03/05/2020 650 Colonoscopy
Author: Tatyana
Colonoscopy is one of the methods for examining the rectum, cecum and colon for various diseases, including cancer. However, due to the specifics of the research process, this method is not suitable for all patients. In modern medicine, there are several alternative procedures that can be used to check the intestines without a colonoscopy.
- 2
Alternative bowel examination methods2.1
MRI and MR colonoscopy
- 2.2
CT scan - 2.3
Ultrasound - 2.4
Capsule examination - 2.5
Irrigoscopy - 2.6
Anoscopy - 2.7
Sigmoidoscopy - 2.8
Endorectal ultrasound - 2.9
Positron emission tomography - 2.10
Hydrogen test - 2.11
Photo gallery
Video
Comments and Reviews
When to check your bowels
Pathologies of the digestive canal are accompanied by:
- prolonged nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- unexplained weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- stool disorders.
Life with a feeling of constant discomfort and pain turns into a nightmare. You will need the help of a gastroenterologist, who needs information to select adequate therapy.
Malignant neoplasms in the lower parts of the digestive canal can be avoided if intestinal polyps as the main cause of their occurrence are promptly identified and treated.
Elena Malysheva, in the program “Live Healthy,” talks about the main methods of diagnosing the intestines.
A detailed examination is prescribed after identifying the main symptom, namely occult blood in the stool.
Analyzes
Laboratory diagnostics include:
- General analysis of capillary blood taken on an empty stomach. Allows you to detect an inflammatory process in the intestine, a violation of its absorption function, disorders, helminthiasis, bleeding, and neoplasms. These diseases are characterized by low hemoglobin levels and high ESR levels.
- Biochemical analysis requires venous blood. With its help, urea, C-reactive and total protein are detected, which are used to determine helminthic infestations, acute infections, cancer, and bleeding.
- A study on tumor markers, which are judged by the decay particles of degenerated cells. Exceeding the norm does not always indicate a malignant neoplasm. The preliminary diagnosis is confirmed or refuted by additional research.
- A general urine test reveals dehydration and impaired absorption. The biomaterial is collected in the morning.
- Coprogram. This is the name for examining stool for intestinal diseases and the presence of parasites. 2 days before analysis, exclude tomatoes, beets and other foods containing pigments from the diet.
- Hidden blood is determined by its traces in the stool, for example, using a fecal immunochemical test performed at home.
- Determination of pathological microbes for suspected acute or chronic infections. Using a special loop, the doctor takes a smear from the rectum for further cultivation of bacteria. Microscopic examination allows us to identify the type of pathogenic microorganisms and their sensitivity to various antibiotics in order to select the most effective therapy.
- Analysis for dysbiosis is carried out using stool culture for flora and counting the number of coli-, lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as hydrogen and other tests.
Palpation
A method for checking the condition of the abdominal organs, the presence of seals, and the degree of pain.
Initially, indicative palpation is performed to determine body temperature and muscle tone. The norm is considered to be a condition when there is no pain when palpated, the organs are mobile, and the abdominal cavity is soft. Muscle tension shows the location of the disease.
The method is used to study the anal canal. It is carried out with the index finger using an anesthetic ointment according to strictly prescribed rules and examination procedures. In 90% of cases, an accurate diagnosis can be made.
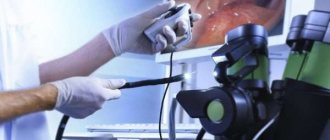
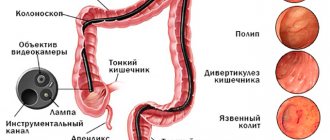
Colonoscopy
An instrumental diagnostic method that can be used to check any part of the large intestine. For this purpose, a device equipped with a miniature video camera is used, which is inserted through the anus. When examining the internal walls of the lower parts of the digestive canal up to the appendix, inflammation, ulcerations, tumors or polyposis are revealed.
New models of endoscopes provide sampling of a tissue fragment for more thorough examination and removal of small formations. Previously, such actions were performed only during the operation.
Preparation for a colonoscopy includes a 3-day diet and taking laxatives on the eve of the procedure. Sometimes it is performed under anesthesia. The pain depends on the level of medical equipment and the qualifications of doctors.
Irrigoscopy
The intestines can be examined without a colonoscopy using a number of techniques, including a non-traumatic X-ray method using barium sulfate. Compared to CT (computed tomography), it is more gentle in terms of radiation exposure. Contrast is administered by enema or orally. On the monitor you can see the nature of the folds of the intestinal wall, study cicatricial narrowings and congenital defects in the development of the digestive canal.
