Computed tomography is widely used to diagnose diseases of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. The high information content of this method and the good quality of CT images allow doctors to determine the presence of surgical or therapeutic pathology with 100% accuracy, predict the further course of the disease and develop the most effective treatment tactics.
Abdominal CT scan is prescribed for examination
- intestines,
- pancreas,
- stomach,
- spleen,
- gallbladder,
- liver.
CT scan of the retroperitoneal organs is visualization
- kidney,
- adrenal glands
- urinary tract,
- blood vessels,
- lymphoid tissue.
Modern tomographs are so functional that they allow virtual colonoscopy (examination of the large intestine) without causing much discomfort to the patient.
CT with contrast
Computed tomography of the abdominal and retroperitoneal space is often performed with contrast enhancement. The introduction of a staining iodine-containing drug allows for better diagnosis of tumor formations and vascular pathologies. Contrast is administered intravenously, orally, or rectally into the patient's body.
The method of drug administration depends on the area being studied:
- the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) are contrasted by drinking a special liquid;
- lower (large intestine) - by giving an enema with a dye;
- To visually highlight blood vessels and parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys), the product is injected into a vein (bolus method).
The contrast agent, without causing any harm to health, is eliminated from the human body naturally within 1-2 days.
Important! The contrast gets into the secretion of the mammary glands, so experts recommend that nursing mothers wean the baby from the breast for 1-2 days, replacing breastfeeding with artificial one.
Indications for CT scan of the abdominal cavity
A CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is usually prescribed by the attending physician in the following cases:
- assessment of the condition of internal organs before surgical treatment;
- diagnosis of acute and chronic pathologies when they cannot be determined by other methods (in the absence of contraindications, it is preferable to use the urography method for examining the kidneys and urinary tract);
- identifying the cause of jaundice and sudden weight loss;
- visualization and assessment of the severity of internal injuries after abdominal injuries;
- suspicion of a mass formation in the abdominal or retroperitoneal cavity;
- determination of the degree of malignancy of the neoplasm;
- monitoring the patient's condition during treatment, as well as postoperative control.
How to prepare for a CT scan with contrast
Computed tomography of the abdominal organs with contrast provides the most reliable results and involves the use of a special contrast agent containing iodine. This drug makes the areas under study clearer and more contrasting, which greatly facilitates diagnosis and allows you to obtain the most complete information about the anatomy of the organ under study, what condition it is in and whether there are any pathologies in it.
As a rule, Urografin is used as a contrast agent, administered to the patient in one of the following ways:
- oral;
- intravenous;
- through a probe;
- using an enema.
The oral route of administration of Urografin involves the following scheme for administering a contrast agent.
The evening before a CT scan with contrast, the examinee takes one and a half liters of water and dissolves Urografin in it, in the amount prescribed by the doctor. He drinks half a liter of the said solution in the evening before going to bed, another half liter of the solution in the morning on an empty stomach, and the last half liter immediately before the procedure. In this case, the contrast, spreading through the intestines, permeates the affected tissues, which leads to the fact that the anatomy of the internal organs is more clearly visible in the photographs. The drug is eliminated naturally – through the intestines.
The evening before a CT scan with contrast, the examinee takes one and a half liters of water and dissolves Urografin in it, in the amount prescribed by the doctor.
He drinks half a liter of the said solution in the evening before going to bed, another half liter of solution in the morning on an empty stomach, and the last half liter immediately before the procedure . Intravenous administration of Urografin makes it possible to enhance the reflection of the X-ray beam when examining parenchymal organs, the anatomy of which is very peculiar.
The introduction is carried out as follows. The drug is administered into the ulnar vein. After administration, the drug quickly spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body. This leads to the fact that the organs being examined are saturated with an iodine-containing substance, and their anatomy is clearly reflected in photographs under the influence of X-ray radiation. The body is cleansed of the drug within 24 hours. The introduction of a contrast agent through a probe is used quite rarely and allows for targeted pigmentation of the organ being examined. The subject is warned in advance about the need for such a procedure.
The administration of contrast through an enema allows for a full examination of the large intestine, thanks to which the anatomy is examined, pathologies are identified and appropriate recommendations are given.
