Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa (in some cases, even deeper layers), leading to dystrophic changes and disruptions in the functioning of the organ itself. Gastritis is accompanied by pain in the upper abdomen and various dyspeptic disorders.
The causes of gastritis include non-compliance with healthy eating rules, abuse of alcohol and smoking, taking certain medications, and chronic stress.
It may also occur against the background of other diseases of the internal organs or as a result of infection with certain bacteria and fungi (in particular the bacterium Helicobacter pylori).
The acute form of the disease without timely treatment quickly becomes chronic, which usually occurs with complications.
What kind of disease is this?
Chronic gastritis is a term used to refer to long-term inflammatory diseases of the stomach, which are characterized by persistent structural changes in its mucous membrane.
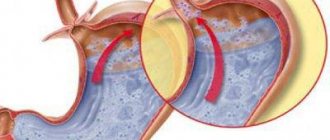
Erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, accompanied by the formation of erosions and hemorrhages (bleeding). Damage affects only the mucous layer; the muscle tissue of the stomach remains unchanged in this disease.
The reasons for the development of erosive gastritis are the following factors:
- uncontrolled use of certain medications (analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.);
- addiction to “unhealthy” foods (smoked meats, marinades, spicy foods, etc.);
- systematically eating too hot food;
- bacteria: Helicobacter pylori, diphtheria bacillus, salmonella;
- alcoholism;
- chronic stress.
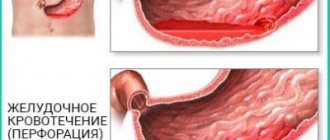
Complications of hemorrhagic gastritis can include repeated gastric bleeding , anemia, ulcer formation, and in rare cases, shock.
Erosive gastritis is considered one of the most dangerous inflammatory diseases of the stomach!
Symptoms
In most cases, erosive hemorrhagic gastritis is manifested by the following symptoms :
- pain in the epigastric region (on an empty stomach and late);
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- sour belching;
- vomiting with blood;
- tendency to constipation with “episodes” of diarrhea.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
The most characteristic symptom of this disease, which distinguishes it from other gastritis, is gastric bleeding , which can be suspected by pale skin, general weakness and frequent dizziness (sometimes with loss of consciousness).
Vomit and feces, stained with blood, become dark or black.
Erosive gastritis caused by taking medications can be asymptomatic .
Diagnosing the disease in this case can be difficult due to the signs of the underlying disease, which are “layered” on the symptoms of progressive hemorrhagic gastritis.
Causes of erosive gastritis
The disease can be caused by both external and internal factors. External ones include the ingestion of chemical and alkaline substances into the body that can corrode the gastric mucosa. Some medications, due to long-term use, can also cause the formation of erosions. This group of factors also includes poisoning and ingestion of salmonella or Helicobacter, junk food, frequent consumption of spicy and sour foods, as well as very hot drinks, which have a detrimental effect on the mucous walls of the stomach.
Diagnostics and necessary examinations
In addition to the external examination and history taking, the patient is prescribed the following diagnostic tests.
Lab tests:
- blood chemistry;
- blood test to detect anemia;
- stool occult blood test;
- bacteriological and toxicological analysis of vomit, food debris, feces.
Instrumental studies:
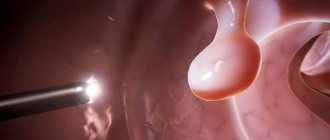
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) with targeted biopsy - performed to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and exclude the oncological nature of the disease;
- X-ray of the stomach - study of the relief of the walls of the stomach;
- intragastric pH-metry – assessment of the acid-forming function of the stomach;
- breath test for helicobacteriosis.
Additionally, immunological studies, tests for syphilis and tuberculosis may be prescribed.
Treatment of erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
Depending on the duration of the disease, hemorrhagic gastritis is divided into acute and chronic . The acute form is cured in 7-10 days, the chronic form can bother the patient for a long time and is much more difficult to treat.
Also, erosive gastritis can be primary (occurring for the first time) and secondary (arising against the background of existing stomach diseases).
The final treatment will depend on what form of hemorrhagic gastritis is diagnosed in the patient’s medical record.
Treatment of erosive gastritis is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. If there is gastric bleeding, hospitalization is required.
The patient is prescribed:
- gentle diet;
- drug therapy (taking into account the form and severity of the disease);
- hemostatic therapy (in case of bleeding);
- herbal medicine (in remission);
- surgical treatment (in exceptional cases, when all possibilities of conservative treatment have been exhausted).
Treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor!
What do doctors usually prescribe?