The darkened areas reveal:
- polyps;
- neoplasms;
- diverticula;
- foreign bodies.
The method is indicated if colonoscopy is impossible or its results are in doubt.
The duration of the procedure is 15-45 minutes. Correct execution eliminates complications. Carrying out irrigoscopy is possible both in a specialized center, clinic, and in a hospital, equipped with appropriate equipment and supported by the skill of a radiologist.
Sigmoidoscopy
A painless diagnostic method that allows you to check a section of the large intestine 30 cm long from the anus. Before the manipulation, a digital examination of the anus is performed to identify contraindications, which include:
- acute form of hemorrhoids;
- anal fissures;
- inflammation in the lower parts of the digestive canal.
Checking the intestines begins with assessing the condition of the mucous membrane, its color, the presence of erosions and ulcerations, swelling, the severity of folds in the walls of the anus and rectum.
A safe diagnostic measure that allows you to examine the intestines for diseases, including in pregnant women and children. It is carried out through the abdominal wall or rectally using a catheter inserted into the rectum.
The second method helps in diagnosing complex neoplasms on the outer layer of the anal canal, “invisible” during colonoscopy. It is performed with a full bladder, which pushes back the loops of the small intestine.
A special diet, enemas, and taking the drug “Fortrans” cleanse the intestines, including gases that interfere with the study. A special liquid is used as a contrast.
The study requires a capsule with a video camera, which is swallowed by the patient. Information is recorded on a special medium. After analyzing it, the doctor selects a treatment regimen. Preparation consists of following a diet and fasting on the eve of the procedure. The price of the procedure can reach 30,000 rubles.
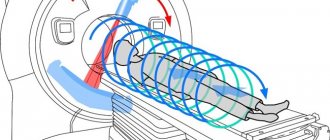
A diagnostic method used in various fields of medicine, including gastroenterology. When examining the digestive canal, MRI is an auxiliary procedure, since problems arise with visualizing the layered loops of the large intestine. The test is painless and does not require special preparation.
Detection of an inflammatory or malignant process using MRI is not a basis for making a diagnosis. A colonoscopy will be required to examine every centimeter of the mucous membrane with the possibility of biopsy and therapeutic measures:
- Cauterization of damaged vessels.
- Elimination of intestinal volvulus.
- Removal of polyps.
The method is not very informative at the initial stage of the disease. But when examining seriously ill patients and pregnant women, it is the only one available.
The abbreviated name is FGDS. It is a progressive and highly informative method of instrumental diagnostics. Provides visualization of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, performing pH measurements, administering medications, stopping bleeding, removing polyps, collecting biomaterial for microscopic examination and detection of Helicobacter pillory.
On the eve of the procedure, which lasts 5-10 minutes, careful preparation is carried out. It can be done under local anesthesia with lidocaine, which relieves discomfort in the pharynx area.
We suggest you read How to quickly cure toenail fungus
FGDS is indicated for all adults after 40 years of age in order to be checked at an early stage for oncological degeneration of the digestive canal organs.
The arsenal of intestinal research methods is wide. Accurate, timely diagnosis is a condition for successful recovery.
Endoscopy: instrumental examination
This is the most progressive method, allowing for the highest quality examination of all parts of the intestine. This includes gastroscopy, rectoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, capsule endoscopy.
Gastroscopy is familiar to many who have seriously wondered how to examine the intestines for diseases. To carry it out, the patient swallows a tube with an endoscope, which transmits an image of the area being examined to a computer. The resulting image allows you to clearly see the areas affected by the disease.
This method makes it possible to examine the stomach and duodenum to detect diseases such as ulcers and cancer.
Using rectoscopy, the condition of the rectum is diagnosed; Romanoscopy – sigmoid colon. For a complete examination of the large intestine, fibrocolonoscopy is used. Capsule endoscopy allows examination of the small intestine.
Capsule endoscopy process
Its essence lies in creating a picture thanks to the movement of a special device through the small and large intestines - an enterocapsule, equipped with a small video camera. Outwardly, it looks like a regular pill, the body of which is made of thin plastic. After passing through the stomach and entire intestines, the capsule leaves the body naturally.
Capsule diagnosis of intestinal disease is carried out in case of unknown abdominal pain, detection of internal bleeding or in case of suspected tumor formation. This method allows you to diagnose such dangerous diseases as intestinal or stomach cancer.