Contraindications
Computed tomography is considered a safe diagnostic method. The radiation dose from CT is significantly less than from traditional radiography of the gastrointestinal tract. However, there are still contraindications.
The main (absolute) contraindications to the procedure are:
- pregnancy - although minimal, radiation exposure can adversely affect the unborn child;
- obesity – weight more than 120 kg will not allow a person to fit comfortably in the tomograph tunnel;
- mentally unbalanced state of the patient - any medical manipulation can cause panic, aggression or other inadequate reactions on the part of the patient;
- hyperkinesis (pathological inability to maintain body stillness) - to obtain high-quality images during scanning, any physical activity of the patient is undesirable;
- individual intolerance to iodine-containing substances - a contrast agent based on iodine can provoke an allergic reaction of varying intensity in the patient, even irreversible.
In some cases, the following may be contraindications:
- age up to 14 years - CT scans for children are performed for emergency indications and in situations where diagnosis cannot be made by other methods;
- chronic renal failure or acute inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract - with contrast-enhanced CT, when the substance is removed from the body, an additional load is created on the urinary organs, which can worsen the course of the disease;
- diabetes mellitus, multiple myeloma, severe cardiovascular diseases, liver damage - for these pathologies it is not recommended to administer a contrast agent;
- X-ray diagnostics of the stomach with a barium suspension, completed less than a week before the planned CT date - residual substances in the stomach can affect the quality of the images.
What diseases does it show?
Using CT, the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, retroperitoneal space, and pelvis is checked. This procedure effectively detects foreign objects in the intestines or stomach, pathologies of the lymph nodes, blood, abscesses, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, damage or bleeding, atherosclerosis, changes in blood vessels, and birth defects.
On this topic
- Tomography
What does a pelvic CT scan show?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 27, 2020
The examination also reveals echinococcosis, stones in the gall bladder, kidneys, cysts, tumor-like formations of a benign or malignant nature.
Computed tomography of the abdomen is performed to diagnose pancreatitis, hemangioma, cystic adrenal lesion, lymphoma, hydronephrosis, polycystic disease, vascular stenosis, aortic aneurysm, appendicitis, or diverticulitis. Sometimes MSCT can detect intervertebral hernia.
Preparing for an abdominal CT scan
At the time of the examination, it is necessary to free the gastrointestinal tract from food as much as possible (the procedure is performed on an empty stomach). Depending on the time of the procedure, the following is allowed:
- a light liquid dinner if the CT scan is scheduled for the morning;
- light breakfast (no later than 5 hours before the appointed time), if you have an appointment for lunch hours;
- liquid breakfast without lunch if the CT scan is performed in the evening.
For 2 days before the examination, you must follow a diet that strictly limits foods that cause bloating:
- alcohol,
- carbonated drinks and juices,
- dairy products,
- vegetables and fruits,
- products made with yeast, etc.
On the day of the study, it is necessary to empty the intestines using a cleansing enema or a special product “Fortrans” (mild laxative). The bladder, depending on the area being examined, may feel slightly full.
Preparing for the study
No preparation is required for a CT scan of the abdomen without intravenous contrast.
To conduct this study with intravenous contrast, you must:
- clarify the presence of contraindications for the administration of a contrast agent;
- For elderly patients, patients with known kidney disease, and patients undergoing chemotherapy, we recommend a blood test to determine the concentration of creatinine in the blood;
- in the presence of allergic reactions or a moderate decrease in the filtration capacity of the kidneys, it is necessary to carry out medicinal preparation for the study;
- do not eat at least 2 hours before the test;
- If you are taking medications that lower blood sugar levels, we ask you to notify your radiologist. Many of them contain metformin, you will need to stop taking them for 2 days after the study with intravenous contrast.
Methodology
The patient must have a referral from a doctor, the results of other diagnostic examinations, for example, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, FGS (fibrogastroscopy) or radiography of the stomach, colonoscopy, etc.
When performing a CT scan with contrast, you will need to sign an official document - permission to perform medical procedures (injection of a contrast agent).
