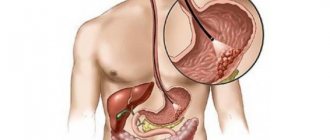
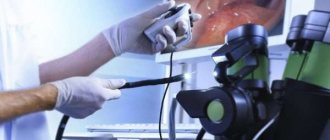
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the colon; it is currently the most informative way to diagnose the initial stage of cancer in this part of the intestine. For the examination, a probe is used - a flexible tube with a light bulb and a miniature camera at the end. Additionally, the probe is equipped with a device for taking a biopsy and removing a polyp.
Indications for use
This procedure is usually recommended for the following indications:
- presence of close relatives with cancer;
- diagnosed with colon cancer;
- suspected Crohn's disease.
To exclude oncopathology, it is recommended to undergo a colonoscopy if you have a history of:
- frequent constipation;
- abdominal pain;
- bloody discharge from the rectum.
Main contraindications
Although doctors assure that the FCS examination does not pose a threat to the patient’s health, there are nevertheless a number of serious contraindications that prevent endoscopic examination of the colon. Thus, any pathology in the acute stage, as well as the patient’s general malaise, make the diagnostic procedure dangerous. In this regard, the doctor selects an alternative research method or suggests waiting for recovery. Fibercolonoscopy is strictly prohibited for those patients who suffer from the following diseases:
heart failure;- ulcerative or ischemic colitis;
- recent stroke;
- advanced arterial hypertension;
- severe form of Crohn's disease;
- inflammatory processes in the rectum that are in the acute stage;
- acute inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity;
- poor blood clotting;
- acute form of blood vessel thrombosis;
- formations of connective tissue between the peritoneal organs and intestinal loops.
What does the diagnosis show?
In the diagnostic results, the specialist must indicate the color of the mucous membrane and the condition of the intestinal walls. Based on the results of the examination, we can conclude that the patient has the following diseases:
- polyps in the colon;
- malignant tumors;
- colon diverticulosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Contraindications
Despite the uniqueness of the method, not everyone and not always can be diagnosed. It is prohibited for people who have been diagnosed with the following diseases:
- acute heart attack, atherosclerosis, stroke;
- rupture of the process of the cecum (peritonitis);
- pulmonary failure;
- umbilical or inguinal hernia;
- perforated intestinal walls.
People with artificial valves and other pathologies are at risk of complications.
For patients with a hereditary predisposition to intestinal diseases, doctors recommend periodic FCS, and people of retirement age should be examined annually to identify pathologies in the early stages.
An advanced disease is sometimes difficult to cure, and sometimes impossible. A person who does not neglect fibrocolonoscopy maintains his own health, and, therefore, gives himself the opportunity to live happily and long.
Kinds
Colonoscopy allows you to visually examine the walls of your colon. This method can also be used to take samples of tumor tissue for analysis and for therapeutic purposes to remove a polyp. The use of anesthesia makes the procedure more comfortable.
Without anesthesia
According to the compulsory medical insurance policy, they offer a free colonoscopy without anesthesia. Local anesthesia is usually used by lubricating the tip of the probe with an anesthetic drug.
In this case, pain from penetration of the endoscope into the anus can be avoided, but discomfort when air is blown into the intestines and when the device passes through it remains.
With anesthesia
When performing a colonoscopy under general anesthesia, two types of anesthesia are used:
- sedation (medical sleep);
- general anesthesia.
These methods have their advantages and disadvantages. With the use of modern anesthesia drugs, anesthesia is usually tolerated without undesirable consequences.
With biopsy
Combining a visual examination of the colon with a biopsy makes it possible to most reliably identify the presence of pathological formations in it. The tissues of the object being examined are removed directly during the diagnostic procedure using a probe.
Features of intestinal colonoscopy
Colonoscopy of the intestine has many features, which is why this diagnostic technique has become indispensable for making the correct diagnosis. Let's consider what capabilities the doctor is endowed with when performing a colonoscopy:
- During the study, the specialist can understand the state of the intestinal mucosa, determine how the body absorbs useful substances, and notice whether inflammation is present;
- it is possible to determine the size of the intestinal lumen and, if it is too narrowed, then expand it;
- Having discovered a foreign object in an organ during an examination, the doctor can remove it;
During the procedure, it is possible not only to detect bleeding in the intestines, but also to eliminate it
- if the presence of a tumor of a benign nature and small size has been noticed, then it is possible to eliminate it during the procedure;
- Internal intestinal bleeding is detected, as well as its cause, and during the procedure it is eliminated using high temperatures.