Conducting such a study requires advance special preparation:
- a short nutritious diet that excludes the consumption of a number of foods;
- 8-10 hours before taking the capsule, do not eat any food at all;
- Take a laxative immediately before the procedure.
The movement of the capsule through the intestines is carried out by peristaltic waves. The camera records its entire path and transmits data to a recording device pre-installed on the patient’s body. The passage of the enterocapsule through the intestines takes about 8 hours. All this time the patient can go about his usual activities. The data received on the recording device is then decrypted by a specialist.
This is a very effective diagnostic method that allows you to absolutely accurately determine the cause of the disease and the location of the pathology. Its disadvantage is its high cost.
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is an innovative method for examining and diagnosing diseases of the digestive tract using a miniature capsule with a built-in camera. Capsule endoscopy has several advantages:
- Absolutely painless. From the moment the capsule is swallowed until it leaves the body naturally, the patient does not experience pain or unusual sensations.
- Safety of the procedure. It is not possible to infect the patient with anything during the examination, since each capsule is sterile and disposable.
- Comfortable conditions for the manipulation. During the process, the patient can read books, watch movies, move around the medical facility and communicate with loved ones.
- Information value. For detecting hidden gastrointestinal bleeding, this is the best option, which is 3-4 times superior to irrigoscopy.
A capsule swallowed by the patient allows one to obtain a detailed image of the mucous membrane of the small intestine, which was inaccessible for examination before the advent of this diagnostic method.
Video capsule is superior to magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing polyposis
Capsule endoscopy is justified in the case of the following pathologies:
- low hemoglobin content in red blood cells;
- bleeding from the digestive tract;
- inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract, in which granulomas are formed;
- long-term inflammatory disease of the large intestine;
- acute or chronic inflammation in the small intestine;
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS);
- a hereditary autoimmune disease caused by persistent intolerance to gluten or gluten;
- neoplasms in the small intestine;
- abdominal pain that cannot be objectively explained by other diagnostic methods;
- prolonged stool disorder;
- rapid weight loss.
Capsule endoscopy is considered the most reliable diagnostic method for diseases of the small intestine. It can even detect problems that were missed during a CT or MRI.
Popular publications:
- Black feces Why? Causes? — 01/07/2015 05:06 — Read 42025 times
- Video capsule endoscopy: frequently asked questions - 11/12/2013 17:02 - Read 39820 times
- Capsule endoscopy. Description, reviews, advantages and disadvantages - 03/24/2013 17:15 - Read 36706 times
- Abdominal syndrome. Abdominal pain - 01/10/2015 05:02 - Read 20976 times
- Capsule colonoscopy - indications, contraindications, price - 30/10/2015 07:20 - Read 16247 times
Key words: Intestinal examination, endoscopy, irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, ultrasound, MRI, capsule endoscopy, video capsule, capsule gastroscopy, capsule colonoscopy
- < Back
- Forward >
Irrigoscopy
Intestinal irrigoscopy is a method of examining the intestines using X-rays and preliminary administration of contrast agents. It allows you to evaluate not only the structural features of the large intestine, but also its functionality. Irrigoscopy has a number of advantages. Allows you to determine the presence of morphological abnormal changes, assesses the size, length and degree of patency of the intestinal lumen.
Indications are diarrhea for a long time, disruption of bowel movements (frequent constipation), discharge of mucous or purulent impurities from the anus, bursting and cutting pain in the lower abdomen, frequent or chronic flatulence.
Irrigoscopy allows you to check the intestines for oncology only partially without colonoscopy. With the X-ray method of examination, the neoplasm itself is detected, but it is impossible to examine its structure or take a sample of biomaterial for histological examination.
Irrigoscopy is a more gentle diagnostic method compared to colonoscopy
Ultrasound diagnostics
Ultrasound reveals most pathologies of all parts of the intestine. It can be used to diagnose tumors, adhesions, paresis after operations and other anomalies.
Modern devices provide a color image that allows for a fairly informative assessment of each area being examined.
On the eve of the ultrasound diagnosis, the patient should take a laxative and for several days before it follow the diet prescribed by the doctor.
Scanning with an ultrasound machine is prescribed for children, pregnant and lactating women, elderly people or weakened patients, for example, in the postoperative period or after an illness.
This is an excellent option for those who are wondering how to examine the intestines as quickly as possible.
Ultrasound diagnostics
This is a new examination method, the principle of which lies in the differences in the magnetic properties of the tissues of healthy and diseased organs. The impact of a magnetic field on these organs creates a resonance, the recording of which using a scanner allows us to determine the state of this organ.
