How are the methods different?
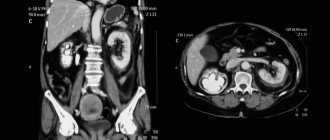
Computed tomography is a type of x-ray examination. Its main principle is the creation of layer-by-layer images of the organ under study, through which X-rays pass in a narrow beam. Different tissues of the human body absorb these rays differently. As a result, the radiation is attenuated. This coefficient is recorded by special sensors, and the radiologist receives sections of any area of the human body. By processing the received data, it is possible to reconstruct the spatial image of the object on the monitor screen.
CT principle
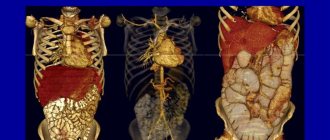
Magnetic resonance imaging is a slightly different study. It is based on the physical phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. When performing a study, the patient is placed in a powerful magnetic field, and an impulse is applied to the organ being studied, which changes its internal magnetization. After this influence ceases, the magnetization returns to the initial level. Its changes are repeatedly read by the computer. As a result, a three-dimensional image of the object under study is formed.
Principle of MRI
Indications
In gastroenterology, the main diagnostic methods are radiological and endoscopic. Of the radiation methods, ultrasound is the most widely used. CT and MRI are prescribed by doctors as additional diagnostic procedures to identify focal formations (tumors), diseases of the liver, spleen and pancreas.
Table 1. Indications for use.
| MRI | CT | |
| Abdominal injury | Violation of integrity, bruises of soft tissue structures | Foreign bodies, damage to parenchymal and hollow organs, hematoma formation |
| Study of the structure of the abdominal organs | Benign and malignant neoplasms, metastatic lesions, cysts, inflammatory diseases | The same clearly visualizes liver cirrhosis |
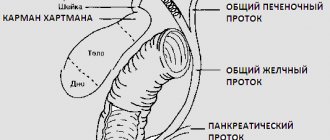
| Assessment of the functioning and condition of the biliary tract | Tumors, cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, clarification of the severity of pathological changes in inflammation of the gallbladder and common bile duct | Same |
| Stomach examination | Detection of oncological pathology, assessment of the prevalence of the tumor process (damage to lymph nodes, germination of nearby structures) | Same |
| Bowel examination | The need to distinguish benign from malignant formations; Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis (virtual colonoscopy) | |
| Lymph node examination | Distinction between tumor and inflammatory infiltration, metastatic lesions | Same |
| Visualization of abdominal vessels | Vascular anomalies, aneurysms, vascular obstruction, narrowing, blood clots | Same |
Reference
The doctor prescribes CT and MRI to study the structure of internal organs that are technically difficult or for some reason impossible to examine using X-rays and ultrasound, as well as in complex diagnostic cases to clarify the data from these studies.
What does an abdominal MRI reveal?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity is performed as an auxiliary diagnosis in cases of unclear clinical picture. This is what distinguishes it from ultrasound radiation, which is prescribed when it is necessary to confirm the suspected diagnosis.
MRI examination is especially effective for detecting tumors.
Abdominal MRI: what else is checked? Patients are sent for this procedure when it is expected to obtain information about the following pathologies:
- processes of growth of cysts, tumors, metastases;
- pathological changes and congenital pathologies of internal organs;
- the presence of stones and other foreign bodies;
- post-traumatic pathologies and scars;
- accumulations of liquids;
- hidden bleeding;
- pancreatic bile ducts;
- anomalies in the development of certain organs of the peritoneum, for example, changes in the shape and size of the gallbladder or torsion (volvulus) of the spleen;
- the presence of pathological processes in blood vessels, for example, thrombosis or aneurysm;
- ischemic processes;
- metabolic disorders;
- gastric and intestinal pathologies;
- renal colic;
- injuries to the peritoneal organs;
- mechanical damage to the kidneys;
- complex liver diseases, for example cirrhosis.
Using abdominal MRI, it is possible to diagnose a variety of changes in the structure of organs or tissues, for example, inflammatory processes, diseases, infections and tumors.
Contraindications
Limitations in the use of CT are associated with the effect of ionizing radiation on the patient’s body. This study is contraindicated in pregnant women. It is not advisable to prescribe it to women who are breastfeeding. Due to the technical capabilities of the device, it is not performed on patients weighing more than 150 kg. Enhanced CT has additional contraindications:
impaired liver and kidney function;- allergy to contrast;
- serious condition of the patient (coma, shock of various nature);
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
Although MRI is considered a safer study, it also has its contraindications:
- metal objects in the human body (foreign bodies, fragments);
- ferromagnetic implants (dentures on metal pins, pacemakers, artificial joints, heart valves, automatic medication dispensers, metal osteosynthesis devices, clamps and clips on blood vessels after surgery, hearing aids).
Under the influence of a magnetic field, they can change their temperature, move when heated and damage surrounding tissue.
Carrying out MRI in patients with fear of closed spaces causes certain difficulties. In this category of people, the study can be performed provided that open-type tomographs are used.
It is difficult for young children, restless patients, and those with neurological pathologies to remain motionless for some time, which is necessary to obtain a clear image. In such cases, short-term anesthesia is used.
Which study should you choose?
It is impossible to say with certainty that one procedure is better than another. Each of them has its own differences, pros and cons.
Advantages
Thanks to the development of computed tomography, doctors have the opportunity to study in detail the structure of organs in the body of a living person, without violating the integrity of the skin or penetrating into its cavities. In this case, it is possible to consider even small structures smaller than a centimeter in size and to distinguish nearby objects from each other with minimal differences in density. Moreover, on the monitor screen, if necessary, you can change their sizes. CT opens up opportunities for a detailed study of pathological changes (their location, size, structure).
note
The disadvantages of the method include radiation exposure and complications associated with the use of contrast.