Preparing for the examination
Colonoscopy requires lengthy preliminary preparation so that the examination is carried out in the most cleansed intestine. Preparation takes place in 2 stages:
- diet;
- purgation.
Diet
3 days before the examination, the patient should switch to a slag-free diet. A detailed list of foods that need to be excluded from the diet will be provided to him at the diagnostic center.
Purgation
The day before the procedure, the patient takes strong laxatives to completely empty the intestines. The medications and regimen for their use will be recommended by the doctor who will conduct the examination.
How is a colonoscopy performed?
The procedure is performed on an empty stomach. If the examination is carried out under anesthesia, it is recommended to do it in a hospital. Diagnosis without anesthesia is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Before the examination, air is pumped into the intestine to straighten its walls and improve visibility of the mucous membrane. The doctor inserts a probe into the patient through the anus and, moving the device through the intestines, examines the condition of its walls.
After diagnostics are carried out, the results are recorded on digital media.
How long does it last?
The time allotted for a colonoscopy depends on many factors. The duration of the procedure is influenced by the doctor’s experience, the condition of the intestines, and the need to perform additional manipulations.
The duration of the procedure without anesthesia is usually 15 – 30 minutes. With the use of anesthesia, it can take about an hour.
Is the procedure painful?
Most patients rate colonoscopy without anesthesia as a very painful procedure. The use of anesthesia makes it quite comfortable.
Intestinal restoration after the study
For some time after the examination, the patient may experience discomfort in the abdomen:
- constipation;
- increased gas formation;
- diarrhea.
To avoid this, it is recommended to follow a gentle diet and drink plenty of water for 2–3 days after the procedure. You may need to take medications. Your doctor will help you choose the right diet and medications.
How often should it be done?
All people over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo this preventive examination every 5 years. If cancerous tumors are found in the colon, a colonoscopy should be done every year to evaluate the effect of the treatment.
Patient reviews
Most patients forced to undergo a colonoscopy admit that they experienced mental and physical suffering during the examination. This procedure is painful and extremely unpleasant.
Price
The cost of a colonoscopy depends on the type of medical facility where the examination is performed. The minimum cost is 500 rubles; if additional services are provided, the price increases.
In a government agency, the procedure is done free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy. In large medical centers, the service can cost 15 thousand rubles.
Survey history
On the forums you can read many patient reviews about the diagnosis. Many of them are glad that they decided to do it, despite their fears and prejudices. If you have been prescribed FCS, do not refuse the study.
Ekaterina: some tips for going through the procedure
The blood in my stool forced me to do an FCC. In horror, I ran to a local proctologist, who recommended an examination.
I won’t dwell on how to properly prepare for it. The attending physician will tell and explain everything to you.
In the office they gave me special underpants with a hole in that very place. A device was inserted through her, but it did not seem to hurt. But when they started moving it through the intestines, it was already quite unpleasant.
How the procedure is performed
The doctor blew air: as he explained to me, this was necessary to straighten the intestine. I felt like I just ate too many peas at night.
During the examination, a biopsy was taken. It turned out that it didn't hurt at all. The whole procedure lasted no more than half an hour.
I believe that the study is the most accurate for diagnosing intestinal problems. It helped me make a diagnosis.
In conclusion, I would like to give advice to those who are still planning to attend the FCC. I hope that with them your procedure will be easy and comfortable.
Recommendations:
- Start preparing at least a day in advance. If you take a laxative and then want to cleanse your colon with an enema, don't do it! Otherwise, you will have to take a laxative again.
- Are you afraid of a colonoscopy? Don't ask your doctor to give you anesthesia. The study can be carried out quite calmly without this. Why expose your body to unnecessary stress?
- Unlike FCS, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is many times worse. Since I went through both examinations in two days, I know what I’m talking about.
In general, the diagnosis is not scary at all. I need to go through it every year, but it’s my own fault that I started my disease this way. Of course, the sensations are not very pleasant, but it’s worth being patient: my health depends on the procedure.
For children
In order not to cause serious mental trauma to the child, children are examined only under general anesthesia. This eliminates the possibility of intestinal damage due to the increased physical activity of a small patient.
There are no age restrictions for this procedure; it is performed even on newborns if there are serious indications:
- suspicion of a congenital anomaly of the large intestine;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- suspected Crohn's disease.
You will have to refuse a colonoscopy if the child has contraindications such as:
- intolerance to medications used for anesthesia;
- acute infectious diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of internal organs.