These methods of intestinal examination provide fairly accurate results. With their help, you can identify diseases such as tumors, ulcers, inflammations; determine the quality of functioning of a particular organ.
To conduct an MRI examination, as a rule, there is no need for special patient preparation. It is enough to adhere to a certain diet the day before and take a laxative.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics - MRI
Methods for examining the intestines without colonoscopy
There are several methods for diagnosing the intestines without the use of colonoscopy. The simplest of them is digital examination or palpation. Obviously, in this way it is possible to tactilely assess the condition and diagnose diseases only in a small area of the intestine, namely in the rectum at a distance of 10-12 cm.
A not much larger area of the intestine can be examined by sigmoidoscopy. Using a special device - a sigmoidoscope, the doctor is able to visually assess the condition of the internal walls of the rectum to a depth of approximately 30 cm. This is a more informative method compared to palpation, but is also limited in scope.
Studies that allow you to “see” the condition of the entire intestine require sophisticated equipment. Thus, irrigoscopy is based on X-ray examination with contrast, ultrasound and magnetic resonance examinations are based on the penetrating action of sound waves and excitation of hydrogen atoms by a magnetic field. All these procedures can be used for certain narrow purposes as preliminary and complementary to each other.
Virtual colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy of the intestine (MSCT) is the reconstruction of a three-dimensional image of the intestine during computed tomography in a special way. During the procedure itself, air is pumped through a tube in the rectum and then, after the patient holds his breath, the abdominal organs are scanned. Visually, the result of MSCT differs from classical colonoscopy only in a clearer image.
Reviews about virtual colonoscopy of the intestine
Advantages of virtual colonoscopy:
- There is no need to introduce endoscopic instruments into the patient's body.
- It can be performed on patients with severe heart failure and those suffering from poor blood clotting.
- The procedure is gentle and comfortable for the patient, so there is no need for anesthesia or sedation.
- The risk of damage to the colon during MSCT is significantly lower than during conventional colonoscopy.
- In parallel with the examination of the intestines, other organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis can be examined.
Virtual colonoscopy is prescribed in the following cases: advanced inflammatory processes in the digestive tract, suspicion of the development of a malignant tumor, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, frequent disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract of unknown etiology. The list includes regular pain and cramps in the abdomen of unknown origin, bleeding that occurs in the lumen of the small or large intestine, patients over 40 years of age.
During virtual diagnostics, it is impossible to take a biopsy sample for research, so it will not be possible to confirm the malignancy of the tumor in this way.
Colonoscopy
The main method for diagnosing colon diseases in women and men is intestinal colonoscopy. It is considered the most effective. During the procedure, a flexible probe with a camera at the end is inserted into the intestines through the anus. This method of checking the intestines allows you to visualize ulcers, polyps, inflammations, tumors, etc. During the examination, a biopsy, removal of polyps and foreign bodies, stopping bleeding, and restoring intestinal patency are possible. The main advantage of the innovation is the study of the entire large intestine.
The following indications exist for intestinal colonoscopy:
- neoplasms on the mucous membrane;
- inflammation and swelling;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- presence of a foreign body in the intestine;
- intestinal obstruction and constipation;
- polyps;
- blood in stool, etc.
The insertion probe is 1.6 m long, soft and flexible, and has a video camera at its end. Local anesthesia is administered intravenously or applied to the endoscope to reduce pain during insertion. General anesthesia is recommended for children under 12 years of age.
Contraindications for colonoscopy:
- pulmonary heart failure;
- peritonitis;
- severe colitis;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- pregnancy.
Cleansing the intestines before the study is the main condition of preparation. This can be achieved by enemas or special laxatives. Castor oil can be used as an additional remedy for severe constipation.
2-3 days before the examination they adhere to a light, slag-free diet. It excludes:
- sources of fiber - greens, vegetables and fruits;
- smoked meats, pickles, marinades, rye bread, chocolate, peanuts, chips, seeds, milk and coffee.
To cleanse the intestines, after consultation with a doctor, you can use Lavacol, Endofalk, Fortrans, Duphalac. The latter is good because it does not irritate the mucous membrane.
Colonoscopy is an unpleasant procedure; insertion of the probe is painful. During the camera examination, the intestine is dilated by injecting air into a balloon for better examination.
This intestinal examination lasts 20-30 minutes. If the approach is incorrect, complications may arise in the form of bleeding, perforation of the wall, and bloating.