MRI is an extremely valuable research method. Let's take a closer look at its advantages:
- does not harm the patient’s health;
- not associated with radiation;
- makes it possible to scan in different projections and at different angles;
- visualizes soft tissue well (muscle, fat and cartilage);
- allows you to examine the vascular bed without introducing contrast;
- can be used in children and pregnant women.
However, it is expensive and has limitations in application.
What is more informative?
Each of the methods has its own capabilities depending on what goal the specialist pursues when prescribing a diagnostic procedure. It is believed that with the help of computed tomography it is better to examine the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract, and magnetic resonance imaging better visualizes soft tissues and is indispensable for identifying oncological processes. But the general indications for these procedures differ little.
MRI is of limited use for diagnosing the digestive organs due to the presence of artifacts from respiratory and other movements. This method is also worse than CT in identifying areas of calcification in organs.
For oncology
Despite the possibility of using CT and MRI for various inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity (for example, cholecystitis), in such cases they are usually not prescribed. After all, there are simpler and more accessible methods for this, and the information content of CT and MRI practically corresponds to the results of ultrasound. But if cancer is suspected, these studies have clear advantages. MRI is considered more informative in identifying malignant neoplasms , as it more subtly studies the vascular structure of the tumor.
Which is safer?
There is currently no evidence that MRI is harmful to patient health. Some authors have suggested that there may be long-term effects of using magnetic fields in the future, but there is no evidence for this. Therefore, MRI is considered an absolutely safe research method. If the procedure is performed with intensification, then side effects are possible. But they occur extremely rarely, since the contrast used for this procedure is safer and does not contain iodine.
Computed tomography is associated with radiation exposure , which contributes to the accumulation of radiation in the body and increases the risk of cancer. Also, the introduction of contrast agents into the body can have a negative impact on the patient’s health. This can trigger hives or even anaphylactic shock. But such complications are rare; in general, the study is well tolerated by patients.
Price
MRI and CT are expensive tests. The price for them is much higher than for a regular ultrasound or x-ray. Therefore, they are used already at the last stages of diagnosis. For example, the cost of an abdominal CT scan in Moscow clinics ranges from 3,700 to 31,800 rubles. Magnetic resonance imaging is even more expensive, the price starts from 4,500 rubles and can be 1.5-2 times higher than that of CT.
Advantages of the research method
MRI of the abdominal cavity allows us to judge the integrity of organs and provides information about the chemical composition of tissues. The main advantages of MRI in the study of peritoneal organs include:
- Safety, painlessness of the study (this diagnostic method does not involve surgical interventions, is not invasive, in addition, the effect of electromagnetic fields is not felt by humans).
- High research productivity due to the accuracy of visualization of the tissue being diagnosed (images do not overlap each other).
- There are no side effects of tomography due to the absence of radiation, which allows diagnostics to be carried out repeatedly at short intervals.
- Possibility of visualization of tumor formations.
Comparison
What's better? Let's summarize.
| CT | MRI | |
| What is the method based on? | Exposure to ionizing radiation | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| Evaluation of results | Informative (better visualizes hollow organs and various injuries) | Informative (reliably identifies the tumor process, allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels and soft tissues) |
| Tolerability of the procedure | Possible complications | Well tolerated, but some patients find it difficult to remain motionless for long periods of time |
| Its duration | Up to 10 minutes | 30-40 minutes |
| Safety | Radiation exposure; side effects associated with contrast administration | Safe |
| Price | High | 1.5-2 times higher |
How to properly prepare for the procedure
In order for an MRI of the abdominal cavity to give the most informative and reliable results, you should undergo simple preparation:
- 2-3 days before the test, exclude from the diet foods that contribute to increased gas formation. These include legumes, fermented milk products, large amounts of raw vegetables and fruits, black bread, carbonated and alcoholic drinks. In addition, it is necessary to stop taking medications that promote gas formation (for example, Normaze, Duphalac).
- If the patient needs an MRI of the pancreas, liver or spleen, then he should follow a carbohydrate-free diet for 2-3 days, which helps relieve the load on these organs.
- If the patient suffers from gas accumulation or constipation, then he is prescribed carminatives and laxatives (or a cleansing enema the day before the procedure). Espumisan and Sorbex can be used as a carminative and laxative.
- If it is necessary to perform an MRI with contrast, to exclude an allergic reaction, test for a contrast agent.
- If the patient suffers from hypermobility, the procedure may be recommended under general anesthesia. In such cases, the patient will need a preliminary consultation with an anesthesiologist.
- If the patient has kidney disease and a study using contrast is planned, then urine and blood tests should be performed to exclude contraindications.
- Women of childbearing age should ensure that they are not pregnant (using a test or ultrasound).
- If it is necessary to relieve anxiety, your doctor may recommend taking a sedative. In some cases, the patient’s relatives may be present at the procedure to eliminate anxiety.
- The last meal should take place 6-7 hours before the procedure. It should consist of light and easily digestible dishes.
- You should stop taking liquids 4 hours before the examination. On the day of the procedure, you should not drink carbonated water; it is also better to avoid coffee or tea.
- Take the findings of previous MRIs with you to compare the results.
- On the day of the examination, you should not use cosmetics, makeup or hairspray, as they may distort the results.
- 30-40 minutes before the study, you should take an antispasmodic drug (No-shpa, Papaverine, Spazmalgon, etc.).
- Before the procedure, visit the toilet.
- Before entering the MRI room, remove metal jewelry, watches, dentures, hair clips, piercings, wigs, etc. Electronic devices and bank cards should also be left in the bag.