Indications and contraindications for using the procedure
A fibrocolonoscopy of the intestine is prescribed to a patient if:
- The patient experiences the appearance of clinical signs indicating a disease such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). These signs include the occurrence of any disorders of the human digestive system, which can manifest themselves in the form of periodically appearing or constant stool disorders, characterized by constipation and diarrhea. In this case, a person may experience pain in the abdomen and a feeling of heaviness that occurs during the process of excessive accumulation of digestive gases in the intestinal tract (flatulence).
- Foreign impurities such as mucus and blood have been found in human feces.
- The patient complains of loss of appetite and a constant feeling of weakness.
- There was a sharp decrease in a person’s body weight without any well-defined reasons.
In addition, FCS of the intestinal tract is prescribed for those patients who have tumor tumors of various etiologies in any part of the large intestine, the presence of foreign objects in the lumen of the abdominal region and inflammatory processes. The use of a colonoscope is also prescribed in case of internal bleeding in the intestinal tract that requires urgent medical attention.
Although fibrocolonoscopy is a safe diagnostic procedure, it cannot be used if the person being examined has the following pathologies:
- cardiopulmonary failure;
- ulcerative or ischemic colitis, which has a severe pathological process;
- recent stroke;
- hypertension occurring in the third degree of severity;
- Crohn's disease, which has a chronic stage of development of the pathological process or occurs in a severe form;
- the development of any inflammatory processes in the rectal area that are acute in nature;
- peritonitis (presence of inflammatory processes in the visceral and parietal abdominal cavity);
- various problems that disrupt blood clotting processes;
- adhesions in the intestines;
- the course of diseases such as thrombosis of blood vessels and acute hemorrhoids.
In addition, this kind of diagnostic procedure cannot be performed on those patients who have recently undergone any surgical operations in the intestinal tract and are undergoing a postoperative recovery period.
During pregnancy
It is highly undesirable to perform a colonoscopy at any stage of pregnancy. The reasons to refuse this procedure are as follows:
- Severe stress experienced by a woman during the examination can adversely affect the development of the fetus.
- Medicines used during anesthesia can disrupt the normal course of pregnancy.
- Tension of the abdominal muscles can cause increased uterine tone and embryo hypoxia.
In the early stages of pregnancy (up to 3 weeks), the consequences of colonoscopy are not so dangerous, but a pregnant woman should resort to it only if there is an immediate threat to her life.
The examination is performed only under local anesthesia. In any case, before deciding to undergo such a traumatic study, it is advisable to consult several specialists.
Can this be done for hemorrhoids?
If a patient has symptoms of hemorrhoids, a colonoscopy may be recommended in the following cases:
- To confirm the diagnosis to exclude colorectal cancer.
- To determine the area affected by hemorrhoids and count the number of nodes.
- To identify the source of bleeding and cauterize it.
Colonoscopy for hemorrhoids is done only with the use of anesthesia or non-invasive (without internal penetration) methods. In the acute course of the disease with severe inflammation, the examination is not carried out due to the inability to fully prepare the intestines for examination.
Complications
As mentioned above, intestinal colonoscopy is practically painless. Reviews from patients who have not undergone anesthesia also note that the procedure leads to maximum discomfort, but does not cause severe pain. However, rarely, but still this procedure can cause certain complications:
- Perforation (tissue rupture) of the intestine. In this case, the patient is prescribed an urgent operation, as a result of which the problem is eliminated.
- Complications may occur due to anesthesia (in approximately 0.5% of cases).
- In 0.1% of cases, intestinal bleeding may occur.
- Very rarely, a patient can become infected with hepatitis C or salmonellosis (if the colonoscope is not properly disinfected).
- In rare cases, the spleen may rupture during a colonoscopy.
If after the procedure the patient has a fever, pain, nausea, vomiting, bloody diarrhea, weakness or discomfort, you should immediately seek medical help.
Consequences
With invasive methods of examining the intestine, it is almost impossible to do without traumatizing it.
The most serious consequences may be associated with damage to the walls of the colon caused by:
- An endoscope as it moves through the intestines.
- Excessive air injection at the initial stage of the examination.
- Therapeutic procedures for polyp removal or biopsy.
If the damage is significant, it can lead to peritonitis and general blood poisoning. Symptoms of perforation are not always obvious during the procedure. After a colonoscopy, the patient may experience slight discomfort for some time, usually within a week.
If your health does not improve after a week, and signs indicating the development of the disease appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
Pain
A dull aching pain in the abdomen may persist for 5 days after the procedure. If during the examination the doctor removed polyps, pain is most likely.
To suppress unpleasant symptoms, antispasmodics are indicated:
- No-shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Spasmalgon.
If the pain does not disappear after a week and the pain intensifies, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps these are the initial symptoms of inflammation.