What is intestinal colonoscopy and why patients prefer to replace it
Colonoscopy helps examine the large intestine. To carry it out, various models of endoscopes are used, with the help of which the examinee examines the inner wall of the intestine, and, if necessary, polyps are immediately removed or a biopsy is performed.
Patients do not like this procedure and want to conduct an intestinal examination without a colonoscopy for the following reasons:
- This is an unpleasant and painful method that requires anesthesia.
- Discomfortable preparation period (dietary nutrition and emptying the intestines of feces).
- Serious mistakes made during a colonoscopy can lead to abdominal surgery.
Many people understand that when a tumor is detected, a biopsy should be taken to determine its nature, however, they are interested in whether it is possible to check the intestines for the presence of cancer without a colonoscopy. Patients also want to know how to examine the small intestine.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Positive aspects of this type of research:
- allows you to identify oncology;
- removes all polyps;
- cauterizes ulcers;
- reveals swelling of large veins;
- finds inflammatory processes;
- studies the mucous membrane more accurately.
It is better to check the intestines without a colonoscopy for people who have:
- liver, pulmonary or heart failure;
- with peritonitis;
- colitis;
- blood clotting disorders;
- acute intestinal infections.
During a colonoscopy, you can damage the intestinal wall, cause an infection, or cause an attack of appendicitis.
PET scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a branch of nuclear medicine that uses a special type of scanner and tagged atoms (a radioactive chemical) to evaluate the condition of internal organs. The effectiveness of this diagnostic method largely depends on the choice of radioactive pharmaceutical drug.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Diet for intestinal diverticulitis in adults
When comparing the detail of images, PEG is inferior to CT or MRI, since it only represents the location of isotope tracers. As a rule, positron emission tomography is performed in conjunction with classical CT. Combining PET scans with CT scans can provide more detailed information about the location of radioactive chemicals.
Positron emission tomography is used to determine the stage of cancer, monitor blood flow, or assess the functionality of internal organs. This examination of the intestines without a colonoscopy allows you to detect cancer at an early stage.
For a malignant neoplasm of the large intestine, this diagnostic method may have the following tasks:
- detection of distant metastases;
- assessment of the tumor process - its quality and how widespread it is;
- diagnosis of possible relapse of malignant neoplasm;
- identifying the stage of cancer pathology;
- monitoring the condition of the intestines after surgery.
In more than 90% of cases of colon cancer detection, colonoscopy and irrigoscopy play a key role. They are necessary to identify primary foci, and for a more detailed study of the pathological process one cannot do without PET.
PET scan allows detection of distant metastases
Alternative bowel examination methods
Of course, an examination of the intestines can be carried out without a colonoscopy. You can check the organs of the lower gastrointestinal tract using the following alternative methods:
- non-invasive instrumental (ultrasound, MRI, CT, PET);
- minimally invasive instrumental (anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, irrigoscopy);
- non-instrumental (physical examination, palpation, laboratory tests).
How to check the intestines without using a colonoscope can best be advised to the patient by the attending physician. However, it should be borne in mind that colonoscopy is used by doctors most often to make a diagnosis. An alternative method is used to evaluate the condition of the small intestine or in cases where colonoscopy cannot examine certain areas.
In cases where there is no need for surgical manipulation, the following diagnostic methods can be used:
- Ultrasound. Transabdominal transducers or endorectal ultrasound may be used.
- CT scan. The second name for the procedure is virtual colonoscopy. The procedure is painless, takes no more than 10 minutes and results in a 3D model of the colon.
- MRI. The accuracy of the results of this examination method is quite high. If there is a need to examine the midgut, then hydro-MRI with double contrast is used.
- PAT. Positron emission tomography is based on the intravenous administration of radioactive sugar, which allows the detection of malignant tumors.
Each of the methods presented has its own strengths, but to make an accurate diagnosis you may need to use several at once.
Most often, examination of the lower gastrointestinal tract requires penetration into the patient’s body:
- Finger method of examining the rectum. Before the digital examination, the doctor examines the anus area, and then carefully inserts the index finger of the right hand into the anus. The doctor has a glove on his hand, and he pre-lubricates his finger with Vaseline.
- Anoscopy. Examination of the lower digestive tract using an anoscope inserted into the anus.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Examination of the intestinal mucosa (up to 30 cm) using a sigmoidoscope.
- Irrigoscopy. Radiation method for diagnosing the colon with contrast.
- Capsule diagnostics. The patient drinks (swallows) a capsule with a video camera, which moves throughout the digestive tract, collects information and transmits it to the carrier.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must collect anamnesis in as much detail as possible and conduct a comprehensive examination.
