medicine
Unfortunately, the effectiveness of alternative medicine against cecal polyps has not been proven. You can try remedies for polyps in the rectum.
Popular herbs for microenemas with decoctions are:
- St. John's wort,
- celandine,
- viburnum berries,
- oak bark,
- yarrow,
- Chaga birch.
Before injecting into the rectal canal or placing tampons, it is important to strain the decoctions well and observe the temperature regime (up to 35 degrees). Read more about the traditional treatment of rectal polyps right here.
Treatment with folk remedies is unjustified due to the delayed onset of therapeutic results, high risks of allergic reactions, and disturbances of intestinal microflora.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including the cecum, are healthy, high-quality, regular nutrition, absence of bad habits, healthy active lifestyle, high-quality water, and lack of stress. Modern life, with its pace, rarely provides a person with the opportunity to easily implement such recommendations. Therefore, it is very important not to ignore preventive medical examinations, but at the first unpleasant symptoms and malaise, immediately contact a specialist so as not to waste time.
We recommend: The most effective folk remedies for the treatment of colorectal cancer
Diet after removal of cecal polyps
Correction of nutrition after removal is required to reduce the digestive load and trauma to the mucous membranes. More proteins are introduced into the diet to restore strength, fiber and aggressive foods are excluded.
The diet is based on the following products:
- fermented milk products (except whole milk);
- soups, broths with lean meat, vegetables;
- pureed dishes, side dishes, cereals.
Fresh bread is excluded; it can be replaced with crackers. A plentiful drinking regime is introduced. All food should be liquid or semi-liquid. Dishes are steamed, stewed, boiled. With the professional participation of nutritionists, all individual characteristics are taken into account.
The location of the cecum and the movement of food through the intestines:
The prognosis for polyps of the cecum is favorable. Tumors form due to inadequate treatment and lack of medical supervision. Drug treatment and folk recipes can aggravate the development of polyps and stimulate the malignancy of neoplasm cells.
What is the threat of a polyp in the maxillary sinus, read our article.
You can make an appointment with a doctor directly on our website.
- 6 minutes to read
In the medical literature, the cecum is the name given to the first section of the large intestine, where the processing of products coming from the small intestine occurs. Its main task is to absorb nutrients and protect against harmful bacteria. The length of the organ is about 10 cm, and the width in the lower part is up to 9 cm. It is located in the right iliac cavity, therefore, the patient’s symptoms manifest themselves on this side.
Content
In case of improper functioning of the cecum or constant reboot, there is a high probability of the appearance of tumor neoplasms of a benign (polyps) or malignant nature.
Polyps grow on the mucous membrane, have a thin stalk or a clearly defined base. They can be either single or numerous.
The risk of developing a tumor increases with age. According to statistics, every second person after 60 years has at least one polyp. The danger of such tumors is that when they reach large sizes they degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
Adenomas are diagnosed with equal frequency in women and men. Most often, people over 45 years of age seek medical help with this problem.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the cecum begins with an external examination of the patient; the doctor should pay attention to the color of the person’s skin and mucous membranes. He also palpates the abdomen to determine the presence of tumors in the intestines and liver. A general blood and stool test is prescribed to check for occult blood in it.
Next, the urologist or gynecologist conducts a digital examination of the rectum and vagina in women. It will help determine the presence of a neoplasm, its approximate location, as well as the condition of the rectum, ovarian uterus and vaginal wall, which may also be involved in the tumor process.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- rectoscopy (examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon using an endoscope inserted through the anus). An accurate method that will allow you to see adenocarcinoma in these parts of the large intestine. Rectoscopy is often used for preventive purposes. But the endoscope does not allow access to the cecum. Therefore, other methods are used;
- colonoscopy. The essence is the same as that of rectoscopy, but this technique allows you to examine the entire large intestine. During this procedure, a piece of tumor tissue may be taken for examination in the laboratory. This procedure is called a biopsy. It is necessary to determine the type of cancer and determine further treatment;
- irrigoscopy. The x-ray method involves the introduction of a contrast agent, which is distributed in the intestines and then viewed on an x-ray. In this way, you can see the contours of the organ and possible defects and complications, but minor deviations cannot be detected using irrigoscopy. Other radiological methods are also used that make it possible to identify metastases in other organs (chest radiography, urography, cystography, urethrography and others);
- More accurate imaging methods include ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs. It shows possible lesions in the intestine and neighboring organs, as well as the depth of tumor infiltration. Ultrasound is a painless and inexpensive method;
- CT and MRI. They provide even more information than ultrasound and show even the smallest defects. They may be prescribed if the results of other studies are unclear.