Slime
The appearance of mucus in the stool indicates intestinal irritation. The mucus may contain minor blood clots.
After a colonoscopy, this condition can last up to 3 days, during which the colon mucosa, traumatized by the passage of the endoscope, must recover. After the procedure, it is recommended to switch to a diet that will help the intestines return to normal faster.
Temperature
A slight increase in temperature may be observed after the procedure for several days. This is a normal reaction of the body to manipulations performed on it.
If the temperature rises sharply, you should call a doctor. This condition may be associated with infection or signal a developing intestinal obstruction.
What it is?
During the examination, the endoscope is advanced along the intestinal tract
Modern medicine allows us to examine a hollow organ without surgery and identify existing disorders. Fibercolonoscopy, or lower endoscopy, is a diagnostic procedure for identifying pathological changes in the intestinal tract. The doctor performs a visual examination of the organ mucosa.
The technique involves using special equipment, a colonoscope. The device is inserted into the anus and moves along the intestinal tract.
This is a flexible hose equipped on all sides with lighting, a camera and medical instruments. It easily penetrates various parts of the intestine. The device sends a signal and an image of the organ is displayed on the monitor. The specialist assesses the condition of the patient's intestines.
What departments can be considered with the FCC? The study examines the condition of the mucous membrane of the large intestine, as well as its ileum.
If the doctor examines the rectum and sigmoid colon, the method is called fibrorectosigmoidoscopy. Diagnostics is carried out with a special device and does not require such thorough preparation as the FCS. However, fibrosigmoscopy does not reveal pathology located in the right sections and transverse part of the colon.
Fibercolonoscopy allows for a biopsy. The doctor takes material that makes him suspicious. Subsequently, the specialist conducts histological and cytological examination.
If necessary, tumors are removed. The procedure is highly accurate and fast. The patient can avoid surgery by replacing it with FCS.
Resection of a polyp using a fiber colonoscope
More details about the method in the video:
Another method
If a patient consults a doctor with complaints of abdominal pain, a specialist can pre-examine him without resorting to hardware methods. Traditionally used procedures:
- finger method;
- palpation.
With the finger method, the doctor, wearing medical gloves, feels the intestines with the middle finger of his hand. At a depth of 10 cm from the anus, it can detect hemorrhoids, tumors and fissures. This method also allows you to assess the condition of the sphincter and examine intestinal motility.
During palpation, the doctor feels the internal organs through the abdominal wall. An experienced specialist can localize spasmodic and painful areas of the intestine.
Examinations carried out using palpation and the finger method are subjective. To confirm the diagnosis made with their help, it is necessary to resort to more accurate diagnostic methods.
How is fiberoscopy performed?
Fibercolonoscopy is a procedure during which a 160-185 cm long probe is inserted into the patient’s intestine through the rectal opening. It is equipped with:
- a camera that visualizes the image on the device monitor;
- optics;
- a special instrument used to collect tissue for biopsy or therapeutic manipulation.
Fibercolonoscopy is performed strictly on an empty stomach.
- In the treatment room, the patient undresses completely, lies on his left side and bends his knees. To make the procedure less unpleasant, the anal area is treated with a special gel containing lidocaine.
- The doctor slowly inserts a fibrocolonoscopy probe into the intestine, periodically introducing gas through a special hole in the tube, which straightens the intestines, allowing the device to move more easily.
- The doctor monitors the movement of the device on the device monitor. If a polyp or other formation is detected, he immediately removes it or collects tissue for subsequent examination in the laboratory.
Fiber colonoscopy lasts on average 20-40 minutes, after which the patient can immediately go home. In order to eliminate the effects of gas entering the intestines, he should take activated charcoal.
You should not be alarmed if you notice small traces of blood in the stool after fibrocolonoscopy. This may be due to the collection of a small area of tissue for examination. If there is significant bleeding, consult a doctor immediately.
Alternative
Examination of the colon with a probe is an unpleasant procedure, and in many patients it causes unpleasant emotions.
Modern medicine provides the opportunity to use other methods of examining the intestines. They have both their pros and cons.
The main disadvantage of non-invasive methods of examining the colon is the impossibility of concomitant treatment and tissue collection for analysis.
Sigmoidoscopy
During the procedure, a sigmoidoscope is used. It consists of a short tube 25–35 cm long, its diameter is 2 cm. This method, like colonoscopy, is invasive.
- (+) duration 7 minutes;
- (-) allows you to examine only 30 cm of the intestine from the anus;
- (-) only the edge of the tumor is accessible for biopsy.
Irrigoscopy
To carry out diagnostics, the patient is given a contrast agent using an enema and an x-ray is taken. The image clearly shows the neoplasms.