The intestines are also checked without a colonoscopy if there are problems in this area that indicate a less serious etiology of the disease. The following methods are considered primary in modern medicine: physical examination, palpation, palpation. In addition, sometimes pathology can be determined by the appearance of the abdomen: the presence of asymmetry, bloating, hollowness). Proctologists and surgeons also pay special attention to the characteristics of pain.
This type of examination, such as a colonoscopy, is not entirely pleasant and requires a lot of special preparation. In medicine, other methods are used as an alternative to colonoscopy.
These include:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography);
- Ultrasound;
- irrigoscopy;
- capsule examination;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- hydrogen test;
- PET positron emission tomography.
Eating before the procedure and the night before after 21:00 is not recommended. This will allow for a better examination.
MRI is considered a good alternative to colonoscopy, but is significantly more expensive. Therefore, it is prescribed as an additional research method in special cases.
This may also include MR colonography. This procedure involves injecting 2 liters of liquid with a contrast agent into the intestine. And using a special apparatus, the state of the organ is viewed in three dimensions. The duration of the procedure is about an hour.
People with a fear of closed spaces should not use this method either.
CT can also be considered an alternative technique. But it has its drawbacks - small tumors are difficult to assess based on the information provided.
The advantages of this technology include the fact that it does not damage the mucous membranes, tissues with a high density are isolated, and it is possible to assess the contours of the pathology and the condition of nearby organs.
This is displayed as a three-dimensional image of the anatomical structure of the organ in good quality.
Ultrasound can be used instead of colonoscopy in selected cases. This examination is a registration of sound waves that are reflected from the boundaries of tissues that differ in structure and density.
This study allows you to evaluate the area of the organ affected by the tumor. It is also possible to see nodes with a diameter of 0.5 to 2 cm.
Irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy allows you to conduct an examination without a colonoscopy - to assess the location of tumors, their size, shape and mobility.
It is carried out by administering a barium enema with a contrast agent, after which an x-ray is taken.
Next, it is possible to introduce air after removing barium sulfate. This allows you to see the outlines of individual parts of the organ. In this case, it is possible to detect congenital pathologies, scars, fistulas, and ulcers. The procedure is painless and safe.
Capsule examination is an alternative to intestinal colonoscopy in cases where it is not possible to undergo the standard method due to individual anatomy.
The mechanism is a capsule with a diameter of about 10 mm and a length of approximately 30 mm. It is equipped with an autonomous power supply and cameras.
The patient swallows the device and it passes through the intestines, photographing it, and is eliminated naturally.
Photos can be taken from 4 to 35 pictures per second, depending on the speed of advancement of the capsule itself. Information is transmitted using electromagnetic waves to special equipment.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Features of post-traumatic eczema
The examination takes from 5 to 8 hours.
Prescribed for hidden bleeding, suspected neoplasms and pathologies. Plus, this method allows you to detect diseases not only in the colon, but also in the stomach itself.
Anoscopy
Anoscopy cannot replace a colonoscopy. With its help, up to 10 cm of the lower rectum is checked.
The procedure involves inserting a special optical device with illumination into the anus. The anoscope is pre-lubricated with Vaseline.
This way you can see tumors, hemorrhoids, inflammations, and polyps. It can also be used to perform a biopsy.
Rectomanoscopy
Rectomanoscopy can be done once every 5 years. This is not an analogue of a colonoscopy, since only 30 cm of the large intestine is examined. In this case, it is possible to take a sample of the edge of the tumor.
This procedure does not give a complete picture of whether there is a disease or not, and at what stage it is.
If pathology is detected at this stage, the patient is prescribed additional examination of the intestines by other methods.
Hydrogen test
The hydrogen test is carried out over 3 hours. In this case, every half hour the patient must exhale into a special tube.
This tests for the presence of large numbers of bacteria in the small intestine.
It works like this - bacteria do not allow fluid to enter the mucous membrane in sufficient quantities, which leads to stool problems.
In this case, carbohydrates are quickly broken down, and hydrogen slowly enters the blood and comes out with respiration.
A PET scan uses radioactive sugar, which is injected intravenously, to detect cancer. Due to the fact that pathological cells absorb large amounts of this substance, you can see where they are and in what quantity.
The procedure lasts about an hour and a half, of which the patient waits for about an hour for the drug to spread.
To summarize, we can conclude that there is only one answer to the question of how to check the intestines besides colonoscopy - using MRI. Other methods are not as effective; they have their own advantages and disadvantages.
But examining the sigmoid colon using this study is not available to a wide range of patients, since MRI is quite expensive.