To examine the kidneys and organs of the urinary system, a specialist may need a fresh (2-3 days old) response from a biochemical blood test (for ALT, AST, creatinine, urea).
Computed tomography does not bring any discomfort to the patient. The patient lies on a mobile tomograph couch, and the scanner rotates around him, taking pictures. The subject is only required to remain completely still. Therefore, you need to prepare in advance lightweight and comfortable clothing that does not irritate the skin, or put on a disposable uniform suggested by the nurse. In order not to hear the hum of the working scanner, you can use headphones.
The duration of the procedure without enhancement is from 15 minutes, CT with contrast – up to half an hour. After an examination by a radiologist, a report is prepared within 1.5-2 hours, which is given to the patient or sent directly to the doctor who prescribed the diagnosis.
Survey results
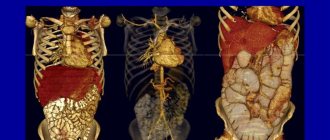
CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space perfectly identifies space-occupying formations (tumors, polyps, cysts, stones). Also, based on the results of the examination, the functionality of the internal organs and tissues of the studied areas is assessed.
What a CT scan can reveal:
- neoplasms of varying degrees of malignancy with determination of the degree of their germination into surrounding tissues;
- metastases in neighboring organs and regional lymph nodes;
- acute and chronic liver damage (hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- violation of the outflow of bile, the presence of stones in the gallbladder and its ducts;
- stones in the kidneys and ureters;
- inflammatory processes of internal organs;
- cystic formations;
- foreign bodies;
- vascular pathologies, including atherosclerosis of abdominal vessels;
- other diseases.
What's happened
Abdominal CT visualizes the organs being examined in the form of a highly accurate three-dimensional image on a screen. Thanks to fast scanning, the results are given to the patient just a few hours after the procedure, and the minimal level of radiation exposure makes tomography a safe examination method.
During the manipulation, specialists look at the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and retroperitoneal space. CT scan of the abdominal cavity allows you to carefully examine the blood vessels and lymph nodes that are located near the pathological focus.
Side effects
The CT procedure itself does not cause serious complications or side effects. Some patients report dizziness and nausea when rotating the scanner, similar to motion sickness on a carousel. At the end of the procedure, these sensations disappear without a trace.
People with hypersensitivity may experience itching and redness at the site where the needle pierced the skin if a bolus of contrast agent was injected. If the drug is administered orally, an unpleasant taste of iodine may remain in the mouth. These symptoms will also disappear on their own.
This reaction to contrast is also considered normal: at the moment the drug enters the blood and spreads through the bloodstream, the patient feels hot or cold. This symptom is short-term and does not require medical attention.
More serious reactions to contrast occur extremely rarely, affecting 1 person out of 100. This happens when the patient did not know about his allergy to iodine. In this situation, the help of medical staff and the use of antihistamines (anti-allergic) drugs will be required. Therefore, you should immediately inform your doctor if you notice any signs of an allergy (skin itching, redness, rashes, swelling, cough, difficulty breathing, etc.).
Benefits of CT Scan
The use of CT in the diagnosis of various diseases and traumatic injuries allows the doctor to accurately identify the cause, localization of the lesion, and extent of spread without the use of additional diagnostic methods (laparoscopy, biopsy).
- CT is a non-invasive procedure (does not require penetration), painless and highly informative;
- CT makes it possible to visualize soft tissues, bone structures and the vascular bed simultaneously;
- CT provides a clear, detailed image in different planes (unlike radiography and ultrasound);
- CT allows you to get results very quickly, which is sometimes extremely important (in emergency situations - internal bleeding, for example);
- CT, unlike MRI, is less sensitive to patient movements during scanning. CT is also performed if there are various implants and electronic life-support devices in the patient’s body.
Abdominal CT results
After the study, the resulting images are processed by computer and placed on the professional workstations of our radiologists.
Most studies in the department are analyzed independently by two specialists and, if necessary, can be discussed by a council of doctors.
The time it takes to obtain research results depends on the complexity of the clinical situation. The patient will receive preliminary information about the results of the study in a conversation with the doctor after the study.