Drug treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis is prescribed individually , taking into account the etiology (causes of the disease) and the results of laboratory and instrumental studies. The list of drugs given below may vary depending on the characteristics of the disease.
- Antibacterial therapy - the choice of antibiotics depends on the causative agent of the infection.
- Proton pump inhibitors - omeprazole, pantoprazole.
- H2-histamine receptor blockers - cimetidine, ranitidine.
- Antacids - aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide.
- Gastroprotectors – bismuth preparations.
- Antispasmodics - atropine, platyphylline, papaverine hydrochloride.
- Prokinetics - metoclopramide, domperidone.
- Remedies – methyluracil, sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil.
- Herbal remedies - decoction of flax seed, plantain, yarrow, chamomile.
On our website: Is it possible to cure alcoholic gastritis?
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine in the fight against erosive gastritis is good as an auxiliary therapy . How can you supplement the main treatment?
- Propolis . A small piece of propolis should be consumed on an empty stomach once a day, chewing it thoroughly. The course of treatment is 1 month.
- Aloe juice. Freshly squeezed plant juice is boiled and then cooled. Drink 1 teaspoon half an hour before meals, 2 times a day. To enhance the effect, you can add a little honey to the juice.
- Lettuce (salad). 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of crushed leaves into 1 cup of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Take the product ½ cup 2 times a day.
- Sprouted wheat. Fill the wheat grains with water so that they are completely hidden and wait for them to germinate. Rinse the sprouts with chilled boiled water and chop. Then add olive oil to them. Take the resulting product 1 teaspoon between meals.
- Mumiyo. This is an incredibly useful remedy from Altai that treats many ailments, including gastritis. Mix 0.25 g. mumiyo with warm milk and a drop of honey. Drink the remedy in the morning on an empty stomach and before bed.
Before using any chosen product, you should always consult your doctor.
Diet for erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis
Diet therapy for hemorrhagic gastritis begins with a two-day fast, then for 4 days the patient is prescribed treatment table No. 0, then for 6-10 days - diet No. 1.
The patient is advised to eat fractional meals in small portions; overeating is excluded. Dishes must be served pureed. Recommended types of heat treatment are boiling, baking, stewing.
Allowed:
- slimy soups and cereals;
- boiled meat and fish;
- vegetable purees;
- low-fat milk and cottage cheese;
- omelettes or soft-boiled eggs;
- jelly, herbal decoctions;
- dried white bread.
On our website: Symptoms of focal atrophic gastritis and its treatment
Prohibited:
- alcohol, coffee, soda;
- canned food, marinades, pickles, smoked meats;
- hot sauces;
- fresh sour vegetables and fruits;
- cabbage, turnips, radishes, legumes (in any form);
- whole milk;
- chocolate;
- fresh bread.
Diet for any form of gastritis is the main component of successful treatment of the disease. In case of erosive gastritis, it should be observed especially carefully, since the slightest error in nutrition can negate all the efforts of doctors.
Description of the disease
Hemorrhagic gastritis is a type of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Its peculiarity is that it occurs against the background of microcirculatory disorders in the submucosal layer. The result is hemorrhages and blood soaking of the mucous membrane, the formation of blood clots on the smallest vessels.
Inflammation develops with leukocyte infiltration at the microscopic level and the formation of small surface defects (erosions), determined visually.
Prognosis: what will happen if left untreated?
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
In the absence of gastric bleeding and timely treatment, the prognosis for recovery in patients diagnosed with erosive gastritis is quite favorable . If the disease is diagnosed for the first time, and treatment measures are carried out in accordance with the therapeutic plan, a complete cure can be achieved even on an outpatient basis.
With delayed diagnosis, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic , which is difficult to treat and often relapses even after surgery.
On our website: How to properly treat gastritis with sea buckthorn oil? Folk recipes
Symptoms
The disease has no specific symptoms. The main symptoms are characteristic of all types of gastritis and peptic ulcers. But there are those that allow us to presumably classify gastritis as hemorrhagic:
| Complaints |
|
| Inspection data |
|
| Diagnostic data |
|
Tips and tricks
Prevention of hemorrhagic erosive gastritis is essentially similar to the prevention of other gastrointestinal diseases.
To prevent the development of the disease, you should follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, and try to avoid stress.
When taking any medications, you must monitor your stomach’s reaction to them.
If medications cause irritation, you should contact your doctor to request a replacement. It is recommended to monitor the condition of your teeth, promptly stop any outbreaks of infection that arise in the body, and regularly undergo preventive examinations at a medical institution.