In addition to colonoscopy, there are 7 instrumental ways to diagnose intestinal conditions. The only thing in which they are inferior to colonoscopic examination is that if negative phenomena are detected in the intestines, it is impossible to take tissue from the problematic formation for analysis.
- virtual colonoscopy;
- CT scan;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Ultrasound;
- irrigoscopy with barium;
- positron emission tomography (PET);
- capsule endoscopy.
Computed tomography is similar to an x-ray, but instead of one image, the tomograph takes them layer by layer, gradually taking a large number of images. Computed tomography examination of the intestines without colonoscopy cannot always detect cancer in the early stages, which is always possible with a proven method.
Virtual tomography works using a program that processes CT results and can detect polyps larger than 1 cm, but this research method is not available in every medical center, and early diagnosis with its use is excluded. And if polyps are detected, they will still have to be removed.
MRI is based on the use of magnets and radio waves, the energy of which is directed at the body and then returned in the form of reflected impulses. This method is based on the introduction of a drug with gadolinium, which behaves differently in diseased and healthy tissues, allowing the identification of polyps based on the decoding of the template into a detailed image using a computer program. This bowel examination is contraindicated in people with kidney disease.
Bowel Check Methods
Methods for examining the intestines without colonoscopy can detect various diseases, but most of them cannot take material for a biopsy. Therefore, if oncology is suspected, after all replacement procedures, this diagnostic method may be required.
Irrigoscopy
Diagnosis is carried out using X-ray equipment. First, bowel preparation is performed: it is cleansed using enemas or laxatives. After this, a contrast agent, barium sulfate, is injected into the cavity of the organ being examined. It fills all bends and sections, making it possible to detect pathology or damage.
Sometimes double contrast is used - barium sulfate is used, which gives a positive image and gas (air), which is displayed as a negative. As a result, the intestinal walls are covered with a thin layer of suspension, stretched with air, and all the relief features of the internal surface (tumors, fistulas) are clearly visible.
After administering contrast agents, the doctor takes targeted and overview photographs. The patient changes position: turns over on his side, then on his stomach. The advantages of the procedure are that it is non-traumatic and painless, allowing you to examine areas that are inaccessible with colonoscopy. Disadvantages include contraindications, including diverticulosis, perforation and intestinal obstruction.
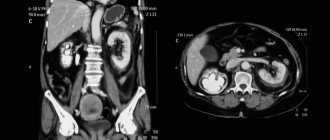
CT scan
This is a non-invasive method of examining the intestines. Special equipment is used - a computed tomograph with an X-ray machine. Bowel preparation is standard: taking laxatives, enemas.
When the cavity is cleaned, the patient lies down on the machine’s couch, and a tube is inserted into the rectum to supply air - this improves the quality of the image. The subject is then placed in the scanner. The X-ray machine begins to rotate in a spiral and take pictures from different angles. The results are processed by a computer and displayed on the monitor.
The patient is periodically asked to hold his breath and roll over onto his side or stomach. The entire examination lasts about 15 minutes. The good thing about this method is that it does not cause pain or discomfort, there is no risk of damage to the walls of the organ (unlike colonoscopy), and it is possible to view all parts of the intestine and neighboring organs.
At the same time, computed tomography is only a diagnostic method; if polyps or other neoplasms are detected, they cannot be removed. Also, the disadvantages include contraindications (obesity, pregnancy) and a large dose of one-time radiation.
Capsule diagnostics
An endoscopic examination method - a capsule with a mini-video camera is placed in the organs being examined. The preparatory stage is cleansing the stomach and intestines. The patient is given an endocapsule and swallows it. Due to natural contractions of the walls of the digestive tract, it moves down.
A special device is installed on the body of the subject and records the location of the camera and its signals. The computer then deciphers the data and the doctor interprets it. The capsule exits through the rectum when visiting the toilet.
This diagnostic method is a modern alternative to intestinal colonoscopy, it is performed without anesthesia, and the video provides information not only about the structure of the organ, but also about its contractions (dynamic aspect).
Disadvantages: not all cities can carry out such an examination; it is carried out for a fee; there is a risk that the capsule will remain in the stomach and will have to be pulled out using instruments.
Finger examination
Allows you to evaluate the reflex ability of the anus and its condition. Preparation for the procedure is standard. During the examination, the patient can be in a knee-elbow position, lying on his side or sitting on a gynecological chair.