- (+) painless;
- (+) safe.
MRI of the intestines
The examination is carried out using a special apparatus using magnetic resonance imaging. 2 liters of a special solution are injected into the patient’s intestines and placed in an electromagnetic field. The result of the scan is a three-dimensional image of the area of the intestine being examined. The duration of the procedure is 1 hour.
- (+) painless;
- (+) safe.
CT
The examination is carried out using computed tomography using a special software and hardware complex. The three-dimensional image obtained as a result of X-ray scanning allows one to assess the condition of the intestinal walls at different depths.
- (+) high information content;
- (+) painless;
- (+) safe;
- (-) does not detect small tumors.
Capsule
The examination is carried out using a special capsule measuring 10 x 30 mm, equipped with a camera and an autonomous power source.
The patient swallows the device, the camera passes through his intestines and leaves the body naturally. During advancement, images taken by the capsule are transferred to special equipment.
- (+) allows you to identify pathology in the stomach;
- (-) the examination lasts 5 – 8 hours.
Virtual
Virtual colonoscopy is performed using computed tomography (CT). Another name is multislice computed tomography (MSCT).
Special equipment allows the doctor to take a virtual tour of the patient’s intestines, examine hard-to-reach parts of the intestine and areas with possible pathology. The entire examination process is recorded, and the video can be provided to specialists for detailed analysis.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a method of examining internal organs using a special endoscope device. Colonoscopy is a special type of endoscopy.
Ultrasound
During an ultrasound examination, internal organs are examined using ultrasonic waves. When colon cancer is detected, ultrasound is used to assess the extent of its damage by metastases.
- (+) painless;
- (+) safe;
- (-) does not allow diagnosing colon cancer at an early stage.
FCC
Fibercolonoscopy of the intestine (FCS) differs from colonoscopy only in the device used during the examination. For the study, a fiber colonoscope is used, which allows you to examine the inner walls of the colon, take a biopsy and remove polyps.
- (+) a thinner and more flexible probe makes the procedure less painful.
What is a colonoscopy
At the moment, doctors practice two research methods - virtual and invasive colonoscopy.
Virtual intestinal colonoscopy is a more modern research method in which the doctor receives an image of the intestine in 2D and 3D format. The image is based on data from computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
This method is most often prescribed when there are contraindications to invasive diagnostics, and it has a number of pros and cons. MRI of the intestine or virtual colonoscopy is a more gentle method of examination and allows diagnosis without the use of additional anesthesia and anesthesia. But a virtual examination will not be as informative as endoscopic diagnostics - it cannot detect minor intestinal injuries, small ulcers and polyps, and it is impossible to perform a biopsy and remove detected tumors.
A typical invasive colonoscopy is performed using an endoscope, which consists of a flexible probe, a special eyepiece, a light, tubes that supply air, and forceps that are used to obtain histological material. The probe is inserted into the rectum and passed through the colon, accompanied by air to improve visibility.
Modern endoscopes have special built-in cameras, with the help of which it is possible to take pictures of even the most remote areas of the intestine and display their image on the screen. Thanks to this opportunity, the doctor can examine in detail the problem areas of the intestine and detect pathologies.
During the invasive examination, anesthesia, sedatives and antispasmodics may be used to ensure maximum patient comfort. In some cases, anesthesia is used, for which there are special indications.
Anesthesia is used:
- If the patient is under 12 years old, anesthesia is recommended for children to avoid psychological trauma;
- If the patient has a low pain threshold;
- If there are adhesions or other destructive disorders in the intestines.
Note! Colonoscopy usually lasts no more than 10-15 minutes, if the diagnosis does not require additional therapeutic measures.
Colonoscopy allows you to quickly obtain indicators that previously could only be obtained as a result of long studies:
- Gives an accurate assessment of the condition of the mucosa, identifies inflammatory processes and intestinal motility.
- Provides an opportunity to clarify the size of the intestinal diameter, and if cicatricial changes are detected, expand the intestinal area.
- Allows you to see the smallest changes on the intestinal walls and pathological neoplasms (hemorrhoids, fissures, ulcers, polyps, foreign bodies, etc.).
- Makes it possible to take pieces of tissue for examination (biopsy).
- Allows the removal of small polyps and benign tumors using endoscopic equipment, which saves the patient from surgical intervention.
- Helps identify the cause of intestinal bleeding and eliminate it on the spot.
- Makes it possible to take detailed pictures of the inner surface of the intestine.
All these possibilities make colonoscopy a unique and most informative diagnostic tool, therefore this study is given the greatest preference when intestinal pathology is suspected.