Read here: Somatostatinoma: features of development and growth
Based on the results obtained, the doctor can prescribe treatment.
Causes
The main reasons contributing to the occurrence of tumors of the cecum continue to be studied by specialists today. However, a number of factors influencing the development of the pathological process should be highlighted:
- Hereditary predisposition, which consists of family diseases that provoke precancerous conditions. Sometimes polyps begin to form in children at an early age without concomitant diseases.
- Inflammation in the cecum (for example, ulcerative colitis). This problem causes a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, leading to the growth of tumors.
- An unbalanced diet with a lot of spicy and fatty foods.
- Viral diseases (human papillomavirus, influenza or herpes) lead to decreased immunity.
- Parasitic diseases of humans that cause damage to the mucous membrane. This process predisposes to its degeneration.
- Smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol, products containing harmful chemicals.
- Sedentary lifestyle, environmental problems, work in hazardous industries.
- Disturbances in the intrauterine development of the intestinal mucosa, which increase the likelihood of a tumor.
Stages of adenocarcinoma of the cecum
There is stage 5 of glandular cancer of the cecum, including stage zero, which is called cancer in situ:
- Stage 0 - at this stage, tumor cells are generated; they are found only in the intestinal mucosa. If such a tumor is detected and removed, a 100% cure is guaranteed;
- Stage 1 is a mobile neoplasm up to 2 cm, delimited from healthy tissue. It affects not only the mucous membrane, but also the submucosal layer. There are no metastases;
- at stage 2, the tumor grows into all layers of the cecum, but does not go beyond it;
- stage 3 cecal adenocarcinoma is characterized by spread to regional lymph nodes, neighboring tissues and organs, but without distant metastases;
- at stage 4, multiple metastases are observed in the lymph nodes, as well as damage to distant organs. This type of cancer is incurable. A feature of colorectal cancer is its slow development. It takes a long time for the tumor to spread through the intestine to neighboring tissues. But a long course causes an inflammatory process, which provokes the appearance of multiple foci of the disease.
Read here: What is ovarian adenocarcinoma?
Symptoms
A tumor of the cecum develops slowly. The patient does not show any signs at first. The disease can manifest itself in different ways, and the symptoms depend on the location of the tumor, its size, and the presence of possible complications caused by concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Quite often, this pathology is mistaken for acute appendicitis due to the similarity of symptoms.
The most common symptom indicating the formation of a tumor is the presence of blood in the stool. In the future, this leads to pale and dry skin.
Surgical treatment of cecal cancer
The extent of surgical intervention is selected only after a complete examination and establishment of the clinical stage.
Before planning treatment, the functional state of all organs and systems must be carefully examined: general clinical blood tests, coagulation system, ECG, ECHO-CG, FGDS, spirometry, ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities, consultations with a therapist, gynecologist, and medical specialists.
If the patient is severely weakened, it is necessary to prepare him for the upcoming operation and subsequent chemotherapy. In case of severe anemia, it is necessary to carry out transfusions of components and blood products, for cachexia - infusions of amino acid hydrolysates, for concomitant diseases - compensation for the functions of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
For cancer of the cecum, the following operations are possible:
- For grade 0 carcinoma, localized only in the mucous layer, endoscopic submucosal resection is possible. The removed drug is examined. For moderately or highly differentiated adenocarcinomas, the absence of damage to the resection margins and metastases to the lymph nodes, the operation is considered radical. Subsequently, dynamic observation is carried out.
- For resectable stage 1-3 cancer, a right hemicolectomy is performed. In this case, the entire right half of the colon and part of the ileum are removed as a single block with the mesentery, tissue and lymph nodes. An anastomosis is formed between the ileum and the transverse colon (ileotransverse anastomosis).
- Symptomatic operations. Such interventions are performed for unresectable tumors to eliminate the symptoms of intestinal obstruction and alleviate the patient’s condition. The primary lesion is not removed. Often they resort to the formation of a bypass ileotransverse anastomosis, or to the formation of an ileostomy (the ileum is sutured to the anterior abdominal wall to drain feces).