The doctor puts on gloves, lubricates his fingers with Vaseline, inserts his index finger into the rectum and feels its walls. The examination can be carried out using the index finger, index and middle fingers, as well as using the second hand placed on the lower abdomen.
The advantage of this method is that it does not require additional tools and equipment, and direct contact with the walls of the intestine allows the doctor to accurately assess their condition and check the rectum without a colonoscopy. The disadvantage is that the examination area is small, so digital examination is only a preliminary stage of diagnosis.
Sigmoidoscopy
An invasive diagnostic method that allows you to examine the condition of up to 30 cm of the large intestine and take material for a biopsy and remove polyps.
The intestines are cleared of contents. The patient stands in a knee-elbow position on the couch. The doctor inserts a sigmoidoscope into the rectum, treating its tube with Vaseline, and examines the condition of the organ.
Disadvantages of this method: unpleasant painful sensations, risk of damage to the walls of the organ, contraindications. During colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and intestinal anoscopy, anesthesia is performed if the patient has increased sensitivity.
The advantages include the ability to take material for a biopsy, remove polyps, as well as the high reliability of the data obtained.
Hydrogen test
A hydrogen breath test is a diagnostic method that does not involve penetration into the body, but allows one to detect pathological changes in it, especially in the digestive tract. In this way, it is possible to establish the true cause of chronic dysbiosis, abdominal pain, lactose intolerance or fructose malabsorption.
The human intestine is filled with a large number of anaerobic bacteria, which produce hydrogen in large quantities. During the breath test, the time of increase in hydrogen concentration is recorded and then, based on these indicators, the section of the intestine in which fermentation processes occurred intensively is determined.
The test is indicated in the following cases:
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- suspicion of intolerance to sugars (lactose, fructose, sorbitol, xylitol);
- inability to digest certain foods or their components (whole milk, fruits, honey);
- increased concentration of microorganisms in the small intestine;
- insufficient secretion of pancreatic juice necessary for digestion;
- irreversible process of replacement of parenchymal liver tissue with fibrous connective tissue;
- symptoms of disturbed microflora (bloating, diarrhea, constipation);
- assessment of the effectiveness of treatment of intestinal diseases associated with atrophy of the small intestinal villi.
In healthy people, hydrogen is practically not formed in those parts of the digestive tract where there is no fecal flora.
Choosing a research method
If the patient has problems with the intestines that do not require surgical intervention and do not threaten the patient’s life, then he can, in agreement with his proctologist, replace colonoscopy with the most appropriate alternative method in his case.
But if there is a need to determine intestinal cancer or the patient has been diagnosed with neoplasms, polyps and other tumors during alternative studies, then the patient will still be prescribed a colonoscopy. Without it, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis and carry out adequate therapy in severe cases.
| Suspected pathology | Eligible Studies |
| Intestinal inflammation | Colonoscopy, x-ray |
| Tumors, oncology | Colonoscopy, CT, MRI, X-ray |
| Polyps | Colonoscopy |
| Intestinal obstruction | CT, MRI, radiography |
| Developmental anomalies | CT, MRI, radiography |
| Intestinal bleeding | Colonoscopy, x-ray |
| Diverticulitis, intussusception | Colonoscopy, X-ray, ultrasound |
Fibercolonoscopy is the “gold” standard for diagnosing most pathologies of the large intestine, which is explained by its high information content and range of capabilities. CT and MRI are not inferior to endoscopy in detecting tumors. X-ray examination allows you to quickly confirm the presence of perforated ulcers or intestinal obstruction and its level.
During a colonoscopy, patients only rarely experience moderate pain, but mostly some discomfort. It is important to understand that the examination will help establish a diagnosis, perform a biopsy and, in some cases, remove the cause of the complaints.
If fear still comes to the fore, then it is recommended to undergo the procedure with anesthesia (pain relief). With this option, before the examination, the patient will need to consult with an anesthesiologist and undergo some tests (ECG, blood test, etc.).
Finger method
This study is mandatory; with the help of it, the proctologist will identify the presence of pathologies. Such a check is prescribed if the patient is bothered by pain in the abdomen, dysfunction of the pelvic organs, impaired evacuation of substances from the intestines, or intestinal obstruction. This method allows you to look at the condition of the epithelium around the anus and mucous membrane, study intestinal motility and the function of sphincter contraction. The doctor may examine rectal discharge.
During the procedure, the patient takes a knee-elbow position, the proctologist puts on medical gloves and the intestines are felt with the index finger. The doctor can determine the presence of benign formations, hemorrhoids, and fissures. But with this method it is possible to examine only 10 cm deep from the anus.